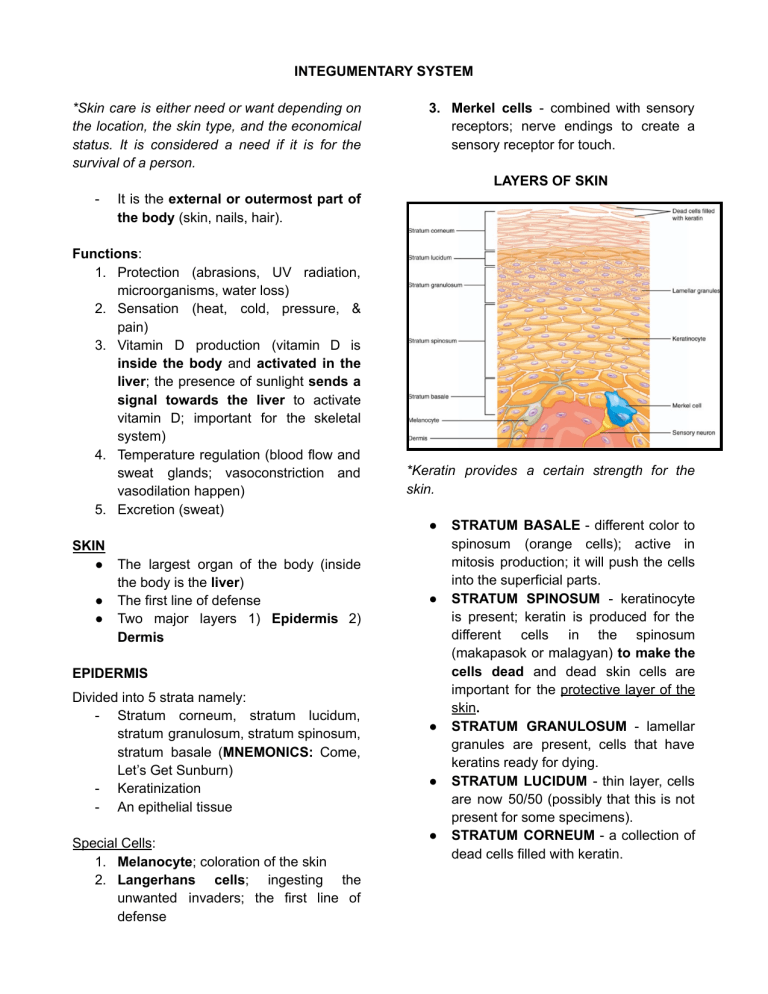
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM *Skin care is either need or want depending on the location, the skin type, and the economical status. It is considered a need if it is for the survival of a person. 3. Merkel cells - combined with sensory receptors; nerve endings to create a sensory receptor for touch. LAYERS OF SKIN - It is the external or outermost part of the body (skin, nails, hair). Functions: 1. Protection (abrasions, UV radiation, microorganisms, water loss) 2. Sensation (heat, cold, pressure, & pain) 3. Vitamin D production (vitamin D is inside the body and activated in the liver; the presence of sunlight sends a signal towards the liver to activate vitamin D; important for the skeletal system) 4. Temperature regulation (blood flow and sweat glands; vasoconstriction and vasodilation happen) 5. Excretion (sweat) *Keratin provides a certain strength for the skin. ● SKIN ● The largest organ of the body (inside the body is the liver) ● The first line of defense ● Two major layers 1) Epidermis 2) Dermis ● EPIDERMIS Divided into 5 strata namely: - Stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum basale (MNEMONICS: Come, Let’s Get Sunburn) - Keratinization - An epithelial tissue Special Cells: 1. Melanocyte; coloration of the skin 2. Langerhans cells; ingesting the unwanted invaders; the first line of defense ● ● ● STRATUM BASALE - different color to spinosum (orange cells); active in mitosis production; it will push the cells into the superficial parts. STRATUM SPINOSUM - keratinocyte is present; keratin is produced for the different cells in the spinosum (makapasok or malagyan) to make the cells dead and dead skin cells are important for the protective layer of the skin. STRATUM GRANULOSUM - lamellar granules are present, cells that have keratins ready for dying. STRATUM LUCIDUM - thin layer, cells are now 50/50 (possibly that this is not present for some specimens). STRATUM CORNEUM - a collection of dead cells filled with keratin. Melanocyte - It is the one producing melanin, a pigment for shielding UV rays from the sun. - In the Philippines, melanin is needed because it is a tropical region. - A specialized cell because it can extend its cell membrane in the spaces of the extracellular matrix of the skin. Cells present in the dermis: 1. Fibroblasts (collagen), adipocytes, and macrophages (immune cells in the dermis) 2. Two major layers: Papillary Layer and Reticular Layer 3. Nerves, Glands, and Capillaries GOLGI APPARATUS - packaging and modifying proteins; creates an organelle called melanosomes, a structure that contains melanin. *Melanosomes are present also in the extension of melanocyte; it is extended to reach the different cells of the epidermis; the melanocyte will stream off itself allowing it to combine with the different cells and will be engulfed by different cells, causing melanin inside the cell. Epidermis Diseases ➢ ALBINISM - a recessive genetic trait that causes a deficiency or an absence of melanin. ➢ VITILIGO - a disease in which the pigment cells of the skin, melanocytes, are destroyed in certain areas. ➢ DANDRUFF - excessive sloughing of stratum corneum cells. ➢ CALLUS - a thickened area of the stratum corneum due to friction. DERMIS *Tension lines are important to learn for incisions; it can lead to the difference of the healing process of the