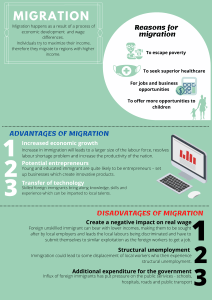
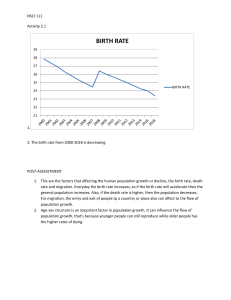
Saskia Sassen - Popularized the term “global city” in the 1990’s Identified three global cities: New York, London, and Tokyo New York - Center of global finance and capitalism London - Considered as the home of world’s top exchange. Tokyo - Majority of major corporations can be found. Indicators for Globality in a City: = Economic Power = Center of Authority = Center of higher learning and culture = Good population satisfactory rate = Cultural Power The Challenges of Global cities - Pollution Consumes most of the world’s energy. Major terror attacks Economic globalization has paved the way for massive inequality. Gentrification – driving out the poor in favor of newer, wealthier residents. Perils of Overpopulation: “An Essay on the Principle of Population” (Thomas Malthus - 1798) - Population growth will inevitably exhaust world food supply by the middle of the 19th century. The Population Bomb (Anne and Paul R. Ehrlich – 1960’s) - Argued that overpopulation in the 1970’s and 1980’s will bring about global environment disasters that would, in turn, lead to food shortage and mass starvation. Population Control = Practice of artificially maintaining the size of any population Malthusian Theory = Population growth will outpace the availability of resources, leading to poverty, famine, and other social problems. Malthus emphasized the idea that population increases geometrically (exponentially), while food production increases arithmetically (linearly). Neo-Malthusian Theory = Same with Malthusian Theory but with additional factors and recommendations. They advocate for population control measures, such as contraception and family planning, to mitigate these issues. Betsy Hartmann = She disagrees with the Neo-Malthusian theory and believes that governments use population control as a substitute for social justice and much-needed reforms such as land distribution, employment creation, provision of mass education and health care, and emancipation. Feminist Perspective = Feminists approach the issue of reproductive rights from another angle. They are, foremost, against any form of population control because they are compulsory in nature, resorting to carrot-and-stick approach (punitive mechanisms co-exists alongside benefits) that does not empower women. Migration = the movement of people from one place to another with intentions of settling, permanently or temporarily, at a new location. 2 types of Migration: Internal = refers to people moving from one area to another within the country International = it is when people cross border of one country to another. 5 Groups of International Migration 1. People who moved permanently to another country (Immigrants) 2. People who work in another country for a fixed period of time 3. People who are living in a country without having official permission to live there (Illegal Immigrants) 4. People whose family has “petitioned” them to move to the destination country. 5. People who are refugees (Asylum Seekers) Top Countries of Origin of Immigrants 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. India Mexico Russia China Syria Top Destinations 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. USA Germany Saudi Arabia Russia UK UAE France Benefits and Detriments of Sending Countries = Remittances = “Brain Drain” - refers to the international transfer of human capital resources, and it applies mainly to the migration of highly educated individuals from developing to developed countries. Human Trafficking - A major problem in migration 90% of the victims are exploited by private enterprises and entrepreneurs 22% are sexually abused 68% are compelled to work - Syndicates, smugglers, and corrupt officials earn up to $150 billion annually (2014) Extra Notes: FAO - Food and Agriculture Organization IOM - International Organization for Migration ILO - International Labor Organization Thomas Malthus (Malthusian Theory) Paul and Anne Ehrlich (The Population Bomb) Temporary Population Control Condoms, Pills Permanent Population Control - Vasectomy, Ligatio