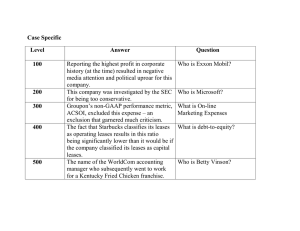
BBMF3063 Financial Statement Analysis Tutorial 4 – Analyzing Investing Activities 1. a. Identify the main concerns in analysis of accounts receivable. One of the main concerns in analysis of account receivable is genuine, due and enforceable. The other concern is the probability of collection is properly evaluated. Although the opinions of an independent auditor can provide certain assurance for these issues, the financial analyst must recognize the possibility of misjudgment and luck of complete independence. b. Describe information, other than that usually available in financial statements, that we should collect to assess the risk of non collectibility of receivables. The description of the receivable usually does not have enough information to reliable determine whether a receivable is genuine, due, and enforceable. Therefore, the knowledge of industry practices and supplementary sources of information must be use for additional assurance. For instance, there is substantial right to return goods for certain companies, so allowance must be provided for this. Hence, the analysts must use their past experience, own judgement and knowledge of the industry to assess the adequacy of provision for uncollectable accounts. 2. Compare and contrast the effects of LIFO and FIFO inventory costing methods on earnings in an inflationary period. Provide Illustration. Answer Last-in, First-Out (LIFO) is one of the inventory costing methods whereby the cost of goods sold is measures by the recent costs and the ending inventory will be the oldest costs. First-In, First-Out (FIFO) is another inventory costing method that the costs of goods sold is based on the oldest costs and the ending inventory will be the recent costs Below is the illustration of coting methods, Inventory on Jan 1, Y2 30 @ 200 RM6000 Inventory Purchased during the year 40 @ 300 RM12000 Cost of Goods available for sale 70 units RM18000 Note: 20 units are sold in Year 2 for RM500 each = Total revenue – RM10000 1 This study source was downloaded by 100000859094778 from CourseHero.com on 12-29-2022 11:16:46 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/83173619/FSA-Tutorial-4-Analyzing-Investing-Activitiesdoc/ BBMF3063 Financial Statement Analysis Tutorial 4 – Analyzing Investing Activities Beginning Inventory + Net Purchase = Cost of goods Sold + End. Inv FIFO RM6000 RM12000 RM4000 RM14000 LIFO RM6000 Rm12000 RM6000 RM12000 Sales - Cost of goods sold = Gross Profit FIFO RM10000 RM4000 RM6000 LIFO RM10000 RM6000 RM4000 From the diagram above we can see that using FIFO costing method has higher earning compare to the LIFO costing method. This is because using FIFO will sell out the older inventories which are lower cost. Thus, the gross profit will be higher. 3. Cost for inventory purposes should be determined by the inventory cost flow method best reflecting periodic income. Required: a. Describe the inventory cost flow assumptions of (1) average-cost, (2) FIFO, and (3) LIFO. 1. FIFO assumes that the first item purchased is also the first one sold. 2. LIFO assumes that the last item purchased is also the first one sold. 3. The average-cost cost flow assumption tends to yield a mid-range cost, and therefore also a mid-range profit. b. Discuss management’s usual reasons for using LIFO in an inflationary economy. Businesses that sell products that rise in price every year benefit from using LIFO. When prices are rising, a business that uses LIFO can better match their revenues to their latest costs. A business can also save on taxes that would have been accrued under other forms of cost accounting, and they can undertake fewer inventory write-downs. Virtually any industry that faces rising costs can benefit from using LIFO cost accounting. For example, many supermarkets and pharmacies use LIFO cost accounting because almost every good they stock experiences inflation. Many convenience stores, especially 2 This study source was downloaded by 100000859094778 from CourseHero.com on 12-29-2022 11:16:46 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/83173619/FSA-Tutorial-4-Analyzing-Investing-Activitiesdoc/ BBMF3063 Financial Statement Analysis Tutorial 4 – Analyzing Investing Activities those that carry fuel and tobacco, elect to use LIFO because the costs of these products have risen substantially over time. c. When there is evidence the value of inventory, through its disposal in the ordinary course of business is less than cost, what is the accounting treatment? What concept justifies this treatment? The proper accounting treatment would be the LCM (lower of cost or market) methodology. The concept under which this treatment is justified is conservatism. Conservatism holds that when you are in doubt, it is best to choose the accounting alternative that will be least likely to overstate assets or income. The usage of the LCM accounting treatment demonstrates the concept of conservatism in that, when the cost of inventory exceeds its expected benefit, a reduction of the inventory to its market value is a better measure of its expected future benefit. 