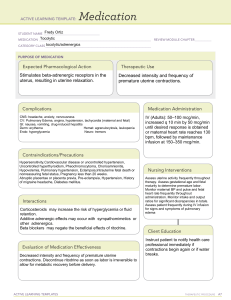
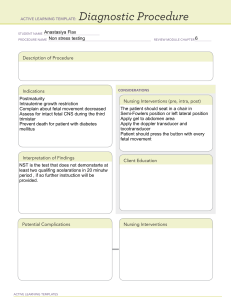
Назва наукового напрямку (модуля): Семестр: 10 Акушерство та гінекологія Тести Опис: 5 курс 10 семестр Перелік питань: 1. A. * B. C. D. E. 2. A. * B. C. D. E. 3. A. B. C. * D. E. 4. A. B. C. D. * E. 5. A. * B. C. D. E. 6. A. B. C. D. E. * 7. A. B. * C. D. Chronic hypertension is hypertension which Detected before pregnancy Detected after 20th week Detected at postpartum period Detected during the labor Detected after delivery The diagnosis of pregnancy is based on the following positive signs of prenancy. Identification of fetal heartbeat Palpation of fetal outline Cessation of menstruation Positive hCG test. Morning sickness Which cervical dilation indicates 5 cm contractile ring station above the symphysis? 1 cm 2 cm 5 cm 3 cm 4 cm What percentages of fetuses are born in the occiput presentation at term? 80% 85% 90% 95% 99% A woman at 10 weeks' gestation who is seen in the prenatal clinic with presumptive signs and symptoms of pregnancy will likely have which of the following? Amenorrhea A positive pregnancy test Chadwick sign Hegar sign Identification of fetal heartbeat What is the most common presentation of the fetus? posterior occiput breech Face brow anterior occiput A positive sign of pregnancy is A positive pregnancy test Fetal movement palpated by the physician Braxton Hicks contractions Quickening E. 8. A. B. * C. D. E. 9. A. B. * C. D. E. 10. A. B. * C. D. E. 11. A. * B. C. D. E. 12. A. * B. C. D. E. 13. A. * B. C. D. E. 14. A. B. * Morning sickness Which of the following is characteristic of synclitism? Sagittal suture is not parallel to the transverse axis of the inlet. Sagittal suture lies midway between the symphysis and sacral promontory. Sagittal suture, although parallel to the transverse axis of the inlet, does not lie exactly midway between the symphysis and sacral promontory. Sagittal suture rotates 45 degrees from the sacral spines. Sagittal suture lies closer to symphysis Sudden onset of severe unilateral lower abdominal pain immediately following strenuous or sexual activity: PID (Pelvic Inflammatory Disease) Ruptured ovarian cyst Vaginal cancer Ovarian torsion Ectopic pregnancy A woman is at 14 weeks' gestation. The physician would expect to palpate the fundus at which of the following levels? Not palpable above the symphysis at this time Slightly above the symphysis pubis At the level of the umbilicus Slightly above the umbilicus At the level of the xyphoideous processus Which of the following is characteristic of posterior asynclitism? Sagittal suture lies closer to symphysis. Sagittal suture lies midway between the symphysis and sacral promontory. Sagittal suture, although parallel to the transverse axis of the inlet, does not lie exactly midway between the symphysis and sacral promontory and lies closer to promontory. Sagittal suture rotates 45 degrees from the sacral spines. None of the above. On physical examination, the physician notes that the lower uterine segment is soft upon palpation. The physician’s assistant would document this finding as: Hegar sign McDonald sign Chadwick sign Goodell sign Braxton Hicks sign During which cardinal movement of labor the fetal head delivered in anterior occiput presentation? extension internal rotation external rotation expulsion flexion A woman is in for a routine prenatal checkup. You are assessing her urine for proteinuria. You know that which of the following findings are considered normal? Dipstick assessment of trace to -1 < 300 mg/24 hours C. Dipstick assessment of +2 D. E. 15. > 300 mg/24 hours This test is not need to perform Cardiovascular system changes occur during pregnancy. Which of the following findings would be considered normal for a woman in her second trimester? Heart sounds (S1, S2) less audible Increase in pulse rate Increase in blood pressure Decrease in red blood cell production There no any changes in cardiovascular system during pregnancy When does the internal rotation of the fetal head begin? in the plane of pelvic inlet in the greatest pelvic dimension in the plane of the least pelvic dimension when the head descents from the plane of the greatest pelvic dimension to the plane of the least pelvic dimension on the pelvic floor A number of changes in the integumentary system occur during pregnancy. Which of the following changes will persist after birth? Epulis Chloasma Telangiectasia Striae gravidarum Chancre The musculoskeletal system adapts to the changes that occur during pregnancy. Which of the following changes can expect to experience woman? Her center of gravity will shift backward. She will experience increased lordosis. She will have increased abdominal muscle tone. She will notice decreased mobility of her pelvic joints. All answers are correct Where does the internal rotation of the fetal head finish? in the plane of pelvic inlet in the greatest pelvic dimension in the plane of the least pelvic dimension when the head descents from the plane of the greatest pelvic dimension to the plane of the least pelvic dimension on the pelvic floor The diagnosis of pregnancy is based on the following positive signs of pregnancy. Palpation of fetal outline Visualization of the fetus Visualization of the fetal genitalia Positive hCG test. Delay of menstrual period Which operation does belong to the birth preparing operations? obstetric forceps A. B. * C. D. E. 16. A. B. C. D. * E. 17. A. B. C. D. * E. 18. A. B. * C. D. E. 19. A. B. C. D. E. * 20. A. B. * C. D. E. 21. A. B. C. * D. E. 22. A. B. C. D. E. * 23. A. B. C. * D. E. 24. A. B. C. * D. E. 25. A. B. C. D. E. * 26. A. B. C. D. * E. 27. A. B. * C. D. E. 28. A. B. C. D. * cesarean section amniotomy craniotomy cervical cerclage Choose indication for cervical cerclage: threatened abortion inevitable abortion incomplete abortion placenta previa cervical incompetence Which operation does belong to the birth preparing operations? obstetric forceps cesarean section amniotomy craniotomy cervical cerclage A major factor for infertility in women is: Mood Weight Anovulation Unknown Marital status Choose indication for cervical cerclage: threatened abortion inevitable abortion incomplete abortion placenta previa cervical incompetence Which operation is performed for fetal shoulders reduction in labor? amniotomy embriotomy craniotomy cleidotomy perineotomy What type of cesarean section is more frequent performed in obstetric? corporal transverse lower segment vertical lower segment extraperitoneal intraperitoneal Women who are trying to conceive should boost their intake of: Nickel Lycopene Potassium Folic acid E. 29. A. B. * C. D. E. 30. A. B. * C. D. E. 31. A. B. * C. D. E. 32. A. B. C. * D. E. 33. A. * B. C. D. E. 34. A. * B. C. D. E. 35. A. * B. C. D. E. 36. A. Protein Choose the contraindications for cesarean section anatomic contracted pelvis endometritis in labor cefaloopelvic disproportion deflexed position of the fetal head breech presentation What is contraindication for performing of operation of external version of the fetus? premature fetus multifetal pregnancy breech presentation transverse fetal lie oblique fetal lie Choose the indication for episiotomy in labor? danger for perineal rupture fetal distress large fetus brow presentation deflexed vertex presentation Which sexually transmitted disease can result in infertility in women? Human papillomavirus (HPV) Genital herpes Pelvic inflammatory disease Chlamydiosis Syphilis Chose the indication for episiotomy? breech presentation uterine inertia placental abruption placenta previa diabetus mellitus in pregnancy Choose the indication for episiotomy? scar in the perineal region placental dysfunction transverse fetal lie oblique fetal lie multifetal pregnancy Choose indications to corporal cesarean section: adhesions in the lower uterine segment breech presentation oblique fetal lie deflexed fetal presentation scar insufficiency in the uterus If a couple is infertile, this means the couple... Will never be able to have children B. * C. D. E. 37. A. B. * C. D. E. 38. A. * B. C. D. E. 39. A. B. C. D. * E. 40. A. B. C. * D. E. 41. A. B. C. * D. E. 42. A. B. * C. D. E. 43. A. B. * C. Could not conceive after 12 months of unprotected sex Should look into adoption Could not conceive after 1 month of unprotected sex Could not conceive after 3 month of unprotected sex Choose indications to corporal cesarean section: breech presentation large intramural node in the lower uterine segment oblique fetal lie scar insufficiency in the uterus placental abruption Perineal ruptures of second degree are repaired by: firstly perineal muscles and vaginal mucous with catgut, after the skin with silk or lavsan firstly commissural posterior, skin, vaginal mucous firstly skin, perineum muscles, vaginal mucus firstly vaginal mucous is sutured, starting from the upper corner, then on the skin silk or lavsan sutures all answers are correct A 35-year-old woman is considered infertile after ____ of trying to conceive. 1 month 2 months 4 months 6 months 12 months Vaginal lacerations are classified into: complete rupture of vagina incomplete rupture of vagina 3 degrees 2 degrees spontaneous, traumatic Perineal lacerations are divided into: complete perineum rupture incomplete perineum rupture 3 degrees 2 degrees 4 degrees What can be specified with the indications for applying obstetrical forceps? Presentation of placenta Placental abruption Excessive uterus activity Contracted pelvis High standing straight head Which of the following is correct regarding infertility? The common cause of infertility is alcohol abuse Female causes are more than male causes in infertility Male causes are more than female causes in infertility D. E. 44. A. B. C. * D. E. 45. A. B. * C. D. E. 46. A. * B. C. D. E. 47. A. B. C. D. * E. 48. A. B. C. D. * E. 49. A. * B. C. D. E. 50. A. B. C. D. E. * 51. Candida vaginitis always leads to infertility Infertility is associated to menopausal age, but only in white women At which term the external cephalic version should be performed ? By 28 weeks At 30 weeks At 32-36 weeks At 36-38 weeks At 40 weeks of pregnancy Danger of perineal rupture is indication for: Hysterotomy Epiziotomy Peryneotomy Forceps application Amniotomy Indicate the definition of infertility: The inability to conceive after 12 months of normal, regular, unprotected sexual activity The inability to conceive after 6 months of normal, regular, unprotected sexual activity Not able to produce enough eggs Over-producing fresh eggs Ovarian cyst uni or bilaterally causing the conceive inability Which type of obstetric forceps are commonly used in modern obstetric practice? Lazarevic Nageli Bush Simpson Sims What of the following is a condition for Cesarean section? Transverse lie of fetus Long without amniotic fluid period Endometritis in labor Alive fetus Cephalopelvic disproportion Which steps are correct in analysis of infertility? First semen then female factor Measuring Basal temperature First semen then after 3 months the female factor First female factor then semen A pelvic ultrasound Which tool is used for cervical fixation? Hehar’s dilators Curette Uterine sound Forceps Tenaculum Contraindications for external cephalic version is: A. B. * C. D. E. 52. A. * B. C. D. E. 53. A. B. C. D. E. * 54. A. B. * C. D. E. 55. A. B. C. * D. E. 56. A. B. * C. D. E. 57. A. B. C. D. E. * 58. A. Premature pregnancy Multifetal pregnancy Pelvic fetal presentation Transverse fetal lie Oblique fetal lie How and when to test for infertility? Patient comes in after intercourse and check also for mucus ferning on microscopy Patient comes in after 1 week after intercourse Patient comes before intercourse Patients collect the samples by themselves at home Patient comes before mensis All of the below analysis should be passed by the woman before C-section EXEPT: Vaginal microflora Fetal ultrasound Biochemical blood analysis Koagulogramm Feces examination What anesthesia is considered optimal for c-section? Intravenous anesthesia Epiduralna anesthesia Spinal anesthesia Endotracheal anesthesia All above How many zygotes are necessary to put into the uterus during the in vitro fertilization? 6 2 4 Many None Indicate the gestational period when pregnant woman should attend the female dispensary firstly: Till 8-weeks of pregnancy Till 12- weeks of pregnancy Till 16 weeks of pregnancy Till 30- weeks of pregnancy Any time At first prenatal visit all of the below methods of investigations should be performed in female dispensary till 12 week EXEPT: Pelvis investigation Speculum examination Bimanual examination Weighting of the woman Determination of uterine height and circumference All of the below methods of investigations should be prescribed in female dispensary for pregnant woman EXEPT: Vaginal smear B. C. D. E. * 59. A. B. * C. D. E. 60. A. B. * C. D. E. 61. A. B. * C. D. E. 62. A. B. C. * D. E. 63. A. * B. C. D. E. 64. A. B. * C. D. E. 65. A. B. * ABO and RhD blood type General urine analysis General blood count X-ray examination of chest Which examination the pregnant woman should not pass in the second half of pregnancy visiting the doctor? Determination of blood pressure Speculum examination Uterine height determination Circumference of the abdomen determination Weighting Indicate the gestational period for the first ultrasonography: 8 weeks 11-13weeks +6days 10 weeks 5 weeks 15 weeks Which parameter in general urine analysis is the most informative during monitoring for pregnant woman? Level of epithelial cells Proteinuria Amount of sugar Amount of leukocytes Transparency Indicate the gestational age for the first prenatal screening test: 2-3 weeks 4-6 weeks 8-13weeks 13-15weeks 18-22weeks Indicate the gestational age for the second prenatal screening test: 14-18 weeks 4-6 weeks 8-13weeks 13-15weeks 18-22weeks When does the pregnant woman obtain vacation before delivery? 22 week of pregnancy 30 weeks of pregnancy 24 week of pregnancy 32 week of pregnancy 35week of pregnancy What is the duration of vacation for pregnancy and delivery? 120 126 C. D. E. 66. A. B. C. D. * E. 67. A. B. C. D. * E. 68. A. B. C. D. * E. 69. A. * B. C. D. E. 70. A. * B. C. D. E. 71. A. * B. C. D. E. 72. A. B. * C. D. E. 140 155 180 Which marker is determined in the first prenatal screening? Progesterone Estriol Prolactin PAPP-A Oxytocin Which marker is determined in the first prenatal screening? Progesterone Estriol Prolactin HCG Alpha-fetoprotein Indicate gestational age for the first fetal heart contractions at ultrasonography: 2-3 day after fertilization 2 week of pregnancy 3 week of pregnancy 4 week of pregnancy 5 week of pregnancy Which disease causes the pelvic deformation? Rachitis Rubella Diabetes Mellitus Varicella Measles Which information about menstrual function can help to determine gestational age of pregnancy? First day of the last menstrual period Regularity of menstruation Duration of menstruation Age of menstrual cycle beginning amount of blood loss Which term indicate normal fetal attitude? Habitus flexus Situs longitudinalis Situs obliques Presentatio cephalica Positio I Which term indicate longitudinal fetal lie? Habitus flexus Situs longitudinalis Situs obliques Presentatio cephalica Positio I 73. A. B. C. D. E. * 74. A. B. C. * D. E. 75. A. * B. C. D. E. 76. A. B. * C. D. E. 77. A. B. C. * D. E. 78. A. B. C. D. * E. 79. A. B. * C. D. E. 80. A. * B. Which term indicate transverse fetal lie? Habitus flexus Situs longitudinalis Situs obliqus Presentatio cephalica Situs transversus Which term indicate oblique fetal lie? Habitus flexus Situs longitudinalis Situs obliqus Presentatio cephalica Positio I In the first fetal position: Fetal back is presented to the left uterine wall Fetal back is presented to the right uterine wall Fetal back is presented to the anterior uterine wall Fetal back is presented to the posterior uterine wall Fetal back is presented to the uterine fundus In the second fetal position: Fetal back is presented to the left uterine wall Fetal back is presented to the right uterine wall Fetal back is presented to the anterior uterine wall Fetal back is presented to the posterior uterine wall Fetal back is presented to the uterine fundus In the anterior fetal variety: Fetal back is presented to the left uterine wall Fetal back is presented to the right uterine wall Fetal back is presented to the anterior uterine wall Fetal back is presented to the posterior uterine wall Fetal back is presented to the uterine fundus In the posterior fetal variety: Fetal back is presented to the left uterine wall Fetal back is presented to the right uterine wall Fetal back is presented to the anterior uterine wall Fetal back is presented to the posterior uterine wall Fetal back is presented to the uterine fundus Fetal lie is: Relation of small parts of the fetus to its body Relation of vertical fetal axis to uterine axis Relation of fetal axis to pelvic axis Relation of fetal back to lateral uterine walls Relation fetal head to the pelvic inlet Fetal attitude is: Relation of small parts of the fetus to its body Relation of vertical fetal axis to uterine axis C. D. E. 81. A. B. C. D. E. * 82. A. * B. C. D. E. 83. A. B. C. D. * E. 84. A. B. C. * D. E. 85. A. B. C. D. * E. 86. A. * B. C. D. E. 87. Relation of fetal axis to pelvic axis Relation of fetal back to lateral uterine walls Relation fetal head to the pelvic inlet Crossing of the fetal axis to uterine axis under 900 indicates Habitus flexus Situs longitudinalis Situs obliqus Presentatio cephalica Situs transversus Crossing of the fetal axis to uterine axis under 900, and location of the fetal head to the right side of the uterine wall indicates: Transverse lie, second position Oblique lie, second position Oblique lie, first position Transverse lie, first position Longitudinal lie, second position Crossing of the fetal axis to uterine axis under 900, and location of the fetal head to the left side of the uterine wall indicates: Transverse lie, second position Oblique lie, second position Oblique lie, first position Transverse lie, first position Longitudinal lie, second position Indicate the best place for fetal heart rate auscultation for longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation, first position, anterior variety: From the right, above umbilicus From the left, above umbilicus From the left, below umbilicus From the right, below umbilicus On the level of umbilicus, from the right Indicate the best place for fetal heart rate auscultation for longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation, second position, anterior variety: From the right, above umbilicus From the left, above umbilicus From the left, below umbilicus From the right, below umbilicus On the level of umbilicus, from the right Indicate the best place for fetal heart rate auscultation for longitudinal lie, breech presentation, first position, anterior variety: From the right, above umbilicus From the left, above umbilicus From the left, below umbilicus From the right, below umbilicus On the level of umbilicus, from the right Indicate the best place for fetal heart rate auscultation for longitudinal lie, breech presentation, second position, anterior variety: A. B. * C. D. E. 88. A. B. C. D. E. * 89. A. B. C. D. E. * 90. A. B. C. * D. E. 91. A. B. C. * D. E. 92. A. B. C. * D. 93. A. B. C. * D. E. 94. A. B. From the right, above umbilicus From the left, above umbilicus From the left, below umbilicus From the right, below umbilicus On the level of umbilicus, from the right Indicate the best place for fetal heart rate auscultation for transverse lie, first position, anterior variety: From the right, above umbilicus From the left, above umbilicus From the left, below umbilicus From the right, below umbilicus On the level of umbilicus, from the left Indicate the best place for fetal heart rate auscultation for transverse lie, second position, anterior variety: From the right, above umbilicus From the left, above umbilicus From the left, below umbilicus From the right, below umbilicus On the level of umbilicus, from the right Indicate the gestational period for the second ultrasonography: 8 weeks 11-13weeks +6days 18 – 20 weeks + 6 days 12 weeks 17weeks Which presentation is presented in transverse lie: Cephalic Foot-link There is no presented part Shoulder Arm Which presentation is presented in oblique lie: Cephalic Foot-link There is no presented part Shoulder Indicate the place for ?