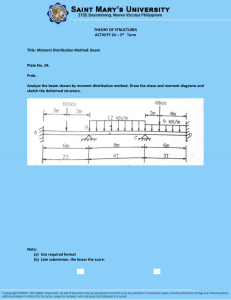
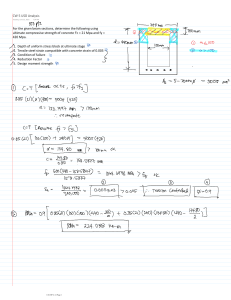
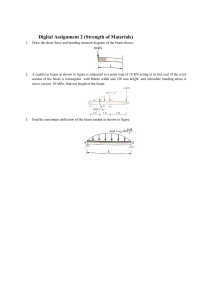
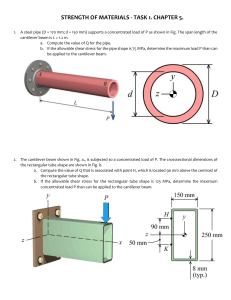
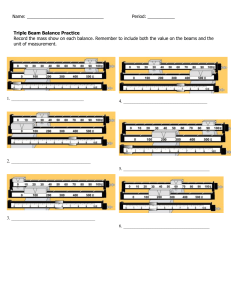
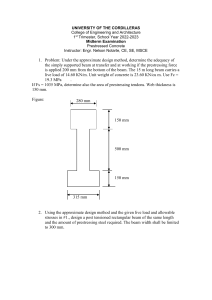
Preboard-3-Struct-nov-2018-Set-B-With-complete-answers
advertisement

MANILA: Room 206, JPD Building, CM Recto Avenue, Manila CEBU: 4/F J. Martinez Bldg., Osmeña Blvd., Cebu City Telephone Number: (02) 516 7559 (Manila) E-Mail: buksmarquez1 @yahoo.com (032) 254-6697 (Cebu) PREBOARD EXAMINATION 3: STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING AND CONSTRUCTION (SET B) INSTRUCTION: Select the best answer to each of the following questions. Mark only one answer for each item by shading the box corresponding to the letter of your choice on the answer sheet provided. STRICTLY NO ERASURES ALLOWED. Use pencil no. 2 only. DO NOT WRITE ANYTHING ON THIS PAPER. DO NOT FOLD OR MUTILATE. 1. As per PD 1096, what is referred to by the total number of persons that may occupy a building or a portion thereof at any one time? A. Building occupancy C. Building usage B. Occupant load D. Unit capacity 2. As per PD 1096, what is the minimum ceiling height of the first story of a habitable room provided with artificial ventilation? A. 2.00m C. 2.10 m B. 2.40 m D. 2.70 m 3. As per PD 1096, under what classification shall factories and workshops using less flammable or non-combustible materials be classified? A. Industrial C. Business and mercantile B. Assembly D. Accessory Yielding on gross area = 0.60 Fy Rupture on net area = 0.50 Fu Shear rupture = 0.30 Fu Bolt stress = 168 MPa 7. Determine the load capacity P (in kN) based on shearing on the 4-25 mmØ bolts. A. 330 B. 770 C. 660 D. 385 8. Determine the load capacity P (in kN) based on rupture on net area. A. 811.2 B. 746.4 C. 1492.8 D. 1622.4 9. Determine the load capacity P (in kN) based on block shear. A. 1136.6 B. 568.3 C. 1129.0 D. 564.5 Situation 3 Refer to FIG. STRST - 157 Situation 1 For the three-story building shown in FIG. ABP-143. Given: Design base shear, V = 500 kN H1 = 3.5 m H2 = 3 m w2 = 1000 kN w3 = 900 kN L=8m H3 = 3 m wR = 750 kN 4. Determine the shear force (in kN) at the roof deck, if the natural period of vibration of the building, T = 0.6 second. A. 207.2 B. 216.2 C. 228.2 D. 125.0 5. Determine the lateral force at the roof deck, if the natural period of vibration of the building, T = 0.9 second. A. 31.5 B. 234.1 C. 202.6 D. 125.0 6. After analysis, the shear force at each level are as follows: Roof deck = 200 kN 3rd Floor = 160 kN 2nd Floor = 120 kN Ground Floor = 0 kN How much is the overturning moment (kN-m) at the base? A. 1500 B. 3120 C. 3360 D. 2650 Situation 2 The 2L-200x150x12 with long legs back-to-back shown in FIG. ABP-134 is connected to the gusset plate. Bolt diameter, db = 25 mm Bolt hole diameter, dh = 27 mm S1 = S2 = 60 mm Properties of 2L-200x150x12: A = 8112 mm² Fy = 248 MPa Fu = 400 MPa x = 37 mm Allowable stresses: Given: Properties of Steel Column: Depth, d = 305 mm Web thickness, tw = 7.5 mm Flange width, bf = 200 mm Flange thickness, tf = 12 mm Base plate, B x N = 300 mm x 450 mm Loads: P = 720 kN H = 160 kN Allowable base plate bending stress, Fb = 186 MPa Allowable bolt shear stress, Fv = 68 MPa