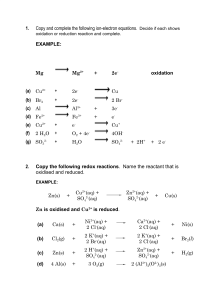
Electron Transfer Reactions Textbook pp. 600-407 Vocabulary oxidation half-reaction equation oxidizing agent reduction oxidation number reducing agent oxidation—reduction (redox) reaction MAIN IDEA: Many reactions involve the transfer of electrons. These reactions are called oxidation—reduction reactions or redox reactions. In a redox reaction, elec trons transfer from one entity to another. Neither oxidation nor reduction can occur without the other Oxidation numbers are assigned to the entities in order to deter mine which is being oxidized and which is being reduced. LEARNING TIP Electron Transfer Remember that in a redox reaction, the number of electrons lost by oxidation must always be equal to the number of electrons gained by reduction. LEARNING TIP 1. Explain in your own words, the process that occurs when an entity undergoes each reaction. C fl (a) oxidation: (b) reduction: 2. Write the oxidation and reduction half-reaction equations for the reactions represented by the following equations. C 2 Fe(s) + ALO3(aq) (a) FeO(aq) -r 2 Al(s) —, A Redox Mnemonic Use the mnemonic “LEO says GER’ to help remember the difference between reduction and oxidation. LEO: Losing Electrons is Oxidation GER: Gaining Electrons is Reduction (b) Cu(s) + 2W (aq) —÷ Cu2(aq) ± H,L (c) SnCI,(aq) + 2 l-IgCI,(aq) (d) 4 NaCIO(aq) + HS(g) — —* SnCl4(aq) + 2 HgCI(aq) 4 NaCI(aq) + H2504(aq) 3. Identify the entity that is oxidized and the entity that is reduced in the chemical reactions represented by the following equations. C (a) Cr9072jaq) + 8 Ht + 3 H,C,04(s) —÷ 2Cr3 (aq) + 7 H10(l) + 6 C02(g) (b) 2 Cr3 (aq) + H,O(l) * 6 ClOj(aq) (c) Cu(s) AgNO3(aq) — Cu(N03),(aq)+ Ag(s) (d) MnO,,(aq) + 5 Fe2(aq) + SHt(aq) 178 Unit 5 • Electrochemistry Cr,07(aq) + 6 ClO,(aq) + 2 Ht(aq) —* Mn(aq) + 5 Fe3(aq) + 4 1-LOll) NEL i 4. Determine the oxidation states of each element in the following chemical compounds. 0 (a) N, (e) GO, (b) NH3 (f) NaNO3 (c) ZnO (g) Na,S04 (d) CaRlO)2 (h) Al(OH), 5. Jermaine says All combustion reactions are redox reactions.” is he correct? 0 Explain. 6. Is it possible to have a reaction in which oxidation occurs and reduction does not? Explain.U3 7. Give oxidation numbers for the underlined atoms in the following molecules and ions. C (a) MgN (e) C204 NLL (b) GaO (1) ZnO,2 (c) CsQ (g) NaBH4 (d) C012 (h) WOI2 9.1 Electron Transfer Reactions 179 8. For (I) (ii) (iii) (a) each of the complete redox reactions given below, do the following: Break down each reaction into its half-reactions. Identify the oxidizing agent. Identify the reducing agent. 0 2Sr+02—.2SrO (b) 2 Li + H, —* 2 NH (c) 2Cs + Br2—*2CsBr (d) 3 Mg + N2 -÷ Mg3N, 9. The compound iron(lll) oxide, Fe203 (more commonly known as rust) is a major contributor to the degradation of vehicles and structures. The oxidation of iron metal occurs when it comes into contact with oxygen in the atmosphere and rust slowly begins to form as the reaction proceeds. o flfl (a) Write the half-reactions for the formation of this compound. (b) Write the balanced overall reaction that results in the formation of Fe,O (c) Galvanization is a process by which a coating of zinc is applied to the iron surface to protect against rust. Describe how this zinc layer protects against rust. 180 Unit 5 • Electrochemistry NEL Balancing Redox Reaction Equations Textbook pp. 608—617 MAIN IDEA: In a balanced redox equation, the total numbers of each type of atom or ion on either side of the equation are equal and the numbers of electrons transferred are equal. Redox equations may be balanced by using the oxidation numbers method or the half-reactions method. These reactions can occur in either acidic or basic conditions. In these cases it may be necessary to add water molecules, hydrogen ions and/or hydroxide ions to balance the equation. 