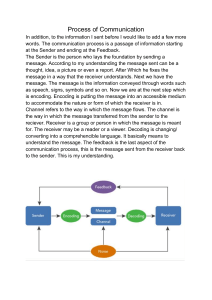
COMMUNICATION Oral Communication in Context The Development of Listening and Speaking Skills and Strategies for Effective Communication in various situations . WHAT IS COMMUNICATION? Is a process of exchanging ideas between two or more persons. The act or process of using words, sounds, signs, or behaviors to express or exchange information or to express your ideas, thoughts, feelings, etc., to someone else A process by which information is exchanged between individuals through a common system of symbols, signs, or behavior . Value of Communication The word communication came from the Latin word “communis” which means common or to “commune” or to come together or to share something in common. Communication in its most basic sense is the cement that holds society together. Without it, society will fall apart. Maslog 1988 THE NATURE OF COMMUNICATION Communication represents the important role inside personal existence, family member’s existence, cultural existence, company existence and many others. 1. Communication is related to human activity: Communication exchanges are actually directly linked with every single ball of human being lifetime. 2. Communication involves two or more parties: At least, two parties are involved in virtually any communication exchange process. 3.Communication could be one-way or maybe two-way process: Communication might take the design involving two-way or maybe one-way process. With two-way communication, the receiver sends his feedback to the sender after receiving the message. 4. Success of communication depends on a proper understanding of the parties involved: Powerful communication comes about if your receiver feels your concept you might say your sender posts the idea. If the receiver doesn’t deliver his or her reaction to your sender, your sender is not going to fully grasp your receiver’s view. 5. Conversation in organization flows in a variety of styles: With organization, information flows in a variety of recommendations, for example way upward direction, down way, horizontal way and many others. 7 Major Elements of Communication Process (1) Sender: The person who intends to convey the message with the intention of passing information and ideas to others is known as sender or communicator. (2) Ideas: This is the subject matter of the communication. This may be an opinion, attitude, feelings, views, orders, or suggestions. (3) Encoding: Since the subject matter of communication is theoretical and intangible, its further passing requires use of certain symbols such as words, actions or pictures etc. Conversion of subject matter into these symbols is the process of encoding. (4) Communication Channel: The person who is interested in communicating has to choose the channel for sending the required information, ideas etc. This information is transmitted to the receiver through certain channels which may be either formal or informal. (5) Receiver: Receiver is the person who receives the message or for whom the message is meant for. It is the receiver who tries to understand the message in the best possible manner in achieving the desired objectives. (6) Decoding: The person who receives the message or symbol from the communicator tries to convert the same in such a way so that he may extract its meaning to his complete understanding. (7) Feedback: Feedback is the process of ensuring that the receiver has received the message and understood in the same sense as sender meant it. Communication Process SPEAKER RECEIVER MESSAGE LINEAR MODEL OF COMMUNICATION The Interactive (stimulus-response) Model of Communication Feed back SPEAKER RECEIVER MESSAGE Feed back Purposive Communication COURSE DESCRIPTION Purposive Communication is about writing, speaking and presenting to different audiences and for various purposes NATURE OF COMMUNICATION Is a process of exchanging ideas between two or more persons. The act or process of using words, sounds, signs, or behaviors to express or exchange information or to express your ideas, thoughts, feelings, etc., to someone else A process by which information is exchanged between individuals through a common system of symbols, signs, or behavior . Communication is: ❖ Reciprocal because we cannot separate communicators into sender and receiver. ❖ Process because it keeps on “evolving and changing”. ❖ involves creating and sharing of meaning. Process of Communication VARIOUS MODEL OF COMMUNICATION Speaker Audience Speech Occasion ARISTOTLE’S MODEL OF COMMUNICATION Effect Wendel Johnson Model of Communication EVENT /SOURCE SENSORY STIMULATION Pre- verbal Neurophysiological State Transformation of pre-verbal into symbolic