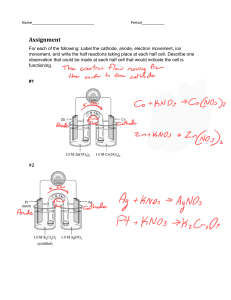
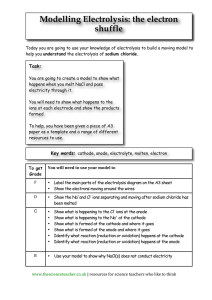
Electrochemistry – I Electrochemical Cells For GCE(O/L) & IGCSE students Redox Reactions • Reduction • Oxidation - Gaining electrons - Losing electrons Mnenomic- “OIL RIG” »Oxidation is Losing »Reduction is Gaining • The reactions in which oxidation occurs with reduction are REDOX REACTIONS. Need to know • Electrode a conductor through which electricity enters or leaves an object, substance, or region. Electrodes • Anode • Cathode - Electrode at which the oxidation half reaction occurs - Electrode at which the oxidation half reaction occurs •Electrolyte - a substance that produces an electrically conducting solution when dissolved in a polar solvent; water Electrochemical cells • Converts chemical energy into electrical energy • In a simple cell – Two electrodes connected by a wire – An acidified solution as the electrolyte • Current passes from cathode to anode (from positive terminal to negative terminal) Electrodes of a Simple Cell Anode Cathode • One electrode is the anode • Other electrode is the cathode • More reactive metal becomes the anode • Less reactive metal becomes the cathode • Oxidation half reaction occurs at anode • Reduction half reaction occurs at cathode • Negative terminal • Positive terminal A Simple Electrochemical Cell Activity- 1 Materials required Method • A small beaker • Diluted sulphuric acid • A zinc metal strip • Add the diluted sulphuric solution to the beaker • Dip a part of the zinc strip into the solution Continued.. Observations •Zn strip dissolve •Gas bubbles are liberated at the Zn strip Continued.. Zn metal dissolves as electrons are leaving from the Zn atoms Zn2+(aq) + 2e Zn(s) Sulphuric acid dissociates H2SO4 2H+ + SO42- H+ takes electrons and hydrogen gas is liberated 2H+ + 2e H2(g) • Oxidation half reaction • Zn(s) Zn2+(aq) + 2e • Reduction half reaction • 2H+ + 2e H2(g) • Balanced ionic equation • Zn(s) + 2H+ Zn2+(aq) + H2(g) • Completed balanced reaction • Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g) Activity - 2 • Observations •Zn strip dissolve •Gas bubbles are liberated at the Cu strip Cont. • Conclusions Zn(s) 2H+ + 2e Zn2+(aq) + 2e H2(g) oxidation reduction • Balanced ionic equation Zn(s) + 2H+ Zn2+(aq) + H2(g) At anode Oxidation Zn At cathode Reduction Cu Negative terminal Positive terminal Activity - 3 Fe Cuu • Observations •Iron strip dissolve •Gas bubbles are liberated at the Cu strip Cont. • Conclusions Fe(s) 2H+ + 2e Fe2+(aq) + 2e H2(g) oxidation reduction • Balanced ionic equation Fe(s) + 2H+ Fe2+(aq) + H2(g) At anode Oxidation Fe At cathode Reduction Cu Negative terminal Positive terminal Activity - 4 • Observations •Zn strip dissolve •Gas bubbles are liberated at the Cu strip Cont. • Conclusions Zn(s) 2H+ + 2e Zn2+(aq) + 2e H2(g) oxidation reduction • Balanced ionic equation Zn(s) + 2H+ Zn2+(aq) + H2(g) At anode Oxidation Zn At cathode Reduction Fe Negative terminal Positive terminal Thank You!