08-Early Childhood: Age 2 to 6 Biosocial Development
advertisement

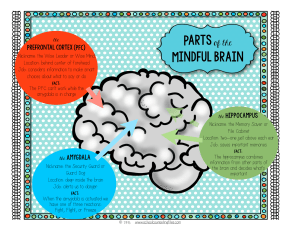
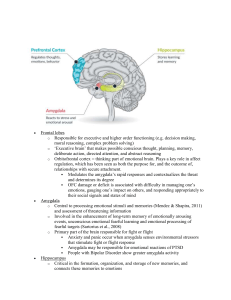
08-Early Childhood: Age 2 to 6 Biosocial Development Body Changes Growth Body slims down – taller & thinner Center of gravity lowers Enables swinging, gymnastics, etc. Nutrition Overweight children = overweight adults Diabetes Heart disease Cavities & gum disease Early tooth decay = most common disease in young children in developed countries Harms permanent teeth Jaw malformation, speech Overall health Brain development Myelination Myelin coating of axons Speeds brain processing Focused on the motor and sensory areas Corpus callosum Connects right and left hemispheres Increases communication between both sides of the brain Increases coordination Lateralization Each side specializing Left hemisphere controls right side Left is language & speech Left is logical Detailed analysis Detail focused Right hemisphere controls left side Creative Emotional Big picture focused All thinking required both sides of the brain Prefrontal cortex “Executive” brain Planning, analyzing, prioritizing Immaturity = Impulsiveness & tendency to persevere (keep repeating) E.g. “Are we there yet?” Longest period of development Matures during adolescence Emotions Based on the limbic system Amygdala Hippocampus Hypothalamus Aid in emotional expression and control Amygdala Registers positive & negative emotions Related to night terrors Children model after parents Hippocampus Memory Can work with amygdala to recall emotions Hypothalamus Produces hormones to activate parts of the body in response to signals from the amygdala and hippocampus. E.g. stress and the fight or flight syndrome Motor skills Gross Large muscles E.g. riding a bike, swinging, kicking a ball Fine Small muscles Writing, drawing, pouring juice Girls tend to develop 6 mos. Earlier than boys Injuries and abuse Three levels of prevention for avoidable injuries Primary prevention Preventing a high risk situation from ever existing E.g. Sidewalks and overpasses Secondary prevention Reducing the risk in an existing high risk situation Salt on roads Crossing guards Tertiary prevention Reducing damage after injury Emergency room procedures Child maltreatment Child abuse Deliberate physical, emotional, or sexual harm Child neglect Failure to meet physical or emotional needs Law required reporting suspected maltreatment Symptoms of maltreatment Injuries Fantasy play – violence & sexual Hostility Impulsive reactions E.g. Cringing Fear of caregiver Hypervigilance