-fetoprotein production: Placenta Fetal kidneys Fetal liver and gastrointestinal tract Decidual mеmbraines Fetal brain High level of a-fetoprotein is presented in abnormal development of the fetal: Cardiovascular system Kidneys C. * D. E. 95. A. B. C. D. E. * 96. A. B. C. D. * E. 97. A. B. C. * D. E. 98. A. * B. C. D. E. 99. A. * B. C. D. E. 100. A. B. C. * D. E. 101. A. B. C. D. * E. Nervous system Gastrointestinal tract Limbs What is middle weight of uterus at once after labor? 100-200 gr 300-400 gr 500-600 gr 700-800 gr 900-1000 gr Duration of early postpartum period is: 30 min 3 days 12 days 2 hours 6-8 weeks Lochia rubra consist of all the following EXEPT: blood shreds of the membranes parts of placenta decidual membrane erythrocytes Lochia alba consist of all the following EXEPT: blood mucus leucocytes decidual cells erythrocytes Uterine fundus on the 1 day of postpartum period is: 2cm below umbilicus 3cm below umbilicus 4cm below umbilicus 5cm below umbilicus at the level of pubis Uterine fundus on the 2 day of postpartum period is: 2cm below umbilicus 3cm below umbilicus 4cm below umbilicus 5cm below umbilicus at the level of pubis Uterine fundus on the 3 day of postpartum period is: 2cm below umbilicus 3cm below umbilicus 4cm below umbilicus 6cm below umbilicus at the level of pubis 102. A. B. C. D. E. * 103. A. B. C. D. E. * 104. A. B. C. D. E. * 105. A. * B. C. D. E. 106. A. B. * C. D. E. 107. A. B. C. D. * E. 108. A. B. C. * D. E. 109. A. B. Uterine fundus on the 4 day of postpartum period is: 2cm below umbilicus 3cm below umbilicus 4cm below umbilicus 6cm below umbilicus 8cm below umbilicus Uterine fundus on the 5 day of postpartum period is: 2cm below umbilicus 3cm below umbilicus 4cm below umbilicus 5cm below umbilicus 10cm below umbilicus Uterine fundus on the 10 day of postpartum period is: 10cm below umbilicus 2cm above umbilicus 4cm above umbilicus 8 cm above umbilicus At the level of pubis symphysis Postpartum lochia during the first three days of postpartum period are: bloody bloody-serosal serosal-bloody serosal mucosal Postpartum lochia from 4 to 6 day of postpartum period are: bloody bloody-serosal serosal serosal-bloody mucosal Postpartum lochia from 7 to 9 day of postpartum period are: bloody bloody-serosal serosal serosal-bloody mucosal Postpartum lochia after 10 day of postpartum period are: bloody bloody-serosal serosal serosal-bloody mucosal For breast proliferation response: prolactin luteinized hormone C. * D. E. 110. A. * B. C. D. E. 111. A. B. C. * D. E. 112. A. B. C. D. E. * 113. A. B. C. D. * E. 114. A. * B. C. D. E. 115. A. B. C. * D. E. 116. A. * B. C. D. E. estrogens prostaglandins corticosteroids What complication in the future would develop due to the incorrect suturing of cervical laceration? cervical ectropion; violation of function of pelvic muscles; prolapse of uterus; endometritis; bleeding. Which statement is wrong in relation to a colostrum? production starts on 2nd day after labor; is the yellow liquid production starts on 4-5th day after labor; contains the high quantity of fats; contains albumens and antibodies. All of the below factors should be supported for adequate lactation EXEPT: early breast feeding correct technique of breast feeding rational maternal nutrition “on call” breast feeding 3 hours interval between breast feeding What hormone is produced by a pituitary gland as a result of nipple stimulation? follicular-stimulating vasopressin progesterone prolactin estradiol All of below belong to the recommendations for postpartum woman nutrition EXEPT: plenty of fluids adequate amount of protein plenty of vitamins, fat, minerals limitation of the liquid high caloric meal What is excluded from the diet of lactating woman? plenty of fluids adequate amount of protein chocolate milk; meat. Uterine subinvolution is: decreasing of uterine involution speed-up of the uterine involution delay of lochia in the uterine cavity initial stage of endometritis slow closing of cervix. 117. A. B. * C. D. E. 118. A. B. * C. D. E. 119. A. B. C. D. E. * 120. A. B. * C. D. E. 121. A. B. * C. D. E. 122. A. B. * C. D. E. 123. A. B. C. * D. E. 124. A. B. Uterine involution is: decreasing of uterine contractions reverse uterine development delay of lochia in the uterine cavity initial stage of endometritis slow closing of cervix Female milk becomes mature in postpartum period: on 2-3day on 5-6day on 8-10day on 10-12day on 15-16day Which statement about cervix just after delivery is correct? cervix is closed cervix is dilated for 2cm cervix is dilated for 4cm cervix is formed cervix is dilated for 10cm Which statement about cervix on the 9 day of postpartum period is correct? the cervix is closed cervix is dilated for 2cm cervix is dilated for 4cm cervix is formed cervix is dilated for 10cm Routine postpartum care should include searching for all of the following EXCEPT: Fever Diabetes Depression Anemia Thrombophlebitis In treatment of hypertonic uterine dysfunction you would apply: Oxytocin Tokolytics Misoprostol Miphepristone Enzaprost In the case of ineffective pushing efforts you would do: Tokolysis Spasmolytic prescription Vacuum extraction Therapeutic rest Amniotomy Precipitious labor last: More than 5 hours Less than 4 hours C. D. E. * 125. A. B. C. D. E. * 126. A. B. C. D. E. * 127. A. B. * C. D. E. 128. A. * B. C. D. E. 129. A. B. C. D. E. * 130. A. B. C. D. E. * 131. A. B. * C. D. E. Less than 6 hours Less than 5 hours Less than 3 hours Uterine inertia means: Presipitious labor Excessive uterine activity Discoordinative uterine activity Hypertonic uterine dysfunction Hypotonic uterine dysfunction Augmentation of labor starts with: Ultrasonography Cordocentesis Fetoscopy Amnioscopy Amniotomy Braxton Hicks contractions are typical for: Spontaneous abortion False labor Preterm labor Molar pregnancy Uterine inertia The first line contractile drug for uterine inertia treatment is: Oxytocin Ginipral Misoprostol Miphepristone Labetolol All of the below are the contraindications to contractile drugs prescriptions in uterine inertia EXEPT: Fetal distress Cephalo-pelvic disproportion Placenta abruption Placenta previa Gestational pyelonephritis What is the maximal rate for oxytocin dropping in uterine inertia? 11-12 drops per minute 25-26 drops per minute 30-32 drops per minute 32-34 drops per minute 40 drops per minute What is the initial rate for oxytocin dropping in uterine inertia? 1-2 drops per minute 5-6 drops per minute 10-12 drops per minute 15-18 drops per minute 20-28 drops per minute 132. A. * B. C. D. E. 133. A. B. C. D. E. * 134. A. B. C. D. E. * 135. A. B. * C. D. E. 136. A. B. C. * D. E. 137. A. * B. C. D. E. 138. A. B. C. D. * E. 139. A. B. * The anatomically contracted pelvis is associated with: true conjugate 9 cm internal conjugate 11.5 cm external conjugate 20.5 cm diagonal conjugate 13.5 cm cephalopelvic disproportion The clinically contracted pelvis is associated with: true conjugate 9 cm true conjugate 11.5 cm true conjugate 12.5 cm true conjugate 13.5 cm cephalopelvic disproportion In a nullipara at term the diagonal conjugate is10.5 cm. What is the true conjugate? 5cm 6cm 7cm 8cm 9cm What is the main cause of cephalo-pelvic disproportion? rachitis fetal macrosomia preterm labor twins fetal distress Excessive compression of birth canal‘ soft tissues would provoke: uterine rupture cervical rupture vesicovaginal fistulas perineal rupture vaginal rupture The complication of cephalopelvic disproportion is: uterine rupture cervical rupture vesicovaginal fistules perineal rupture vaginal rupture The pathological contractile ring is a sign of: anatomically contracted pelvis fetal distress fetal macrosomia danger of uterine rupture fetal distress Management of the clinically contracted pelvis is: normal vaginal delivery cesarean section C. D. E. 140. A. * B. C. D. E. 141. A. B. C. D. E. * 142. A. B. * C. D. E. 143. A. B. C. * D. E. 144. A. B. C. D. * E. 145. A. * B. C. D. E. 146. A. B. * C. D. E. obstetrical version fetal destroying operation external cephalic version Female pelvic sizes are: 25 – 28 – 31 – 20 cm. What is the pelvic type? normal pelvis generally contracted pelvis flat pelvis flat rachitic pelvis transverse contracted flat pelvis Female pelvic sizes are: 23 – 26 – 29 – 17 cm. What is the pelvic type? normal pelvis transverse contracted pelvis flat pelvis flat rachitic pelvis generally contracted pelvis Female pelvic sizes are: 23 – 26 – 29 – 18 cm. What is the pelvic type? normal pelvis generally contracted pelvis flat pelvis flat rachitic pelvis transverse contracted pelvis Female pelvic sizes are: 25 – 28 – 31 – 18 cm. What is the pelvic type? normal pelvis generally contracted pelvis simple flat pelvis flat rachitic pelvis transverse contracted pelvis Female pelvic sizes are: 26 – 26 – 31 – 17 cm. What is the pelvic type? normal pelvis generally contracted pelvis flat pelvis flat rachitic pelvis transverse contracted flat pelvis Generally contracted pelvis is characterized by: Decreasing of all pelvic diameters Decreasing of all pelvic anteroposterior diameters Decreasing of all pelvic transverse diameters Decreasing of true conjugate and increasing of the pelvic outlet Combination of generally contracted and flat pelvis Simple flat pelvis is characterized by: Decreasing of all pelvic diameters Decreasing of all pelvic anteroposterior diameters Decreasing of all pelvic transverse diameters Decreasing of true conjugate and increasing of the pelvic outlet Combination of generally contracted and flat pelvis 147. A. B. C. D. * E. 148. A. * B. C. D. E. 149. A. B. C. * D. E. 150. A. * B. C. D. E. 151. A. B. * C. D. E. 152. A. B. * C. D. E. 153. A. B. C. * D. E. 154. Flat rachitic pelvis is characterized by: Decreasing of all pelvic diameters Decreasing of all pelvic anteroposterior diameters Decreasing of all pelvic transversal diameters Decreasing of true conjugate and increasing of the pelvic outlet Combination of generally contracted and flat pelvis What is the cause of cephalo-pelvic disproportion? Face presentation anterior Face presentation posterior Preterm labor Twins Fetal distress Transverse contracted pelvis is characterized by: Decreasing of all pelvic diameters Decreasing of all pelvic anteroposterior diameters Decreasing of all pelvic transverse diameters Decreasing of true conjugate and increasing of the pelvic outlet Combination of generally contracted and flat pelvis The true conjugate of the flat pelvis is 9.5 cm. What is the degree of pelvic contraction? I degree II degree III degree IV degree V degree The true conjugate of the flat pelvis is 8.5 cm. What is the degree of pelvic contraction? I degree II degree III degree IV degree V degree The true conjugate of the flat pelvis is 8.0 cm. What is the degree of pelvic contraction? I degree II degree III degree IV degree V degree The true conjugate of the generally contracted pelvis is 7.0 cm. What is the degree of pelvic contraction? I degree II degree III degree IV degree V degree The true conjugate of the generally contracted pelvis is 6.5 cm. What is the degree of pelvic contraction? A. B. C. * D. E. 155. A. B. C. D. * E. 156. A. * B. C. D. E. 157. A. * B. C. D. E. 158. A. * B. C. D. E. 159. A. B. * C. D. E. 160. A. B. * C. D. E. 161. A. * B. I degree II degree III degree IV degree V degree The true conjugate of the generally contracted pelvis is 5.0 cm. What is the degree of pelvic contraction? I degree II degree III degree IV degree V degree Indicate “rare occurred” type of contracted pelvis: osteomalatic pelvis generally contracted pelvis flat pelvis flat rachitic pelvis generally contracted pelvis Management of the patients with I degree of pelvic contraction and probable fetal weight 2900g: vaginal delivery cesarean section only vaginal delivery or cesarean section fetal destroying operation labor preparing operation Management of the patients with II degree of pelvic contraction and probable fetal weight 2800g: vaginal delivery cesarean section only vaginal delivery or cesarean section fetal destroying operation labor preparing operation Management of the patients with III degree of pelvic contraction: vaginal delivery cesarean section only vaginal delivery or cesarean section fetal destroying operation labor preparing operation Management of the patients with IV degree of pelvic contraction: vaginal delivery cesarean section only vaginal delivery or cesarean section fetal destroying operation labor preparing operations What is the cause of cephalo-pelvic disproportion? sinciput vertex presentation and large fetus face presentation posterior C. D. E. 162. A. B. * C. D. E. 163. A. B. C. D. E. * 164. A. B. C. * D. E. 165. A. B. C. D. * E. 166. A. B. C. D. * E. 167. A. B. C. D. * E. 168. A. B. C. D. * E. occiput presentation foot-link presentation knee-link presentation What is the cause of cephalo-pelvic disproportion? frank breech presentation sinciput vertex presentation and III degree of pelvic contraction occiput presentation foot-link presentation knee-link presentation Which of the following is associated with meconium-stained amniotic fluid? fetal macrosomia vaginal delivery cesarean section chorioamnionitis fetal distress What is the normal average baseline fetal heart rate at term? 100 to 140 bpm 110 to 150 bpm 110 to 170 bpm 120 to 140 bpm 160-179 bpm What is bradycardia? baseline fetal heart rate < 130 for > 5 min baseline fetal heart rate < 140 for > 15 min baseline fetal heart rate < 120 for > 5 min baseline fetal heart rate < 110 for > 15 min baseline fetal heart rate < 120 for > 3 min Which of the following is NOT associated with fetal bradycardia? head compression congenital heart block fetal distress gestational pyelonephritis placental abruption Acceleration defines as: increasing of fetal heart rate for 10 bpm for 10 sec increasing of fetal heart rate for 15 bpm for 10 sec increasing of fetal heart rate for 10 bpm for 15 sec increase of fetal heart rate for 15 bpm for 15 sec increasing of fetal heart rate for 5 bpm for 15 sec Fetal heart rate monitoring includes evaluation all of the below parameters EXEPT: baseline rhythm fetal heart rate variability presence of accelerations ratio between amplitude and rhythm of oscillations presence of decelerations 169. A. B. C. D. * E. 170. A. B. C. * D. E. 171. A. B. * C. D. E. 172. A. * B. C. D. E. 173. A. B. C. D. E. * 174. A. B. C. D. * E. 175. A. B. C. D. * E. 176. A. B. * Which method is the best for evaluation of fetal well-being: amnioscopy ultrasonography fetal heart rate monitoring biophysical profile determination of a-fetoprotein in amniotic fluid How many minutes do you need for fetal heart rate monitoring? 10 20 30 40 50 Nonstress test – is: amount of amniotic fluid response of the fetal heart rate to the fetal movement response of the fetal heart rate to physical irritation response of the fetal heart rate to contractile drugs response of the fetal heart rate to spasmolytics Reactive nonstress test is: increasing of fetal heart rate at least 15 bpm over a period 15 seconds following a fetal movement increasing of fetal heart rate at least 1 bpm over a period 1 seconds following a fetal movement decreasing of fetal heart rate at least 15 bpm over a period 15 seconds following a fetal movement decreasing of fetal heart rate at least 15 bpm over a period 15 seconds following a fetal movement absence of accelerations in response of fetal movement Nonreactive nonstress test is: increasing of fetal heart rate at least 15 bpm over a period 15 seconds following a fetal movement increasing of fetal heart rate at least 1 bpm over a period 1 seconds following a fetal movement decreasing of fetal heart rate at least 15 bpm over a period 15 seconds following a fetal movement decreasing of fetal heart rate at least 15 bpm over a period 15 seconds following a fetal movement absence of accelerations in response of fetal movement How many parameters of fetal wellbeing are presented in determination of biophysical profile? 2 3 4 5 6 All of the below are the parameters of biophysical profile EXCEPT: amount of amniotic fluid fetal tone reactive nonstress test fetal urine output fetal breathing movements Biophysical profile determines: during fetal heart rate monitoring in ultrasonography C. D. E. 177. A. B. C. D. * E. 178. A. B. * C. D. E. 179. A. B. C. * D. E. 180. A. B. C. D. E. * 181. A. B. C. D. * E. 182. A. B. * C. D. E. 183. A. B. C. D. E. * in cordocentesis in amnioscopy in amniocentesis How many points of biophysical profile is considered to be normal? 