Allowable weld shear stress, Fw = 124 MPa 10. Find the required base plate thickness (mm). Consider fixity at the edges of a rectangle whose sides have dimensions equal to 0.80bf and 0.95d. Neglect the effect of the lateral force H. A. 21 B. 24 C. 28 D. 32 11. Using 16 mmØ, how many are required to resist the lateral load? A. 8 bolts B. 12 bolts C. 16 bolts D. 4 bolts 12. Using 8 mm thick fillet weld, what is the total length (mm) required to resist the lateral load? A. 137 B. 161 C. 228 D. 1020 13. It is defined as the rigidity of the structure. A. Toughness C. Stiffness B. Ductility D. Elasticity 14. It is defined as the flexibility of the structure. A. Reciprocal of Deformation B. Reciprocal of Stiffness C. Reciprocal of Ductility D. Reciprocal of Elasticity Situation 4 The vertical member consisting of 2 (two) unequal leg angles with long legs back to back are welded to the 8-mm thick gusset plate as shown in FIG. STRST – 278. MANILA: Room 206, JPD Building, CM Recto Avenue, Manila CEBU: 4/F J. Martinez Bldg., Osmeña Blvd., Cebu City Telephone Number: (02) 516 7559 (Manila) E-Mail: buksmarquez1 @yahoo.com (032) 254-6697 (Cebu) Given: Angle dimension = 75 mm x 50 mm x 6 mm a = 25 mm Area of two angles = 1535 mm2 Weld thickness = 5 mm Steel yield stress, Fy = 248 MPa Allowable weld shear stress, Fw = 124 MPa Allowable beam shear stress at ultimate loads = 0.76 MPa Use ρb = 0.026 15. Due to a force P = 60.5 kN, what is the length of weld L 2 (mm) so that each fillet weld is equally stressed in shear? Neglect end returns. A. 23 B. 69 C. 46 D. 83 22. If the effective depth of the beam is 500 mm, evaluate the nominal moment capacity, in kN-m. A. 366 B. 407 C. 427 D. 452 16. If L1 = 50 and L2 = 50, determine the capacity of the member based on shearing of the welds, in kN. A. 87.3 B. 43.0 C. 33.6 D. 67.2 17. If instead of welds, two (2) bolts are used, find the minimum bolt diameter (mm) to carry a force P=80 kN. Allowable bolt stress=68 MPa. A. 14 B. 18 C. 20 D. 28 Situation 5 Refer to figure STFRAME-001 and figure ST-1 Given: S = 3m L = 10m Superimposed Dead Load = 6.0 kPa Live Load = 4.8 kPa Properties of Beam CG: Section = 468 mm x 97 kg/m Area, A = 12,324 mm^2 Depth, d = 465 mm Flange width, bf = 193 mm Flange thickness, tf = 19 mm Web thickness, tw = 11 mm Moment of Inertia, Ix = 445 x 10^6 mm^4 Moment of Inertia, Iy = 23 x 10^6 mm^4 Yield Strength, Fy = 344 MPa rT = 50 mm Considering bending about x – axis 18. Which of the following gives the maximum bending stress in Beam CG? A. 217 B. 145 C. 248 D. 98 19. If lateral supports are to be provided, calculate the biggest spacing to be specified so that the maximum allowable flexural stress, Fb = 0.66 Fy. A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 20. What is the permissible flexural stress if the compression flange of the beam is laterally supported only at midspan? Cb = 1.0 A. 117 B. 126 C. 130 D. 142 Situation 6 Refer to FIG. STRRC - 012 Given: Beam width, b = 400 Total depth, h = 600 mm x = 56 mm Diameter of tension reinforcements, D1 = 28 mm Diameter of compression reinforcements, D2 = 25 mm Diameter of stirrups, ds = 12 mm Clear concrete cover = 40 mm Concrete, f’c = 21 MPa Main reinforcements, Fy = 345 MPa Stirrups, Fyt = 278 MPa 21. Evaluate the minimum value