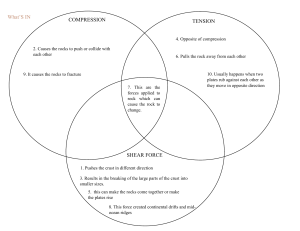
CHAPTER 1. I. GEOLOGY IN CIVIL ENGINEERING SCOPE OF GEOLOGY Geology is the science of the Earth, it is not a basic science like mathematics, physics, chemistry, or biology, but is an application of these basic sciences to Earth. Engineering geology may be defined as the branch of applied science which deals with the application of geology fora safe and economic design and construction of a civil engineering projects. The basic objective of engineering geology are two folds: 1. It enables a civil engineer to understand the engineering implications of certain condition should relate to the area of construction which is essentially geological in nature. 2. It enables a geologist to understand the nature of the geological information that is absolutely essentially for a safe design and construction of a civil engineering projects. Rocks are the most common material which is used in the construction of foundation. The local geology of an area is important when planning a major construction. The full knowledge of geology increase the strength, stability, and durability of civil engineering projects. ROLE OF KNOWLEDGE OF GEOLOGY IN CIVIL ENGINEERING Geology plays a very important role in the field of civil engineering. Some applications of the knowledge of geology are given below. It provides knowledge about materials used for construction Its knowledge is helpful for river control and shipping work. Its knowledge is helpful for constructing dams. Geotechnical engineers needs knowledge about this subject for digging work. Its knowledge is required for foundation faults. For design of highways and roads. In construction of tunnels Soil tests are done before any project. Economical design is advanced. Nature of soil materials can be find out. SCOPE OF GEOLOGY IN CIVIL ENGINEERING It is defined as that of applied science which deal with the application of geology for a safe, stable and economic design and construction of a civil engineering project. Engineering geology is almost universally considered as essential as that of soil mechanics, strength of material, or theory of structures. The application of geological knowledge in planning, designing and construction of big civil engineering projects. The scope of engineering geology is best studied with reference to major activities of the profession of a civil engineer which are A) Construction B) Water resource development C) Town and Regional Planning A) Construction Civil construction falls in the category of civil engineering which is all about designing, constructing and maintaining the physical and naturally built environment. Civil construction is the art of building bridges, dams, roads, airports, canals, and buildings. Following work comes under construction Planning Designing Execution Planning :Following geological information is greatly useful in planning an engineering project. Study of photograpic maps : i) Topographical maps: Such maps give details of relief features and are essential to understand relative merit and demerit of all the possible sites. ii)Hydrological Maps: These maps give broad details about the distribution and geometry of the surface water channels and also the occurrence and depth contour of groundwater. iii) Geological Maps: Petrological characters and structural disposition of rock types as developed in the proposed area depicted in geological maps. (insert geological map Phil) Designing: Matter of designing an engineering project, the role of geological information is very important. Existence of hard bed rocks & their depth from & inclination with the surface. Mechanical properties along & across of site Compressive strength Shear strength Porosity & permeability Modulus of elasticity On earth surface plane of weakness Zone of weak material Ground water table Seismic zone (earthquake zone) Site Execution: At every project site, Bond sets up a site management and supervision team that prepares the project site covering all aspects of coordination, administration, planning, etc. to ensure smooth functioning of work on site. Few of the functions of the site execution team is to establish project site guide, progress monitoring, quality assurance, ensuring safety at site, supervision of civil and construction work, receiving & storage of equipment, supervision of erection and installation, finalization of the project and implementation of site environment compliance requirements. B.) Water Resources Development Exploration and development of water resources have become very important areas of activities for scientists, technologists and engineers in all parts of the world. The water resource engineers has to understand the