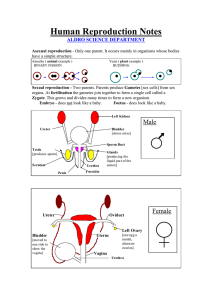
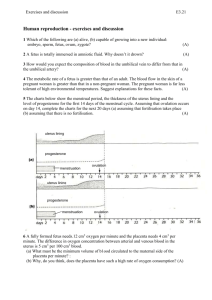
Science Notes Chapter 4: Reproduction Human Reproductive System Male reproductive system Part Seminal vesicle Urethra Sperm duct Penis Prostate glands Testis Scrotum Female reproductive system Function Secretes nutritional fluid for the sperms A channel to discharge sperms and urine from the body Transports sperm from testis to the urethra Transfers sperms into vagina during copulation Secrete fluid which contains nutrients and protect sperm cell Produce male gametes (sperm) and male sex hormones Holds and protects the testes Part Fallopian tube Ovary Uterus Cervix Vagina 1 Function Place where fertilisation between sperm and ovum occurs Produces female gamete (ovum) and female sex hormone Place where the embryo develops and grows Produces mucus to enable sperms to swim into the uterus Receives sperms and as a channel through which a baby is born Comparison between Sperm and Ovum Sperm Ovum Able to move Produced by testis Male gamete Smallest cell in the male’s body Not able to move Produce by ovary Female gamete Largest cell in the female’s body Carries genetic information Sexual reproductive cell Voice Male Female - Vocal cord (larynx) enlarges - Voice becomes deeper Body - Moustache and beard begin to grow - Hair grows on the face, armpits, and chest - Breasts grow - Hair grows on the armpits 2 Reproductive organs - Testes produces sperms and sex hormones - Hair grows at pubic region - Penis and scrotum enlarge - Ovaries produces ova and sex hormones - Hair grows at pubic region - Menstrual cycle begins Menstrual Cycle Definition: Menstruation is the breakdown of the lining of the uterine wall and discharge of blood through vagina. The uterine lining continues to thicken and becomes richly supplied with blood vessels. Implantation of an embryo is ready if fertilisation occurs. The uterine lining breaks down as menstruation begins and discharged together with blood, unfertilised ovum, and mucus. The menstrual cycle will repeat if fertilisation does not occur. 1 4 1 Day 18 - 28: Premenstrual phase Day 1 - 5: Menstruation phase Day 12 - 17: Fertile phase Day 6 - 11: Repair phase 2 3 2 An ovum is released from the 3ovary on the 14th day (ovulation). The uterine lining continues to thicken. Uterine lining starts to thicken. Blood vessels in uterine lining are formed and ready to receive the implantation of fertilised ovum. Fertilisation is like to occur if sperms are present 3 Fertilisation and Pregnancy The process of fertilisation and embryo implantation 1. Sperms will swim into the vagina during copulation. 2. If an ovum is present in the Fallopian tube, fertilisation may occur. Sperm will fuse with ovum in the Fallopian tube and form zygote. 3. After fertilisation, zygote will divide itself and become a ball of cells known as embryo. The embryo will be implanted on the uterine wall at the uterus. Stages of Pregnancy The growth of zygote to embryo and foetus Week 1-4 • Hands and feet will start to form • The embryo has a tiny tail Week 7-9 • Nose, ears, and fingers will be visible Week 10-19 • Embryo will look like a baby • The embryo is now called a foetus Week 20-37 • Foetus will resemble a baby Week 38-40 • Foetus is formed completely • The foetus turns until the head is engaged at the cervix • The muscle of the uterine lining will contract strongly, the amnion will burst, and amniotic fluid will be released. • Foetus is pushed out of the uterus through the vagina and then out of the body. 4 Factors Affecting the Development of a Foetus and Baby A pregnant woman should consume more calorie than the usual amount to maintain good health, deliver a healthy baby and for a better development of the offspring Example of difference in calorie intake of a pregnant and not pregnant woman. Type of nutrients Woman Not pregnant Pregnant Carbohydrate 9450 kJ 11592 kJ Protein 39 kJ 85 kJ Calcium 400 – 500 mg 1000 – 15000 mg The effects of smoking, intake of alcoholic drinks and drugs on a pregnant woman. Substance