of x in the figure based on code requirement. A. 56 B. 60 C. 53 D. 44 23. If the effective depth of the beam is 500 mm, evaluate the nominal shear strength of the beam at section where stirrups are spaced at 100 mm center-to-center, in kN. A. 396 B. 466 C. 350 D. 542 Situation 7 A prestressed concrete pile with a cross section of 30cm by 30 cm by 20m long is used in a certain construction project. The prestressed piles are prestressed with 8 – 10mm diameter strands with a total effective stress of 70,000 kg after losses due to creep, shrinkage of concrete etc. The foreman desires to place two pick up points in handling the piles during the loading and unloading process. 24. Where must the pick up points (at equal distances at the ends) (m) be placed in order that the stresses in the pile shall be kept minimum. A. 3.30 C. 4.14 B. 3.75 D. 4.52 25. Compute the moments(kg-m) at the pick up points. A. 1176 C. 1851 B. 1519 D. 2206 26. Determine the total stress(kg/cm^2) in the pile at this condition. A. 119 C. 104 B. 111 D. 127 Situation 8 Given the following data for the beam shown in figure: Beam dimension: Beam width, bw = 260mm fc’ = 21 MPa Overall depth, h = 600mm fy = 415 MPa Effective depth, d = 540mm fyv = 275 Beam length, L = 7.5m Stirrup diameter, db= 10mm Loads (factored) Pu = 147 KN Wu = 19.6 KN/m 27. Calculate the spacing (mm) of stirrups at critical section near the support. A. 124 B. 112 C. 148 D. 136 28. Calculate the spacing (mm) of stirrups at the third point of the beam. A. 165 B. 195 C. 154 D. 182 29. Calculate the spacing (mm) of stirrups at midspan. A. 300 B. 150 C. 270 D. 135 30. Diaphragm discontinuity is a type of: A. Vertical irregularity B. Plan irregularity C. Continuous irregularity D. Geometric irregularity MANILA: Room 206, JPD Building, CM Recto Avenue, Manila CEBU: 4/F J. Martinez Bldg., Osmeña Blvd., Cebu City Telephone Number: (02) 516 7559 (Manila) E-Mail: buksmarquez1 @yahoo.com (032) 254-6697 (Cebu) 31. Mass irregularity said to exist if the mass of any storey is more than ___ of the adjacent storey. A. 120% C.130% B. 140% D. 150% 32. Vertical geometric irregularity said to exist if the horizontal dimension in any storey is more than ___ of the adjacent storey A. 120% C. 130% B. 140% D. 150% Situation 9 A column 3m high has a solid circular cross section and carries an axial load of 10,000 kN. If the direct stress in the column is limited to 150N/mm2 Take E=200 000N/mm2 and ν =0.3. 33. Determine the minimum allowable diameter (mm)of the column. A. 211 B. 250 C. 345 D. 292 31. Calculate the shortening of the column (mm) due to this load. A. 2.24 B. 2.50 C.2.45 D.2.91 32. Calculate the increase (mm)in the diameter. A. 0.066 B. 0.005 C. 0.089 D. 0.333 Situation 10 For the singly-reinforced beam shown in FIG. STRRC - 0113 Given: Beam width, b = 300 Diameter of tension reinforcements, D1 = 28 mm Diameter of stirrups, ds = 12 mm Spacing of stirrups = 100 mm Clear concrete cover = 40 mm Concrete, f’c = 21 MPa Main reinforcements, Fy = 345 MPa Stirrups, Fyt = 278 MPa Allowable beam shear stress at ultimate loads = 0.78 MPa 33. If the nominal shear capacity of the beam is 300 kN, evaluate the required total depth. A. 348 B. 414 C. 475 D. 530 34. If the nominal moment capacity of the beam is 275 