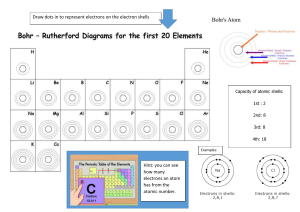
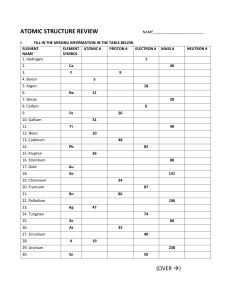
• Use page to make notes • Liquid at room temperature: BROMINE •AND Vertical MERCURY Columns: I VIIII II III IV V VI VII GROUPS • • • • • • • • • Metals: • Horizontal MOSTLY Rows:SOLIDS PERIODS • Non-metals: MOSTLY • Elements GASES arranged according to 7 diatomic INCREASING elements: 𝑯𝟐ATOMIC 𝑵𝟐NUMBER 𝟎𝟐 (position) 𝑭𝟐 𝑪𝒍𝟐 𝑩𝒓𝟐 𝑰𝟐 1 2 3 14 13 16 15 18 17 • VALENCE ELECTRONS = GROUP NUMBER Number of electrons in outermost energy level • 𝟏𝒔𝟐 • 𝟏𝒔𝟐 𝟐𝒔𝟐 𝟐𝒑𝟔 • 𝟏𝒔𝟐 𝟐𝒔𝟐 𝟐𝒑𝟔 𝟑𝒔𝟐 𝟑𝒑𝟔 • LAST ENERGY LEVEL= PERIOD NUMBER ELEMENTS IN THE SAME GROUP HAVE THE SAME VALENCE ELECTRON STRUCTURE • Metals: Reactivity increases from top to the group Potassium is more reactive bottom in than sodium • Non-metals: Reactivity increases from bottom to top in a group Fluorine is more reactive than iodine • Metals & Non-metals: Reactivity increases from right to left in period a • Atomic mass increases from left to right in a period • Atomic mass increases from top to bottom a group • Density increases from left to right in a period • Density increases from top to bottom a group • Hoe werk dit??? • Intermolecular theory • Dink aan atomic mass en nommer van paticles. • Forces – stronger – closer together – density increases. • Metals (solid) – non metals (gas) – move apart – less force – density decreases. • Hoe werk dit? • The stronger the • Metals: M&B points intermolecular forces the decrease from greater the energy needed to top to bottom break the inforces a group • Strong intermolecular forces cause melting points and boiling points increase M & Btopoints increase from left • So the melting and boiling tolarge rightmolecules in a period. points of with strong intermolecular forces are high • Non-metals: M & B points increase from top to bottom in a group M & B points decrease from left to right in a period. • ` • Atomic radius decreases from left to right in a period • Hoe werk dit? • As the atomic mass increases, the number of protons in the nucleus increases • The nucleus exerts a stronger attractive force on the electrons causing them to move closer to the nucleus and thus decreasing the radius • Atomic radius increases from top to bottom in a group as the amount of energy levels increases. • Definition: The energy required to remove one electron from an atom in • CATIONS the gaseous phase Low ionisation energies • The first ionization energy to remove first • ANIONS electron, 2nd IE 2nd • High ionisation energies electron etc • IE increases from top to bottom in aGeneral group. • Discuss • Greater the IE – more observations page 91 difficult it is to remove an electron. 1. Position on the periodic table 2. Valence electrons 3. Atomic radius • The tendency of an atom to accept an electron and form a negative ion (anion) • Energy is released during the process • DEFINITION E.A. is the amount of energy released when a neutral atom in the gaseous state accepts an additional electron • The ability of an atom to attract an electron. • DEFINITION • The electro negativity of an atom is a measure of the attractive force of an atom for the bonding pair of electrons between the two atoms. • It is therefore an indication of the bonding ability of the element. • Increases from bottom to top in a group. • Increases from left to right in a period. Homework: Summary of Periodicity Exercise 7 pg. 94 Hopefully classwork Test Examples