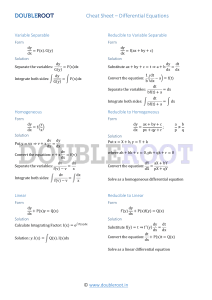
Table of some basic integrals n x dx x 1 n 1 x C ; n 1 n 1 x a dx x x e dx e C 1 dx dx ln | x | C x ax C ; a 0, a 1 ln a sin xdx cos x C 1 tan xdx ln | cos( x) | C a 2 1 1 x dx arc tan C 2 x a a 1 1 x 1 1 x 2 2 x dx tan x C ; |x|<1 1 cosh sinh xdx cosh x C 1 cos 2 x dx ar sinh x C ln( x 1 x 2 ) C 2 1 1 x dx ar tanh x C ; |x|<1 1 ( x a) dx tanh x C n dx 1 C ;(n 2) (1 n)( x a) n 1 x 2 1 x2 1 dx ar cosh x C ; x>1 dx ar coth x C ; |x|>1 ax a dx ln | x 2 b | C b 2 2 Some integration rules: g 1 ( b ) b Substitution: f ( x)dx a f (ax b)dx f ( g (t )) g (t )dt with x g (t ); t g 1 ( x) (inverse function) 1 g (a) 1 F (ax b) C mit F ( x) f ( x) (linear substitution) a Integration by parts: f ( x) g ( x)dx f ( x) g ( x) f ( x) g ( x)dx Complex numbers: z a bi x iy r (cos i sin ) r e i i Be w r e : equation z w has n solutions: zk n n r e 2k i n n ; k 0,1, 2,..., n 1 f gf fg d f ( x) ; ln[ f ( x)] 2 dx f ( x) g g Some differentiation rules: Function y = f(x) be invertible: x = g(y)=f-1(y) is the inverse function: then: g ( y ) 1 1 ; or ( f 1 )( y ) f ( x) f ( f 1 ( y )) Hyperbolic functions: sinh( x) 0,5 e e x x ; cosh( x) 0,5 e x e x Taylor series expansion: f ( x) n0 Some power series: e x f ( n ) ( x0 ) n x x0 ; n! xn (1) n 1 n ; ln(1 x ) x for |x|<1 ; n n 0 n ! n 1 Convergence of series: an1 | 1 , then the series converges absolutely an Ratio criteria: If lim | Root criteria: If lim n | an | 1 , then the series converges absolutely n n Ordinary Differential Equations: Separable ODE: dy 1 y f ( x) g ( y ) dy f ( x) dx dx g ( y) Linear ODE of 1st order: y f ( x) y g ( x) solution of the homogeneous DE: yh ( x) C e f ( x ) dx C h( x ) Variation of constant: y ( x) C ( x) h( x) with C ( x) g ( x) dx K h( x ) y ay by g ( x) Linear ODE of 2nd order and constant coefficients: Characteristic equation: 2 a b 0 Solution yh of the homogeneous DE: depends on roots: Two real roots 1 , 2 : yh C1 e 1 x C2 e2 x Double real root 1 2 : yh C1 C2 x e x x conjugated complex roots: 1,2 i : yh e A sin( x) B cos( x) Particular solution y p : e.g. approach with type of right hand side e.g.: g ( x) Pn ( x) ecx sin(ax) and c+ia is no solution of the characteristic equation cx solution approach: y p ( x) e (Qn ( x)sin(ax) Rn ( x) cos(ax)) with Pn, Qn, Rn : polynomial of grade n General solution of ODE: y yh y p Systems of ODE: two linear ODE of 1st order: Characteristic equation: y1 a11 y1 a12 y2 g1 ( x) y2 a21 y1 a22 y2 g 2 ( x) 2 (a11 a22 ) (a11a22 a12 a21 ) 0