kN-m, evaluate the required total depth. A. 404 B. 419 C. 470 D. 485 35. Evaluate the required minimum width of the beam. A. 280 B. 291 C. 300 D. 318 Situation 11 Refer to FIG. RCD-10.013 Given: Concrete, f’c = 27.5 MPa Steel, fy = 415 MPa Clear Concrete Cover to 12 mm diameter stirrups is 40 mm Slab thickness, t = 100 mm Steel ratio at balanced condition, pb = 0.028 Given: Beam width, bw = 400 mm, Effective depth, d = 500 mm 36. Using 28 mm diameter main reinforcement bars, which of the following gives the ultimate moment capacity (kN-m) of the section? A. 495 37. Given: B. 551 C. 351 D. 316 Mu = 550 kN-m, bw = 400 mm, Effective depth, d = 500 mm Which of the following gives the required diameter (mm) of the reinforcing bars of the section? A. 28 B. 20 C. 25 D. 32 38. Which of the following gives the required minimum width of the beam, bw (mm) based on code requirements for concrete cover of rebars? A. 344 B. 316 C. 356 D. 304 Situation 12 A cantilever beam 5m long carries a concentrated load P at 3.75m from the fixed end. Beam Inertia = 1.6x10^9mm^4 E = 25GPa P = 150KN 39. What is the maximum deflection (mm) of the beam under the load P? A. 59 B. 65 C. 78 D. 99 40. Determine the maximum beam deflection (mm). A. 59 B. 65 C. 78 D. 99 41. What upward force (KN) is to be applied at the free end to prevent the beam from deflecting? A. 59 B. 95 C. 150 D. 99 Situation 13 A simply supported girder spans 10m. The girder carries 3 concentrated loads each 30KN. At 2.5m spacing. The girder also carries a uniformly distributed load of 15 KN/m throughout its length. Given: Girder properties: Section: 460 x 97 kg/m Area, A = 12320 mm^2 Depth, d = 465 mm Flange width, bf = 193mm Flange thickness, tf = 19mm Web thickness, bw = 11mm Moment of Inertia: Ix = 445 x 10^6 mm^4 Iy = 23 x 10^6 mm^4 Yield strength, Fy = 248 MPa Rt = 50mm 42. Which of the following gives the maximum bending stress in MPa. A. 365.10 B. 176.33 C. 182.55 D. 352.67 43. Which of the following gives the maximum web shear stress in MPa. A. 23.46 B. 24.39 C. 14.12 D.13.58 44. Calculate the maximum shear stress in MPa at the neutral axis. A. 27.23 B. 26.19 C.15.76 D.15.16 MANILA: Room 206, JPD Building, CM Recto Avenue, Manila CEBU: 4/F J. Martinez Bldg., Osmeña Blvd., Cebu City Telephone Number: (02) 516 7559 (Manila) E-Mail: buksmarquez1 @yahoo.com (032) 254-6697 (Cebu) A footing supports a 250mm thick concrete wall. Given: Allowable soil bearing pressure = 192 kPa Thickness of footing = 350 mm Concrete, fc’ = 27.50 MPa Steel, fy = 415 MPa Situation 16 – Identify the following: 45. The footing is subjected to a moment of 126 kN-m and a total vertical load of 280 kN. Find the minimum width (m) of the footing to prevent uplift. A. 2.7 B. 1.4 C. 1.0 D. 2.3 55. It is the point through which the applied lateral force acts. A. Shear wall C. Center of mass B. Center of rigidity D. Eccentricity 54. It is the point through which the resultant of the resistance to the applied lateral force acts. A. Shear wall C. Center of mass B. Eccentricity D. Center of rigidity 46. Given: Resisting Moment, Mr = 440 kN-m Overturning Moment, Mot = 260 kN-m Total Vertical Load = 265 kN Find the minimum width (m) of the footing to prevent uplift. A. 4.1 B. 1.4 C. 2.9 D. 2.1 47 .Given: Footing width = 3.00 