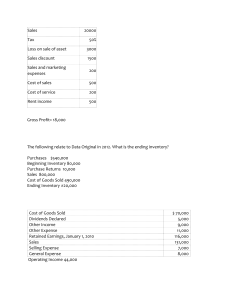
Every PollEverywhere Questions in Class Updated on 12/8/2022 1) The Pioneer Company has provided the following account balances: Cash $38,000; Short-term investments $4,000; Accounts receivable $48,000; Supplies $6,000; Long-term notes receivable $2,000; Equipment $96,000; Factory Building $180,000; Intangible assets $6,000; Accounts payable $30,000; Accrued liabilities payable $4,000; Short-term notes payable $14,000; Long-term notes payable $92,000; Common stock $180,000; Retained earnings $60,000. What are Pioneer's total current assets? A) $48,000. B) $96,000. C) $90,000. D) $42,000. Answer: B Explanation: Current assets = $96,000 = $38,000 + $4,000 + $48,000 + $6,000. 2) Which of the following accounts would be reported as assets on the balance sheet? A) Cash, accounts payable, and notes payable. B) Cash, retained earnings, and accounts receivable. C) Cash, accounts receivable, and inventories. D) Inventories, property and equipment, and common stock. Answer: C Explanation: Assets include but are not limited to cash, accounts receivable, and inventories. They are considered to be economic resources of a business. 3) Which of the following is the amount of revenue reported on the income statement of a retail company? A) The cash collected from customers during the current period. B) Both cash and credit sales for the period. C) Cash sales for the period and collections from customers. D) Cash sales and stockholders' investments. Answer: B Explanation: Revenue for a retail company includes all sales earned during the accounting period, both cash and credit. 4) Willie Company's retained earnings increased $20,000 during the current year. What was Willie's current year net income or loss given that Willie declared $25,000 of dividends during this year? A) Net income was $5,000. B) Net income was $45,000. C) Net loss was $45,000. D) Net loss was $5,000. Answer: B Explanation: Net income is equal to $45,000, calculated as the increase in retained earnings, $20,000, plus dividends of $25,000. 5) During the current fiscal year, a company had revenues of $400,000, cost of goods sold of $280,000, and an income tax rate of 30 percent on income before income taxes. What was the company's current year net income? A) $120,000 B) $36,000 C) $84,000 D) $400,000 Answer: C Explanation: ($400,000 − $280,000) = Income before income taxes, $120,000. Income tax expense = 30% × $120,000 = $36,000. Net income = $120,000 − $36,000 = $84,000. 6) How are creditor and investor claims reported on a balance sheet? A) The claims of creditors are liabilities and those of investors are assets. B) The claims of both creditors and investors are liabilities, but only the claims of investors are considered to be long-term. C) The claims of creditors are reported as liabilities while the claims of investors are recorded as stockholders' equity. D) The claims of creditors and investors are considered to be essentially equivalent. Answer: C Explanation: Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity are the sources of financing for the firm's economic resources. Creditors' claims are reported as liabilities while investors' claims are reported as stockholders' equity. 7) True or False: Liability and stockholders' equity accounts normally have credit balances and are decreased by debiting the accounts. Explanation: The normal balance for liabilities and stockholders' equity is a credit balance; accounts are increased on the same side as their position in the accounting equation. Liability and stockholders' equity accounts are on the right side of the accounting equation and therefore they are increased on the right. A right-side entry is a credit. Therefore they are decreased with a leftside entry, which is a debit. 8) Which of the following statements is incorrect? A) Stockholders' equity accounts normally have credit balances. B) Liability accounts are decreased by credits. C) Stockholders' equity accounts are increased by credits. D) Asset accounts are increased by debits. Answer: B Explanation: Liability accounts are increased by credits. 9) Which of the following direct effects on the accounting equation is not possible as a result of a single business transaction which impacts only two accounts? A) An increase in an asset and a decrease in another asset. B) An increase in an asset and an increase in stockholders' equity. C) A decrease in stockholders' equity and an increase in an asset. D) An increase in a liability and an increase in an asset. Answer: C Explanation: With one transaction impacting only two accounts, a single transaction that results in a decrease in stockholders' equity and an increase in an asset is not possible; both items are recorded as debits and thus the accounting equation would not be in balance. 