water cycle in all essential details. Study of water cycle is an essential prerequisite for effective planning and execution of major water resource development programmers on national and regional level. C.) Town and Regional Planning A town planner is concerned essential with land utilization in as best and as aesthetics a manner as possible for developing cities and towns for meetings social needs in different areas. The regional Town Planner is responsible for adopting an integrated approach in all such cases of allocation of land for developmental projects. Thus a change induced in the natural setup of an area due to a proposed new project is going to lead a series of changes in the adjoining and even in distant places. In nature, nothing works in isolation. As such all sound planning must be in tune with the natural features and processes of a region. II. EARTH STRUCTURE AND COMPONENTS Have you ever wondered how do scientists know the structures of the Earth? Well, they use a device called seismograph. Scientists use waves (generated through seismograph) to study the different layers of the earth. Usually, they use seismic waves, which are waves generated by earthquakes or nuclear-test explosions. So, scientists study the path and speed of these waves through the earth to decipher boundaries and the materials that make up the layers. While we can't see deep into the Earth, geologists have a variety of neat tricks to create a picture of our Earth's layers. The Earth is composed of three main layers: Crust, mantle, and core. Layers of the Earth: 1. CRUST Earth's crust is what we walk on every day. It is the thin (relatively) outermost layer that wraps around the Earth and ranges in temperature from 500 to 1,000°C. The crust is split into two types, continental and oceanic. Earth's crust is 5 to 70 km thick. Continental crust makes up the land on Earth, it is thicker (35 - 70 km), less dense and mostly made up of the rock granite. Oceanic crust makes up most of the ocean, it is thinner (5 - 7 km), denser and mostly made up of the rock basalt. Fun fact: The crust makes up only 1% of the volume of Earth. 2. MANTLE Just below the crust lies the mantle. The mantle is semi-liquid, sort of like a malleable plastic and makes up 84% of Earth's volume. Earth's mantle is 2,900 km thick and is broken down into 3 main zones, the lithosphere, asthenosphere, and mesosphere. 3. CORE The core is the innermost layer of the Earth and is subdivided into two parts: Outer core and Inner core. The outer core lies beneath the mantle. This liquid iron and nickel layer spins as the planet rotates and creates Earth's magnetic field. This magnetic field helps to protect us from the Sun's solar radiation. The outer core is 2,200 km thick and very hot at up to 6,100°C! The inner core is the deepest layer on Earth. It is also made up of iron and nickel but the pressure is so high that it is no longer liquid. The temperatures in the inner core are as hot as the surface of the sun, about 5505 °C. Earth's inner core is 1,230 to 1,530 km thick. Fun Fact: Earth's inner core is growing in size by 1mm per year. Eventually, the entire outer core will solidify as part of the inner core. But don't worry, that won't happen for many billions of years. Sources: 4 Layers Of The Earth Made Easy (forbes.com) earth's structure and components - Bing images III. GEOLOGICAL PROCESS The term "geological processes" describes the natural forces that shape the physical makeup of a planet. Plate tectonics, erosion, chemical weathering and sedimentation are all examples of forces that significantly affect the Earth’s surface and account for its major features. EARTH SYSTEM AND ITS COMPONENT The planet Earth is compost of four subsystem that consist the Earth land masses, water sources, living things, and gases. These four subsystem is also known as sphere the Geosphere, Hydrosphere, Biosphere, and Atmosphere. Geosphere The geosphere includes all the elements that form the crust and core of the Earth. Rocks and sand particles ranging from drylands to those found at the bottom of the ocean are examples of the geosphere. Examples also involve minerals, lava, molten magma and mountains. The geosphere undergoes constant processes that modify other spheres. One of the examples is the rock cycle. Hydrosphere The hydrosphere includes all the water parts of the planet. It includes water on the surface, subsurface and water vapour in the atmosphere. It undergoes infinite processes every day. The water cycle is one way to understand what is the importance of the hydrosphere, its functions and how it supports other spheres. Biosphere The Biosphere comprises all the living components of the Earth. It also