1-2 3-4 5-6 7- 10 12-14 Two points for normal fetal breathing movements (FBM) in biophysical profile mean: at least 5 FBM for 5 seconds in 10 minutes at least 1 FBM for 60 seconds during 30 minutes observation at least 1 FBM for 20 seconds during 30 minutes at least 1 FBM for15 seconds during 15 minutes at least 2 FBM for 30 seconds during 30 minutes Two points for normal fetal tone in biophysical profile mean: at least 2 episodes of active extension with return to flexion of fetal limbs/trunk during 30 minutes at least 3 episode of active extension with return to flexion of fetal limbs/trunk in 15 minutes at least 1 episode of active extension with return to flexion of fetal limbs/trunk in 30 minutes at least 2 episodes of active extension with return to flexion of fetal limbs/trunk during 10 minutes at least 1 episode of active extension without return to flexion of fetal limbs/trunk during 10 minutes All of the below complications should be presented during amniocentesis EXCEPT: maternal trauma fetal trauma infection abortion placenta previa All of below are the main indications for cordocentesis EXCEPT: fetal distress fetal isoimmunization metabolic fetal disorders maternal pregnancy induced hypertension fetal karyotyping Cordocentesis – is: puncture of amniotic sac percutaneous umbilical blood sampling skin sample chorionic villus sampling fetoscopy Decreasing of fetal heart rate below baseline is called as: feceleration acceleration doceleration perceleration deceleration 184. A. * B. C. D. E. 185. A. * B. C. D. E. 186. A. * B. C. D. E. 187. A. * B. C. D. E. 188. A. B. C. * D. E. 189. A. * B. C. D. E. 190. A. * B. C. D. E. Variable decelerations are closely connected with: umbilical cord occlusion placental abruption placental previa diabetes mellitus pregnancy induced hypertension What is the normal perception of fetal movement by pregnant woman? more than 10 movements during 12 hours 2 movements for 2 hours 3 movements in 1 hour 5 movements in 30 minutes 1 movement for 24 hours Normal amount of amniotic fluid volume in the biophysical profile mean: at least 1 pocket of amniotic fluid that measures at least 2 cm in two perpendicular planes during 30 minutes at least 2 pockets of amniotic fluid at least 1 cm in two perpendicular planes during 30 minutes at least 1 pocket of amniotic fluid at least 1 cm in two perpendicular planes during 15 minutes at least 3 pockets of amniotic fluid at least 1 cm in two perpendicular planes during 20 minutes at least 1 pocket of amniotic fluid at least 1 cm in two perpendicular planes during 50 minutes During cordocentesis all of the below complications should be presented EXCEPT: oligohydramnios fetal trauma fever abortion placenta abruption How many points does the woman receive at biophysical profile for one fetal breath movement by 60 seconds duration during 30 minutes observation? 0 1 2 3 4 How many points does the woman receive at biophysical profile for absence of active extension with return to flexion of fetal limb/trunk during 30 minutes observation? 0 1 2 3 4 Biophysical profile of the fetus determines from: 30 week of gestation 16 week of gestation 12 week of gestation 40 week of gestation 34 week of gestation 191. A. B. * C. D. E. 192. A. * B. C. D. E. 193. A. * B. C. D. E. 194. A. B. C. D. E. * 195. A. * B. C. D. E. 196. A. B. * C. D. E. 197. A. B. * C. D. E. 198. A. * B. Equivocal biophysical fetal profile has: 4 points and lower 5-6 points 7-10 points 3-6 points 5-10 points Abnormal biophysical fetal profile has: 4 points and lower 5-6 points 7-10 points 3-6 points 5-10 points What you should do in case of abnormal biophysical fetal profile: Emergent delivery To continue observation To stop delivery stimulation To perform ultrasonography To change maternal position In case of fetal distress in labor we undergo all below prescriptions EXEPT: Avoid supine position of the patient Stop oxytocin dropping Vacuum extraction Forceps delivery Continue oxytocin dropping In case of fetal distress in the first period of labor we: Perform Cesarean section immediately Continue observation Continue oxytocin dropping Perform vacuum extraction Prescribe tokolytics In case of fetal distress in the second period of labor in breach presentation we: Perform Cesarean section immediately Perform breech extraction Continue oxytocin dropping Prescribe intravenous metabolic drugs Perform vacuum extraction How many degrees of fetal growth retardation have been distinguished during ultrasonography? 2 3 4 5 6 The first degree of fetal growth retardation during ultrasonography corresponds with: 2 weeks retardation 3 weeks retardation C. D. E. 199. A. B. C. * D. E. 200. A. B. C. D. E. * 201. A. B. C. * D. E. 202. A. B. C. * D. E. 203. A. * B. C. D. E. 204. A. * B. C. D. E. 205. A. B. C. * D. E. 4 weeks retardation 5 weeks retardation 1 week retardation The second degree of fetal growth retardation corresponds with: 2 weeks retardation 6 weeks retardation 3-4 weeks retardation 5 weeks retardation 1 week retardation The third degree of fetal growth retardation corresponds with: 2 weeks retardation 3 weeks retardation 4 weeks retardation 1 week retardation more than 4 weeks retardation Fetal heart rate auscultation by obstetric stethoscope auscultation is performed from: 20th week of pregnancy 15th week of pregnancy 23-24th week of pregnancy 28th week of pregnancy 30th week of pregnancy Puncture of the fetal cord vessels is called as: Amnioscopy Fetoscopy Cordocentesis Amniocentesis Culdocentesis How is macrosomia defined? Birthweight > 4000 g Birthweight > 4100 g Birthweight > 4500 g Birthweight > 5000 g Birthweight > 5100 g Which of the following is a risk factor for macrosomia? Diabetes Pregnancy induced hypertension Maternal anemia Gestational age > 42 weeks Preterm labor Cesarean section undergo all types of multiple pregnancies EXCEPT: Breech – breech presentation Breech – transverse presentation Cephalic – cephalic presentation Breech– cephalic presentation Transverse – transverse 206. A. B. C. D. * E. 207. A. * B. C. D. E. 208. A. B. C. * D. E. 209. A. B. C. * D. E. 210. A. B. C. D. E. * 211. A. B. C. * D. E. 212. A. B. * C. D. E. 213. A. B. * Which fetus is called as “giant”? Birthweight > 4000 g Birthweight > 4100 g Birthweight > 4500 g Birthweight > 5000 g Birthweight > 5100 g Which of the following is NOT a complication of macrosomia? Placenta abruption Brachial plexus injury Shoulder dystocia Cephalopelvic disproportion Uterine rupture The most common sign for dichorionic diamnionic twin pregnancy is: Discordance Sonographic measurement of the dividing membranes thinner than 1 mm Two separate placentae Fetal growth retardation Placenta presentation With twins, which of the following is NOT true? Pregnancy hypervolemia approximates 50 to 60% Cardiac output is increased Pulse rate is decreased Stroke volume is increased The body weight increased Which of the following is NOT a specific complication of monoamnionic twins? Cord entanglement Discordancy Conjoined twins Preterm labor Postdate labor Spontaneous vaginal delivery undergoes all types of clinical situations EXCEPT: Cephalic –cephalic presentation Cephalic –breech presentation Breech – cephalic presentation Cephalic – transverse presentation All of the above What is the best management of labor in breech – breech presentation? vaginal delivery cesarean section vacuum extraction forceps application breech extraction What is the best management of labor in breech –cephalic presentation? vaginal delivery cesarean section C. D. E. 214. A. * B. C. D. E. 215. A. * B. C. D. E. 216. A. B. * C. D. E. 217. A. B. C. * D. E. 218. A. B. * C. D. E. 219. A. B. * C. D. E. 220. A. B. C. * D. E. vacuum extraction forceps application breech extraction What is the best management of labor in cephalic – breech presentation? vaginal delivery cesarean section vacuum extraction forceps application breech extraction What is the best management of labor in cephalic – cephalic presentation? vaginal delivery cesarean section vacuum extraction forceps application breech extraction What is the best management of labor in breech – transverse presentation? vaginal delivery cesarean section vacuum extraction forceps application breech extraction A twin fetus is at risk for all of the below complications EXCEPT: Stillbirth Abnormal fetal development Macrosomia Malpresentation Umbilical cord entanglement All of the below are patients at risk for macrosomic fetus EXCEPT: endocrine disorders multiple pregnancy obesity diabetes mellitus excessive nutrition What congenital anomaly is associated with polyhydramnion? ventral septal defect spina bifida omphalocele hypoplastic kidneys fetal anemia At which gestational age amniotic fluid volume reach approximately 1-1,5 mL? 16 weeks 28 weeks 36 weeks 40 weeks 42 weeks 221. A. B. C. D. E. * 222. A. B. C. D. * E. 223. A. * B. C. D. E. 224. A. B. C. D. E. * 225. A. B. C. D. E. * 226. A. B. C. * D. E. 227. A. * B. C. D. E. 228. A. B. Polyhydramnios defines as increasing of amniotic fluid more than: 1000 mL 1400 mL 1600 mL 1800 mL 2000 mL Which of the following anomalies are not associated with polyhydramnios? central nervous system abnormalities duodenal atresia esophageal atresia renal agenesis immune hydrops What is the major source of amniotic fluid? amniotic epithelium fetal urination fetal swallowing fetal inspiration placental production What is the most likely cause of polyhydramnion? maternal anemia maternal cardiac diseases decreasing of maternal urination increased blood pressure maternal infections Which of the following maternal symptom is NOT associated with acute polyhydramnios? edema respiratory distress enlarged abdomen preterm labor normal maternal condition What is a frequent maternal complication of polyhydramnios? preeclampsia hypertonic uterine activity placental abruption postterm pregnancy anemia What are the main compounds of the amniotic fluid? vernix and ectodermal fetal cells mononuclear cells and macrophages lymphocytes eosinophils and vernix erythrocytes What is the most common cause of oligohydramnios? renal anomalies fetal growth retardation C. D. * E. 229. A. B. C. D. * E. 230. A. B. * C. D. E. 231. A. B. C. D. E. * 232. A. B. * C. D. E. 233. A. * B. C. D. E. 234. A. * B. C. D. E. 235. A. * B. C. D. E. twin–twin transfusion premature rupture of fetal membranes Diabetus mellitus What is recommended for labor’ induction in patients with polyhydramnion? stimulation of uterine contractions episiotomy cesarean section early amniotomy obstetrics forceps Polyhydramnios is a risk factor of : postpartum infections early postpartum bleeding fetal macrosomia fetal malformations Pregnancy induced hypertension Which complication is typical for I stage of labor in patients with polyhydramnios? placenta Previa bleeding maternal infection fetal distress hypotonic uterine contractions What is the minimal physiologic blood loss in labor? 100 ml 250 ml 300 ml 350 ml 450 ml What is the management of the total placenta percreta? total hysterectomy manual separation and removal of the placenta hysterotomy subtotal hysterectomy ligation of the vessels What is the management of the partial placenta percreta? total hysterectomy manual separation and removal of the placenta hysterotomy subtotal hysterectomy ligation of the vessels What is the management of the focal placenta percreta? total hysterectomy manual separation and removal of the placenta hysterotomy subtotal hysterectomy ligation of the vessels 236. B. Which highest dose of oxytocin is prescribed in the uterine atony? 5 units 10 units 15 units 20 units 25 units Which dose of misoprostol is prescribed in the uterine atony? 800 mkg 600 mkg 400 mkg 200 mkg 100 mkg Couvelaire uterus is the complication of : placental abruption placental adherence placental accreta placental percreta uterine atony What is the best method of genital tract trauma diagnosis? vaginal examination speculum inspection patients complaints female history ultrasonography Which of the following is the most ideal method of delivery for severe abruption in the second stage of labor in breech presentation? forceps delivery immediate cesarean section cesarean section after blood replacement breech extraction vacuum application What is the best management in the mild form of placental abruption? forceps delivery immediate cesarean section C. D. * E. 242. A. B. C. D. * E. 243. A. cesarean section after blood replacement observation vacuum application Which of the following is NOT characteristic of early hypovolemic shock? decreased mean arterial pressure decreased stroke volume increased arteriovenous oxygen content difference increased central venous pressure there is no correct answer Which of the following is characteristic of the secondary phase of amniotic fluid embolism? pulmonary hypertension A. B. C. D. * E. 237. A. * B. C. D. E. 238. A. * B. C. D. E. 239. A. B. * C. D. E. 240. A. B. C. D. * E. 241. A. B. C. D. * E. 244. A. B. C. D. * E. 245. A. * B. C. D. E. 246. A. B. C. * D. E. 247. A. B. C. * D. E. 248. A. B. C. D. E. * 249. A. B. C. * D. E. 250. A. B. C. decreased systemic vascular resistance decreased left ventricular stroke index lung injury and coagulopathy there is no correct answer How many degrees of hemorrhagic shock severity do you know? 1 2 3 4 5 What is the blood loss in the first degree of hemorrhagic shock? 750-1000ml 1000-1500ml 1500-2500ml 500-750ml >2500ml What is the blood loss in the second degree of hemorrhagic shock? 500-750ml 750-1000ml 1000-1500ml 1500-1800ml >1800ml What is the blood loss in the third degree of hemorrhagic shock? 500-750ml 750-1000ml 1500-2500ml 1000-1200ml 1200-1300ml What is the blood loss in the fourth degree of hemorrhagic shock? 500-750ml 750-1000ml 1500-2000ml 2000-2200ml >2500ml All of the above are the main causes of disseminated intravascular clotting (DIC) syndrome EXCEPT: Placenta abruption Embolic fluid embolism Chronic bronchitis Pregnancy induced hypertension Hypotonic bleeding What is the volume of infusion therapy in the mild degree of hemorrhagic shock ? 500 ml 1000 ml 1500 ml D. A. * B. 2000 ml 2500 ml Which dose of colloids is recommended in the mild degree of hemorrhagic shock? 5 ml / kg 10 ml / kg 15 ml / kg 20 ml / kg 25 ml/kg All of the below belong to the widely used colloids in obstetrics EXCEPT: Refortan Gelofusin Ringer-Lokka Stabisol Fresh-frozen plasma What is the volume of infusion therapy in the moderate degree of hemorrhagic shock? 1000 ml 1500 ml 2000 ml 2500 ml 3000 ml What is the volume of infusion therapy in the severe degree of hemorrhagic shock? 1500 ml 2000 ml 2500 ml 3000 ml 4000 ml What is the first stage of Disseminated Intravascular Clotting syndrome? hypocoagulation without generalizing fibrinolysis hypercoagulation hypocoagulation with generalizing fibrinolysis total fibrinolysis local fibrinolysis What is the second stage of Disseminated Intravascular Clotting syndrome? hypocoagulation without generalizing fibrinolysis hypercoagulation C. D. E. 257. A. B. C. * D. E. 258. hypocoagulation with generalizing fibrinolysis total fibrinolysis local fibrinolysis What is the third stage of Disseminated Intravascular Clotting syndrome? hypocoagulation without generalizing fibrinolysis activation hypercoagulation hypocoagulation with generalizing fibrinolysis activation total fibrinolysis local fibrinolysis What is the fourth stage of Disseminated Intravascular Clotting syndrome? E. * 251. A. B. * C. D. E. 252. A. B. C. * D. E. 253. A. B. C. D. E. * 254. A. B. C. D. E. * 255. A. B. * C. D. E. 256. A. E. * hypocoagulation without generalizing fibrinolysis activation hypercoagulation hypocoagulation with generalizing fibrinolysis activation total fibrinolysis Local fibrynolysis All of the below are the main signs of Disseminated Intravascular Clotting syndrome EXCEPT: Hemorrhages into skin and mucous membranes Hemorrhages from the places of injections, incisions, uterus Necrosis of some areas of skin and mucous membranes Hypertension Central nervous system impairment, acute renal, liver, pulmonary insufficiency. Which drug is contraindicated in all stages of Disseminated Intravascular Clotting syndrome? Heparin Fresh frozen plasma Contrical Transamacha acid Gordox Which drug is contraindicated in all stage of Disseminated Intravascular Clotting syndrome? Fresh frozen plasma Fibrinogen Aminocapronic acid Tranexamic acid Proteolytic enzymes inhibitors All of the below are the main signs of Cardiorespiratory collapse in amniotic fluid embolism EXCEPT: Severe pain in the chest Cough Feeling of the death, cyanosis Hypertension Sudden dyspnea, hypotension In which level of hemoglobin blood transfusion in hemorrhagic shock is indicated? < 120 g/l < 110 g/l < 100 g/l < 80 g/l < 70 g/l 264. A. * B. C. D. E. 265. A. B. Shock index is 0.8-1. What is the blood loss? 750-1000ml 1000-1200 1200-1500 1500-1700 1800-2000 Shock index is 1.0-1.5. What is the blood loss? 400-600ml 750-900ml B. C. D. * E. 259. A. B. C. D. * E. 260. A. * B. C. D. E. 261. A. B. * C. D. E. 262. A. B. C. D. * E. 263. A. B. C. D. C. * B. C. 1000-1500ml 200-400ml 900-1000ml Shock index is 1.5 – 2.0. What is the blood loss? 400-600ml 750-900ml 1000-1500ml 1500-2500ml 900-1000ml Shock index is >2.0. What is the blood loss? 750-1000ml 1000-1200 1200-1500 1500-1700 >2500 All of the below are risk factors for amniotic fluid embolism EXCEPT: excessive labor contractions manual removal of placenta placenta abruption chronic pyelonephritis hemorrhagic shock All of the below are risk factors for septic shock EXCEPT: Placenta abruption Septic abortion Chorionamnionitis Pyelonephritis Endometritis Which dose of colloids is recommended in the moderate degree of hemorrhagic shock? 5 ml / kg 10 ml / kg 15 ml / kg 20 ml / kg 25 ml/kg Which dose of fresh-frozen plasma is recommended in the moderate degree of hemorrhagic shock? 5 - 10 ml / kg 10 - 15 ml / kg 15 - 20 ml / kg D. E. 272. A. B. * C. D. E. 20 - 25ml / kg 25 - 30ml/kg Which dose of blood transfusion is recommended in the severe degree of hemorrhagic shock? 5 ml / kg 10-20 ml / kg 30 ml / kg 40 ml / kg 3ml/kg D. E. 266. A. B. C. D. E. 267. A. B. C. D. E. 268. A. B. C. D. * E. 269. A. * B. C. D. E. 270. A. B. * C. D. E. 271. A. * 273. 279. Which dose of crystalloids is recommended in the severe degree of hemorrhagic shock? 7 ml / kg 10 ml / kg 15 - 20 ml / kg 25ml / kg 25 - 30ml/kg Which dose of fresh-frozen plasma is recommended in the severe degree of hemorrhagic shock? 