10) A corporation purchased factory equipment using cash. Which of the following statements regarding this purchase is correct? A) The cost of the factory equipment is an expense at the time of purchase. B) The total assets will not change. C) The total liabilities will increase. D) The current stockholders' equity will decrease. Answer: B Explanation: The purchase of equipment is not expensed and, therefore, has no effect on the income statement. Instead, one asset (cash) is exchanged for another asset (equipment), which means that total assets will not change. 11) Which of the following describes the impact on the balance sheet when a company uses cash to purchase the stock of another company? A) Total assets increase. B) Stockholders' equity increases. C) Stockholders' equity decreases. D) Total assets remain the same. Answer: D Explanation: Cash decreases by the same amount that the investment in the other company increases. 12) Revenue may be recognized: A) Before goods are delivered B) After goods are delivered C) When goods are delivered D) Either before goods are delivered, after goods are delivered, or when goods are delivered. Answer: C Explanation: The revenue recognition principle specifies that a company recognizes revenue when goods or services are transferred to customers. 13) True or False: Reporting revenues on the income statement that were previously reported as unearned revenues on the balance sheet results in a decrease in liabilities and an increase in net income, retained earnings, and stockholders' equity. Answer: TRUE Explanation: Recording revenues increases net income, which flows through the financial statements to increase retained earnings and stockholders' equity. When unearned revenue is earned, the liability account decreases. 14) Which of the following is an example of revenue or expense to be recognized in the current period's income statement? A) Cash received from a client before the service is provided. B) Inventory purchased for sale to customers. C) Wages owed to employees who worked during the period. D) Cash collected from an account receivable. Answer: C Explanation: Expenses are recorded when incurred in generating revenues and revenues are recorded when goods or services have been transferred to customers. Wages owed to employees for work during a period need to be recorded as an expense during that period. 15) True or False: Cash received prior to the providing of the goods or services results in an increase in both assets and liabilities. Answer: TRUE Explanation: Collecting cash increases assets (debit), and if collection occurs before services are provided, the liability "unearned revenue" increases (credit). 16) True or False: Credit terms of "3/10, n/30" mean that if payment is made in three days, a 10% discount will be given; if not paid within three days, the full invoice price will be due in thirty days. Answer: FALSE Explanation: The credit term means 3% will be given if the sales amount is paid within the first 10 days, if not, the net amount is due in 30 days. 17) When a credit sale is made with terms of 2/10, n/30 on May 10 and the customer's check is received on May 19, which of the following is true about the May 19 journal entry? A) The debit to cash will equal the credit to accounts receivable because the discount was recorded on May 10. B) There will be a debit to sales discounts on May 10. C) The debit to cash will be less than the credit to accounts receivable on May 19. D) There will be a credit to sales discounts on May 19. Answer: C Explanation: The customer paid within the discount period so the discount is recognized on May 19. The discount reduces the cash received so the debit to cash is less than the credit to accounts receivable. 18) True or False: Gross profit decreases when sales discounts increase. Answer: TRUE Explanation: Sales discounts reduce net sales and decrease gross profit. More sales discounts will further decrease gross profit. 19) The CHS Company paid $30,000 cash to its landlord on November 1, 2019 for rent covering the six-month period from November 1, 2019 through April 30, 2020. The books are adjusted only at year-end. Which of the following does not correctly describe the effect on CHS Company's financial statements of the December 31, 2019 adjusting entry? A) Net income decreases $10,000. B) Prepaid rent decreases $10,000. C) Rent expense increases $10,000. D) Stockholders' equity increases $10,000. Answer: D Explanation: The time period from November 1, 2019 to December 31, 2019 consumes two months of rent expense ($10,000), which results in a decrease to stockholders' equity. 20) On January 1, 2019, the general ledger of Global Corporation included supplies of $1,000. During 2019, supplies purchased amounted to $5,000. A physical count of inventory on hand at December 31, 2019 determined that the amount of supplies on hand was $1,200. How much is the supplies expense for year 2019? A) $6,000. B) $5,200. C) $4,800. D) $1,000. Answer: C Explanation: Supplies expense = $4,800 = $1,000 + $5,000 − $1,200. 