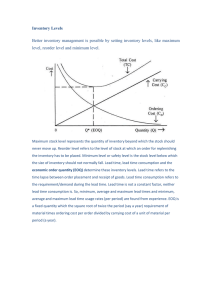
The goal of the basic EOQ model is to: Minimize the sum of ordering and holding costs. Aggregate operations planners seek to match supply and demand at minimum overall cost and: by staying within company policy. Which of the following is not included in ordering cost? Cost of the items purchased Master production scheduling (MPS) involves long term capacity planning that typically covers a time horizon of one to three years. FALSE A fill rate is the percentage of _ filled by stock on hand demand Which one of the following is not a determinant of the reorder point (ROP)? Purchase cost A "chase" demand strategy in aggregate operations planning would be attempting to match capacity and demand, period by period. TRUE The goal of the basic EOQ model is to: Minimize the sum of ordering and holding costs. Among the basic demand options in aggregate operations planning are promotion and the use of overtime. FALSE If average demand for an item is 20 units per day. safety stock is 50 units. and lead time is four days. the reorder point (ROP) will be: 130 One advantage to using graphs in the development of aggregate plans is the ability to visualize a production plan. TRUE The reorder point (ROP) models determine the point at which the inventory, in terms of quantity must be reordered. TRUE Which one of the following is not an input in an MRP system? Planned-order releases Using the EOQ model. the maximum inventory level is equal to Q or economic order quantity. FALSE The MRP input stating which end items are to be produced, when they are needed, and what quantities are needed, is the: master production schedule. The A-B-C approach involves classifying inventory items based on their unit cost. FALSE In MRP, "scheduled receipts" are: open orders already scheduled to be delivered. In the A-B-C approach to classify inventory, items that have high unit costs are always classified as "A" category items. FALSE The hierarchical diagram that depicts the subassemblies and components that are needed to produce and/or assemble a product is called a(n): product structure tree. The average inventory level and the number of orders per year are inversely related; as one increases. the other decreases. TRUE Inspection of goods for quality and quantity upon arrival is part of ordering cost. TRUE What three things are needed when updating the monthly sales and operations plan? Previous months sales records, production levels, inventory levels Changes in this MPS zone require middle management approval. Zone 1 What cannot take place when using the transportation model in aggregate planning? Holding costs The gross requirements of a given part or component are determined from: planned order release of the immediate parent(s) Which is true of a net-change system? The basic production plan is modified to reflect changes as they o cur. The three basic inputs of MRP are: 1) the bill of material; 2) inventory on hand, open orders and lead times; and 3) planned order releases. FALSE The MRP requires a list of the individual parts that will be converted to finished goods. TRUE Dependent demand is derived demand. TRUE The main disadvantage(s) of trial-and-error techniques used for aggregate operations planning is (are): that they are expensive to do. Which of the following is NOT a consideration in the decision to use hiring and laying off permanent full-time workers as a capacity option? Finished goods inventory that is stockpiled Load reports compare planned capacity requirements with projected capacity and availability. TRUE Fixed-interval ordering in MRP places orders that cover a predetermined number of periods. TRUE The output of MRP is a schedule of planned orders for all parts and end items. TRUE Which one of the following is implied by a “lead time” service level of 95 percent? The probability is .95 that demand during lead time will not exceed the amount on hand at the beginning of lead time. Which one of the following is implied by an annual service level of 95 percent? Approximately 95 percent of all demand will actually be satisfied directly from on-hand inventory. Which is not considered a holding cost? Preparing purchase orders In the basic EOQ model, the annual ordering cost is equal to: ordering cost multiplied by the ratio of annual demand to the EOQ. A fixed order quantity/reorder point model for inventory control is usually used with perpetual tracking. TRUE Purchase cost is not generally determinant of the reorder point. FALSE In the A-B-C classification of inventory, C items typically range from 50 to 60 percent of the number of items, but only 5 to 10 percent of the annual dollar value (ADV). TRUE Inspection of goods for quality and quantity upon arrival is part of ordering cost. TRUE The service level for inventory planning is associated with the risk of a stock-out. TRUE