5 - 10 ml / kg 10 - 15 ml / kg 15 - 20 ml / kg 20 - 25ml / kg 25 - 30ml/kg All of the below are indicated in the infusion therapy in the hemorrhagic shock EXCEPT: Reopolyglycin Isotonic solution Refortan Gelofusin Blood transfusion All of the above are indicated in the infusion therapy in the hemorrhagic shock EXCEPT: Isotonic solution 5 % glucose Stabisol Gelofusin Blood transfusion What is the initial rate of infusion therapy in the case of hemorrhagic shock and low arterial blood pressure? 50 ml per minute 100 ml per minute 200 ml per minute 150 ml per minute 250 ml per minute What is the female heart rate in the mild degree of hemorrhagic shock? 70-80 beats per min 90 -100 beats per min 100-110 beats per min 110-120beats per min 120-130 beats per min What is the female heart rate in the moderate degree of hemorrhagic shock? A. B. C. * D. E. 280. A. 70-80 beats per min 90 -100 beats per min 110-120 beats per min 120 -140beats per min 160 beats per min What is the female heart rate in the severe degree of hemorrhagic shock? 70-80 beats per min A. * B. C. D. E. 274. A. B. * C. D. E. 275. A. * B. C. D. E. 276. A. B. * C. D. E. 277. A. B. C. * D. E. 278. A. B. C. * D. E. B. C. D. E. * 281. A. B. * C. D. E. 282. A. B. C. * D. E. 283. A. B. C. D. * E. 284. A. B. C. D. E. * 285. A. B. * C. D. E. 286. A. B. C. D. E. * 287. A. 80 -90 beats per min 90-100 beats per min 100 -110beats per min 120-140 beats per min What is the level of systolic blood pressure in the mild degree of hemorrhagic shock? 120 mm Hg 90-100 mm Hg 70 – 90 mm Hg 50- 70 mm Hg < 50 mm Hg What is the level of systolic blood pressure in the moderate degree of hemorrhagic shock? 120 mm Hg 90-100 mm Hg 70 – 90 mm Hg 50- 70 mm Hg < 50 mm Hg What is the level of systolic blood pressure in the severe degree of hemorrhagic shock? 20 mm Hg 90-100 mm Hg 70 – 90 mm Hg 50- 70 mm Hg < 50 mm Hg What is the level of systolic blood pressure in the considerable degree of hemorrhagic shock ? 120 mm Hg 90-100 mm Hg 70 – 90 mm Hg 50- 70 mm Hg < 50 mm Hg Predomination of amniotic pressure over venous is presented in Amniotic fluid embolism in all below situations EXCEPT: excessive labor contractions preterm labor placenta abruption uterine cervix dystocia multiple pregnancy Trauma of venous uterine vessels is presented in Amniotic fluid embolism in all below situations EXCEPT: placenta abruption puerperal hypotonic hemorrhage cesarean section manual removal of placenta postdate pregnancy Differential diagnosis of Amniotic fluid embolism is performed with all of the below diseases EXCEPT: Myocardial infarction B. E. 294. Pulmonary artery thrombembolism Pneumonia Air’ embolism Mendelson’ syndrome When does hypotonic uterine bleeding start: at cervical stage at the expulsive stage after the delivery of the fetus after the placental separation At pelvic stage All of the below are the main reasons for postpartum hemorrhages EXEPT: Birth canal trauma Violation of the uterine contractile activity DIC syndrome Hypertonic disease Lacerations of birth canal In the early postpartum bleeding you should perform firstly: Inspection and suturing of birth canal lacerations Colposcopy Hysterotocography Laparoscopy Ultrasonography First aid in case of early postpartum bleeding includes: Contractile drugs prescription Diuretics administration Vessels ligation Using of mezaton because of low blood pressure Hysterectomy Retained placenta in uterine cavity is diagnosed firstly by: Abnormal shape of the placenta Delay of amniotic membranes Broken vessels in the placenta Thin placenta Hypertension Retained placenta in uterus in late postpartum period is diagnosed by: Uterine palpation Ultrasound examination X ray examination Vaginal examination Colposcopy Management of bleeding on 6 day of postpartum period: A. B. * C. D. Manual exploration of the uterine cavity Uterine curettage Pudendal block Puncture of the Douglas space C. * D. E. 288. A. B. C. D. * E. 289. A. B. C. D. * E. 290. A. * B. C. D. E. 291. A. * B. C. D. E. 292. A. B. C. * D. E. 293. A. B. * C. D. E. C. Nothing above The next step after prescription 2-3 line contractile drugs for atonic postpartum bleeding treatment is: External massage of the uterus Oxytocin prescription Bimanual uterine compression Tranexamic acid prescription Balloon tamponade of the uterus The next step after bimanual uterine compression for atonic postpartum bleeding treatment is: External massage of the uterus Oxytocin prescription Manual exploration of uterine cavity Tranexamic acid prescription Balloon tamponade of the uterus Which blood loss in uterine atony is indication for laparotomy? 1, 5% and more from body weight more than 250 ml more than 400 ml more than 100 ml 0,5 % from body weight Methods of surgical hemostasis for uterine devascularization? bilateral ligation of uterine vessels bilateral ligation of ovarian vessels compressive sutures bilateral ligation of a.iliaca interna all of the above Indications for hysterectomy in the case of postpartum bleeding? Placenta accreta Placenta increta Placenta percreta Uterine rupture All of the above Management of uterine inversion in postpartum period: Reposition of the uterus Total uterine hysterectomy Subtotal uterine hysterectomy Tamponade of the uterus Ligation of uterine vessels What is the most characteristic sign of amniotic fluid embolism during cesarean section in general anesthesia? Cough Bradycardia Hypertension D. E. * Hypothermia Unexplained decreasing of saturation to 70-85% 295. A. B. C. * D. E. 296. A. B. C. D. E. * 297. A. * B. C. D. E. 298. A. B. C. D. E. * 299. A. B. C. D. E. * 300. A. * B. C. D. E. 301. A. B. 302. D. E. 309. What is the most characteristic sign of amniotic fluid embolism during cesarean section in general anesthesia? Cough Bradycardia Hypertension Hypothermia Wet wheezing in the lungs Which of the following could be risk factor for ectopic pregnancy? Previous pelvic/tubal surgery- PID (Pelvic Inflammatory Disease) Ovarian torsion HIV Maternal obesity Maternal trauma, such as a car accident Pregnancy induced hypertension is hypertension which Detected before pregnancy Detected after 20th week Detected before 20th week Detected 45 days after delivery Detected during pregnancy Indications for drug therapy in woman with chronic hypertension include Diastolic BP>110 Systolic BP >140 Diastolic BP>130 Systolic BP >160 Elevated BP Which drug is contraindicated for woman with chronic hypertension? Peripheral vasodilatators Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors β-blockers Ca-channel blockers α 2-receptor agonists Which drug is contraindicated for woman with chronic hypertension? Peripheral vasodilatators Diuretics ?-blockers Ca-channel blockers ?2-receptor agonists What is the first sign of fluid retention suggestive of pregnancy-induced hypertension? Abdominal enlargement Facial swelling Sudden weight gain Swelling of the feet and ankles General edema At the result of the internal rotation of the fetal head the sagittal suture is A. in the transversal size of pelvic inlet A. B. C. D. E. * 303. A. * B. C. D. E. 304. A. B. * C. D. E. 305. A. * B. C. D. E. 306. A. B. * C. D. E. 307. A. B. * C. D. E. 308. A. B. C. * B. C. D. E. * 310. A. B. C. * D. E. 311. A. * B. C. D. E. 312. A. * B. C. D. E. 313. A. * B. C. D. E. 314. A. B. C. * D. E. 315. A. B. C. * D. E. in the oblique size of the greatest pelvic dimension in the anterior-posterior size of the greatest pelvic dimension in the anterior-posterior size of the least pelvic dimension in the anterior-posterior size of the pelvic outlet The patient with gestational hypertension has all the signs below. The most dangerous symptom is: Diarrhea Decreased urine output Blurred vision Backache Facial swelling What is the main recommendation for pregnant with chronic hypertension during routine check up? Activity restriction Balanced nutrition Increased fluid intake to ensure adequate hydration Instruction about the effect of diuretics Increased nutrition The objective of magnesium sulfate therapy for the patient with preeclampsia is to: Prevent convulsions Promote diaphoresis Increase reflex irritability Act as a saline cathartic Increase peripheral circulation Which assessment should be performed during intravenous magnesium sulfate infusion therapy for management of severe preeclampsia? Count respirations and report a rate of less than 12 breaths per minute. Count respirations and report a rate of more than 20 breaths per minute. Check blood pressure and report a rate of less than 100/60. Monitor urinary output and report a rate of less than 100 ml per hour. Monitor reflexes and report increased reflexes Which drug should be available for immediate IV administration when magnesium sulfate toxity is developed: Ergonovine maleate Oxytocin Calcium gluconate Hydralazine ?2-receptor agonists Several pregnant clients are waiting to be seen in the triage area of the obstetrical unit. Which client is the highest priority? A client at 13 weeks' gestation experiencing nausea and vomiting three times a day with + 1 ketones in her urine. A client at 37 weeks' gestation who is an insulin-dependent diabetic and experiencing 3 to 4 fetal movements per day. A client at 32 weeks' gestation who has preeclampsia and + 3 proteinuria who is returning for evaluation of epigastric pain. A primigravida at 17 weeks' gestation complaining of not feeling fetal movement at this point in her pregnancy. A multigravida at 38 weeks’ gestation with mild irregular abdominal pain 316. A. B. C. * D. E. 317. A. * B. C. D. E. 318. A. B. C. * D. E. 319. A. B. * C. D. E. 320. A. B. C. * D. E. 321. A. * B. C. D. E. 322. A. B. C. D. * E. What is the most appropriate client centered recommendation for a primigravid client at 30 weeks' gestation diagnosed with mild preeclampsia Return visit to the prenatal clinic in approximately 4 weeks. Decreased edema after 1 week of a low-protein, low-fiber diet. Bed rest on the left side during the day, with bath-room privileges. Immediate reporting of adverse reactions to magnesium sulfate therapy. Call physician immediately after development of swelling of the feet and ankles What is NOT the typical complication of preeclampsia? Hydrocephalic infant. Abruptio placentae. Intrauterine growth retardation. Poor placental perfusion. Preterm labor During which cardinal movement of labor the anterior shoulder appears under the symphysis? extension expulsion external head rotation descent internal head rotation Which of them is shown on ultrasound in case of ovarian torsion? Cylindric features Adnexal mass with absent doppler flow to ovary Bilateral ovarian masses Multiple spots on ovaries excessive intra-ovarian venous flow Which of the following types of diet should be physician discussed with a multigravid client diagnosed with mild preeclampsia? High-residue diet. Low-sodium diet. Regular diet. High-protein diet. Low-protein diet. Which of the following assessment findings would alert the physician to suspect magnesium sulfate toxity? Decreased deep tendon reflexes. Cool skin temperature. Rapid pulse rate Tingling in the toes. Decrease of ankle edema What is the aim of magnesium sulfate therapy prescribed for treatment of severe preeclampsia Decreased generalized edema within 8 hours. Decreased urinary output during the first 24 hours Sedation and decreased reflex excitability within 48 hours. Absence of any seizure activity during the first 48 hours. Decreased breath movement less than 12 per minute 323. A. B. C. * D. E. 324. A. * B. C. D. E. 325. A. * B. C. D. E. 326. A. B. C. * D. E. 327. A. B. C. * D. E. 328. A. * B. C. D. E. 329. A. B. C. * D. E. Which group of drug does magnesium sulfate used for treatment of severe preeclampsia belongs to? Peripheral vasodilator Antihypertensive. Central nervous system depressant. Sedative-hypnotic. Diuretic Which of the following assessment findings should be report immediately during a continuous intravenous infusion of 4 g of magnesium sulfate in Ringer's solution? Respiratory rate of 12 breaths /minute Patellar reflex of+2. Blood pressure of 160/88 mm Hg. Urinary output exceeding intake. Increase of deep tendon reflexes Choose the cardinal movement of labor when the base of the occiput is brought into contact with the inferior margin of the symphysis : extension expulsion descent flexion external rotation How do you explain the ovarian apoplexy? Cancer of ovary Shrinken ovaries Sudden rupture in the ovary Female organ prolapse Benign tumor on ovary What is the first action at the beginning of a seizure in client diagnosed with severe preeclampsia? Insert an airway to improve oxygenation. Note the time when the seizure begins and ends. Call for immediate assistance. Turn the client to her left side. Catheterize central vein What complication of labour can be suspected after eclampsia? Abruptio placentae. Transverse lie. Placenta accreta. Uterine atony. Placenta previa Which of the following assessments should the physician prescribe during intravenous magnesium sulfate infusion for treatment of severe preeclampsia? Urinary output even'8 hours. Deep tendon reflexes even' 4 hours. Respiratory rate every hour. Blood pressure every 6 hours. Uterine contraction every 4 hours 330. A. B. C. D. * E. 331. A. B. C. D. E. * 332. A. B. * C. D. E. 333. A. * B. C. D. E. 334. A. * B. C. D. E. 335. A. B. * C. D. E. 336. A. B. C. * D. E. Which of the following actions should the physician do first in case of seizure developed in woman with severe preeclampsia? Pad the side rails of the client's bed. Turn the client to the right side. Insert a padded tongue blade into the client's mouth. Call for immediate assistance in the client's room. Catheterize central vein What is the leading point at the anterior occiput presentation? fossa occipitalis tuber occipitalis the area of the border of the hair part the midpoint of sagittal suture small fontanel Healing of true erosion is going with: connective tissue single-layered cylindrical epithelium multilayer pavement epithelium growth of secretory glands metaplasia What is immediate action in case of seizure Turn the client's head to the side Place an airway into the client's mouth Check the client for a spontaneous birth Assess the fetal heart rate for decelerations Monitor uterine contraction The physician should teach the pregnant client has been diagnosed with gestational hypertension that her pregnancy diet now requires: No changes Limited proteins Restricted sodium Increased carbohydrates Increased liquid What is the next step of assessment after obtaining the vital signs in a client with preeclampsia: Call the nurse Check the client's reflexes Determine the client's blood type Administer intravenous normal saline Catheterize urinary bladder Before administering IV magnesium sulfate therapy to a client with preeclampsia, the physician should assess the client's: Temperature and respirations Urinary glucose and specific gravity Urinary output and patellar reflexes Level of consciousness and funduscopic appearance Fetal heart rate and cervical dilatation 337. A. B. C. D. * E. 338. A. B. C. D. * E. 339. A. B. C. * D. E. 340. A. * B. C. D. E. 341. A. * B. C. D. E. 342. A. B. * C. D. E. 343. A. * B. C. D. E. Magnesium sulfate is being given for treatment of severe preeclampsia primarily because it is a: Hypotensive that relaxes smooth muscles Cholinergic that increases the release of acetylcholine Muscle relaxant that decreases the severity of uterine contractions Central nervous system depressant that blocks neuromuscular transmissions Source of microelements What is the leading point in the posterior occiput presentation? fossa occipitalis tuber occipitalis the area of the border of the hair part the midpoint of sagittal suture small fontanel Which of the following sign or symptom would most likely indicate the potential for a seizure in client with severe preeclampsia? Audible crackles Blurring of vision Epigastric discomfort Generalized facial edema Uterine contraction When measuring the blood pressure to ensure consistency and to facilitate early detection of blood pressure changes consistent with preeclampsia, the physician should: Place the woman in a seated or a left lateral position Allow the woman to rest for 15 minutes after positioning before measuring her blood pressure Use the woman's right arm if she is lying on her left side. Use a proper sized cuff that covers at least 50% of her upper arm there are no any rules for measuring blood pressure in pregnant women Which one of the following assessment findings would be indicated by progress mild preeclampsia to severe preeclampsia? Proteinuria greater than 4+, in two specimens collected 6 hours apart Dependent edema in the ankles and feet at bedtime Deep tendon reflexes 2+, ankle clonus is absent Blood pressure of 154/94 and 156/100, 6 hours apart Urinary output more than 100 ml per hour How many centimeters does the suboccipito-bregmatic diameter have? 14 cm 9,5 cm 12 cm 11 cm 10 cm True erosion is diagnosed with: Colposkopy Bimanual assessment Ultrasonography Smear bacterioskopy cytology 344. A. B. * C. D. E. 345. A. B. C. * D. E. 346. A. B. C. * D. E. 347. A. B. C. * D. E. 348. A. B. C. D. * E. 349. A. B. * C. D. E. 350. A. B. * C. D. E. The primary expected outcome for care associated with the administration of magnesium sulfate would be met if the woman: Exhibits a decrease in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure Experiences no seizures States that she feels more relaxed and calm Urinates more frequently resulting in a decrease in pathologic edema Feel fetal movement well The patient with gestational hypertension has all the signs below. Which sign should be alert because of development complication: Diarrhea Decreased urine output Blurred vision Backache Frequent urination What is the first fixing point in the posterior occiput presentation? small fontanel tuber occipitalis the area of the border of the hair part the midpoint of sagittal suture fossa suboccipitalis Which of the following should concern physician that monitoring primigravida in prenatal clinic for preeclampsia? Blood pressure increase to 138/86 mm Hg Weight gain of 0.5 kg during the past 2 weeks A dipstick value of 3+ for protein in her urine Pitting pedal edema at the end of the day Increased urinary output to 2000 ml per 24 hours The physician's primary duty during the seizure in a woman with preeclampsia is to: Insert an oral airway Suction the mouth to prevent aspiration Administer oxygen by mask