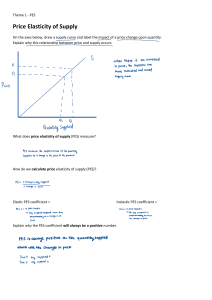
Worksheet Key term price elasticity of supply a measure of the sensitivity of quantity supplied of a good or service to a change in the price of that good or service, measured as: PES = % change in the quantity supplied % change in price AS/Year 1 Macroeconomics Edexcel A level Economics Elasticity of supply Figure 1 shows the position of the supply curve in both the short and long run. In the longer run, the firm is more flexible and can respond more easily to a change in the price of the good or service being produced. For example, it might introduce additional machinery or even build an additional factory to increase output if the price were to rise. Figure 1 Short- and long-run supply Figure 2 Perfectly elastic and inelastic supply Theme 1: Introduction to markets and market failure © Hodder & Stoughton Limited 2015 1 Given the following numerical values of the PES, complete the table: Numerical value of the PES Elastic, inelastic or unitary? Give an example of a product 1 0.5 2 2 Now complete this table: Numerical value of the PES Perfectly elastic or perfectly inelastic? AS/Year 1 Macroeconomics Edexcel A level Economics 1 Give an example of a product (or one that might approximate to it) 0 ∞ 3 If the price of a good rises by 25% and the quantity supplied increases by 10%, is the supply price elastic, price inelastic or perfectly elastic? Justify your answer. ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… 4 The price of the good falls by 8% and this leads to a fall in the quantity supplied in the region of 10%. Calculate the PES and comment on whether supply is price elastic or inelastic. ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… 5 The price of product A falls by 80p. It was originally £1.99. This leads to a fall in the volume supplied from 325,000 to 140,000 units. Calculate the PES. Show all your working out. ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… Theme 2: Introduction to markets and market failure © Hodder & Stoughton Limited 2015 2 The price of product B increases from £1.79 to £2.09 per unit. The volume supplied increases from 80,000 to 95,000 units. Calculate the PES. Comment on the size of the co-efficient. ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… Theme 2: Introduction to markets and market failure © Hodder & Stoughton Limited 2015 AS/Year 1 Macroeconomics Edexcel A level Economics 6 3