21) True or False: When using an allowance for doubtful accounts and a particular account receivable is determined to be uncollectible, the journal entry to write off the account reduces net income. Answer: FALSE Explanation: The entry to write off an account receivable includes a debit to the allowance for doubtful accounts and a credit to accounts receivable; this entry does not affect the income statement. 22) Which of the following statements does not correctly describe the allowance for doubtful accounts balance? A) It is reported on the balance sheet as a component of current assets. B) It is a contra-asset account. C) It is reported on the balance sheet as a component of stockholders' equity. D) It is created as a result of the adjusting entry to record bad debt expense. Answer: C Explanation: Allowance for doubtful accounts is a contra-asset account and does not affect stockholders' equity. 23) At year-end, Chief Company has a balance of $10,000 in accounts receivable of which $1,000 is more than 30 days overdue. Chief has a credit balance of $100 in the allowance for doubtful accounts before any year-end adjustments. Using the aging of accounts receivable method, Chief estimates that 1% of current accounts and 10% of accounts over thirty days are uncollectible. What is the amount of bad debt expense? A) $90. B) $190. C) $290. D) $100. Answer: A Explanation: Allowance for doubtful accounts desired balance, $190 = ($1,000 × 0.10) + ($9,000 × 0.01). Bad debt expense, $90 = Allowance for doubtful accounts desired balance, $190 − Allowance for doubtful accounts current balance = $100. 24) Which of the following statements is correct? A) The journal entry to record bad debt expense requires a debit to bad debt expense and a credit to accounts receivable. B) The journal entry to record bad debt expense requires a debit to bad debt expense and a credit to allowance for doubtful accounts. C) The journal entry to record the write off of an uncollectible account receivable requires a debit to bad debt expense and a credit to accounts receivable. D) The journal entry to record the write off of an uncollectible account receivable requires a debit to bad debt expense and a credit to allowance for doubtful accounts. Answer: B Explanation: The journal entry to record bad debt expense requires a debit to bad debt expense and a credit to allowance for doubtful accounts. ---------------------------------------------- After the midterm ---------------------------------------------12) If sales revenue was $1,800,000 and accounts receivable decreased $40,000 during the year, then cash collected from customers equals $1,840,000. Answer: TRUE Explanation: Cash collected from customers = $1,840,000. Sales + Accounts receivable decrease Cash collected from customers $ 1,800,000 40,000 $ 1,840,000 32) Which of the following transactions would not create a cash flow from operating activities? A) Collecting cash from a customer. B) Paying cash to a supplier. C) Paying cash to stockholders for dividends. D) Paying cash for a utility bill. Answer: C Explanation: Payments of cash dividends are reported as cash flows from financing activities. 40) Which of the following would be subtracted from net income when determining cash flows from operating activities under the indirect method? A) An increase in accounts payable. B) Depreciation expense. C) A decrease in prepaid insurance. D) A gain on the sale of a depreciable asset. Answer: D Explanation: A gain on the sale of a depreciable asset would be subtracted from net income because when net income was computed, the gain increased net income. However, the transaction is an investing cash flow and the amount reported is the cash received, not the gain. 14) Under the indirect method, a decrease in inventory is subtracted from net income because inventory purchases are less than cost of goods sold. Answer: FALSE Explanation: A decrease in inventory is added to net income under the indirect method because cost of goods sold is a deduction toward net income but inventory purchases are less than the cost of goods sold deduction. 54) Allen Company's 2019 income statement reported total revenues, $850,000 and total expenses (including $40,000 depreciation) of $720,000. The company's accounting records showed the following: accounts receivable—beginning balance, $50,000 and ending balance, $40,000; accounts payable—beginning balance, $22,000 and ending balance, $28,000. Therefore, based only on this information, how much was the 2019 net cash provided by operating activities? A) $126,000. B) $166,000. C) $174,000. D) $186,000. Answer: D Explanation: Net cash provided by operating activities = $186,000 Net income ($850,000 − $720,000) $ Depreciation expense Accounts receivable decrease Accounts payable increase Net cash provided by operating activities 130,000 40,000 10,000 6,000 $ 186,000 21) When a company purchases equipment using common stock, the equipment purchase is reported as a financing activity. Answer: FALSE Explanation: Purchasing equipment using common stock does not involve a cash flow and is therefore not reported either in the investing or the financing section of the cash flow statement. 