1. ‘Write the balanced half-reactions for each of the following. (a) 2 Fe(s) + 3 C12(g) —> 2 FeCI3(s) Reduction: Oxidation: (b) Mg(s) + 2 AgNO,( q) Oxidation: —> STUDY TIP Different Methods of Solution It is helpful to know multiple methods of solution. You can use one method to solve a problem and another to verify your work. Mg(NO,),(aq) + 2 Ag(s) Red u c t ion: (c) 2 MnO4jaq) + 16 H(aq) + 5 C2042jaq) —. 2 Mn2 + 10 C02(g) + 8 H,O(l) Reduction: Oxidation: (d) 2 Al(s) + 3 1(s) —*2 AP(aq) + 6 1(aq) Reduction: Oxidation: 2. Balance the following equations for reactions occurring in acidic conditions: (a) Cr20,2(aq) + I (aq) —> Cr’(aq) + 12(g) —* (c) Fe2(aq) + H,02(1) Fe3 (aq) + 1-1,00) —, (d) Cr0-2 (aq) + SO,2Qq) NEL Cl,(g) (b) MnOj(aq) + Cr(aq) Mn2(aq) Cr (aq) + S042(aq) 9.2 Balancing Redox Reaction Equations 181 3. Balance the following equations for reactions occurring in basic conditions. El (a) CN(aq) + Mn04(aq) —* CNOiaq) + Mn02(s) (b) Br2(g) —> Br01(aq) + Br(aq) (c) Mn2(aq) + H202(l) —> Mn02(s) + F110(I) (d) Bi(OH)3(aq) + SnO,2(aq) —. Sn032(aq) + Bi(s) 4. Consider the following reaction: Pb(OH)42(aq) + C10(aq) , PbO(s) + C1(aq) (a) How many electrons are transferred for each Pb(OH)42 ion? (b) How many electrons are transferred for each Cl0 ion? (c) Write the balanced chemical equation using the oxidation numbers El method assuming the reaction occurs in basic conditions. 182 Unit 5 . Electrochemistry NEL i 5. Potassium permanganate is a deep purple compound that can be used to determine the concentration of sulfur dioxide in the atmosphere. Sulfur dioxide is one of the compounds responsible for acid precipitation. The reaction between sulfur dioxide and potassium permanganate is shown below: SO(g) + Mn04(aq) —* SO4(aq) + Mn24(aq) Balance the above equation in acidic conditions, using either the oxidation fl numbers method or the halt’- reactions method. 6. When a current is passed through copper(l) ions in solution, the reaction S produces copper solid and copper(II) ions. reaction using the halfthis (a) Write the balanced chemical equation for reaction method. (b) What is unusual about the role of the copper(I) ion in this reaction? NEL 9.2 Balancing Redox Reaction Equations 183 Predicting Redox Reactions Textbook pp. 618423 Vocabulary table Main Idea: A relative ranking of the strength of oxidizing and reducing agents has been developed from empirical evidence. Redox tables list the strongest oxidizing agent in the top left corner of the table and the strongest reducing agent in the boffom right corner of the table, Redox tables can be used to predict whether a redox reaction occurs spontaneously. 1. Rank the strength of the following as oxidizing agents, from strongest to weakest. Cu2 (aq), Co2 (aq), Au3 (aq). Ag (aq) 2. Rank the strength of the following as reducing agents, from strongest to weakest. Zn(s), Ba(s), Mg(s), Ni(s) 3. Which of the following equations represent(s) spontaneous reactions? 