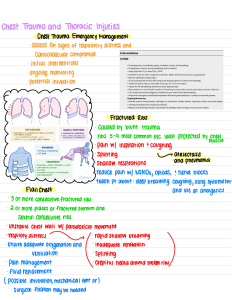
Name: _____________________________________________________ Date: _______ N420 Module 3 Medical Terminology 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 8 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 Across 2. Is decreased oxygenation of arterial blood 5. a life-threatening condition caused by rapid accumulation of fluid (usually blood) in the pericardial sac 6. High- or low-pitched whistling, musical sound heard during inspiration and/or expiration 7. High-pitched, continuous sound heard over upper airway; a crowing sound 9. Is decreased oxygenation at the tissue level 12. Coarse, continuous, low-pitched, sonorous, or rattling sound 13. Is a measure, or stretchability, of the lung and chest wall 14. produced by blunt trauma to the chest, frequently resulting in death at the scene of the traumatic event 15. the bruising of lung tissue 18. Measures the saturation of oxygen in pulsatile blood (SpO2), which reflects the SaO2. 19. defined as an inability of the respiratory system to provide oxygenation and/or remove carbon dioxide from the body. ARF is classified as oxygenation failure resulting in hypoxemia without a rise in carbon dioxide levels, or ventilation failure resulting in hypercapnia and hypoxemia 20. Is the obstruction of a pulmonary artery or one of its branches that is usually produced by a blood clot which has originated in a vein of the leg or pelvis and traveled to the lungs and that is marked by labored breathing, chest pain, fainting, rapid heart rate, cyanosis, shock, and sometimes death 21. A pneumothorax resulting from a wound in the chest wall which acts as a valve that permits air to enter the pleural cavity but prevents its escape Down 1. The surgical formation of an opening into the trachea through the neck especially to allow the passage of air 3. The movement of gases (oxygen and Co2) in and out of the alveoli 4. Coarse, grating, squeaking, or scratching sound, as when two pieces of leather rub together 8. Refers to the opposition to the flow of gases in the airways 10. Is a collection of blood in the pleural space 11. An acute disease that is marked by inflammation of lung tissue accompanied by infiltration of alveoli and often bronchioles with white blood cells (such as neutrophils) and fibrinous exudate, is characterized by fever, chills, cough, difficulty in breathing, fatigue, chest pain, and reduced lung expansion, and is typically caused by an infectious agent (such as a bacterium, virus, or fungus). 16. Discontinuous, explosive, bubbling sounds of short duration 17. the addition of positive pressure into the airways during expiration.