forms Verbal Formulation Berlos’s SMCR Model of Communication Source Message Encodes Channel Decodes Receiver Conversation Skills Content Hearing Conversation Skills Attitudes Elements Seeing Attitudes Knowledge Treatment Touching Knowledge Social System Structure Smelling Social System Culture Code Tasting Culture GIVE THE SIX BASIC ELEMENTS OF COMMUNICATION SIX BASIC ELEMENTS OF COMMUNICATION SENDER/RECEIVER MESSAGE CHANNEL FEEDBACK NOISE SETTING PERSONS TOPIC / INFORMATION MEDIUM/ TOOL REACTION/RESPONSE DISTURBING FACTOR TIME/ PLACE VERBAL AND NON-VERBAL COMMUNICATION • Non-verbal communication is a form of sharing insights and ideas ,information, experiences etc. without the use of words. • Most of the time verbal communication is supported by non-verbal communication to better portray the meanings a speaker would like to share. Types of Non- Verbal Communication 1. Body Movements / Body Kinetics They come in the following categories: a. EMBLEMS – these are body movements which have direct translation into words. Ex . Thumbs up b. Illustrators – these are used to accent, emphasize or reinforce words. Ex. Pointing fingers when giving direction c. Regulators – these are signs showing control at the back and forth natures of speaking and listening. Ex. head nods, hand gestures, shifts in posture during interaction d. Display of feelings – a persons face or body movements may convey how intense his emotions is. Ex. Tight hug signify an intimate relationship e. Adaptors – these are non- verbal ways used in adapting to the communication situation. Ex. A woman visited a friend’s house and when she was there, she started picking up scattered things on the floor. She implied that her friend could hardly clean her house. 2. Paralanguage-refers to the ways of saying something. It includes the characteristics as: 3. Body Types can also communicate a message • Rate – speed of speaking • Pitch – highness/lowness of tone • Volume- loudness • Quality- pleasing / unpleasing sound a.Ectomorphs (thin people) b.Endomorphs ( fat people) c.Mesomorphs ( athletic people) 4. Attractiveness can get positive response than those who are perceived not to be attractive. Physical attributes of a person may mean something to the people around her. 5.Body Adornment involves form of clothing, make up, jewelry and hairstyle Ex. An applicant who is dressed appropriately might likewise be hired than those who are not. 6. Space and Distance/ Proxemics It concerns the way a person uses the space around him as well as the distance where he stands. It may be explained through the following: a.Intimate distance b.Personal distance c.Social distance d.Public distance 7. Touch- the kind of touch used in communication reflects meaning about the relationship between the sender and the receiver. The more intense the relationship, the more frequent and more intimate the touch 8. There are two kinds of people based on time; punctual and late CULTURAL DIFFERENCES What is culture? - Culture influences many parts of people’s lives including: Food Clothes Opinions Identity and etc. More so, according to Tyler (1870) culture… is that complex whole which includes knowledge, belief, art, morals, law, custom, and many other capabilities and habits acquired by man as a member of society. Lastly, culture is the collective programming of the mind which distinguishes the members of one group or category of people from another. (Hofstede, 1994) Culture SENSITIVITY? Cultural Sensitivity begins with a recognition that there are differences between cultures. Cultural sensitivity is more than an awareness that there are differences in culture in order to interact effectively either through verbal and non-verbal communication. Sensitivity to culture is a set of skills allows you to understand about people whose cultural background is not the same as yours. Are you culturally sensitive? A culturally competent person views all people as unique individuals and realizes that their experiences, beliefs, and language affects their perceptions. Are you culturally sensitive? People who don’t recognize differences between cultures fall on stereotyping and discriminating minority groups. SENSITIVITY to GENDER Aspects of Gender: Assignment - This is the gender from birth, either being male and female, it is also the gender prescribed by the society. (1) Aspects of Gender: Role – This is the set of behaviors, mannerisms, and other traits that society use to express as part of the gender assigned. (2) Aspects of Gender: Identity – This is what we think the gender should be in any given time. (3) Aspects of Gender: Attribution – This is the gender assigned to people when we first meet them