Call for help Catheterize central vein Which diameter of the fetal head presents in the anterior occiput presentation? fronto-occipitalis suboccipito-bregmatic biparietal sagittal suture bitemporal Which of the following symptom alert about development of magnesium sulfate toxity? A sleepy, sedated affect A respiratory rate of 10 breaths per minute Deep tendon reflexes of +2 Absent ankle clonus Facial edema 351. A. * B. C. D. E. 352. A. B. C. * D. E. 353. A. B. C. D. * E. 354. A. B. C. * D. E. 355. A. B. C. D. * E. 356. A. B. C. * D. E. 357. A. B. * C. D. E. HELLP syndrome is associated with an increased risk for adverse perinatal outcomes including which of the following? Placental abruption Placenta previa Hepato-splenomegalia Cirrhosis Preterm rupture of membranes HELLP syndrome is associated with an increased risk for adverse perinatal outcomes including which of the following? Glomerulonephritis Placenta previa Renal failure Cirrhosis Cystitis HELLP syndrome is associated with an increased risk for adverse perinatal outcomes including which of the following? Macrosomia Placenta previa Cirrhosis Maternal and fetal death Constipation What are the cardinal movements of labor in anterior occiput presentation (in order)? descent, flexion, internal rotation, extension, expulsion flexion, engagement, internal rotation, external rotation flexion, internal rotation, extension, external rotation of the head, internal rotation of the body flexion, descent, internal rotation, extension, expulsion internal rotation, extension, external rotation, flexion What changes of multilayer squamosus epithelium is common for true erosion? Proliferation desquamation Ectopia Metaplasia Regeneration The antidote administered to reverse magnesium toxicity is calcium phosphate calcium succinat calcium gluconate calcium chloridum calcium sulfate Which effect of magnesium sulfate which used for treatment of preeclampsia is suspected? tocolytic. anticonvulsant. antihypertensive. diuretic. spasmolytic 358. A. B. C. D. * E. 359. A. B. C. * D. E. 360. A. B. * C. D. E. 361. A. B. * C. D. E. 362. A. B. C. * D. E. 363. A. * B. C. D. E. 364. A. B. C. D. * E. 365. What are the cardinal movements of labor in posterior occiput presentation (in order)? descent, flexion, internal rotation, extension, expulsion flexion, engagement, internal rotation, external rotation flexion, internal rotation, extension, external rotation flexion, internal rotation, additional flexion. extension, expulsion additional flexion, internal rotation, extension, additional extension, external rotation What is the only known cure for preeclampsia? Magnesium sulfate Antihypertensive medications Delivery of the fetus Administration of aspirin every day of the pregnancy Diuretics Which intrapartal assessment should be avoided when caring for a woman with HELLP syndrome? Auscultation of the heart and lungs Abdominal palpation Checking deep tendon reflexes Venous sample of blood Sonographyc examination of liver Which of the following assessments in a client diagnosed with pregnancy-induced hypertension who is taking magnesium sulfate would indicate a therapeutic level of medication? Urinary output of 20 ml/hr Normal deep tendon reflexes Respiratory rate of 10 to 12 breaths/minute Drowsiness Blurred vision A woman taking magnesium sulfate has respiratory rate of 10 breaths/minute. In addition to discontinuing the medication, the physician should: vigorously stimulate the woman. instruct her to take deep breaths. administer calcium gluconate. increase her IV fluids. auscultate fetal heart rate Which of the following is a classic sign of preeclampsia? proteinuria fever glycosuria vomiting constipation What is the most appropriate tactic in incomplete abortion? Hemostatic drugs Blood transfusion Spasmolytic A dilatation and curettage (D&C) Bed rest and Vitamin supplements Which circumference the fetal head is delivered in anterior occiput presentation? A. * B. C. D. E. 366. A. * B. C. D. E. 367. A. B. C. * D. E. 368. A. B. * C. D. E. 369. A. B. * C. D. E. 370. A. B. C. * D. E. 371. A. B. C. * D. E. 372. 32 cm 33 cm 34 cm 36 cm 38 cm What is the most common site of implantation of fertilized egg outside the uterus? Fallopian tube. Intestine. Interstitial lining. Ovary. Uterine cervix Before surgery to remove an ectopic pregnancy and the fallopian tube, which of the following would alert to the possibility of tubal rupture? Amount of vaginal bleeding and discharge. Falling hematocrit and hemoglobin levels. Slow, bounding pulse rate of 80 bpm. Marked abdominal edema. Abdominal cramping Which circumference the fetal head is delivered in posterior occiput presentation? 32 cm 33 cm 34 cm 36 cm 38 cm Which process represents the IIIa type of smear at oncocytological examination? the unchanged epithelium mild or moderate dysplasia cancer inflammatory process suspicion on malignisation Which of the following would assess in addition to monitoring the client's blood pressure before surgery in case of ruptured ectopic pregnancy? Uterine cramping. Abdominal distention. Hemoglobin and hematocrit. Pulse rate. Vaginal discharge What is the predisposing factor for development of ectopic pregnancy? Urinary tract infection. Marijuana use during pregnancy. Episodes of pelvic inflammatory disease. Use of estrogen-progestin contraceptives. Constipation Which of the following may be ordered for treatment ectopic pregnancy if fallopian tube has not ruptured yet? A. B. C. * D. E. 373. A. * B. C. D. E. 374. A. B. C. D. E. * 375. A. B. * C. D. E. 376. A. B. * C. D. E. 377. A. B. C. D. E. * 378. A. B. * C. D. E. 379. Progestin contraceptives Medroxyprogesterone (Depo-Provera). Methotrexate. Betamethasone Oxytocin True erosion is diagnosed with colposcopy smear bacterioskopy ultrasound bimanual assessment cytology Which of the following is essential for the generation of uterine contractions? prostaglandins calcium estrogen oxytocin all of the mentioned Which of the following signs and symptoms would be most important for early detection after a dilatation and curettage (D&C) to evacuate a molar pregnancy? Urinary tract infection. Hemorrhage. Abdominal distention. Chorioamnionitis. Vaginal infection After evacuation of a hydatidiform mole the patient is at risk of development of Ectopic pregnancy. Choriocarcinoma. Multifetal pregnancies. Infertility. Septic abortion Where is oxytocin primarily synthesized? adrenal gland placenta anterior pituitary ovary posterior pituitary Which time spans the client should avoid pregnancy after suction and evacuation of a complete hydatidiform mole? 6 months. 12 months. 18 months. 24 months. 30 months Which of the following signs and symptoms will most likely make the physician suspect that the patient is having hydatidiform mole? A. B. * C. D. E. 380. A. * B. C. D. E. 381. A. B. * C. D. E. 382. A. B. * C. D. E. 383. A. B. C. * D. E. 384. A. * B. C. D. E. 385. A. B. C. D. E. * 386. Slight bleeding Passage of clear vesicular mass per vagina Absence of fetal heart beat Enlargement of the uterus Purulent vaginal discharge All processes play the part in the labor initialization EXEPT progesterone increases prostaglandins increase oxytocin increases estrogens increases serotonin increases Which of the following signs will distinguish threatened abortion from inevitable abortion? Severity of bleeding Dilation of the cervix Nature and location of pain Presence of uterine contraction Gestational age Discharge recommendations after placement of cerclage because of a history of recurrent pregnancy should emphasize that Any vaginal discharge should be reported immediately to her care provider. The presence of any uterine cramping or low backache may indicate preterm labor and should be reported. She will need to make arrangements for care at home because her activity level will be restricted. She will be scheduled for a cesarean birth. She have a risk for development of placenta previa Methotrexate is recommended as part of the treatment plan for which of the following obstetric complications? Complete hydatidiform mole Missed abortion Unruptured ectopic pregnancy Abruptio placentae Cervical incompetence Spontaneous termination of a pregnancy is considered to be an abortion if: the pregnancy is less than 20 weeks. the fetus weighs less than 1000 g. the products of conception are passed intact. there is no evidence of intrauterine infection. the fetus length less than 20 cm All of the bllow are the basic elements of the uterine contractile system EXСEPT: actin myosin adenosine triphospate calcium estrogens An abortion in which the fetus dies but is retained in the uterus is called: A. B. * C. D. E. 387. A. B. C. D. * E. 388. A. * B. C. D. E. 389. A. B. * C. D. E. 390. A. B. C. * D. E. 391. A. B. C. D. * E. 392. A. B. * C. D. E. 393. A. inevitable abortion. missed abortion. incomplete abortion. threatened abortion. recurrent abortion In which of the following situations would a D&C be indicated? Complete abortion at 8 weeks Incomplete abortion at 16 weeks Threatened abortion at 6 weeks Incomplete abortion at 10 weeks Recurrent abortion Which of the following orders should the physician prescribe for a client admitted with a threatened abortion? Pad count Ritodrine IV Nothing per os Metotrexate 50 mg every 3 hours im Oxitocin Which of the following pieces of data found on a client’s health history would place her at risk for an ectopic pregnancy? Use of oral contraceptives for 5 years Recurrent pelvic infections Ovarian cyst 2 years ago Heavy menstrual flow of 4 days’ duration Use of condom for last year Which of the following findings might suggest a hydatidiform mole at 10 weeks of gestation? Complaint of frequent mild nausea Blood pressure of 120/80 Fundal height measurement of 18 cm History of bright red spotting for 1 day weeks ago Low abdominal cramping What is the main principle of care for primigravida with ectopic pregnancy? bed rest and analgesics are the recommended treatment. she will be unable to conceive in the future. a D&C will be performed to remove the products of conception. hemorrhage is the major concern. urinary tract infection is the main predisposing factor for development of this problem Sharon Baker's history reveals recurrent abortions. What does this mean? She has never carried a pregnancy to term. At least three of her pregnancies terminated before age of viability. She has experienced at least one early abortions. She has experienced at least two late abortions. She has experienced at least one preterm labour What is the most important in the characteristic of the uterine contractions? strong B. * C. D. E. 394. A. B. C. * D. E. 395. A. B. * C. D. E. 396. A. * B. C. D. E. 397. A. B. C. D. * E. 398. A. B. * C. D. E. 399. A. B. C. * D. E. 400. A. B. * C. D. regular moderate painful strength Etiological factors of psedoerosin is all EXCEPT: Dyshormonal disturbances Autoimmune process Alimentary factor Changes of humoral immunity Inflammatory process What is the aim of prescription of contractile drug (Oxytocin) after incomplete abortion? to prevent intrauterine infection to avoid placental fragment retention to reduce the risk of hypertension to allow hormone levels to return to normal to avoid future infertility What is the risk factor for an ectopic pregnancy? history of pelvic inflammatory disease grand multiparity (five or more births) use of an intrauterine device for 1 year use of an oral contraceptive for 5 years use of an condoms for 3 years Which three tests typically are ordered to identify ectopic pregnancy? serum test for beta-hCG, ultrasonography, and amniocentesis serum test for progesterone, laparoscopy, and culdocentesis serum test for estrogen, ultrasonography, and nitrazine paper test serum test for beta-hCG, ultrasonography, and laparoscopy serum test for beta-hCG, nitrazine paper test, and colposcopy Which labor forces are presented in I stage of labor? false uterine contractions true uterine contractions uterine contractions and pushing pushing all of the above Cancer prevention program for women include all of the following except: Smoking cessation Periodic screening Bone density index measurement Elimination of unopposed estrogen use for menopause Human papillomavirus (HPV) tests. What ultrasonography findings are typical for gestational trophoblastic disease empty gestational sac grapelike clusters severely malformed fetus ectopic pregnancy E. 401. A. * B. C. D. E. 402. A. * B. C. D. E. 403. A. B. C. * D. E. 404. A. B. * C. D. E. 405. A. B. * C. D. E. 406. A. B. * C. D. E. 407. A. B. C. * D. E. 408. A. two babies Which of the following is a common adverse effect of ritodrine? tachycardia pohuria hypertension hyporeflexia hypotermia Which of these is a hormone needed to produce an egg? Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) Follicle producing hormone (FPH) Egg producing hormone (EPH) None of these Follicle realizing hormone (FRH) Which labor forces are presented in II stage of labor? false uterine contractions true uterine contractions uterine contractions and pushing pushing all of the above For polyp treatment we use all except: cryodestruction conization of cervix endocervical curettage Coagulation polyp twisting What does the Basal Body Temperature (BBT) chart tell you? Problems with ovulation When you ovulated When is your next ovulation None of these When previous ovulation was During the menstrual cycle, progesterone is produced by the secondary oocyt the corpus luteum. the stroma of the ovary. primary follicles. pituitary gland Which labor forces are presented in III stage of labor? false uterine contractions true uterine contractions uterine contractions and pushing pushing all of the above During the menstrual cycle, progesterone would be at its highest levels during the menstrual phase B. C. D. * E. 409. A. * B. C. D. E. 410. A. * B. C. D. E. 411. A. B. C. * D. E. 412. A. B. C. D. E. * 413. A. B. C. * D. E. 414. A. B. C. * D. E. 415. A. B. * C. D. just prior to ovulation just after ovulation late in the postovulatory phase before period Which moment is the beginning of I stage of labor? onset of regular uterine contractions complete dilatation of cervix rupture of amniotic sac onset of pushing delivery of the fetus To the risk factors for dysplasia belong all EXCEPT: hyperprogesteronemia hyperestrogenemia cervical trauma during delivery and abortion A lot of sexual partner Early sexual activity The main function of progesterone during the menstrual cycle is to initiate ovulation initiate menstruation thicken the endometrium repair the surface of the ovary after ovulation repair the surface of the uterus after menstruation Which moment is the end of II stage of labor? onset of uterine contractions complete dilatation of cervix rupture of amniotic sac complete cervical effacement delivery of the fetus If fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum is expelled into the pelvic cavity. begins to secrete low levels of FSH. degenerates into the corpus albicans. continues to secrete progesterone until the next ovulation. start to secrete estrogen About the time of ovulation, the anterior pituitary gland releases a relatively large quantity of estrogen progesterone LH androgen oxytocin Secondary contraceptive effects of the gestaginic component of the combination oral agents include: Endometrial alterations, decrease in cervical mucus viscosity Endometrial alteration, increase in cervical mucus viscosity Stimulation of endogenous estrogen production Increase in cervical mucus viscosity, stimulation of endogenous estrogen production E. 416. A. B. C. D. * E. 417. A. B. C. D. E. * 418. A. * B. C. D. E. 419. A. B. * C. D. E. 420. A. B. C. D. * E. 421. A. * B. C. D. E. 422. A. * B. C. Suppression of endogenous estrogen production All of the following contraceptive methods have theoretical effectiveness (lowest expected) failure rates of < 1% EXCEPT: Oral contraceptives Progestin implant Male sterilization Condoms Intrauterine device What sign is not typical for proliferative myoma? increased mitotic activity fast growth plenty of lymphoid cells plenty of plasmatic cells Atypical growth Which moment is the beginning of III stage of labor? separation of placenta complete dilatation of cervix rupture of amniotic sac complete cervical effacement delivery of the fetus. Which of the following instructing should be given for client about basal body temperature method for family planning? Check the cervical mucus to see if it is thick and spars Take her temperature at the same time every morning before getting out of be Document ovulation when her temperature decreases at least 1°F. Avoid coitus for 10 days after a slight rise in temperature you still infertile before rising temperature Which moment is the end of 3 stage of labor? onset of pushing complete dilatation of cervix separation of placenta expulsion of placenta delivery of the fetus When instructing a client about the proper use of condoms for pregnancy prevention, which of the following instructions would be included to ensure maximum effectiveness? Place the condom over the erect penis before coitus. Withdraw the condom after coitus when the penis is flacci Ensure that the condom is pulled tightly over the penis before coitus. Obtain a prescription for a condom with nonoxynol 9. All recommendations are correct The most common technique used for the medical termination of a pregnancy in the second trimester would be: Administration of prostaglandins Instillation of hypertonic saline into the uterine cavity Intravenous administration of Pitocin D. E. 423. A. * B. C. D. E. 424. A. B. C. * D. E. 425. A. B. * C. D. E. 426. A. B. * C. D. E. 427. A. * B. C. D. E. 428. A. B. C. D. E. * 429. A. * B. C. D. E. 430. Vacuum aspiration Dilatation and curettage Besides the condom, which is another barrier method of birth control? Diaphragm Intrauterine Device (IUD) Withdrawal Sterilization Pill How long is the vaginal ring left in place? 1 week 2 weeks 3 weeks 3 months 4 weeks Which of the following is NOT associated with II stage of labor? uterine contractions placental separation fetal expulsion pushing fetal internal rotation In diagnostic of cervical dysplasia we use all EXCEPT: colposcopy metrosalpingography cytogenetic examination histochemical examination cytological examination How long is the hormonal patch left in place? 