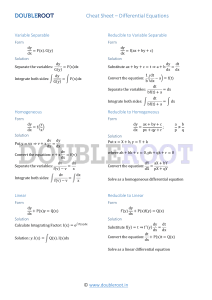
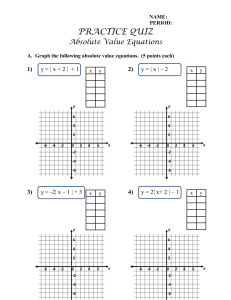
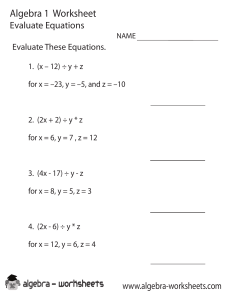MATH 212 WORKSHEET 1 1.3 Classification of Differential Equations 1. State the order of the given ordinary differential equations. Determine whether the equation is linear or nonlinear. ′′ d2 y ii) y 2 = dx ′ i) (2 − t)y + 2ty = cos t, iii) y 3 y (4) + y = cos x, s 1+( dy 2 ), dx iv) x2 R(6) + 2eR = 0. 2. Verify that the given function y = ϕ(x) or y = ϕ(t) is an explicit solution of the given first order differential equation. i) (y − x)y ′ = y − x + 8, ii) 2 dy = y 3 cos t, dt ′ iii) y + 2xy = 1, √ ϕ(x) = x + 4 x + 2, 1 ϕ(t) = (1 − sin t)− 2 ϕ(x) = e −x2 Z x 0 z2 2 e dz + C1 e−x . 3. Find an ordinary differential equation satisfied by the function f (y) such that ϕ(x, y) = f (y) sin x is a solution of the partial differential equation uxx + uyy = 0. 2.1 Linear Equations; Method of Integrating Factors 4. Find the general solutions of the following linear first order differential equations: dy C ln t + , ii) t − y = t2 sin t, Ans. y = Ct − t cos t, t t dt 2 t t 11 iii) y ′ = 2y + t2 + 5, Ans. y = Ce2t − − − , 2 2 4 t+1 iv) (t2 − 1)y ′ + 2y = (t + 1)2 , Ans. y = (C + t)( ). t−1 i) t2 y ′ + ty = 1, Ans. y = 5. Solve the given initial value problems. dy 1 5 6t − 2 = 2t − 3y, y(0) = , Ans. y = e−3t + , dt 3 9 9 dy ex + 2 − e ii) x + y = ex , y(1) = 2, Ans. y = . dx x i) 6. If the general solution of y ′′ + 4y = 0 is given by y(t) = C1 sin(2t) + C2 cos(2t), then solve the initial value problem: y ′′ + 4y = 0 π π y( ) = 1, y ′ ( ) = 1, 4 4 Ans. y(t) = sin(2t) − 1 cos(2t). 2 2.2 Separable Equations 7. Solve the following initial value problems. dy 1 = y − y 2 , y(0) = − , dx 3 dy = y − y 2 , y(−1) = 2, ii) dx i) ex , ex − 4 2ex+1 Ans.y = x+1 . 2e −1 Ans.y = 8. Solve the given differential equation by separation of variables. q √ i) x 1 + y 2 dx = y 1 + x2 dy, q √ Ans. 1 + x2 = 1 + y 2 + C, dy 6 cos2 (3x) cos3 (3x) = 0, Ans.y = , dx C cos2 (3x) + 1 dy xy + 3x − y − 3 iii) = , Ans.y − 5 ln(y + 3) = x − 5 ln(x + 4) + C, dx xy − 2x + 4y − 8 dy 1 iv) (ex + e−x ) = y 2 , Ans.y = − . dx arctan(ex ) + C ii) y 2 sin(3x) +