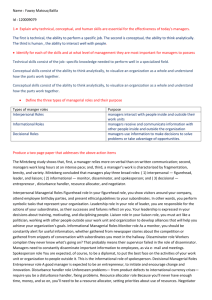
Chapter 1 Introduction to Managers and Management g Manager ¾ A person who coordinates and oversees the work of other people so that organizational goals can be accomplished. Individuals in an organization who direct the activities of others. Cl Classifying if i M Managers ¾ First-line Managers Individuals who manage the work of nonmanagerial employees. ¾ Middle iddl Managers Individuals who manage the work of first-line managers. g ¾ Top Managers Individuals who are responsible for making organization wide decisions and establishing organization-wide plans and goals that affect the entire organization. Managerial Levels What is Management Management involves coordinating and overseeing the work activities of others so that their activities are completed efficiently and effectively. effectively What is Management ¾ Managerial g Concerns ◦ Efficiency x “Doing things right” ◦ Getting G tti th the mostt output t t for the least inputs ◦ Effectiveness x “Doing the right things” ◦ Attaining organizational goals Effectiveness and Efficiency in Management What Managers Do? ¾ Three Approaches to Defining What Managers Do. Functions they perform. Roles they play. play Skills they need. Functions Manager’s g Perform ¾Planning Defining g g goals,, establishing g strategies g to achieve goals, developing plans to integrate and coordinate activities. ¾Organizing Arranging and structuring work to accomplish organizational goals. ¾Leading Working with and through people to accomplish goals. ¾Cont olling ¾Controlling Monitoring, comparing, and correcting work. Management Functions What Managers Do? y Roles Manager’s Play ◦ Roles are specific actions or behaviors expected of a manager. ◦ Mintzberg identified 10 roles grouped around interpersonal relationships, the transfer of information, and decision making. Wh t M What Managers D Do? ? y Management Roles (Mintzberg) ◦ Interpersonal roles x Figurehead, g , leader,, liaison ◦ Informational roles x Monitor, disseminator, spokesperson ◦ Decisional D i i l roles l x Entrepreneur, disturbance handler, resource allocator, negotiator Mintzberg’s Managerial Roles y Interpersonal Roles • Figurehead Fi h d • Leader • Liaison y Informational Roles • Monitor • Disseminator • Spokesperson y Decisional Roles • • • • Entrepreneur Disturbance Dist bance handler handle Resource allocator Negotiator What Managers Do? y Skills Managers Skill M Need N d ◦ Technical skills x Knowledge and proficiency in a specific field ◦ Human skills x The ability to work well with other people ◦ Conceptual skills x The ability to think and conceptualize about abstract and complex situations concerning the organization Skills Needed at Different Management Levels How The Manager’s Manager s Job Is Changing y The Increasing Importance of Customers ◦ Customers: the reason that organizations exist x Managing customer relationships is the responsibility of all managers and employees. x Consistent high quality customer service is essential for survival. y Innovation ◦ Doing things differently, exploring new territory, i and d taking ki risks i k x Managers should encourage employees to be aware of and act on opportunities pp for innovation. Changes g Affecting a Manager’s Job What Is An Organization? y An Organization Defined ◦ A deliberate arrangement of people to accomplish some specific purpose (that individuals independently could not accomplish alone). y Common Characteristics of Organizations ◦ Have a distinct purpose (goal) ◦ Composed of people ◦ Have a deliberate structure Why y Study y Management? g y The Value of Studying Management ◦ The universality of management x Good management is needed in all organizations. ◦ The reality of work x Employees either manage or are managed. ◦ Rewards and challenges of being a manager x Management offers challenging, exciting and creative opportunities for meaningful and fulfilling work. g receive significant g monetary y x Successful managers rewards for their efforts. Rewards and Challenges of Being A Manager Manage