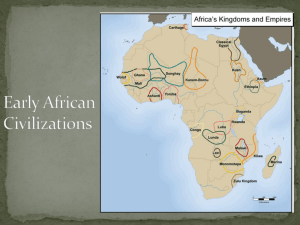
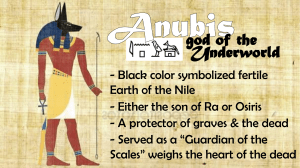
The River Valley Civilizations Tigris-Euphrates, Ancient Egypt, and Indian and Chinese River Valley Civilizations. Tigris-Euphrates • First civilization formed along Tigris and Euphrates Rivers in Mesopotamia. – Middle East leaders in agriculture, metalworking, and village structure. – Civilization formed from scratch. • By 3500 BC the Sumerians had established Cuneiform. – Began as pictures, but later used geometric shapes Cuneiform Tablets Sumerian Ziggurat Tigris-Euphrates • Sumerian Art: – Statues filled the temples of the gods. Statues of gods in individual homes. • Sumerian Science: – Learned about movement of sun and stars. Created constellation charts still used today. • Sumerian Religion: – Complex rituals with patron gods for each city. – Ziggurats – massive towers operated by professional priests. Polytheistic. Prayer very important to them. Tigris-Euphrates • Sumerian Politics: – Tightly organized city-states ruled by a king who claimed divine authority. Court system in interest of justice. Had slavery (original slave owners). • Sumerian Economy: – Agriculture. Used fertilizer. Used silver as early form of money. Tigris-Euphrates • This region was hard to defend and was always a temptation to invaders (even today). – Fell to Akkadians who continued much of culture. – Later conquered by Babylonians – King Hammurabi. • Hammurabi’s Code: rules of procedure for courts of law and harsh punishments for crime. Ideas used for most judicial systems today. Egyptians • Built up along Nile River in North Africa around 3000 BC. • They traded with Mesopotamian societies but their culture was very different. • Less open to invasion, and actually maintained a unified state. Egyptians • Pharaoh was the ruler – had immense power. • Economy more government directed due to need for complex irrigation. • Pharaohs thought of as gods. – Elaborate pyramids built for them from 2700 BC – This framework of Egyptian society lasted till after 1000 BC. • Neither hieroglyphs nor science as elaborate as Sumerian, but math more advanced. Idea of 24 hour day. Egyptian Pyramids Great pyramids of Giza. One of the 7 wonders of the World. Egyptian • Art: Lively with cheerful colorful pictures in tombs, palaces, and furnishings. • Religion: polytheistic. – Ra: god of the sun. Eye of Ra popular in decorations. Many other gods and goddesses. Egyptian Mythology • • • • • • • • • • • Ra - God of the Sun Isis - Mother Goddess Osiris - God of the Underworld, God of the Dead Anubis - God of Mummification/Afterlife - Jackal head Horus - God of the Sky - Falcon head- son of Isis/Osiris Hathor - Goddess of Love and Fertility Apep (Apophis) - God of Darkness - serpent head Ammit - Devourer of the Dead - crocodile head Amun - The Creator God Baal - God of Storms Setesh (Seth) - God of the Desert - dog/fox head Egyptian Mythology Indus River Civilization • Indus River civilization emerged by 2500 BC – Many large cities: Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro – Houses had running water!!! • Developed own distinct writing and art. • Indo-Europeans invaded and destroyed this society, so very little is known about the nature of this culture or its influence on India. – Harappan writing has yet to be deciphered. Indus River Valley City Chinese Civilization • Civilization along the Huang-he (Yellow River) developed in considerable isolation. – Civilization legendary in China and people revered as godlike kings. • Chinese had elaborate concept of their history. – Part fact-part fiction records of early kings. Chinese Civilization • Accomplishments: – By 2000 BC had advanced technology and elaborate intellect. – Learned to ride horses and make pottery. – By 1000 BC were using iron and coal. • Writing evolved from knotted ropes to scratches on bone to the type of symbols we know today. Ancient Chinese Writing Judaism • The Jews gave the world the first monotheistic religion. • Settled near the Mediterranean around 1200 BC • Jewish culture remains much the same today. • Basis for both Christianity and Islam. • Religion for Jews is a way of