22) When a company sells equipment for cash at a loss, cash flows from investing activities decreases. Answer: FALSE Explanation: Investing cash flows increase by the cash received from the sale of the equipment. 34) Which of the following statements regarding use of the direct and indirect methods of determining cash flows from operating activities is incorrect? A) The indirect method starts with net income. B) The direct method calculates cash collected from customers. C) The majority of U.S. companies use the indirect method. D) The FASB recommends use of the indirect method. Answer: D Explanation: The FASB recommends use of the direct method. 5) A decrease in the merchandise inventory account occurs when units of inventory purchased are greater than units of goods sold. Answer: FALSE Explanation: An increase in the merchandise inventory account occurs when inventory purchases are greater than goods sold. 6) Goods available for sale are allocated to both ending inventory and cost of goods sold. Answer: TRUE Explanation: Cost of goods available for sale minus ending inventory equals cost of goods sold. 35) A company reported the following information for its most recent year of operation: purchases, $100,000; beginning inventory, $20,000; and cost of goods sold, $110,000. How much was the company's ending inventory? A) $10,000. B) $20,000. C) $15,000. D) $30,000. Answer: A Explanation: Beginning inventory + Purchases – Cost of Goods Sold = Ending inventory. $20,000 + $100,000 – $110,000 = X; Ending inventory = X = $10,000. 43) A company provided the following data: sales, $500,000; beginning inventory, $40,000; ending inventory, $45,000; and gross profit, $150,000. What was the amount of inventory purchased during the year? A) $385,000. B) $355,000. C) $345,000. D) $145,000. Answer: B Explanation: Sales – Cost of goods sold = Gross profit. $500,000 – Cost of goods sold = $150,000. Cost of goods sold = $350,000. Beginning inventory + Purchases – Ending inventory = Cost of goods sold. $40,000 + Purchases – $45,000 = $350,000. Purchases = $355,000. 44) Lauer Corporation has provided the following information about one of its laptop computers: Date Transaction 1/1 Beginning Inventory 5/5 Purchase Number of Units 100 200 Cost per Unit $ 800 $ 900 8/10 Purchase 10/15 Purchase 300 200 $ $ 1,000 1,100 During the year, Lauer sold 750 laptop computers. What was ending inventory using the FIFO cost flow assumption? A) $60,000. B) $55,000. C) $45,000. D) $40,000. Answer: B Explanation: Ending inventory, $55,000 = $1,100 × 50. 74) Under what conditions would a company most likely adopt the double-declining-balance method for financial reporting? A) The company has high technology, robotic equipment in its plant that becomes obsolete quickly and declines in utility to the company more rapidly in the early years of the assets' lives. B) The company wants to maximize its net income during the earlier years of the asset's life. C) The company wants to maximize the asset's book value in the earlier years of the asset's life. D) The company wants to maximize the total depreciation expense over the life of the asset. Answer: A Explanation: The double-declining-balance depreciation method results in more depreciation in the earlier years of an asset's life, which will best fit the robotic equipment scenario. 18) Use of the double-declining-balance method of depreciation results in increasing amounts of depreciation expense over an asset's life. Answer: FALSE Explanation: The double-declining-balance method is an accelerated depreciation method, which results in decreasing amounts of depreciation expense due to the decrease in the underlying asset's book value. 43) Rice Company, a retailer, has provided the following information pertaining to its recent year of operation: • Net income, $100,000 • Accounts receivable increased $9,000 • Prepaid insurance decreased $3,000 • Depreciation expense was $15,000 • Gain on sale of land, $2,000 • Wages payable decreased $7,000 • Unearned revenue increased $11,000 Using the indirect method, how much was Rice's net cash provided by operating activities? A) $89,000. B) $115,000. C) $125,000. D) $111,000. Answer: D Explanation: Net cash provided by operating activities = $111,000 Net income $ 100,000 Depreciation expense 15,000 Gain on sale of land (2,000) Accounts receivable increase (9,000) Prepaid insurance decrease 3,000 Wages payable decrease (7,000) Unearned revenue increase 11,000 Net cash provided by operating activities $ 111,000 84) KAJ Incorporated purchased a machine costing $250,000 by paying $35,000 and signing a $215,000 note payable. How would this transaction be reported within the cash flow from financing activities section of the cash flow statement? A) An inflow of $215,000. B) An outflow of $215,000. C) An outflow of $35,000. D) It would not be reported in the financing activities section. Answer: D Explanation: The signing of the note payable did not involve a cash flow. The financing would be reported in separate disclosure and not in the financing activities section of the cash flow statement. 