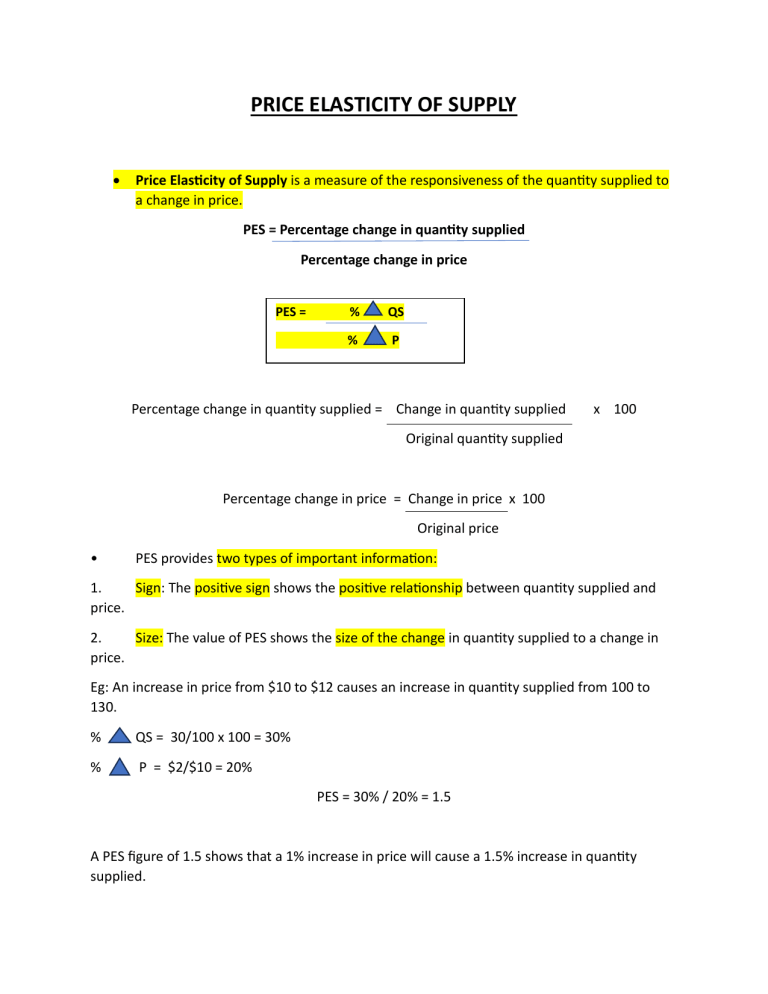
PRICE ELASTICITY OF SUPPLY Price Elasticity of Supply is a measure of the responsiveness of the quantity supplied to a change in price. PES = Percentage change in quantity supplied Percentage change in price PES = % QS % P Percentage change in quantity supplied = Change in quantity supplied x 100 Original quantity supplied Percentage change in price = Change in price x 100 Original price • PES provides two types of important information: 1. Sign: The positive sign shows the positive relationship between quantity supplied and price. 2. Size: The value of PES shows the size of the change in quantity supplied to a change in price. Eg: An increase in price from $10 to $12 causes an increase in quantity supplied from 100 to 130. % QS = 30/100 x 100 = 30% % P = $2/$10 = 20% PES = 30% / 20% = 1.5 A PES figure of 1.5 shows that a 1% increase in price will cause a 1.5% increase in quantity supplied. There are 5 types of Price Elasticity of Supply: TYPE OF PES Elastic Supply Inelastic Supply Unit Elasticity of Supply Perfectly Elastic Supply Perfectly Inelastic Supply 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. PES VALUE 1-∞ 0 – 1 (greater than 0, but less than 1) 1 ∞ 0 1. Elastic supply : when a change in price causes a greater change in quantity supplied. • The PES figure will be greater than 1, but less than infinity. • The supply curve will be shallow as a small change in price causes a greater percentage change in quantity supplied. The supply curve will touch the vertical axis if extended. Price ($) S P1 P Quantity Supplied 0 Q Q1 2. Inelastic supply: when a change in price causes a smaller change in quantity supplied. • The PES figure will be less than 1, but greater than 0. • The supply curve will be steep as a change in price will only cause a small change in quantity supplied. The supply curve will touch the horizontal axis if extended. Price ($) S P1 P 0 Quantity Supplied Q Q1 3. Unit Elasticity of Supply : when a percentage change in price causes an equal percentage change in quantity supplied. ● The PES figure will be 1. The supply curve will be a straight line that goes through the origin. Price ($) S P1 P 0 Q Q1 Quantity Supplied 4. Perfectly Elastic Supply : when a change in price causes a complete change in quantity supplied. ● PES will be infinity. ● The supply curve will be horizontal to show a complete change in quantity supplied. ● Firms would supply whatever quantities people demand at the given price. ● An increase in demand will not cause price to increase, only the quantity supplied will change. A fall in demand, that causes a fall in price will cause quantity supplied to fall to 0. Price ($) S P 0 Q Q1 Quantity supplied 5. Perfectly Inelastic Supply: when a change in price does not cause any change in quantity supplied. • PES will be 0. • The supply curve will be vertical to show no change in quantity supplied. Price ($) S P1 P 0 Quantity Supplied Q DETERMINANTS OF PES There are 3 main factors that determine the PES of a product: 1. The time taken to produce it: If a product takes a long time to produce, then the supply for the product will be inelastic. Eg: Seats at a Cinema. However, if the production can be quickly increased, then the supply will be elastic. Eg: Production of T-shirts. 2. The cost of altering supply: If it costs a lot to increase the supply of a product, then its supply will be inelastic. Eg: It will cost a lot to increase the seats at a cinema as they will have to spend a lot to renovate/ build a new cinema. However, if the cost of increasing the supply of a product is low, then the supply will be elastic. Eg: It will cost less to increase the production of t-shirts as it does not usually require new machinery and equipment to produce a few more t-shirts. 3. The feasibility of storing it: If it is difficult to store a product, then the supply for it will be inelastic. Eg: Agricultural products such as mangoes cannot be stored. However, if a product can be stored, then the supply will be elastic as supply can be increased or reduced easily. Eg: Plates can be stored easily. PES can vary with time. In the long run, the PES for most products tend to become more elastic as suppliers can adjust their supply, given more time. Eg: Suppliers can switch production to/from other products, build new factories and offices/ sell off existing resources. PES can vary with advances in technology. New technology will allow PES for products to become more elastic by reducing the production period and by lowering costs of production. THE ROLE OF PES IN DECISION MAKING Consumers: consumers benefit from PES being elastic as suppliers will quickly respond to increases in demand without raising the price of the product by much. Price ($) P1 S P D D1 0 Quantity Q Q1 Producers: producers benefit from PES being elastic as they will be able to earn higher profits by quickly responding to increases in demand. Governments: if governments want to encourage the consumption of a product, they will look to subsidize products with price elastic supply. This is because producers will be able to use the subsidy to easily increase their supply and thereby allow consumers to increase their consumption of the product.