m Resisting Moment, Mr = 500 kN-m Overturning Moment, Mot = 265 kN-m Total Vertical Load = 335 kN Which of the following gives the maximum soil bearing pressure (MPa)? A. 290 B. 279 C. 223 D. 319 Situation 14 A 4-m long beam is fixed at the left end and is supported by a spring at the right end. The spring stiffness is equal to 60 kN/m. Determine the following if the entire length of the beam is subjected to a uniformly distributed load of 800 N/m. For the beam, E = 10 GPa and I = 80 x 106 mm4. 48. Determine the deflection (mm) at the right end of the beam when the spring is removed. A. 32 B. 27 C. 22 D. 42 49. Determine the deflection (mm) of the spring. A. 13.2 B. 27 C. 12.3 D. 14.1 50. Determine the moment (KN -m) at the fixed end. A. 13.2 B. 27 C. 12.3 D. 3.45 Situation 15 Given: in FIG. STRRC - 234 b x h = 450mm x 600mm Main reinforcement, Ast = 8 – 28mm ϕ Lateral ties = 10mm ϕ Yield strength, fy (main bars) = 415 MPa Yield strength, fyv (lateral ties) = 275 MPa Concrete strength, fc’ = 28 MPa Spacing of ties = 100 mm on centers Modulus of Elasticity = 25000 MPa Concrete cover to center of main bars = 70mm Concrete unsupported height, Lu = 2.5m Effective length factor, k = 1.0 51.What is the nominal axial strength (KN) of column (Pn)? A. 6,663 B. 4678 C. 5012 D. 8354 52. Find the critical buckling load Pc (KN). A. 63,955 B. 35,975 C. 31,978 56. It is the distance between the center of rigidity and the center of mass. A. Deflection C. Drift B. Pitch D. Eccentricity Situation 16 A steel W 410 X 100 column is encased in a 450 mm x 450 mm concrete section and has unsupported height = 6m. k = 1.0, fc’ = 20.7 MPa , fy = 276.5 MPa. Properties of W 410 x 100 column At = 12700 mm2 I = 398 x 106 mm4 57. Find the radius of gyration (mm) of the composite section using the formula r A. 190 0.2E c I g E s I t 0.2E c A g E s At B. 113 C. 166 58. Find the slenderness ratio of the column. A. 36 B. 53 C. 32 D. 159 D. 38 59. Find the safe ultimate axial load (KN) of the column. A. 3837 B. 4514 C. 3261 D. 4796 Situation 17 A 12m simply supported beam is 300mm wide and 600 mm deep. It is prestressed with 1150 KN applied at an eccentricity of 150 mm and which Ec = 27606 MPa. 60. Compute the deflection (mm) at initial condition. A. 7.68 B. 13.15 C. 20.83 D. 28.51 61. Compute the deflection (mm) at full service condition. A. 7.68 B. 13.15 C. 20.83 D. 0 62. The safe uniform live load capacity (KN/m)of the beam is most nearly equal to A 4.24 B. 7.26 C. 7.2 D. 8.35 Situation 17 Refer to the FIG.SMN10.09 Frame ACGE is on hinged supports at A and at E. To resist the cable pull, T, the frame is braced at B and at F. Given: T = 18 kN a=1m b=2m c=1m D. 17,988 53. Calculate the nominal shear strength for bending about the y axis. A. 553.75 B. 447.30 C. 380.2 D. 470.69 63. Calculate the reaction (kN) at D. A. 54.0 B. 25.4 C. 108 D. 76.4 64. Find the stress (MPa) in the brace BD which has an outside diameter of 75 mm and is 6 mm thick. MANILA: Room 206, JPD Building, CM Recto Avenue, Manila CEBU: 4/F J. Martinez Bldg., Osmeña Blvd., Cebu City Telephone Number: (02) 516 7559 (Manila) E-Mail: buksmarquez1 @yahoo.com (032) 254-6697 (Cebu) A. 83 B. 58.7 C. 19.5 D. 41.5 65 . If brace BD consists of 2 flat bars bolted to the post AC at B using 20 mm diameter