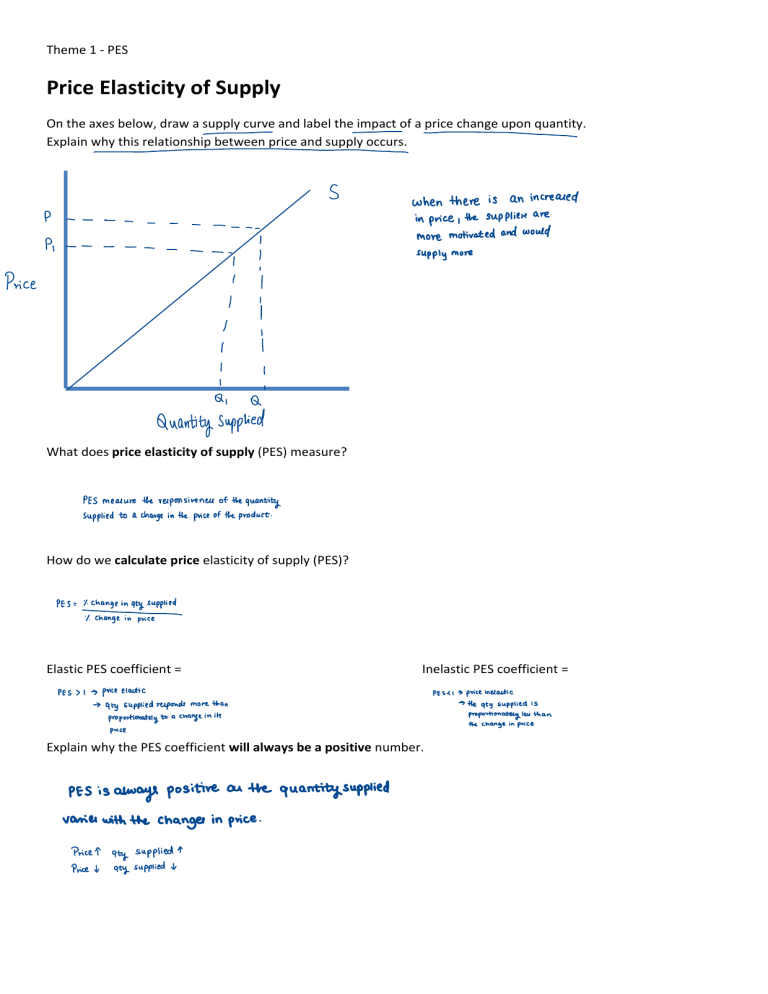
Theme 1 - PES Price Elasticity of Supply On the axes below, draw a supply curve and label the impact of a price change upon quantity. Explain why this relationship between price and supply occurs. - e S P P, - when there is in - --- - - - the price, I more I supply an increased supplies motivated and are would more I Price I I I I I I I b I I I I I Q Q Quantity Supp lied What does price elasticity of supply (PES) measure? PES measure supplied to a the responsiveness change t he of quantity of the product. price in the How do we calculate price elasticity of supply (PES)? PES = % change in qty supplied %. change in price Elastic PES coefficient = PES> 1 -> -> price Inelastic PES coefficient = elastic PESC1 - aty supplied responds proportionately to a than more change in the change in Explain why the PES coefficient will always be a positive number. always positive varies with the changes supplied aty Price aty supplied Pricey to 4 inelastic proportionately len its price PES is price He qty supplied -> in on the price. supplied quantity is than price Theme 1 - PES Elastic and inelastic supply curves S S Price Price quantity supplied supplied quantity Draw and annotate an elastic supply curve Draw and annotate an inelastic supply curve In terms of the relationship between price and quantity supplied - goods with an elastic supply curve mean…. when the change in quantity supplied is greater than the change in price In terms of the relationship between price and quantity supplied - goods with an inelastic supply curve mean… When the change in quantity supplied lea than the change is in price. Mr Wilson’s Thinking Further Challenge How might PED and PES impact the success of the price mechanism and ultimately the argument for/against a market free from government intervention? number indicate the PES and PED Both of good when or changel service in demand leads occur. price lower to demand. This is the buying comumen in PED a affects supplied, aty consume supply on lower and PES affects intervention market against power mainly units of market the affect supply as commer's the good. the of Theme 1 - PES Use the formula and your own intuition to calculate the following questions: 1) A firm’s market price increases from £1 to £1.10, and its supply increases from 10m to 12.5m. PES is: - - - - /10m) x 100 PES (mm> = ( 110-1) 11) x100 2.5 = 2) PES is 2.0 for CDs and the firm supplied 4,000 when the price was £30. If the price increased from £30 to £36, what will be the new quantity supplied? - e - - e - - n PES 2.0 = /4000) x100 (136 30(/30) - 1/n-4000)/4000) n - 4000 2.0 = x100 x100 40 = 1 600 = x 5600 = 3) Consider a product that has a supply which is fixed in the short-term, what do you think the supply curve would look like? Give an example of such a product. - land S price 4) Consider a product which can immediately respond to any given price change, what do you think the supply aty supplied curve would look like? Give a possible example of such a product. - - Price -- -- I I I I I I I i I 1. Gold I - I aty supplied Theme 1 - PES B 2. D 3. B Theme 1 - PES There are two main types of factor immobility: occupational and geographical immobility. Occupational immobility: occurs when there are barriers to the mobility with regards to any of the factors of production between different sectors of the economy. For example, workers may not have the skills to switch from the mining sector to the banking sector (structural unemployment). Or capital may be so specialised in one sector, such as a nuclear reactor, that it cannot be used/adapted in a different sector like a book publisher. Geographical immobility: refers to barriers people moving from one area to another to find work. This could due to simple large distances, or it could be due to family ties, differences in house prices or lack of transportation. 