wound. Across the cleavage line (perpendicular) = can gap, slow healing, and will leave a mark or scar Parallel to the cleavage line = less gaping, faster healing, and less scar tissue - The deepest layer of cell in the stratum basale is the basement membrane. Beneath the basement membrane is the connective tissue. PAPILLARY DERMIS - the waves is important because it is the fingerprints. The line and ridges along the fingerprints are just followed by the epidermis. Fingerprints are because of the orientation of the papillary layer of the dermis. RETICULAR DERMIS - deepest layer of the dermis; the area that is damaged when a stretch mark is present (collagenous fibers | it is strong but resists stretching). HYPODERMIS ● A minor layer of the skin; subcutaneous tissue ● Attaches the skin to the underlying muscles and bones ● For insulation and energy storage SEBACEOUS GLAND - produces sebum (made up of lipids), on oily, white substance rich in lipids; too much sebum can cause acne or pimples - During puberty, this gland is active and accumulates too much oil, causing bacterial accumulation because of sweat and oil = inflammation = acne or pimple. SUDORIFEROUS GLAND - produces sweat. Either ECCRINE (water secretion; sweats and salts) or APOCRINE (with part of cells; the presence of biomolecules) - Body odor is present in the armpit because it is APOCRINE; the presence of biomolecules | bacterial accumulation is present | there is moisture - Ex. wet rice is prone to pagpapanis because of biomolecules and moisture ACCESSORY SKIN STRUCTURE Glands ● Exocrine glands; 1) holocrine - whole cells are removed from the lining of gland 2) merocrine - mode of secretion is very intact and only secretion is released 3) apocrine - pinched off a portion of the cell that is joined in the secretion ● All these are able to discharge their products via a duct system ● Endocrine glands are direct to the bloodstream Hair 1. Hair Shaft - above skin surface; dead keratinized cells 2. Hair Bulb - the base of hair root; receives the nutrients 3. Hair Root - a hair inside the skin; still not protruded 4. Hair follicle - entire thing that covers the hair bulb; it can be circular (hair is straight) and flat (hair is curly). 5. Hair papilla - found inside the hair bulb; creates intertwining of different arteries and veins (supply of oxygen and nutrients for it to create new hair cells). It leads to keratinization later on. 6. Arrector pili - a smooth muscle associated per hair strand ( it is the reason why hair goosebumps) is erecting = NAIL MATRIX - mitosis is active; cells are produced for cells and where keratinization happens. NAIL BED - the entire thing where the nail rest. LUNULA - a nail root that is supposedly under the skin but extended outside; can be present sometimes or not; it is because of deficiency that there’s no lunula or there is a certain indication. *Nails are important and placed in their position for better grasping and providing rigidity. ––––––––—–— *Hair loss is NORMAL. Nails ➢ A thin plate consisting of dead stratum corneum cells that contain a very hard type of keratin. ➢ Cuticle = eponychium BP CONTINUATION… Body Parts and Regions 1. Orbital (eye) 2. Nasal (nose) 3. Oral (mouth) 4. Buccal (cheek) 5. Cervical (neck) 6. Axillary (armpit) 7. Cranial (skull) 8. Occipital (base of the skull) 9. Olecranon (point of the elbow) 10. Calcaneal (heal)






