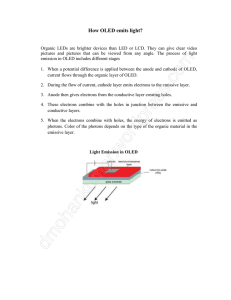
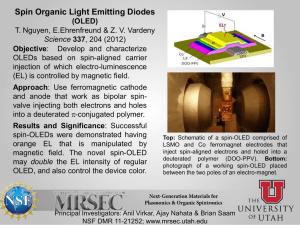
OLED Technology: An Overview of Organic Light Emitting Diodes
advertisement
OLED TECHNOLOGY Introduction • Uses organic light emitting diode(OLED). • Emerging Technology for displays in devices. • Main • principle behind OLED technology is electroluminescence. • Offers brighter, thinner, high contrast, flexible displays. What is an Oled? • OLEDs are solid state devices composed of thin films of organic molecules that is100 to 500 nanometres thick. • They emits light with the application of electricity. • They doesn't require any backlight. i.e., they are self emitting. • They are made from carbon and hydrogen. History • The first OLED device was developed by Eastman Kodak in 1987. • In 1996, pioneer produces the world's first commercial PMOLED. • In 2000, many companies like Motorola, LG etc developed various displays. • In 2001, Sony developed world's largest fullcolor OLED. History (Contd.) • In 2002, approximately 3.5 million passive matrix OLED sub-displays were sold, and over 10 million were sold in 2003. • In 2010 and 2011, many companies announced AMOLED displays. • OMany developments had take place in the year 2012. Features • Flexibility. • Emissive Technology. • Light weight and thin. • Low power consumption. • High contrast, brighter and perfect display from all angles. Structure of Oled • Substrate. • Anode. • Organic layer. • -Conductive layer (Hole Transport Layer). • . made up of polyaniline or metal- phthalocyanine • -Emissive layer( Electron Transport Layer). • made up of polyfluorene or metal chelates. • Cathode. Structure of Oled (Figure) •. Oled Fabrication • Substrate preparation. • Device deposition ★ Deposit and pattern anode. ★ Pattern organic layers. ★ Vacuum deposit and pattern cathode, • Encapsulation. • Also involves making backplane. Oled Deposition • Organic layers can be applied to the using the following methods. • — Evaporation and shadow masking • — Inkjet printing • — Organic vapour phase deposition Evaporation and Shadow Masking Inkjet Printing Organic Vapour Phase Depostion Colour Generation • Differnt approaches for fabricating red , green and blue pixels. • —Red , green and blue individual pixels. • — white emitter and colour filters • — blue emitter and colour converters • — Stacked OLED Colour Generation (Figure) Working Principle • A voltage is applied across the anode and cathode. • Current flows from cathode to anode through the organic layers. • Electrons flow to emissive layer from the cathode. • Electrons are removed from conductive layer leaving holes. • Holes jump into emissive layer. • Electron and hole combine and light emitted. Working Principle (Figure) Oled Device Operation Types of Oled • Six types of OLEDs :• Passive matrix OLED(PMOLED). • Active matrix OLED(AMOLED). • Transparent OLED(TOLED). • Top emitting OLED. • Flexible OLED(FOLED). • White OLED(WOLED). Passive Matrix Oled Active Matrix oled Transparent Oled Top Emitting Oled Flexible Oled White Oled Oled Advantages • Thinner, lighter and more flexible. • Do not require backlighting like LCDs.. • Can be made to larger sizes. • Large fields of view, about 170 degrees. • Faster response time. • Brighter. • High resolution, <5µm pixel size. Oled Diadvantages • Expensive • Lifespan • Water damage • Color balance issues. Oled Vs . Lcd • OLED • Greater view angle • High contrast • Faster response time • Do not require backlighting . • Temperature (50°C — 80°C). • LCD • Limited view angle. • Low contrast • Slow response time. • Require backlighting. • Temperature (0°C— 100°C) Applications • Major applications of oled technology • OLED TV • Mobilephones with OLED screens. • Rolltop Laptop Oled TV Mobile Phones with oled screen Rolltop Laptop Conclusion • Organic Light Emitting Diodes are evolving as the next generation displays. • As OLED display technology matures, it will be better able to improve upon certain existing limitations of LCD including • High power consumption • Limited viewing angles • Poor contrast ratios. Thank you