0 (a) Sn(s) + 2 Cu2(aq) —* Sn2’ (aq) + 2 Cu’(aq) (h) Mg2 (aq) + 2 Ag(s) —* (c) Ca(s) + Cd2(aq) (d) 2 B((aq) + Sn2(aq) Mg(s) + 2 Agt(aq) J Ca2(aq) + Cd(s) —, Br2(g) + Sn(s) 4. A piece of solid silver is placed into a solution containing nickel(II) ions. (a) Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction that produces solid nickel and silver ions. (b) Predict whether the reaction is spontaneous. Explain your prediction. 5. Which of the following reagents can oxidize H20(l) to H(aq), CL(aq), CL(g). Cu2’ (aq), PbNaq), Mn04(aq) (in acid) 184 Unit 5 • Electrochemistry NEL 6. Consider the following half-reactions: Mn04jaq) + 8 H4(aq) + 5 e STUDY TIP —* Mn2(aq) + 4 H20(l) (a) Predict whether NO ions will oxidize Mn2 to MoO1. Explain. Using Tables Copy tables of information that you will use over and over again onto index cards. Give each table an appropriate title and keep in a handy location. (b) Rearrange and/or balance the equation that shows the spontaneous reaction for N03 and Mn2 0 LEARNING TIP NO3 (aq) + 4 H4(aq) + 3 e —> NO(g) + 2 H20(l) 7. Use the Standard Reduction Potentials table in your textbook (Table 1 in Appendix 87) to answer the following questions. (a) Predict which species in each pair is a better oxidizing agent: (i) Br,(l) or Au3’ (aq) (ii) H2(g) or Ag (aq) (iii) Cd2 (aq) or Cr3 (aq) (b) Predict which species in each pair is a better reducing agent. (i) Na(s) or Li(s) (ii) Fe2(aq) or Ag(s) (iii) H(g) or h(s) Halt-Reactions Involving Water There are several half-reactions that include water listed in Table 1 in Appendix B7. For example, 8042(aq) + H20(l) -I- 2 e S0321aq) - 2 0H(aq) ED,= —0.93V The only equation for which water is reduced is: 2 FIO(1) + 2 e H2(g) + 2 OFh(aq) F°,= —O.83V The only equation in which only water is oxidized is: O1(g) + 2 H(aq) + 4 e 2 H20(l) Et= -l-0.70\’ (c) Identify the strongest reducing agent and the strongest oxidizing agent from parts (a) and (h). Justify your answer. LEARNING TIP 8. (a) Which of the following pairs of substances, when combined, would result in a spontaneous chemical reaction? 0 (i) Au1 — (aq) and Al(s) (iii) AgCl(s) and Br (aq) k (ii) Kt(aq) and Cr(s) (iv) Fe2(aq) and Na(s) Metals and Metal Ions Elemental metals always lose electrons in redox reactions to form cations (postively charged ions). As a result, metals are reducing agents. Conversely, metal cations usually gain electrons to form metal atoms. Hence, metal ions are usually oxidizing agents. There are some exceptions. For example, the iron(ll) ion can be both oxidized and reduced: Oxidation: Fe2(aq) — Fe3(aq) ± e Reduction: Fe2(aq) * 2 e —* Fe(s) (b) Write a balanced chemical equation for each reaction in part (a) that you predict will occur. NEL 9.3 Predicting Redox Reactions 185 9. A student chemist prepared several solutions to use in a chemical analysis, as outlined below. Each of the solutions was stored in a different type of container. 0 Sn (1) irontlI) nitrate in an aluminum flask (ii) nickel(ll) sulfate in a copper flask (Hi) magnesium nitrate in a copper flask (iv) copper(ll) sulfate in an iron drum (a) Predict whether the student will notice any changes a day later. Explain your reasoning. (b) For each solution that you predict will react, what evidence of change do you think the student will observe? (c) Write a balanced equation for each predicted reaction. 186 Unit 5 • Electrochemistry NEL