life, not just traditions and ceremonies. Accomplishments of These Civilizations • Pyramids • Taming the horse • Creation of alphabets and writing systems – Almost all alphabets today derived from some river valley writing system. • Development of key math concepts (square roots) • Development of well organized monarchies and beurocracies. • Invention of functional calendars. Decline of River Valley Civilizations • By 1000 BC most river valley civilizations in decline. • They flourished for 2500 years and influenced later cultures, such as Greeks. • Phonecians devised simplified alphabet with 22 letters – predecessor of Greek/Latin alphabet. Egyptian Gods & Goddess Ra / Re / Amen-Ra King of the Gods Sun god Falcon head with a sun on top. Sometimes seen as the creator of men (Egyptians called themselves "the cattle of Ra”) ■ Since heaven and the underworld have water, Ra uses a boat (Madjet (“strong”) while rising and Semektet ("becoming weak") when setting. He often has help from other gods to successfully navigate his boat. ■ He constantly had to fight monsters (Sebau, Nak, and Apep) ■ The phoenix is one of his symbols ■ ■ ■ ■ Osiris ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ God of the earth and vegetation Symbolized the yearly drought and flooding of the Nile. Gave Egypt civilization. Married his sister, Isis Osiris rules Egypt and he leaves Isis in charge when he is gone Set and 72 conspirators kill him by chopping him up into pieces Isis found almost all the pieces and put him back together (making the missing part out of clay) King of the afterlife Usually shown as a bearded, mummified human with green skin and wearing the atef crown. His hands come out from the mummy wrappings and hold the flail and crook. Horus ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ Falcon headed The Pharaoh was supposed to be his earthly embodiment. Son of Osiris (after his resurrection) Set is always trying to hurt him Stunted from his waist down In art, he is often shown standing on crocodiles His sons are born from Isis. Each take care of the organs during the mummification process ■ Duamutef (stomach) ■ Imsety (liver) ■ Hapi (lungs) ■ Qebehsenuef (intestines) Isis ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ Isis was the sister/wife of Osiris Shown as a a woman wearing a vulture head-dress and the solar disk between a pair of horns Isis suckles the pharohs May be one of the judges of the dead Has great magical powers Created the cobra and uses the cobra bite to make Ra reveal to her his secret name The purest example of the loving wife and mother Set ■ God of evil, the desert, storms, ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ and chaos A devil figure Antelopes are sacred to him Hates Osiris (jealous) Kills Osiris and becomes king before he is killed by Horus Part pig and part donkey Hathor ■ Usually depicted as a cow or as a ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ beautiful woman wearing a horned headdress She is both wife/ daughter of Ra Also married Horus Suckled Horus when he was young and took care of him after Set blinded him Her milk is food of the gods She offers food and drink to the dead Women aspire to be her Anubis ■ Son of Nephthys and either ■ ■ ■ ■ Set or Ra – adopted servant of Isis Head of a jackal Guides the dead to the underworld and weighs their heart (bad deeds make your heart weigh more) Works with Osiris in the underworld Mummification god Ammut ■ “Eater of the Dead” ■ She stands by the scales of the hearts and eats the hearts of the wicked (a final death) ■ Head of a crocodile, body of a leopard, hind legs of a hippo (apparently wicked hearts are fattening – who knew?) Thoth ■ Moon god ■ Head of an ibis ■ Scribe (records the weight of the hearts in the underworld) ■ Invented writing ■ From the Book of the Dead: “Hear the word of the very truth. I have judged the heart of the deceased, and his soul stands witness for him. His deeds are righteous in the great balance and no sin has been found in him.” Sekhmet ■ Lion headed ■ Wife of Ptah (an early creator god) ■ Breathes fire against her enemies ■ Delivers punishment to the gods