4. A 5. D 6. D Theme 1 - PES Factors impacting price elasticity of supply PES Factors Question Scarcity of raw materials or land (factor or production). Explain how scarcity impacts upon PES. Can you give an example of a good that requires a scarce raw material in its production and is therefore inelastic? Explain why agricultural goods are inelastic during some periods of the year and elastic during others. The length of time it takes to produce a product. Stocks of finished products and components: Some goods are easier and more practical to store. Why might a product be difficult to store? How could this problem be combatted by a firm? What are the problems with your solution to this problem? How easily resources can be used transferred to making other products. Outline two goods in which it would be difficult to switch resources from producing one to the other. Explain this problem in terms of opportunity cost. Factor immobility – when the factors of production are available, but cannot get to where they are required. If a firm located itself in the mountains, why might land, labour and capital be difficult to acquire? How might high house prices create immobility in terms of labour? Answer reduces Scarcity be low. For raw material and therefore the scarce requires example jewelry raw PES would materiall and the refore inelastic. Due weather condition the supply is unitable. to of goods, so is harder to elastic. However when it it is and there are grow goods len not the available. Due to scarcity fruits and vegetables be combated cost to There stored for a long period substitutes available mountains and to travel as capital it is well more as to place. Aho consuming in the difficult move the to time as harder is it is allo to build the well. Increased price would increase the living h ome of employees, the of cost have to travel longer reach to work. In the long-run, supply for goods tends to be more elastic. In relation to oil, explain why oil might be more PES elastic in the long-run, as opposed to PES inelastic in the short-run. What might happen? Why might wheat also be inelastic in the SR? They increase demotivate worken It so shifts. could do this This would might run by adding more work but the production during the work time, to work longer hours. out and become it is inelastic. However there available to oil so it replace demanded and price elactic more are might in the as is there the of good plentiful good, it b ecomes it product. Some goods oft he it c an easily refrigerated place. However cooled there goods. Transportation more in them by storing n ature the to a gold jewelry are no produce land store due buinen. the Petrol and to hard to be cannot goods mightbe Some they How could a firm solve the problem of having a low-production capacity? Suggest one reason the firm would want to do this and one reason why they wouldn’t. season t hat particular of inclactic and would Spare production capacity left within a firm. during the When it is season during the is scarce substitutes be len long run be such as spoilt. This problem this method can would increase the