1 week 2 weeks 3 weeks 3 months 4 weeks Which of the following is NOT associated with III stage of labor? uterine contractions placental expulsion placental separation pushing fetal internal rotation The woman starts taking the birth control pills on about day ________ of the cycle 1 7 10 14 28 Use of the pill is associated with an increased risk of: A. * B. C. D. E. 431. A. B. C. * D. E. 432. A. B. * C. D. E. 433. A. B. C. D. E. * 434. A. * B. C. D. E. 435. A. B. C. * D. E. 436. A. B. C. D. * E. 437. A. * heart attack and stroke endometrial cancer ovarian cancer all of the above varicose vein In what type of ovarion tumour do we have an endometrium hyperplasia? papillary cystoma paraovarian cyst follicle cyst ovarian cancer yellow body cyst Oral contraception in the form of a combination of low-dose estrogen and progesterone: Reduces the pH of cervical mucus, thereby destroying sperm Protects against iron deficiency anemia by reducing blood loss with menses Prevents the transmission of sexually transmitted diseases Is 90% effective in preventing pregnancy when used correctly Increase peristaltic of uterine tube, thereby prevent conception Which of the following characterizes I stage of labor? myometrial relaxation uterine awakening fetal expulsion pushing cervical dilatation The most common, and for some women the most distressing side effect of Norplant (progestin only implant), is Irregular menstrual bleeding Headache Nervousness Nausea Constipation A woman with an Intrauterine Device (IUD) should confirm its placement by checking the IUD’s string: Before each menstrual period After intercourse At the time of ovulation During menstrual bleeding During routine checkup one time a year When teaching women about the effective use of chemical barriers, the physician should tell them to: Insert foams at least 1 hour prior to coitus Insert suppositories just prior to penile contact with the vagina Douche immediately after last intercourse Reapply before each act of coitus Insert foams not later 12 hours after intercourse In diagnostic of cervical leucoplacia we use all EXCEPT: culdoscopy B. C. D. E. 438. A. B. C. * D. E. 439. A. B. * C. D. E. 440. A. B. C. D. * E. 441. A. * B. C. D. E. 442. A. * B. C. D. E. 443. A. B. C. * D. E. 444. A. B. C. colposcopy biopsy cytology Speculum assessment Which contraction duration (sec) characterizes active labor? 20 30 60 90 100 When using a cervical cap, the woman should: Apply spermicide inside the cap and around the rim Leave it in place for a minimum of 8 hours and maximum of 4g hours after the last act of coitus Continue to use the cap during menstrual periods Check the position of the cap and insert additional spermicide before each act of coitus Use separate cap during each intercourse What is the minimal dilatation during the first stage of labor in multiparous? 0,5-0,8 cm/hour 0,8-1.0 cm/hour 1.0-1.2 cm/hour 1.2-1.5 cm/hour 2.0-2.5 cm/hour A woman has chosen the calendar method of conception control. During the assessment process, it is most important that the physician: Obtain a history of menstrual cycle lengths for the last 6 to 12 months. Determine her weight gain and loss pattern for the previous year. Examine skin pigmentation and hair texture for hormonal changes. Explore her previous experiences with conception control. Ask about ability to check fertile period every day Which of the following statement is true about tubal ligation? “It is highly unlikely that you will become pregnant following the procedure” “This is an effective form of 100% permanent sterilization. You will not be able to get pregnant. “Sterilization offers some form of protection against sexually transmitted infections.” “Your menstrual cycle will greatly increase after your sterilization.” “Your husband should sing permission for this procedure” Injectable progestins (DMPA, Depo-Provera) are a good contraceptive choice for women who: Desire menstrual regularity and predictability. Have a history of thrombotic problems or breast cancer. Have difficulty remembering to take oral contraceptives daily. Are homeless or mobile and rarely receive health car Have more than 1 sexual partner What is the most important measure of labor progression? contraction frequency contraction intensity contraction duration D. * E. 445. A. B. C. D. * E. 446. A. B. C. D. E. * 447. A. * B. C. D. E. 448. A. * B. C. D. E. 449. A. * B. C. D. E. 450. A. B. C. D. * E. 451. A. B. cervical dilatation cervical effacement What the major differences are between the cervical cap and diaphragm? “No spermicide is used with the cervical cap, so it is less messy.” “The diaphragm can be left in place longer after intercours” “Repeated intercourse with the diaphragm is more convenient.” “The cervical cap can safely be used for repeated acts of intercourse without adding more spermicide later.” “The main difference is the size of cap and diaphragm” Node consistency of uterine fibromyoma depends on: node size vessels' amount fatty tissue amount presence of endometrioid tissues correlation of parenchyma and stroma Which contraceptive method should be avoided by couple if a woman was treated recently for toxic shock syndrome? Cervical cap Condom Vaginal film Vaginal sheath Combine contraceptive pill Which of the following characterizes phase 2 of labor? fetal expulsion uterine awakening cervical effacement cervical dilatation placental separation Postcoital contraception with Postinor: Requires that the first dose be taken within 72 hours of unprotected intercourse Requires that the woman take second and third doses at 24 and 36 hours after the first dos Has an effectiveness rate in preventing pregnancy of approximately 50%. Is commonly associated with the side effect of menorrhagia Will be more effective if takes 1 hour before intercourse Which of the following statements is most appropriate for the physician to make for a married couple is discussing male and female sterilization? “Male and female sterilization methods are 100% effective” “A vasectomy may have a slight effect on sexual performance” “Tubal ligation can be easily reversed if you change your mind in the future” “Major complications after sterilization are rar” “A vasectomy is more preferable than tubal ligation” A woman will be taking oral contraceptives using a 28-day pack. To be protected from pregnancy, the physician should advise this woman to: Limit sexual contact for one cycle after starting the pill. Use condoms and foam instead of the pill for as long as she takes an antibiotic C. * D. E. 452. A. * B. C. D. E. 453. A. B. C. D. E. * 454. A. B. C. D. E. * 455. A. B. * C. D. E. 456. A. B. C. D. E. * 457. A. * B. C. D. E. Take one pill at the same time every day. Throw away the pack and use a backup method if she misses two pills during week one of her cycle Use barrier method during fertile period Although reported in small numbers, toxic shock syndrome (TSS) can occur with the use of the contraceptive diaphragm. The physician should instruct the woman about ways to reduce her risk for toxic shock syndrome. This would include: “You should always remove your diaphragm 6-8 hours after intercourse, not use the diaphragm during menses, and watch for dangers signs of toxic shock syndrome which include a sudden onset fever of greater than 38.4TРC, hypotension, and a rash. “You should remove your diaphragm right after intercourse to prevent TSS.” “It’s okay to use your diaphragm during your menstrual cycle. Just be sure to wash it thoroughly first to avoid toxic shock syndrom” “Make sure that you don’t leave your diaphragm in for more than 24 hours or you may get toxic shock syndrome” “Modern diaphragms are not related to development of toxic shock syndrome” Which of the following characterizes III stage of labor? myometrial tranquility fetal expulsion cervical effacement cervical dilatation placental separation What is typical for proliferative myoma? presence of atypia atypical localization multiple nodes node calcification increased mitotic activity When assessing the timing for ovulation and possible fertilization, the physician understands that the client with a 30-day menstrual cycle would probably ovulate on which day? Day 30 Day 15 Day 10 Day 13 Day 11 Indicate the place for prostaglandins synthesis: adrenal gland placenta posterior pituitary ovary decidua The female client indicates understanding of teaching when she says that the cause of menses is: Declining progesterone levels Rising estrogen levels Increasing LH levels Declining FSH levels Estrogen/progesterone imbalance 458. A. B. C. * D. E. 459. A. * B. C. D. E. 460. A. B. C. * D. E. 461. A. B. C. D. E. * 462. A. B. C. * D. E. 463. A. B. C. D. E. * 464. A. B. C. D. E. * 465. Which method of birth control is most suitable for the client with diabetes? Vaginal ring Oral contraceptives Diaphragm Contraceptive sponge Progestine only pill How many eggs does a normal healthy ovary produce every month? One Two Three Four Five In the menstrual cycle, estrogen functions to stimulate uterine wall development, whereas progesterone functions to stimulate erection of the clitoris cause ejection of milk from the mammary glands stimulate the uterine lining to become more glandular inhibit the release of FSH; stimulate the release of FSH What sign is not typical for proliferative myoma? increased mitotic activity fast growth plenty of lymphoid cells plenty of plasmatic cells Atypical growth In the menstrual cycle, estrogen functions to _____, whereas progesterone functions to stimulate the uterine lining to become more glandular stimulate erection of the clitoris cause the formation of milk stimulate uterine wall development; inhibit the release of FSH stimulate the release of FSH Subserouse fibromyoma node is localizes in: between broad ligament layers behind cervix in myometrium under uterine mucous layer under peritoneum How often should the fetal heart rate be auscultated during the second stage of labor? 5 min 10 min 15 min 30 min after every uterine contraction During the menstrual cycle, LH is at its highest levels A. D. * during the menstrual phase just prior to ovulation just after ovulation just before menstruation begins in the middle of proliferative During the menstrual cycle, the endometrium would be at its thickest during the menstrual phase just prior to ovulation just after ovulation late in the postovulatory phase during proliferative phase The part of the female reproductive system that is shed during menstruation is the myometrium Vaginal mucus tunica albuginea stratum functionalis of the endometrium Basal lay of endometrium What is the maximal duration of the second stage of labor in primaparas? 5 min 20 min 50 min 100 min 120 min Which sexual practices as high-risk factors for contracting HIV? Heterosexual intercourse Absent of intercourse A monogamous relationship French kissing Hugs Submucous myoma node is localized: between broad ligament layers behind cervix in myometrium under uterine mucous layer E. 471. A. B. C. * D. E. 472. A. B. C. * under peritoneum The success of the rhythm method depends on the: Age of the client Frequency of intercourse Regularity of the menses Range of the client’s temperature Quantity of partners When the cervix and vagina should be inspected for lacerations? after first signs of placental separation after fetal delivery after placental delivery B. * C. D. E. 466. A. B. C. D. * E. 467. A. B. C. D. * E. 468. A. B. C. D. E. * 469. A. * B. C. D. E. 470. A. B. C. D. E. 473. A. B. C. D. * E. 474. A. * B. C. D. E. 475. A. B. C. D. E. * 476. A. B. C. * D. E. 477. A. B. C. D. * E. 478. A. B. C. D. E. * 479. A. B. C. * after suturing of the lacerations of vagina 2 hours after delivery Intramural myoma node is localized: between broad ligament layers under uterine mucous layer behind cervix in myometrium under peritoneum Which statement made by the client who has just had a mammogram indicates a need for clarification regarding the importance or purpose of this procedure? “Now that I have had a mammogram, my risk for getting breast cancer is reduced.” “Even though I have had a mammogram, I should still perform a breast self-examination monthly.” “Yearly mammograms can reduce my risk of dying from breast cancer.” “The amount of radiation exposure from a mammogram is low.” “Sonography does not rule out need of mammography” What is the most reliable indicator of rupture of the fetal membranes? fluid per cervical os positive nitrazine test positive ferning test membranes are not palpated all of the above Which characteristic of a breast lump or mass is more associated with breast cancer than with benign breast disease? Lump or mass present in same area of both breasts Pain or discomfort caused by palpation Attached firmly to the chest wall Appeared suddenly Skin is not changed above the lump The reservoirs for storing milk in the breast are: Lobules Alveoli Montgomery’s glands Lactiferous sinuses Nipples Which moment of the fetal membranes rupture is considered as a normal? before the beginning of uterine contraction at the beginning of I stage of labor at the end of I stage of labor at the beginning of II stage of labor all of the above When teaching the breast self-examination, you would inform the woman that the best time to conduct breast self-examination is: at the onset of the menstrual period on the 14th day of the menstrual cycle on the 4h to 7th day of the cycle D. B. * just before the menstrual period any time during the cycle The examiner is going to inspect the breast for retardation. The best position for this part of the exam is: lying supine with arms at the sides leaning forward with hands outstretched Sitting with hand pushing onto hips One arm at the side, the other arm elevated All position is available for examination A bimanual technique of Clinical Breast Examination may be the preferred approach for a woman: who is pregnant who is having the first breast exam by a health care provider with pendulous breasts who has felt a change in the breast during self examination for teenagers What is the maximal duration of the third stage of labor? 5 min 20 min 30 min 50 min 120 min Interstitial myoma node is localized: between broad ligament layers in myometrium under uterine mucous layer under peritoneum behind cervix During the breast examination, you detect a mass. Identify the description that is most consistent with cancer rather than benign breast disease round firm, well demarcated irregular poorly defined, fixed rubbery, mobile, tender lobular, clear margins, negative skin retraction mobile, well demarcated, negative skin retraction How often during the first stage of labor should the fetal heart rate be auscultated in a low-risk pregnancy? every 5 min before a contraction every 15 min after a contraction C. D. E. 486. A. B. C. every 40 min before a contraction every 45 min after a contraction after every uterine contraction During the examination of the breast of pregnant woman, you would expect to find: peau d’orange nipple retraction a unilateral, obvious venous pattern E. 480. A. B. C. * D. E. 481. A. B. C. * D. E. 482. A. B. C. * D. E. 483. A. B. * C. D. E. 484. A. B. * C. D. E. 485. A. D. * B. * a blue vascular pattern over both breasts decrease size of breast Intraligamentary myoma node is localized: between broad ligament layers in myometrium behind cervix under uterine mucous layer under peritoneum Which of the following women should not be referred for further evaluation? a 26-year-old with multiple nodules palpated in each breast a 48-year-old who has a 6-month history of reddened and sore left nipple and areolar area a 25-year-old with asymmetrical breasts and inversion of the nipples since adolescence a 64-year-old with unclear area at tip of right nipple, no masses, tenderness, or lymph nodes palpated a 34-year-old with enlarged breast to size 7 What factor is determining the forming of pain intensity during labor? level of oxytocin in the organism; level of pain sensitiveness; force of cerebral impulses; force of uterine contractions; patient’s behavior. Breast asymmetry: increases with age and parity may be normal indicates a neoplasm is accompanied by enlargement axillary lymph nodes inquired abnormalities At what age does the American Cancer Society recommend that women perform monthly breast self-examination? At menarche At onset of sexual activity Starting at age 20 Starting at age 35 At onset of menopause Which client should the physician encourage to seek genetic counseling regarding her risk for BRCA1 or BCRA2 gene mutation–related breast cancer? 55-year-old woman whose father had lung cancer and mother had leukemia, and whose two siblings have had malignant melanoma 45-year-old woman whose brother and sister have breast cancer and whose mother has ovarian cancer C. 65-year-old woman whose fraternal twin sister has breast cancer D. E. 493. A. B. 25-year-old woman who has bilateral benign breast disease 35-year-old woman who has endometriosis, irregular bleeding Fibrocystic change in breasts is: A disease of the milk ducts and glands in the breasts. A premalignant disorder characterized by lumps found in the breast tissue. E. 487. A. * B. C. D. E. 488. A. B. C. * D. E. 489. A. B. * C. D. E. 490. A. B. * C. D. E. 491. A. B. C. * D. E. 492. A. C. * E. 500. Lumpiness with pain and tenderness found in varying degrees in breast tissue of healthy women during menstrual cycles. Lumpiness accompanied by tenderness after menses. Breast cancer The physician who is teaching a group of women about breast cancer would tell the women that: Risk factors identify more than 50% of women who will develop breast cancer. One in ten women in the United States will develop breast cancer in her lifetime. Nearly 90% of lumps found by women are malignant. The exact cause of breast cancer is unknown. Women who breastfeed baby have higher risk of breast cancer than if not What is an obligatory condition for the beginning of the medicinal anaesthetizing of labor? the fluid gash; normal feto-pelvic proportions; physiology duration of labor; presence of regular uterine contractions and opening of uterine cervix on 3-4 cm; primapara. Retrocervical myoma node is localized: between broad ligament layers under peritoneum under uterine mucous layer behind cervix in myometrium Which of the following diagnostic tests is used to confirm a suspected diagnosis of breast cancer? Mammogram Ultrasound Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) CA 15-3 MRI What condition is obligatory for the beginning of the medicinal anaesthetizing of labor? opening of uterine cervix on 3-4 cm; normal feto-pelvic proportions; physiology duration of labor; the fluid gash; primapara. Which recommendation is the American Cancer Society guideline for early detection of BC? Beginning at 18 y.o. have a biannual clinical breast exam Beginning at 30 y.o. perform monthly breast self exams. Beginning at 40 y.o., receive a yearly mammogram. Beginning at 50 y.o. have a breast sonogram every 5 yrs Beginning after completion of breastfeeding What is typical for hormonal status of patient with fibromyoma? A. * B. C. D. high level of estrogens high level of progesteron high level of androgens high level of chorionic gonadotropin D. E. 494. A. B. C. D. * E. 495. A. B. C. D. * E. 496. A. B. C. D. * E. 497. A. B. C. * D. E. 498. A. * B. C. D. E. 499. A. B. C. * D. E. C. high level of pituitary gland hormons Which side effect of promedol limits the term of its introduction in labor? depresses the respiratory center of fetus; causes bradicardia at a mother; causes a somnolence; causes tachicardia at a mother; causes the allergic reactions. When teaching a 22-year-old patient about breast self-examination (BSE), the physician will instruct the patient that BSE will reduce the risk of dying from breast cancer. performing BSE right after the menstrual period will improve comfort. BSE should be done daily while taking a bath or shower. annual mammograms should be scheduled in addition to BSE. You should start to do BSE when become pregnant How many lobes does the breast contain? 