4. Droog Co. is a retailer dealing in a single product. Beginning inventory at January 1 of this year is zero and operating expenses for this same year are $5,000. The following purchases are made this year: Ending inventory at December 31 is 800 units. End-of-year assets, excluding inventories, amount to $75,000, of which $50,000 of the $75,000 are current. Current liabilities amount to $25,000, and long-term liabilities equal $10,000. Required: 3 This study source was downloaded by 100000859094778 from CourseHero.com on 12-29-2022 11:16:46 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/83173619/FSA-Tutorial-4-Analyzing-Investing-Activitiesdoc/ BBMF3063 Financial Statement Analysis Tutorial 4 – Analyzing Investing Activities a. Determine net income for this year under each of the following inventory methods. Assume a sales price of $25 per unit and ignore income taxes. (1) FIFO (2) LIFO (3) Average cost Answer Ending inventory = 800 units, total inventory = 1000 units, sold = 1000 units, sales price =$25 per unit FIFO Sales (100 x 25) = 2500 (300 x 25) = 7500 (600 x 25) = 15000 Cost of Goods Sold (100 x10) = 1000 (300 x 11) = 3300 (600 x 12) = 7200 Gross Profit 1500 4200 7800 13500 Sales (500 x 25) = 12500 (300 x 25) = 7500 (200 x 25) = 5000 Cost of Goods Sold (500 x 15) = 7500 (300 x 14) = 4200 (200 x 12) = 2400 Gross Profit 5000 3300 2600 10900 Cost of Goods Sold 128900 Gross Profit 12110 Total LIFO Total Average cost Sales 25000 23200/18000 = 12.89 x 1000 = 12890 b. Compute the following ratios under each of the inventory methods of FIFO, LIFO, and average cost. (1) Current ratio (2) Inventory turnover (3) Gross margin as a percent of sales (4) Net profit as a percent of sales (5) Debt to equity ratio (1) Current Ratio = Current Asset/Current Liabilities FIFO = 50000 + (300 x 14) + (500 x 15)/ 25000 = 61700/25000 4 This study source was downloaded by 100000859094778 from CourseHero.com on 12-29-2022 11:16:46 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/83173619/FSA-Tutorial-4-Analyzing-Investing-Activitiesdoc/ BBMF3063 Financial Statement Analysis Tutorial 4 – Analyzing Investing Activities 2.468 LIFO =5000 + (400 x 12) + (300 x 11) + (100 x 10) / 25000 =59100/25000 = 2.364 Average Cost = 5000 + (800 x 12.89)/ 25000 = 2.4125 (2) Inventory turnover = Cost of Sales/ Average inventory FIFO = 11500/ (800/2) = 28.75 LIFO = 14100/ (800/2) = 35.25 Average cost = 12890/ (800/2) = 32.225 (3) Gross margin as a percent of sales = [(Sales – COGS)/ Sales] x100 FIFO = [(25000-11500)/ 25000] x 100 = 54% LIFO = [(25000-14100)/ 25000] x 100 = 43.6% Average cost = [(25000 – 12890)/ 25000] x 100 = 48.44% (4) Net profit as a percent of sales = (Net income/ Sales) x 100 FIFO 5 This study source was downloaded by 100000859094778 from CourseHero.com on 12-29-2022 11:16:46 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/83173619/FSA-Tutorial-4-Analyzing-Investing-Activitiesdoc/ BBMF3063 Financial Statement Analysis Tutorial 4 – Analyzing Investing Activities = [(25000- 11500 – 5000)/ 25000] x 100 = 34% LIFO = [(25000- 14100 – 5000)/ 25000] x 100 = 23.66% Average cost = [(25000 – 12800 – 5000)/ 25000] x 100 = 28.44% (5) Debt to equity ratio = Total Liability/ Shareholder equity FIFO = (10000 + 25000)/ 51700 = 0.677 LIFO = (10000 + 25000)/ 49100 = 0.7128 Average cost = (10000 + 25000)/ 50312 = 0.6957 c. Discuss the effects of inventory accounting methods for financial statement analysis given the results from parts a. and b. Based on the result from part a and b, we found out that the FIFO method may generate higher profit since the gross profit from part a and the gross margin and net margin are higher than LIFO method and average cost. Thus, FIFO may ranking the first, Average cost second and LIFO third. 6 This study source was downloaded by 100000859094778 from CourseHero.com on 12-29-2022 11:16:46 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/83173619/FSA-Tutorial-4-Analyzing-Investing-Activitiesdoc/ Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)