and is based on a set of cues that differentiate to culture. (4) CULTURAL APPROPRIATION AND APPRECIATION APPROPRIATION VERSUS APPRECIATION knowing what sets them apart HERE’S THE DIFFERENCE APPROPRIATION APPRECIATION it is defined as the act of taking something for one’s own use without the creator’s or owner’s permission. it is the recognition and enjoyment of the good qualities of someone or something. ? Cultural Appreciation is when elements of a culture are used while honoring their sources. This incorporates respect and value. It does not destroy the significance of one’s culture and practices. Cultural Appropriation It is the act of taking intellectual property, traditional knowledge, cultural expressions, or artifacts from someone else’s culture without permission. This is an insensible act of a dominant group towards the minority as they adopt their cultural elements. WHY IS IT OFFENSIVE? Think about it… “ CULTURE IS NOT A COSTUME. 51 steps in avoiding cultural appropriation 52 CULTURAL APPROPRIATION AND APPRECIATION EXAMPLES OF CULTURAL DIFFERENCES ITALIAN SPAGHETTI • Sauce is made from fresh tomato sauce. • Olive oil and freshly minced garlic are added. • Usually pasta is cooked in an al dente manner. FILIPINO SPAGHETTI • Usually made with sweet tomato/banana sauce/ketchup. • Slices of red hotdogs are often added. • Somewhat overcooked noodles. Examples of cultural differences CHINESE TEA AMERICAN ICED TEA ENGLISH TEA • Thus, culture makes up a large part of everything that we do in our day to day life. Cultural awareness therefore is needed in order to create crosscultural understanding and acceptance. Examples of cultural differences Here below are some of the expressions from varying cultures. In Mediterranean European countries, Latin America, and Sub Saharan Africa, being half an hour late is… NORMAL In most Northern European Countries this is… EXTREMELY RUDE EXAMPLES OF CULTURAL DIFFERENCES In Western Cultures a handshake is commonly used for GREETING In other eastern cultures bowing comes first prior to greetings as a sign of In the Philippines “Mano po” gesture is a sign that honors the elderly. RESPECT HONORING GESTURE EXAMPLES OF CULTURAL DIFFERENCES In England, this gesture usually means… OK Whereas in France this gesture that forms an “o” means… NOTHING or WITHOUT VALUE EXAMPLES OF CULTURAL DIFFERENCES In some countries laughing is considered as… HAPPINESS In Japan however, it is considered as a sign of… CONFUSION or EMBARASSMENT Examples of cultural differences In most counties shaking the head from side to side is considered as a…, NO Whereas in India, this gesture usually means… YES CULTURAL DIFFERENCES: terminologies FART In English this word is a verb that means “to expel intestinal gas from the anus.” However in Denmark, Norway, and Sweden, this word usually means speed. GIFT In English this word usually denotes a positive and pleasant meaning, such as an act of endowment, present, donation, bestowal and others. In Germany however, this word means poison. CRAP In English this word as a verb means to defecate, while as a noun it means feces. Whereas in Romania, this word pertains to a type of fish. BRAT In English, this word as a noun means an illmannered annoying child. However in countries such as Russia, Poland, Ukraine, Croatia, and Serbia, this word means brother. KISS In English this word as a noun means “a gentle touch or contact,” and “a caress with the lips.” On the other hand, in Sweden, this word means Pee. PRESERVATIVE In English this word is usually associated within a process of preserving or saving something from decomposition. In France however, préservatif vulgarly means condom. Lol As an Internet slang it usually is an acronym that means “Laughing Out Loud.” In Dutch however, this word actually means Fun. SLUT In English this word is associated with a promiscuous woman. On the other hand, in Sweden this word means End. Visible but often not decipherable Greater level of awareness Artifacts and Creations Visible & Audible Behavior Patterns Technology Art Values Basic Assumptions Relationship to Environment •Taken for Nature of Reality, Time & granted Space •Invinsible Nature of Human Nature Nature of Human Activity •Pre-consious Nature of Human Relationships & their Interaction Figure 1: The Levels of Culture (Minor adaptation of Schein 1984: 4) TIPS ON HOW TO BE CULTURALLY AWARE: 1. Engage with other’s cultures by asking questions. 2. Be open! Don’t get into the habit of thinking your way is the only way of doing something. 3. Think about what you can learn from them no matter how unusual it is. 4. Invite someone to share his/her culture with you. 5. Overcome Stereotypes.