15-20 20-25 25-30 5-10 10-15 What is the peculiarity of introduction of promedol for anaesthetizing of labor? should be given at least 2 hours to the birth of fetus; should be given only in the ІІ period of labor; should be given only one time; should be given only intravenously; should be given in combination with spasmolytics. Each lobe of breast contains lobules Glands Cells Sinuses Alveoli What requirement is obligatory for medicines, which are used for the medicinal anaesthetizing? to decrease the uterine contractions; to improve the state of fetus; do not depress the contractive activity of uterus; not to cause a somnolence; to have short time of action. How do the estrogens effect on breast? increased breast size in puberty cyclic decrease in breast size due to ovarian cycle decrease in size in pregnancy D. E. 508. is not influence on breast stimulate milk production How do the estrogens effect on breast? 501. A. * B. C. D. E. 502. A. B. * C. D. E. 503. A. * B. C. D. E. 504. A. * B. C. D. E. 505. A. * B. C. D. E. 506. A. B. C. * D. E. 507. A. * B. A. * E. 515. cyclic increase in breast size due to ovarian cycle decrease milk production stimulate development of breast cancer responsible for development of fibroadenoma increase sensation to prolactin How do the estrogens effect on breast? increase in size in pregnancy increase sensation to prolactin is not influence on breast cyclic decrease in breast size due to ovarian cycle stimulate development of breast cancer Which hormone causes growth in lobules Progesterone Prolactin Testosterone Estrogen insulin How does the progesterone effect on breast? Causes growth in lobules Stimulate milk production Suppress proliferation of epithelium Do not influence on the breast Stimulate growth of breast What is the diagnosis for fibrocystic changes? Palpation, biopsy, ultrasonography Breast self examination, mammography, MRI CT, X-ray, MRI Palpation, mammography, X-ray Biopsy, breast self examination, palpation What part of the body is normally involved in fibrocystic changes? upper/outer breast quadrant is more frequent segment involved upper/inner breast quadrant is more frequent segment involved lower/outer breast quadrant is more frequent segment involved lower /inner breast quadrant is more frequent segment involved nipple The second stage of labor at patient is finished by obstetric forceps applying. What method of anesthesia is the best? inhalation anesthesia; epidural anesthesia; intravenous anesthesia; local anesthesia; it is possible to perform without any anesthesia. What is the etiology of fibrocystic changes? A. * B. unknown but thought to be related to hormones unknown but thought to be related to infections B. C. D. E. 509. A. * B. C. D. E. 510. A. * B. C. D. E. 511. A. * B. C. D. E. 512. A. * B. C. D. E. 513. A. * B. C. D. E. 514. A. B. C. * D. C. D. E. 516. A. * B. C. D. E. 517. A. * B. C. D. E. 518. A. B. C. D. * E. 519. A. * B. C. D. E. 520. A. * B. C. D. E. 521. A. B. C. * D. E. 522. A. B. C. unknown but thought to be related to trauma unknown but thought to be related to level of physical activity unknown but thought to be related to food What sign is typical for submucous myoma? hyperpolymenorrhea amenorrhea foamy vaginal discharge symptomless tumour destruction Benign, slow-growing breast tumor with epithelial and stromal components in women elder than 30 y.o. is: Fibroadenoma Breast cancer fibrocystic breast disease mastitis Lactostasis Which of the follows is the most effective for cervical dilation in the I stage of labor? analgin in pills; no-shpa in pills; novocaine 0,25%; baralgin 5 ml intravenously; papaverin 2% 2 ml i/m. What is Fibroadenoma’s claim to fame? women < 30 years Postmenopausal women women < 40 years women > 30 years girls in puberty What method of anaesthesia is used in I and ІІ stage of preterm labor? epidural anesthesia; inhalation anesthesia; intravenous anesthesia; local anaesthesia; spasmolitics. "Orange peel" appearance caused by edema from blocked lymphatic drainage in advanced cancer Colostrum Gynecomastia Peau d'orange Galactorrhea Mastitis Thick, yellow discharge that may leak from breasts in the month prior to birth in preparation for lactation Peau d'orange Galactorrhea Gynecomastia D. * E. 523. A. B. C. D. E. * 524. A. B. C. * D. E. 525. A. B. C. D. E. * 526. A. B. C. D. * E. 527. A. * B. C. D. E. 528. A. B. * C. D. E. 529. A. * B. C. D. E. Colostrum Mastitis Mobile, Firm, Well-Delineated Lumps 1-5 cm in diameter, Freely movable, Asymptomatic, Single tumor near the nipple or in the upper outer quadrant is Carcinoma Intraductal Papilloma Benign Breast Disease Gynecomastia Fibroadenoma Which disease manifesting with Dimpling of the skin, Deviation of the nipple, Nipple retraction, Change in the shape of one breast, Edema, Discharge? Benign Breast Disease Fibroadenoma Carcinoma of the Breast Mammary Duct Ectasia Intraductal Papilloma The sebaceous glands on the areola, which enlarge and produce a secretion that protects and lubricates the nipples is Suspensory ligaments Acini cells Areola Mammary ridge Montgomery's glands (tubercles) What affirmation in relation to the state of cervix just after labor is correct? the cervix is closed; the cervix admits a 1 transversal finger; the cervix admits 3-4 transversal fingers; the cervix is formed. the cervix admits a hand; What sign is typical for retrocervical myoma? rectum dysfunction infertility amenorrhea foamy vaginal discharge hyperpolymenorrhea Lactation not associated with childbearing or breast-feeding is Colostrum Galactorrhea Peau d'orange Gynecomastia Lactostasis What complications can develop due to the incorrect suturing of cervical rupture in a future? cervical ectropion; violation of function of pelvic muscles; prolaps of uterus; endometritis; bleeding 530. A. B. * C. D. E. 531. A. * B. C. D. E. 532. A. B. C. D. * E. 533. A. B. * C. D. E. 534. A. B. C. D. E. * 535. A. B. C. * D. E. 536. A. B. C. D. * E. Which of the following positions accentuates the presence of dimpling during the inspection phase of breast assessment? Sitting with arms relaxed at the sides Sitting with arms raised over the head Supine with arm elevated Leaning forward with arms in front of the client All positions are available for performing the inspection phase breast assessment Which disease characterized by Lumps, Pain or Tenderness, and Nipple Discharge as a Result of Thickening of the Breast Tissue Benign Breast Disease Carcinoma of the Breast Mammary Duct Ectasia Fibroadenoma Intraductal Papilloma Which of the following hormones is predominantly essential for maintaining pregnancy? Estrogen hCG Oxytocin Progesterone Testosteron Physiological blood loss of puerperal woman with 76 kg mass is: 260 ml; 380 ml; 320 ml; 240 ml; 450 ml. What method should be used for diagnostic of subserous myoma? curettage of uterine cavity hysterography uterine probing hysterosalpingography ultrasound All of the following are normal gastrointestinal changes in pregnancy EXCEPT: Ptyalism Pyrosis Pica Decreased peristalsis Constipation What hormone is produced by a pituitary gland under the act of nipple compression at feeding of child? oxythocin; vasopressin; progesteron; prolactin; estradiol. 537. A. * B. C. D. E. 538. A. B. * C. D. E. 539. A. B. C. * D. E. 540. A. B. * C. D. E. 541. A. B. * C. D. E. 542. A. B. C. * D. E. 543. A. B. C. D. E. * 544. A. * Appendicitis may be difficult to diagnose in pregnancy because the appendix is: Displaced upward and laterally, high and to the right. Displace upward and laterally, high and to the left. Deep at McBurney’s point. Displaced downward and laterally, low and to the right. Displaced posteriorly and covered by the uterus What are probable signs of pregnancy? Determined by ultrasound. Observed by the health care provider. Reported by the client. Diagnostic tests. Determined by X-ray The diagnosis of pregnancy is based on the following positive signs of pregnancy. Quickening Verification of fetal sex Verification of fetal movement by examiner Positive hCG test. Delay of the period When is the fetus begins to descend and drop into the pelvis: Attitude Lightening Presentation Chloasma Station Which of the following include signs and symptoms that a woman should report immediately to her health care provider? Fetal movement Heartburn accompanied by severe headache Decreased libido Urinary frequency Morning sickness Whant is the maximal physiologycal blood lost in labor? 0,1 % of body weight 0,3 % of body weight 0,5 % of body weight 0,7 % of body weight 1 % of body weight What method should be used for diagnostic submucous myoma? puncture of abdominal cavity through posterior vaginal fornix laparoscopy biopsy Doppler assessment hysteroscopy Prenatal care should ideally begin: Before the first missed menstrual period. B. C. D. E. 545. A. B. C. D. * E. 546. A. * B. C. D. E. 547. A. B. C. * D. E. 548. A. B. C. D. * E. 549. A. B. * C. D. E. 550. A. B. C. * D. E. 551. A. B. * After the first missed menstrual period. After the second missed menstrual period. After the third missed menstrual period. After the birth Physiologycal blood loss of puerperal woman with body weight 68 kg is: 260 ml; 380 ml; 360 ml; 340 ml; 420 ml. For which of the following women is recommended HIV prenatal testing? All women, regardless of risk factors A woman who has had more than one sexual partner A woman who has had a sexually transmitted infection A woman who is monogamous with her partner This test is not indicated for pregnant woman Which of the following is characteristic of true labor? Irregular contractions Discomfort in lower abdomen Cervical dilatation Discomfort relieved by sedation Passage of the blood-tinged Which of the following symptoms would be considered a first trimester warning sign and should be reported immediately by the pregnant woman to her health care provider? Nausea with occasional vomiting Fatigue Urinary frequency Vaginal bleeding Fetal movement Condoms should be used in pregnancy by: Unmarried pregnant women Women at risk for acquiring or transmitting sexually transmitted infections All pregnant women Women at risk for candidiasis Using of condoms is not recommended for pregnant woman When should the fetal heart rate be auscultated during observation for labor in the II stage? Before the contraction During the contraction At the end and immediately after a contraction Any time After delivery Which of the following blood pressure (BP) assessment findings during the second trimester indicates a risk for pregnancy-induced hypertension? Baseline BP 120/80, current BP 126/85 Baseline BP 100/70, current BP 130/85 C. D. E. 552. A. * B. C. D. E. 553. A. B. * C. D. E. 554. A. B. C. D. * E. 555. A. * B. C. D. E. 556. A. B. C. D. E. 557. A. B. C. * D. E. 558. A. Baseline BP 140/85, current BP 130/80 Baseline BP 110/60, current BP 110/60 Baseline BP 120/80, current BP 116/75 The triple marker test is used to assess the fetus for which condition? Down syndrome Diaphragmatic hernia Congenital cardiac abnormality Anencephaly Cleft lips A woman who is 32 weeks pregnant is informed by the physician that a danger sign of pregnancy could be: Constipation Alteration in the pattern of fetal movement Heart palpitations Edema in ankles and feet at the end of the day Braxton Hicks contractions For which of the following reasons would breastfeeding be contraindicated? Hepatitis B Everted nipples History of breast cancer 3 years ago Hepatitis C Herpes simplex type I Which of the following include signs and symptoms that a woman should report immediately to her health care provider? Vaginal bleeding Fetal movement Decreased libido Urinary frequency Constipation A woman is 3 months pregnant. At her prenatal visit, she tells the physician that she doesn’t know what is happening; one minute she is happy that she is pregnant, and the next minute she cries for no reason. Which of the following responses by the physician is most appropriate? “Don’t worry about it; you’ll feel better in a month or so.” “Have you talked to your husband about how you feel?” “Perhaps you really don’t want to be pregnant.” “Hormone changes during pregnancy commonly result in mood swings.” “It is abnormal situation, you should be examined by psychiatrist” Which of the following is the partner’s main role in pregnancy? Provide financial support. Protect the pregnant woman from “old wives’ tales”. Support and nurture the pregnant woman. Ensure that the pregnant woman keeps prenatal appointments. Pregnant woman do not need any partner What is the station where the fetal head is visible at the introitus? +2 B. * C. D. E. 559. A. B. * C. D. E. 560. A. B. * C. D. E. 561. A. B. C. * D. E. 562. A. * B. C. D. E. 563. A. B. C. D. * E. 564. A. B. * C. D. E. 565. A. +3 +4 +5 0 What method should be used for diagnostic interstitial myoma? hysterosalpingography ultrasound hysteroscopy curettage of uterine cavity uterine probing During the first trimester of pregnancy, a woman can expect which of the following changes in her sexual desire? An increase because of enlarging breasts A decrease because of nausea and fatigue No change in the first trimester An increase because of increased levels of female hormones A decrease because of decreased levels of female hormones What is the most reliable indicator of rupture of the fetal membranes? Fluid per cervical os Positive nitrazine test Positive ferning Positive oncofetal fibronectin Bloody discharge Which of the following behaviors indicates that a woman is “seeking safe passage” for herself and her infant? She keeps all prenatal appointments. She “eats for two.” She drives her car slowly. She wears only low-heeled shoes. She stops driving to avoid stressful situation In what form of uterine fibromyoma we have such complication as node twisting? retrocervical interstitial submucosal subserosal intraligamentous Which of the following include signs and symptoms that a woman should report immediately to her health care provider? Fetal movement Rupture of membranes Decreased libido Urinary frequency Braxton Hicks contractions What is the station where the presenting part is at the level of the ischial spines? -2 B. C. * D. E. 566. A. B. C. * D. E. 567. A. B. C. D. * E. 568. A. * B. C. D. E. 569. A. B. * C. D. E. 570. A. B. * C. D. E. 571. A. B. * C. D. E. 572. A. B. -1 0 +1 +2 Which meal would provide the most absorbable iron? Toasted cheese sandwich, celery sticks, tomato slices, and a grape drink Oatmeal, whole wheat toast, jelly, and low-fat milk Black bean soup, wheat crackers, ambrosia (orange sections, coconut, and pecans), and prunes Red beans and rice, cornbread, mixed greens, and decaffeinated tea Burgers, pizza, Cola During the third stage of labor, which of the following is NOT a sign of placenta separation? A gush of blood Uterus rises in the abdomen Umbilical cord protrudes out of the vagina A sudden, sharp, unrelenting contraction Nothing above Which nutrient’s recommended dietary allowance (RDA) is higher during lactation than during pregnancy? Energy (kcal) Iron Vitamin A Folic acid Weight (grams) Pregnant woman experiencing nausea and vomiting should: Drink a glass of water with a fat-free carbohydrate before getting out of bed in the morning Eat small, frequent meals (every 2 to 3 hours) Increase the intake of high-fat foods to keep the stomach full and coated Limit fluid intake throughout the day Be hospitalized for additional assessment To prevent GI upset, clients should take iron supplements: On a full stomach At bedtime After eating a meal With milk One hour before eating a meal Women with an inadequate weight gain during pregnancy are at higher risk for giving birth to an infant with: Spina bifida Intrauterine growth retardation Diabetes mellitus Down syndrome Pregnancy induced hypertension For what are pregnants adolescents at high risk due to lower BMIs and “fad” dieting? Obesity Diabetes C. * D. E. 573. A. B. C. D. * E. 574. A. B. C. * D. E. 575. A. B. C. * D. E. 576. A. B. C. D. * E. 577. A. * B. C. D. E. 578. A. * B. C. D. E. 579. A. * B. C. D. Low birth weight babies High birth weight babies Postpartum hemorrhage Which of the following assessments are not included in fetal biophysical profile (BPP)? Fetal movement Fetal tone Fetal heart rate Placental grade Amount of amniotic fluid In pregnancy maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein (MSAFP) levels have been used as a screening tool for: abdominal wall defects intestinal defects neural tube defects palate defects heart defects Intrauterine growth restriction is associated with what pregnancy related risk factors? Ovarian cyst Premature rupture of membranes Poor nutrition Neural tube defects Polyhydramnios Intrauterine growth restriction is associated with what pregnancy related risk factors? Premature rupture of membranes Ovarian cyst neural tube defects Pregnancy-induced hypertension Preterm labor Which analysis of maternal serum may predict chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus? Multiple-marker screening Lecithin-sphingomyelin ratio Biophysical profile Blood type and crossmatch of maternal and fetal serum Doppler velocimetry Which of the following is an indication for fetal diagnostic procedures? Maternal diabetes Maternal age older than 30 y.o. Previous infant more than 3000 g at birth Weight gain of 11,500 kg Father’s age alder than 35 y.o. When is the most accurate time to determine gestational age through ultrasound? First trimester Second trimester Third trimester There is no difference in accuracy between the trimesters. E. 580. A. B. * C. D. E. 581. A. B. C. * D. E. 582. A. * B. C. D. E. 583. A. B. C. D. E. * 584. A. B. * C. D. E. 585. A. B. C. D. * E. 586. A. B. * C. D. Before delivery The primary reason for evaluating alpha-fetoprotein levels in maternal serum is to determine whether the fetus has: hemophilia a neural tube defect. sickle cell anemia a normal lecithin-sphingomyelin ratio diabetes Chorionic villus sampling can be performed during pregnancy as early as: 4 weeks. 