98) Atomic Company did not record a December 2019 purchase of inventory on credit until January 2020. Assume that the December 31, 2019 ending inventory was correctly determined. What is the effect of this error on the financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2019? A) Net income is correct. B) Stockholders' equity is understated. C) Net income is overstated. D) Current assets are understated. Answer: C Explanation: The 2019 purchases are understated, which causes cost of goods sold to be understated and net income to be overstated in 2019. 62) On January 1, 2019, Woodstock, Inc. purchased a machine costing $40,000. Woodstock also paid $1,000 for transportation and installation. The expected useful life of the machine is 6 years and the residual value is $5,000. If Woodstock uses the straight-line depreciation method, which of the following statements is incorrect? A) The annual depreciation expense is $6,000. B) The December 31, 2019 book value is $35,000. C) The December 31, 2021 accumulated depreciation balance is $18,000. D) The December 31, 2020 book value is $24,000. Answer: D Explanation: Annual depreciation expense = $6,000 = ($40,000 + $1,000 − $5,000) ÷ 6. December 31, 2019 book value = $35,000 = $41,000 − $6,000. December 31, 2121 accumulated depreciation balance = $18,000 = $6,000 × 3 years. Two years have passed to December 31, 2020. Book value after two years = $29,000 = $41,000 – ($6,000 × 2). 64) Warren Company plans to depreciate a new building using the double declining-balance depreciation method. The building cost is $800,000. The estimated residual value of the building is $50,000 and it has an expected useful life of 25 years. What is the building's book value at the end of the first year? A) $736,000. B) $768,000. C) $686,000. D) $690,000. Answer: A Explanation: Year 1 depreciation expense = $64,000 = $800,000 × 2/25. Book value at the end of Year 1 = $736,000 = $800,000 – $64,000. 65) Warren Company plans to depreciate a new building using the double declining-balance depreciation method. The building cost is $800,000. The estimated residual value of the building is $50,000 and it has an expected useful life of 25 years. Assuming the first year's depreciation expense was recorded properly, what would be the amount of depreciation expense for the second year? A) $30,720. B) $32,000. C) $58,880. D) $64,000. Answer: C Explanation: Year 1 depreciation expense = $64,000 = $800,000 × 2/25. Book value at the end of year 1 = $736,000 = $800,000 − $64,000. Year 2 depreciation expense = $58,880 = $736,000 × 2/25. 62) Which of the following transactions would not be reported within the investing section of the cash flow statement? A) The cash sale of land. B) The purchase of a building for cash. C) The purchase of a stock investment for cash. D) The cash receipt of a dividend from a stock investment. Answer: D Explanation: Cash dividends are reported as cash flows from operating activities. 71) Flow Company has provided the following information for the year ended December 31, 2019: • Cash paid for interest, $20,000 • Cash paid for dividends, $6,000 • Cash dividends received, $4,000 • Cash proceeds from bank loan, $29,000 • Cash purchase of treasury stock, $11,000 • Cash paid for equipment purchase, $27,000 • Cash received from issuance of common stock, $37,000 • Cash received from sale of land with a $32,000 book value, $25,000 • Acquisition of land costing $51,000 in exchange for preferred stock issuance • Payment of a $100,000 note payable by exchanging used machinery with a $77,000 book value and $100,000 fair value How much was Flow's net cash flow from investing activities? A) A net outflow of $2,000. B) A net inflow of $2,000. C) A net outflow of $53,000. D) A net inflow of $49,000. Answer: A Explanation: Net cash outflow from investing activities = $2,000 Cash paid for equipment purchase $ + Cash received from land sale Net cash outflow from investing activities $ (27,000) 25,000 (2,000) 105) Which of the following statements is correct when inventory unit costs are decreasing? A) FIFO's cost of goods sold will be the largest among the inventory costing methods. B) LIFO's income tax will be the lowest among the inventory costing methods. C) Ending inventory using the FIFO cost method will be higher than the ending inventory when the LIFO method is used. D) Cost of goods sold using the average cost method will be less than cost of goods sold when the LIFO method is used. Answer: A Explanation: FIFO has the largest cost of goods sold during a period of decreasing unit costs.