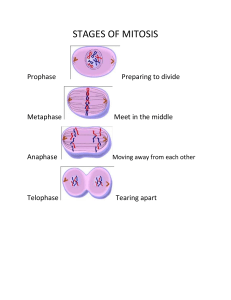
Activity 1--Stages of the Cell Cycle Chromosome Cell Membrane Spindle Fiber Nuclear Membrane Chromatin (genetic material) Interphase Mitosis: Prophase Mitosis: Metaphase Mitosis: Anaphase Mitosis: Telophase Cytokinesis Activity 2--Untitled Stages of the Cell Cycle Chromosome Cell Membrane Chromatin (genetic material) Spindle Fiber Nuclear Membrane Stage: ________________ Stage: ________________ Stage: ________________ Stage: ________________ Stage: ________________ Stage: ________________ Cell Cycle Manipulatives Preparing the Activity Cards This activity is intended to be completed by partners, but can completed by individual students or larger groups. You will need to make copies of however many pages you will need to accommodate the number of groups/students in your class. It is strongly recommended that these cards are printed on card stock and are laminated to increase their durability, and so that they may be reused. After laminating the cards, cut the cards out along the individual outlines. Each group/student should receive 2 decks of cards--one consisting of the 6 cards with the stage names and one consisting of the 6 untitled cards. Prior to the Activity Prior to beginning the activity, students will need to learn and study the cell cycle. Background information can be found below in the "Background " section. Students should be familiar with the relevant parts of cells. This information is also included in the "Background" section below. Summary of the Activity Students should work with a partner while completing this activity. Students should discuss the characteristics of the cell in each stage in each diagram as they complete both parts of this activity. Activity 1--During the first activity students will put the stages of the cell cycle in order using cards that have both the names of each stage and a diagram of each stage. When students have completed activity 1, the instructor should collect these cards and give students the untitled ones. Activity 2--During the second part of the activity students will again put the stages of the cell cycle in order, but with only the diagrams and no names. If the cards are laminated, students can write the stage/phase names on the untitled card using a dry erase marker. Post-Activity--After the activity students should complete the "Cell Cycle Activity Follow-up Questions" worksheet with their partner(s). Background The cell cycle is a process by which cells divide by copying genetic material, cell parts, and organelles, and then splitting into two identical daughter cells. The cell cycle consists of three basic stages--interphase, mitosis (which consists of prophase, metaphase, anaphase, & telophase), & cytokinesis. Cells divide via the cell cycle in order for an organism to grow, develop, repair injuries, & to replace dead or worn-out cells. During interphase the cell grows (it doubles in size), and copies all of its organelles, cell parts, and genetic material. During this stage the cell has twice as much genetic material as prior to interphase. During mitosis the cell goes through four phases--prophase, metaphase, anaphase, & telophase--in order to divide its genetic material (in the form of chromosomes) and form two nuclei (one for each daughter cell that will form). During mitosis: prophase the chromatin condenses and forms thickened, rod-shaped structures called chromosomes, and the nuclear membrane breaks down and disappears. During mitosis: metaphase the chromosomes form a line in the center of the cell. Background (continued) During mitosis: anaphase the spindle fibers connect to the centromeres that connect the chromosomes, and start pulling the chromosomes to opposite ends of the cell. During mitosis: telophase a nuclear membrane forms around both sets of chromosomes, and the cell becomes deeply pinched in the center. During cytokinesis the cell membrane actually separates, and one cell splits into two completely separate daughter cells. The rods that comprise the chromosomes loosen and return to being stringy chromatin. Chromatin--loose, winding strands of DNA that contain genetic material. Chromosome--a rod of condensed chromatin that carries genes. Spindle Fibers--protein fibers that divide the genetic material (chromosomes) between two cells when the cells are dividing. Nuclear Membrane--a semipermeable structure that surrounds the nucleus of a cell. NAME:________________________________________________________________________DATE:____________________________CLASS:__________ Cell Cycle Activity Follow-up Questions Directions: After finishing the activities with the cell cycle cards, discuss the following questions with a partner. Answer each of the following questions USING COMPLETE SENTENCES with as much detail as possible. 