Cigarette Alcohol drink Drug • • • • • • • • • Effects The baby may have low birth weight The baby may have a higher mortality rate The baby may become retarded and have physical abilities The baby may be born premature Miscarriage of foetus may happen The baby may be born with Foetal Alcohol Syndrome Foetal development may be delayed The brain, nervous system and the heart may be damaged Foetal defects may occur The importance of breast milk: • • • • Contains all the essential nutrients for a baby. Contains antibodies that can protect a baby from a certain disease. Relationship between mother and baby will become closer. Baby that consumes breast milk has better digestion compared to formula milk. 5 Iron 10 mg 15 mg Vitamin A 750 µg 900 µg Vitamin C 30 mg 50 mg Infertility and Contraception Definition Infertility Contraception Known as birth control by using medicines, devices, or surgery to prevent pregnancy. The inability to produce offspring Factors affecting infertility in males and females Male Female Testes cannot produce sperms Ovaries cannot produce ovum Low sperm count Blockage in the fallopian tubes Produces low quality sperms Abnormal uterus Impotent Tumour in the uterus Hormone imbalance Diabetes Defective reproductive organs Methods to Overcome Infertility • • • Hormone treatment Surgery In vitro fertilisation (IVF) Methods of Contraception • • • • • • Contraceptive pills Implants Use of condom Intrauterine contraceptive device (IUCD) Vasectomy Ligation Contraceptive pills Implants Use of condom IUCD Vasectomy Ligation Prevent ovulation Secrete a hormone that prevent the ovary from producing ovum Worn over the penis before copulation Contraceptive device is inserted inside the woman’s uterus Sperm duct is cut and then tied to prevent the sperm from being transported to urethra The fallopian tube is cut and the two ends are tied to prevent ovum from meeting the sperms 6 Plant reproduction Unisexual Parts of plant Bisexual Male Female Ovary ✓ ✓ Ovule ✓ ✓ Stigma ✓ ✓ Style ✓ ✓ Pistil Anther ✓ ✓ Filament ✓ ✓ Stamen Petal Sepal 7 ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ Type of pollination Self-pollination Pollinating agents Cross-pollination - Pollen grains are transferred to stigma of another flower on the same plant. - Pollen grains are transferred to the stigma of the same flower - Pollen grains are transferred to the stigma of another flower on a different plant of the same species. A, B C Animals and insects • Pollen grains stick on the beak or body of the animal. • Characteristics of the flower: - Have big and colourful petals - Have nectar and smell nice - Produce rough and sticky pollen grains - Examples: Durian, rambutan, papaya, hibiscus, sunflower, rose Wind • Light pollen grains are blown by wind and reaches the stigma of another flower. • Characteristic of flowers: - Have a long and furry stigma - Have plenty of small, smooth, and light pollen grains - Have a long filament and style - Examples: Corn, grass, and paddy Advantage of cross-pollination 1. Produce new plants that are more resistant to pests and diseases. 2. New plants can adapt better to changes in the environment 3. New varieties of plants 4. Good quality seeds 8 Fertilisation Process 9 Structure of Seeds and Type of Germination Type of seeds Monocotyledon Dicotyledon Type of germination Epigeal germination Hypogeal germination 10 Function of Seed Structures The structure and functions of a seed Part External Embryo Structure Function Testa Protects the seed Hilum Place where the seed sticks to the fruit Micropyle Small hole to allow air and water to enter the seed Plumule Part of the embryo which develops into a new shoot Radicle Part of the embryo which develops into the root Cotyledon Stores and provides food for the seed The Conditions Required for Germination of Seeds • • • Water Air Suitable temperature Importance of Reproduction • • • • Ensures the continuity of the species Prevent species extinction Helps to increase the number of species in the ecosystem Maintain genetic variation 11