includes organic matter that has not yet decayed. The sphere hugely depends on the other three spheres. Atmosphere The gaseous component above the surface of the Earth is known as the atmosphere. It is made of gaseous components and tiny water particles. The gases in the atmosphere are kept in place by the force of gravity. The heat from the sun is radiated to the Earth and is reflected in the atmosphere. The heat from the sun warms up the surface of the earth and causes evaporation, thereby sending moisture into the atmosphere. WEATHERING Is the breaking up and dissolving of rocks in the surface of the Earth. Process of Weathering Disintegration -The process of breaking up of rocks into smaller pieces by mechanical agents. Decomposition -The process of breaking up of minerals into another composition by chemical actions. Denudation -The process when the Earth's surface is worn away by the mechanical and chemical action. Type of Weathering Mechanical Weathering -Disintegration of rocks take place without any change in chemical constituents of rocks. Factors such as temperature, moisture, frost action and wind cause physical break-up of rocks. It is more rapid in desert climates. Chemical Weathering -Decomposition of rocks take place with changes in the chemical constituents of rocks. Temperature, moisture, etc., cause minerals in rocks to either dissolve in water or change their composition. It occurs in moist and cold climates. Biological Weathering -It is also known as Organic Weathering. Its main agents are animals, insects, plants and man. In all the cases, however, both physical disintegration and/or chemical decomposition are involved. This is because all biological matter is made up of oxygen and water, the two substances that set off reaction of minerals in rocks. PLATE TECTONICS The Earth's crust is broken into many pieces. These pieces are called plates. The movement of these plates is called plate tectonics. A plate boundary occurs where two plates come together. There are three kinds of plate boundaries. 1. Convergent 2. Divergent 3. Transform A convergent boundary -Is where two plates collide to form mountains or one plate riding above the other driving the thinner denser plate down into the mantle creating a subduction zone -There are 3 types of convergent boundaries, all of which are the result of compression forces (pressing together): Ocean-to-ocean -where 2 oceanic plates collide, forming a subduction zone, a trench and a volcanic island arc chain. (example: Aleutian Island Arc Chain, Alaska and the Japanese Island Arc Chain) Ocean-to-continent -where an oceanic plate collides with a continental plate, forming a subduction zone, a trench and continental volcanoes. (example: Andes Mountains of South America) Continent-to-continent -where 2 continental plates collide forming folded and faulted mountains with no volcanoes. (example: Appalachian Mountains and Himalayan Mountains) A divergent boundary -Is where two plates are moving in opposite directions. -Divergent boundaries cause the oceans to spread apart (as a result of tension force, pulling apart) while convergent boundaries cause the oceans to shrink. -There are two types of divergent boundaries. Seafloor spreading -is where two oceanic plates are moving apart and a mid-ocean ridge is formed. A rift valley -can also be the result of two continental plates moving apart. A transform boundary -is where two plates are sliding past each other by a force called shearing. GROUNDWATER - Underground water found in saturated areas below the surface of the soil. Freshwater that soaks into the soil from rain or snow or any kind of precipitation. Most abundant source of freshwater available for human consumption. Cementing agent to aid the formation of sedimentary rocks. AQUIFERS - A body of porous rock or sediment filled with groundwater. Groundwater enters an aquifer as precipitation seeps through the soil. Water is in it and can move through it. It is can be made of sand, gravel, sandstone, or basically any surface that is permeable. - TWO TYPES OF AQUIFERS: ● Confined Aquifer - a type of an aquifer that has a confining layer above it. A confining layer or unit is a material that has low hydraulic conductivity or its able to transmit water. ● Unconfined Aquifer - a type of an aquifer that doesn’t have anything on top of it as a confining layer. Unconfined aquifers. Unconfined aquifers are found where the rock is directly exposed at ground level and where groundwater is continuously supplied. WATER TABLE - The boundary between the saturated and unsaturated zones of the earth's crust is the water table. Groundwater fills any voids between rocks and sediments below the water table.