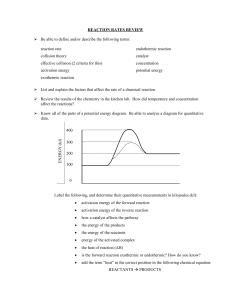
Work hard. Be nice. Name: ____________________________________ Period: ________ KIPP NYC College Prep UNIT 9: Kinetics and Equilibrium Date:___________________ General Chemistry Lesson 2: Potential Energy Diagrams By the end of today, you will have an answer to: How does a potential energy diagram further explain collision theory? Do Now: Explain why the following reactions will or will not occur based on collision theory. 1. In order for particles to react, they must have enough ___________________ and the correct _______________________. 2. You’ve just discovered a method to make a new medicine, but the reaction is very slow. List 3 ways S this medicine faster. that you could speed up the reaction to produce (a) (b) (c) “It’s all about the ENERGY baby!” http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VbIaK6PLrRM Notes: Particle A ACTIVATION ENERGY Definitions: Particle B Activation Energy [Ea] Delta H [H] N2 + O2 2NO Work hard. Be nice. Table I Practice Activity: 1. What units is the H values in? ____________ This is a unit for energy. 2. What are two differences between the H values for the following two reactions? C(s) + O2(g) CO2 (g) List 2 differences between the H values: N2(g) + 2O2(g) 2NO2 (g) 1. 2. 3. According to the asterisk (*) on the bottom of Table I, what does the minus sign for H mean? Exothermic versus Endothermic Reactions Table I. Exothermic Reaction Energy is… H Potential Energy Potential Energy diagram Example Chemical Reaction Endothermic Reaction Work hard. Be nice. Name:_____________________________ CW 9.2: Exothermic vs. Endothermic reactions Date:___________________________ General Chemistry PARTNER PRACTICE. 1. DIRECTIONS: Determine whether the following is an exothermic or endothermic reaction. Draw a Potential energy diagram to correspond with your answer. Scenario 1. C + O2 CO2 H =-393.5 kJ Scenario 2. Scenario 3. Scenario 4. KNO3 K+ + NO3- N2 + 3H2 2NH3 + 91.8kJ 2C + 2H2 + 52.4kJ C2H4 H = +34.89 kJ Endo/ Exo H + or - PE Diagra m 2. Given the balanced equation representing a reaction: Which statement is true about energy in this reaction? (1) The reaction is exothermic because it releases heat. (2) The reaction is exothermic because it absorbs heat. (3) The reaction is endothermic because it releases heat. (4) The reaction is endothermic because it absorbs heat. 3. What is the H for the reaction in #2? _____________ Work hard. Be nice. 4. Which change is exothermic? (1) freezing of water (3) vaporization of ethanol (2) melting of iron (4) sublimation of iodine 5. Given the balanced equation: Which phrase best describes this reaction? (1) endothermic with H = +1640 kJ (2) endothermic with H = -1640 kJ (3) exothermic with H = +1640 kJ (4) exothermic with H= -1640 kJ 6. Which statement correctly describes an endothermic chemical reaction? (1) The products have higher potential energy than the reactants, and the H is negative. (2) The products have higher potential energy than the reactants, and the H is positive. (3) The products have lower potential energy than the reactants, and the H is negative. (4) The products have lower potential energy than the reactants, and the H is positive. 7. Which of the following potential energy diagrams represent: a) A endothermic reaction? _______ b) An exothermic reaction? _______ A B C D 8. Given the following reaction: S(s) + O2 (g) SO2 (g) + energy Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic? ________________ 9. In a chemical reaction, the difference between the potential energy of the products and the potential energy of the reactants is defined as (1) activation energy (2) ionization energy (3) heat of reaction (4) heat of vaporization 10. Exothermic reactions ________________ heat and endothermic reactions _______________ heat. Work hard. Be nice. Name:_____________________________ Exit Slip 9.2: Exothermic vs. Endothermic reactions Date:__________________ General Chemistry 1. In terms of collision theory, why is activation energy necessary for a reaction to occur? 2. Sketch a potential energy diagram for the following reaction. Name:_____________________________ Date:__________________ Exit Slip 9.2: Exothermic vs. Endothermic reactions Chemistry General 1. In terms of collision theory, why is activation energy necessary for a reaction to occur? 2. Sketch a potential energy diagram for the following reaction. Work hard. Be nice. Name:_____________________________ Homework 9.2: Exothermic vs. Endothermic reactions Date:__________________ General Chemistry 1. According to Table I, which equation represents a change resulting in the greatest quantity of energy released? (1) 2C(s) + 3H2(g) C2H6(g) (2) 2C(s) + 2H2(g) C2H4(g) (3) N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) (4) N2(g) + O2(g) 2NO (g) 2. Given the balanced equation representing a reaction at 101.3 kPa and 298 K: N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) + 91.8 kJ Which statement is true about this reaction? (1) It is exothermic and H equals -91.8 kJ. (2) It is exothermic and H equals +91.8 kJ. (3) It is endothermic and H equals -91.8 kJ. (4) It is endothermic and H equals +91.8 kJ. 3. Given the balanced equation representing a reaction: N2(g) + O2(g) + 182.6 kJ 2NO (g), draw a potential energy diagram for this reaction on the axes below. 4. The potential energy diagram and balanced equation shown below represent a reaction between solid carbon and hydrogen gas to produce 1 mole of C2H4(g) at 101.3 kPa and 298 K. a) Which arrow represents the activation energy of the reaction? ____________ b) Which arrow represents the heat of reaction? __________ c) Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic? _____________________ d) What is the H value of the reaction? ________________ Work hard. Be nice. Summary Use the space below to create a summary that links all of the following terms you have learned: Collision Theory Energy Particles Potential Energy Diagram Exothermic Temperature Endothermic Heat of reaction Pressure Orientation Activation energy Concentration What is collision theory? What is an effective collision? How can the rate of a reaction be increased? Explain in terms of collisions. Why is activation energy necessary for a reaction to happen? How does a potential energy diagram illustrate the breaking and forming of new bonds? What is the difference between exothermic and endothermic reactions?