bolt, what is the average shear stress (MPa) in the bolt? A. 171.9 B. 40.4 C. 85.9 D. 121.5 Situation 18 The 8.5m span beam shown in Fig. STR 1 – 1O.1 carries a monolithic slab cantilevering 1.8m past the beam centerline. The resulting L beam supported a liveload of 13.16 KN/m along the beam centerline plus a 2.4KPa load uniformly distributed over the upper slab surface. The effective depth to the flexural steel centroid is 546mm, and distance from the beam surfaces to the centroid of stirrup steel is 44mm. fc’ = 20.7 MPa U = 1.4D + 1.7L 73. Find the force in cable FC (KN)? A. 4.7 B. 2.3 C. 3.8 Situation 22 A column carrying a load of 800KN is supported on a pedestal type footing weighing 200KN. At the base of the column (on top of the pedestal) which is 1.8m above the base of the footing, a horizontal transverse force of 36KN and a horizontal longitudinal force of 54 KN are applied. The footing base is 3m x 2.4m. Thickness of the footing is .0.6m, height of the backfill on top of the footing is 0.9m. Concrete unit weight is 24KN/m3. Unit weight of soil is 17KN/m3. 74. Calculate the maximum net soil pressure (KPa). A. 196 B. 188 C. 214 D. 202 75. What is the required soil bearing capacity (KPa). A. 226 B. 218 C. 244 D. 232 For monolithic or fully composite construction, a beam includes that portion of a slab on each side of the beam extending a distance equal to the projection of the beam above or below the slab, whichever is greater, but not greater than four times the slab thickness. 66. Determine the design shear force Vu (KN) at critical section. A. 188.1 B. 124.4 C. 109.6 D. 164.3 Fig. EMM 15.38 67. Determine the torsional moment Tu(KN-m) at critical section. A. 5.6 B. 6.63 C. 53.7 D. 55.2 68. What is the allowable factored torsional moment (KN-m) using reduction factor 0.85 based on code requirement. Tu A.9.45 φ f c ' Acp 2 12Pcp B. 7.31 Fig. SMN 10.09 C. 11.45 D. 7.50 69. Private garages, carports, sheds and fences over ______ high are under miscellaneous structures as stated in NSCP. A. 2m B. 2.5m C. 1.5m D.1.0 70. Soft story is one in which the lateral stiffness is less than _________ percent of the stiffness above. A. 60 B. 70 C. 50 D.40 Situation 19 – Refer to Fig. EMM 15.38 Diagonals BG, CF, CH, and DG can brace the truss in tension only. Given: P1 = 0 KN P2 = 3 KN P3 = 3 KN F = 1.5 KN Dimensions: H=3m S1 = S2 = 3 m S3 = S4 = 2.25 m 71. What is the force in member FB (KN)? A. 2.3 B. 1.7 C. 3.3 D. 4.7 72. What is the force in member HD (KN)? A. 2.7 B. 0 C. 4.5 D. 3.4 D. 0 MANILA: Room 206, JPD Building, CM Recto Avenue, Manila CEBU: 4/F J. Martinez Bldg., Osmeña Blvd., Cebu City Telephone Number: (02) 516 7559 (Manila) E-Mail: buksmarquez1 @yahoo.com (032) 254-6697 (Cebu) Fig STR 1 – 10.1 FIG. STRST - 157 FIG. SSE 10.102 Fig. STFRAME-001 Fig. STRC – 11.5 Fig. STRC – 11.5 FIG. RC – 5 FIG. STCNM 16.023 wR = 750 kN w3 = 900 kN H3 = 3 m m w2 = 1000 kN H2 = 3 m m L=8m H1 = 3.5 m m FIG. ABP-143 FIG ST - 1 FIG. ABP-134 MANILA: Room 206, JPD Building, CM Recto Avenue, Manila CEBU: 4/F J. Martinez Bldg., Osmeña Blvd., Cebu City Telephone Number: (02) 516 7559 (Manila) E-Mail: buksmarquez1 @yahoo.com (032) 254-6697 (Cebu) Refer to FIG. STRRC - 012 h x b FIG. STRRC - 0113 h b FIG. RCD-10.013 FIG. STRRC - 234 FIG. STRST – 278