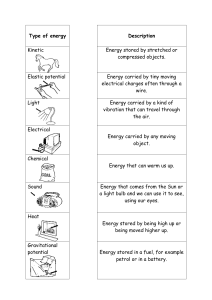
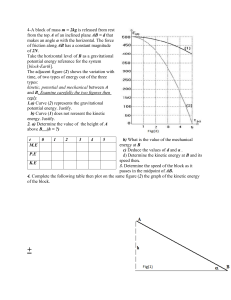
Mr. Saltz Physics Review: Newton’s Law of Gravitation, Mechanical Energy, Work, Power Definitions 1. Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation describes the magnitude of the gravitational force between two masses. Because this is a force, the unit is newtons. 𝐹=𝐺 𝑚1𝑚2 2 𝑟 −11 2 2 G, the gravitational constant, is the value of 6. 67 × 10 𝑁· 𝑚 /𝑘𝑔 . The m values in the numerator represent the masses of the two objects, and the r in the denominator represents the distance between the two objects. Sample problems: 27 1. What is the gravitational force between Jupiter, with a mass of 1. 898 × 10 𝑘𝑔, 23 and its largest moon, Ganymede, with a mass of 1. 482 × 10 𝑘𝑔? The average 6 distance between them is 1. 07 × 10 𝑘𝑚. 2. What would a 100 kg astronaut weigh on the surface of Ganymede? The radius of the moon is 2634 km. 3. On Earth, Mr. Saltz weighs about 810 newtons. If the mass of the Earth is 24 5. 97 × 10 𝑘𝑔, what is the radius of the Earth? 1 2. The Law of Conservation of Energy states that energy can never be created or destroyed in any chemical or physical process, but it can be transformed from one kind to another or transferred from one system to another. Energy (initial) = Energy (final) 3. Mechanical energy is the sum of the potential and kinetic energy in a system. The unit for energy is joules. 𝐸𝑀 = 𝐸𝑝 + 𝐸𝑘 Potential energy can be thought of as energy due to position (a stretched spring, distance above the ground, and bonding arrangements between atoms are some examples). Although there are various forms of potential energy, we have only examined one, gravitational potential energy. Energy is always conserved, so whatever energy is present in a system is also present after that system undergoes a change. (𝐸𝑀)𝑖𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑎𝑙 = (𝐸𝑀)𝑓𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑙 This means that if potential energy decreases, kinetic energy must increase and vice versa. Note that energy can be lost as thermal energy. This does not violate the law of conservation of energy. a. Gravitational potential energy is calculated by EP =mgh where m is the mass of the object, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height of the object above a reference point. Sample problem 1. What is the potential energy of a 10 kg mass positioned 5 m above the ground? 2. A physics textbook has a mass of 2.0 kg and a potential energy of 20J. What is its height? 2 b. Kinetic energy is calculated by EK = ½ mv2 Notice that this means that kinetic energy is heavily dependent on the velocity. Sample Problem A 25 kg mass has 5000J of kinetic energy. How fast is it going? If it is moving straight up and is not being propelled by any force, how high will it go? You can solve this with kinematics or with energy equations. 4. Work is either a transfer of energy or force applied over a distance, such as a truck towing (pulling on) a car. It is calculated by w = Fnet x where x simply represents distance. The unit is joules, the same as energy. If the work is in a vertical direction, the variable could be y. a. Remember that F = ma, so ma can be substituted for F in the equation for work. b. Work involves force, so it is a vector. That means that direction matters. If the work and the force are not in the same direction, then no work is done. Example: carrying a backpack is not work because there is no force opposing the motion of the backpack. Lifting the backpack is work because gravity opposes the motion, and you have to exert a force on the backpack to counteract gravity. Walking on level ground is not work, but climbing stairs is. c. Sample Problems i. How much work is done by an elevator that lifts a 1500 kg load a distance of 20 meters? 3 ii. How much work is done by pushing a box on the floor a distance of 5 meters when there is a frictional force of 50N? What about when there is no frictional force? 5. Power is the rate at which work is done. The unit for power is watts and power is calculated by 𝑝 = 𝑤/𝑡 You should keep in mind that work in this equation is Fx, and F = ma. These substitutions can help you to figure out all kinds of things. a. Sample Problems i. What is the power of an elevator that does 5000J of work in 20 seconds? In 50 seconds? ii. How long does it take a 1500W microwave oven to produce 300J of thermal energy? 4