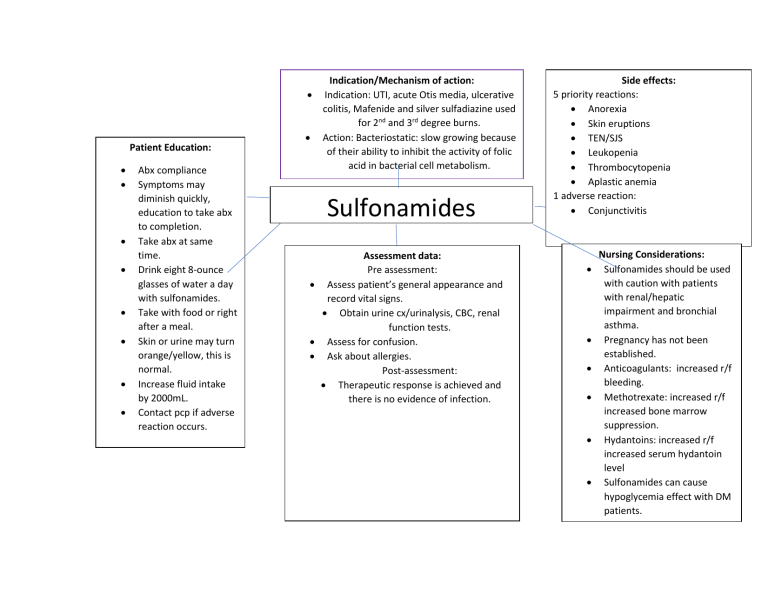
Patient Education: • • • • • • • • Abx compliance Symptoms may diminish quickly, education to take abx to completion. Take abx at same time. Drink eight 8-ounce glasses of water a day with sulfonamides. Take with food or right after a meal. Skin or urine may turn orange/yellow, this is normal. Increase fluid intake by 2000mL. Contact pcp if adverse reaction occurs. Indication/Mechanism of action: • Indication: UTI, acute Otis media, ulcerative colitis, Mafenide and silver sulfadiazine used for 2nd and 3rd degree burns. • Action: Bacteriostatic: slow growing because of their ability to inhibit the activity of folic acid in bacterial cell metabolism. Sulfonamides Assessment data: Pre assessment: • Assess patient’s general appearance and record vital signs. • Obtain urine cx/urinalysis, CBC, renal function tests. • Assess for confusion. • Ask about allergies. Post-assessment: • Therapeutic response is achieved and there is no evidence of infection. Side effects: 5 priority reactions: • Anorexia • Skin eruptions • TEN/SJS • Leukopenia • Thrombocytopenia • Aplastic anemia 1 adverse reaction: • Conjunctivitis • • • • • • Nursing Considerations: Sulfonamides should be used with caution with patients with renal/hepatic impairment and bronchial asthma. Pregnancy has not been established. Anticoagulants: increased r/f bleeding. Methotrexate: increased r/f increased bone marrow suppression. Hydantoins: increased r/f increased serum hydantoin level Sulfonamides can cause hypoglycemia effect with DM patients.