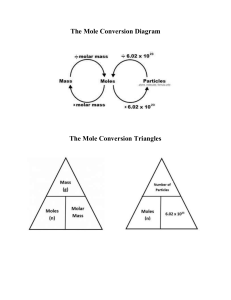
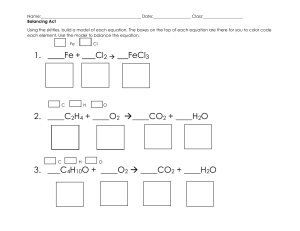
Chemistry_BSC16 4 Lecturer: Dr. Ahmad Mustafa LA: Eng. Hoda Anwar Course Contents ILO’s for this Chapter • Reviewing some engineering chemistry basics that relates to the course progress. • Identifying the measurement systems and differentiate between units and dimensions. • Explaining the difference between mole, molecular weight and mass. • Differentiate between molarity, molality and Normality. What is the difference between Unites & Dimensions? Mathematics and Engineering • It is about consistency. Common Systems of Units • Let us practice: • Convert 2200 ft/s to mi/h 2200 ft 1 mi 60 s 60 min s 5280 ft 1 min 1h • Convert 400 in3/d to cm3/min 400 in3 (2.54)^3 cm3 1d 1h d 1 in3 24 h 60 min Temperature Conversion 0 OC = 273 K = 492 OR T (K) = 492/273 T(OR) T (K) = 1.8 T(OR) Example • The temperature of ambient air in a certain location is measured to be 25 ◦C. Express this temperature in Fahrenheit (F), Kelvin (K) and Rankine (R) units Amount of Substance • What is Mole? Molecular weight • Calculate the molecular masses (g/mole) of: • Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4) • ammonia (NH3) • Sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) • Nitric acid (HNO3) • [Atomic mass of N=14, Na=23, H=1, S=32, O=16) Amount of Substance • Calculate the number of moles of the following substance • 1-10 g of NaOH • 2-100 ml of HCl • 3-23 g of AgNO3 • [Atomic weight of Na=23, O=16, H=1, Cl=35.5, Ag=108, N=14 g/mol] • [density of HCl=1.18 g/ml] Amount of Substance • How many molecules are there in a drop of water weighting 0.05 g? Example • Acetylsalicylic acid C9H8O4 is the principle ingredient of Aspirin. What is the mass in grams of 0.287 mole of Acetylsalicylic acid? Equation Balancing • Chemical equation must contain equal number of each type of atom on each side. • N2H4 (l) + N2O4 (l) → N2 (g) + H2O (g) • Balance the following Equation N2H4 (l) + N2O4 (l) → N2 (g) + H2O (g) N2 (s) + H2 (g) → NH3 (g) NaOH (s) + CO2 (g) → Na2CO3 (s) + H2O (l) PH3(g) + O2(g) → P4O10(s) + H2O(g) Equation Balancing - Exercise • Chemical equation must contain equal number of each type of atom on each side. • N2H4 (l) + N2O4 (l) → N2 (g) + H2O (g) • Balance the following Equation 2N2H4 (l) + N2O4 (l) → 3N2 (g) + 4H2O (g) N2 (s) + 3H2 (g) → 2NH3 (g) 2NaOH (s) + CO2 (g) → Na2CO3 (s) + H2O (l) 4PH3(g) + 8O2(g) → P4O10(s) + 6H2O(g) End of Chapter One Faculty of NAME HERE