1. What are the stages of the cell cycle in order from beginning to end? 2. After observing the untitled card for interphase, what did you see in the diagram that led you to believe that it was interphase? 3. After observing the untitled card for mitosis: prophase, what did you see in the diagram that led you to believe that it was mitosis: prophase? 4. After observing the untitled card for mitosis: metaphase, what did you see in the diagram that led you to believe that it was mitosis: metaphase? 5. After observing the untitled card for mitosis: anaphase, what did you see in the diagram that led you to believe that it was mitosis: anaphase? 6. After observing the untitled card for mitosis: telophase, what did you see in the diagram that led you to believe that it was mitosis: telophase? Over, please. Cell Cycle Activity Follow-up Questions 7. After observing the untitled card for cytokinesis, what did you see in the diagram that led you to believe that it was cytokinesis? 8. What happens after cytokinesis? 9. A mnemonic is a trick for remembering the first letters of something by creating a statement that helps you remember them. For example, the four nitrogen bases in a DNA strand are adenine, thymine, cytosine, & guanine. By using the statement: "all turkeys can grow", a person can remember the first letter of each base. Create your own mnemonic for the first letters of the cell cycle--I, P, M, A, T, C. 10. Draw 6 symbols that help you remember what occurs during each of the 6 stages of the cell cycle. Answer Key Cell Cycle Activity Follow-up Questions Directions: After finishing the activities with the cell cycle cards, discuss the following questions with a partner. Answer each of the following questions USING COMPLETE SENTENCES with as much detail as possible. 1. What are the stages of the cell cycle in order from beginning to end? The stages of the cell cycle in order from beginning to end are: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, & cytokinesis. 2. After observing the untitled card for interphase, what did you see in the diagram that led you to believe that it was interphase? Students should note that it is a single cell with the nuclear membrane in-tact, and that the genetic material is still in the form of chromatin. 3. After observing the untitled card for mitosis: prophase, what did you see in the diagram that led you to believe that it was mitosis: prophase? Students should note that the nuclear membrane is breaking down, and that there is not chromatin in the cell/chromosomes have formed. 4. After observing the untitled card for mitosis: metaphase, what did you see in the diagram that led you to believe that it was mitosis: metaphase? Students should note that the chromosomes have lined up in the center of the cell, and that spindle fibers have attached to the chromosomes. 5. After observing the untitled card for mitosis: anaphase, what did you see in the diagram that led you to believe that it was mitosis: anaphase? Students should note that the chromosomes have split and are being pulled to opposite ends of the cell by the spindle fibers. 6. After observing the untitled card for mitosis: telophase, what did you see in the diagram that led you to believe that it was mitosis: telophase? Students should note that two nuclear membranes/nuclei have formed, but the genetic material is still in the form of chromosomes, not chromatin. Also, the cells have not completely separated. Over, please. Answer Key Cell Cycle Activity Follow-up Questions 7. After observing the untitled card for cytokinesis, what did you see in the diagram that led you to believe that it was cytokinesis? Students should note that the cells have completely separated/there are two cells, and that the chromosomes have turned back into chromatin. 8. What happens after cytokinesis? The two cells will go through the cell cycle again. As the cell cycle is a cycle, it will repeat over and over again. 9. A mnemonic is a trick for remembering the first letters of something by creating a statement that helps you remember them. For example, the four nitrogen bases in a DNA strand are adenine, thymine, cytosine, & guanine. By using the statement: "all turkeys can grow", a person can remember the first letter of each base. Create your own mnemonic for the first letters of the cell cycle--I, P, M, A, T, C. Any answer that contains a statement that includes all of the first letters of the stages of the cell cycle is acceptable. 10. Draw 6 symbols that help you remember what occurs during each of the 6 stages of the cell cycle. Any symbol that represents anything logical about each stage is acceptable. There should be 6 individual symbols--one for each stage of the cell cycle.