8 weeks. 10 weeks. 12 weeks. 16 weeks On which of the following aspects of fetal diagnostic testing do parents usually place the most importance? Safety of the fetus Duration of the test Cost of the procedure Physical discomfort caused by the procedure Maternal’s desire The physician’s role in diagnostic testing is to provide: advice to the couple. assistance with decision making. information about the tests. reassurance about fetal safety. prescription of the test Which of the following would be considered a contraindication for transcervical chorionic villus sampling? Rh-negative mother Positive for group B streptococcus Maternal age less than 35 years Gestation less than 15 weeks Agent placenta Which diagnostic test evaluates the effect of fetal movement on fetal heart activity? Contraction stress test Sonography Biophysical profile Nonstress test Doppler velocimetry Which physician’s intervention is necessary prior to a second trimester transabdominal utrasound? Ensure the client is NPO for 12 hours. Instruct the client to drink 1 to 2 quarts of water. Administer a soap suds enema Perform an abdominal prep. E. 587. A. B. C. D. * E. 588. A. B. C. * D. E. 589. A. * B. C. D. E. 590. A. B. C. D. * E. 591. A. B. * C. D. E. 592. A. B. C. * D. E. 593. A. B. C. D. * There no any recommendation how to prepare to this procedure The major advantage of chorionic villus sampling over amniocentesis is that it: is not an invasive procedure. does not require hospitalization. has less risk of spontaneous abortion. requires less time to obtain results. Increase risk of gestational diabetes development What is the purpose of amniocentesis for a client hospitalized at 34 weeks of gestation with pregnancy-induced hypertension? To identify abnormal fetal cells To detect metabolic disorders To determine fetal lung maturity To identify the sex of the fetus To detect quantity of amniotic fluid Post-surgery care after amniocentesis includes: monitoring uterine activity. placing the client in a supine position for 2 hours. applying a pressure dressing to the puncture site. forcing fluids by mouth. bed rest during next 3 days A nonstress test in which there are two or more fetal heart rate accelerations of 15 or more beats per minute with fetal movement in a 20-minute period is termed: nonreactive. positive. negative. reactive. normal The purpose of initiating contractions in a contraction stress test is: to determine the degree of fetal activity. to apply a stressful stimulus to the fetus. to identify fetal acceleration patterns. to increase placental blood flow. to evaluate quantity of amniotic fluid A score of 9 on a biophysical profile is considered: abnormal. equivocal. normal. negative positive Which diagnostic test would be the most important to have for a primigravid client in the second trimester of her pregnancy? Culdocentesis to detect abnormalities. Chorionic villus sampling. Ultrasound testing. a-fetoprotcin (AFP) testing. E. 594. A. B. * C. D. E. 595. A. B. * C. D. E. 596. A. B. C. * D. E. 597. A. B. C. * D. E. 598. A. B. C. * D. E. 599. A. * B. C. D. E. 600. A. B. C. Doppler velocymetry After reviewing the physician's explanation of amniocentesis with a multigravid client, which of the following, if reported by the client as a primary risk of the procedure, would indicate successful teaching? Premature rupture of the membranes. Possible premature labor. Fetal limb malformations. Fetal organ malformations. polyhydramnios Which of the following statements about a fetal biophysical profile would be incorporated into the teaching plan for a primigravid client with insulin-dependent diabetes? It determines fetal lung maturity. It is noninvasive using real-time ultrasound It will correlate with the newborn's Apgar score. It requires the client to have an empty bladder. Has increased risk of preterm labour As part of preparing a 24-year-old woman at 42 week’s gestation for a nonstress test, the physician would: Tell the woman to fast for 8 hours prior to the test Explain that the test will evaluate how well her baby is moving inside her uterus Show her how to indicate when her baby moves attach a spiral electrode to the presenting part to determine FHR patterns show the baby’s sex In what form of uterine fibromyoma we have such complication as node delivering? retrocervical interstitial submucous subserous intraligamentous What endometrium conditions belong to the premalignant disease? glandular-cystic hyperplasia endometritis polyposis of endometrium endometriosis glandular hyperplasia What is typical for hormonal status of patient with hyperplasia of endometrium? high level of estrogens high level of pituitary gland hormons high level of androgens high level of progesteron high level of chorionic gonadotropin How pregnancy does influence on fibromyoma’s growth? doesn’t effect at all promote fibromyoma’s elimination promote fibromyoma’s malignization D. E. * 601. A. * B. C. D. E. 602. A. B. C. * D. E. 603. A. B. C. D. E. * 604. A. B. * C. D. E. 605. A. B. C. * D. E. 606. A. B. C. * D. E. 607. A. * B. C. D. E. 608. promote necrosis of node promote fast growth of fibromyoma What substance is in IUD for fibromyoma treatment? levonorgestrel synestrol 17-oxiprogesteroni capronat Zoladex Etinilestradiol At what type of ovarian tumour does endometrium hyperpasia develop? papillary cystoma paraovarian cyst follicular cyst ovarian cancer yellow body cyst What tumour of external genitalia develops from connective tissue? papilloma hemangioma myxoma lipoma fibroma What tumour of external genitalia develops from fatty and connective tissue? fibroma lipoma myxoma hemangioma papilloma What treatment should be prescribes for patient with dermoid cyst? antibacterial therapy Zoladex cystectomy substitutive hormonal therapy combined oral contraceptives Bilateral ovarian cyst on ultrasound, associated with molar pregnancy and multiple gestation is? Metastasis Endometriosis Theca luteum cyst PID (Pelvic inflammatory disease) lipoma Bilateral solid ovarian masses on ultrasound, metastases from primary GIT cancer is suggestive for? Krukenberg tumor Luteoma Fibrosis Endometriosis Theca luteum cyst Cervical pap smear test is recommended to this age group with the timing of: A. B. C. D. * E. 609. A. B. C. * D. E. 610. A. B. C. * D. E. 611. A. B. C. D. * E. 612. A. B. C. D. E. * 613. A. B. C. D. E. * 614. A. B. C. D. E. * 615. A. B. * Twice in a lifetime- <25 years old Once a lifetime- all ages Every 10 years- >65 years Every 3 years- 21 to 65 years Every year- 5 to 18 years Name the ovarian cyst with thick sebaceous yellow fluid in and ectodermal (hair) component. Hydatid mole Trauma-related cyst Mature cystic teratoma (dermoid cyst) Cancerous cyst Adenocarcinoma Call the benign uterine fibroids, causing enlarged uterus with an irregular contour: Adenocarcinoma Fibroma Leiomyoma uteri Carcinoma Mole Yellow or yellow-brown masses, solid ovarian mass on ultrasound, 50% bilateral, regress after delivery is? Bartholian Cancer Krukenberg tumor Luteoma Theca luteum cyst Diagnostic method to diagnose uterine Leiomyomas (fibroids): Normal observation MRI of pelvis Bimanual exam Pelvic x-ray Ultrasound of pelvic Which of them is NOT an indication for endometrial biopsy? Lynch syndrome in patient <45 years Atypical glandular cells on pap test Postmenopausal bleeding Obesity/anovulation Sheehan syndrome Soft mobile mass, normally asymptomatic, commonly on the base of the labium major (vulva) is: Syphilis related mass Malignancy HSV related cyst HPV (wart) Bartholin duct cyst Cyst resulting from incomplete regression of the wolffian duct during fetal development? Vaginal cancer Gartner duct cyst C. D. E. 616. A. * B. C. D. E. 617. A. B. * C. D. E. 618. A. B. C. D. E. * 619. A. B. C. D. * E. 620. A. * B. C. D. E. 621. A. * B. C. D. E. 622. A. B. C. * D. E. Fibroid Fissure/ Fistula Bartholin cyst Theca lutein cyst is an ovarian hyperstimulation due to? Gestational trophoblastic disease X-linked related Autoimmunity Anatomically malformation Krukenberg tumor Leiomyomata uteri (fibroids) are a common cause of? Vaginal itching Heavy menstrual bleeding Ectopic pregnancy Severe pelvic and leg pain Vaginal discharge (yellowish) Which of the following is correct regarding polyps? Polyps are the most common cysts in the fallopian tubes Polyps are similar to the fistula Polyps causing secondary amenorrhea but only age after 52y Polyps are always associated with pain Polyps are not associated with pain Choose the most common benign neoplasm of the female genital tract: Endometrial cancer Cervical cancer Vagina cancer Uterine leiomyoma (fibroids) Polyps Which of the following describes the uterine leiomyoma? Discrete/ round ,firm Attached, triangle-like, dense Single, huge, full of pus, dense Cuboid-shaped, pinkish-color, firm Cylendric-chain looking, irregular borders Indicate the key words about uterine myomas and their effects on body: On physical exam uterus is irregular and mobile On physical exam uterus is innervated and shrinky There is lots of yellowish-brownish discharge Heavy bleeding, leading to anemia (only at age <35.y.) None of them If a uterine mass continue to grow after menopausa, suspect……? PID (Pelvic inflammatory disease) Chronic abscess Malignancy Fistula Normal, will be self-limited 623. A. B. C. D. * E. 624. A. * B. C. D. E. 625. A. * B. C. D. E. 626. A. B. C. D. E. * 627. A. B. C. * D. E. 628. A. * B. C. D. E. 629. A. B. * C. D. E. 630. A. B. * What for the Gardasil vaccine may be used? Endometrial cancer Types of breast cancer For protecting the recurrent miscarriage Genital warts and cervical cancer Reduces the development of ovarian cancer in young women Choose a symptom of uterine prolapsed: all of them vaginal pressure sensation vaginal fullness problems with sexual intercourse the uterus or cervix protruding out of the vagina. Indicate the explanation for the cystocele: Bladder prolapse into the vagina Bladder prolapse under the diaphragm Bladder rupture Fistula in the vaginal canal Partially rupture of the bladder Indicate the types of incontinence: Stress-mechanical Stress-physiological Urge-mechanical Urge-neurological Stress-urge Indicate testing for stress incontinence: Muscle strength + sphincter test Needle biopsy + nerve study Pelvic exam + Q-tip test Inguinal canal exam Schiller's test Choose example of anatomically caused incontinence Vesicovaginal fistula Vaginal canal fistula Uterine tumor Ovarian tumor Uterine cancer Which process represents the IIIa type of smear at oncocytological examination? the unchanged epithelium mild or moderate dysplasia cancer inflammatory process suspicion on malignisation For polyp treatment we use all except: cryodestruction conization of cervix C. D. E. 631. A. * B. C. D. E. 632. A. B. C. D. E. * 633. A. B. * C. D. E. 634. A. B. C. * D. E. 635. A. * B. C. D. E. 636. A. B. C. D. E. * 637. A. B. C. D. E. * endocervical curettage Coagulation polyp twisting To the risk factors for cervical dysplasia belong all EXCEPT: hyperprogesteronemia hyperestrogenemia cervical trauma during delivery and abortion A lot of sexual partner Early sexual activity What sign is not typical for proliferative myoma? increased mitotic activity fast growth plenty of lymphoid cells plenty of plasmatic cells Atypical growth In diagnostic of cervical dysplasia we use all EXCEPT: colposcopy metrosalpingography cytogenetic examination histochemical examination cytological examination In what type of ovarion tumour do we have an endometrium hyperplasia? papillary cystoma paraovarian cyst follicle cyst ovarian cancer yellow body cyst In diagnostic of cervical leucoplacia we use all EXCEPT: culdoscopy colposcopy biopsy cytology Speculum assessment Node consistency of uterine fibromyoma depends on: node size vessels' amount fatty tissue amount presence of endometrioid tissues correlation of parenchyma and stroma What is typical for proliferative myoma? presence of atypia atypical localization multiple nodes node calcification increased mitotic activity 638. A. B. C. D. E. * 639. A. * B. C. D. E. 640. A. * B. C. D. E. 641. A. B. C. * D. E. 642. A. * B. C. D. E. 643. A. B. C. D. E. * 644. A. * B. C. D. E. 645. A. B. What sign is not typical for proliferative myoma? increased mitotic activity fast growth plenty of lymphoid cells plenty of plasmatic cells Atypical growth What sign is typical for submucous myoma? hyperpolymenorrhea amenorrhea foamy vaginal discharge symptomless tumour destruction What sign is typical for retrocervical myoma? rectum dysfunction infertility amenorrhea foamy vaginal discharge hyperpolymenorrhea What endometrium conditions belong to the premalignant disease? glandular-cystic hyperplasia endometritis polyposis of endometrium endometriosis glandular hyperplasia What is typical for hormonal status of patient with hyperplasia of endometrium? high level of estrogens high level of pituitary gland hormons high level of androgens high level of progesteron high level of chorionic gonadotropin How pregnancy does influence on fibromyoma’s growth? doesn’t effect at all promote fibromyoma’s elimination promote fibromyoma’s malignization promote necrosis of node promote fast growth of fibromyoma What substance is in IUD for fibromyoma treatment? levonorgestrel synestrol 17-oxiprogesteroni capronat Zoladex Etinilestradiol At what type of ovarian tumour does endometrium hyperpasia develop? papillary cystoma paraovarian cyst C. * D. E. 646. A. B. C. * D. E. 647. A. B. C. D. * E. 648. A. B. C. * D. E. 649. A. B. C. D. * E. 650. A. B. C. D. E. * 651. A. B. C. D. E. * 652. A. B. C. D. follicular cyst ovarian cancer yellow body cyst What treatment should be prescribes for patient with dermoid cyst? antibacterial therapy Zoladex cystectomy substitutive hormonal therapy combined oral contraceptives Cervical pap smear test is recommended to this age group with the timing of: Twice in a lifetime- <25 years old Once a lifetime- all ages Every 10 years- >65 years Every 3 years- 21 to 65 years Every year- 5 to 18 years Call the benign uterine fibroids, causing enlarged uterus with an irregular contour: Adenocarcinoma Fibroma Leiomyoma uteri Carcinoma Mole Yellow or yellow-brown masses, solid ovarian mass on ultrasound, 50% bilateral, regress after delivery is? Bartholian Cancer Krukenberg tumor Luteoma Theca luteum cyst Diagnostic method to diagnose uterine Leiomyomas (fibroids): Normal observation MRI of pelvis Bimanual exam Pelvic x-ray Ultrasound of pelvic Which of them is NOT an indication for endometrial biopsy? Lynch syndrome in patient <45 years Atypical glandular cells on pap test Postmenopausal bleeding Obesity/anovulation Sheehan syndrome Soft mobile mass, normally asymptomatic, commonly on the base of the labium major (vulva) is: Syphilis related mass Malignancy HSV related cyst HPV (wart) E. * 653. A. B. * C. D. E. 654. A. B. * C. D. E. 655. A. B. C. D. E. * 656. A. B. C. D. * E. 657. A. * B. C. D. E. 658. A. * B. C. D. E. 659. A. B. C. * D. E. 660. A. Bartholin duct cyst Cyst resulting from incomplete regression of the wolffian duct during fetal development? Vaginal cancer Gartner duct cyst Fibroid Fissure/ Fistula Bartholin cyst Leiomyomata uteri (fibroids) are a common cause of? Vaginal itching Heavy menstrual bleeding Ectopic pregnancy Severe pelvic and leg pain Vaginal discharge (yellowish) Which of the following is correct regarding polyps? Polyps are the most common cysts in the fallopian tubes Polyps are similar to the fistula Polyps causing secondary amenorrhea but only age after 52y Polyps are always associated with pain Polyps are not associated with pain Choose the most common benign neoplasm of the female genital tract: Endometrial cancer Cervical cancer Vagina cancer Uterine leiomyoma (fibroids) Polyps Which of the following describes the uterine leiomyoma? Discrete/ round ,firm Attached, triangle-like, dense Single, huge, full of pus, dense Cuboid-shaped, pinkish-color, firm Cylendric-chain looking, irregular borders Indicate the key words about uterine myomas and their effects on body: On physical exam uterus is irregular and mobile On physical exam uterus is innervated and shrinky There is lots of yellowish-brownish discharge Heavy bleeding, leading to anemia (only at age <35.y.) None of them If a uterine mass continue to grow after menopausa, suspect……? PID (Pelvic inflammatory disease) Chronic abscess Malignancy Fistula Normal, will be self-limited What for the Gardasil vaccine may be used? Endometrial cancer B. C. D. * E. 661. A. * B. C. D. E. 662. A. B. C. D. E. * 663. A. B. C. * D. E. 664. A. B. * C. D. E. 665. A. B. * C. D. E. 666. A. B. C. D. * E. 667. A. B. C. D. Types of breast cancer For protecting the recurrent miscarriage Genital warts and cervical cancer Reduces the development of ovarian cancer in young women Indicate the explanation for the cystocele: Bladder prolapse into the vagina Bladder prolapse under the diaphragm Bladder rupture Fistula in the vaginal canal Partially rupture of the bladder Indicate the types of incontinence: Stress-mechanical Stress-physiological Urge-mechanical Urge-neurological Stress-urge What kind of endometriosis belongs to internal? endometriosis of uterine cervix endometriosis of vagine endometriosis of uterus endometriosis of perineum endometriosis of Umbilicus Commonest site of endometriosis: vagina uterus. urinary bladder peritoneal cavity. umbilicus Which of medicines should NOT BE USED for treatment of endometriosis? danasol sinestrol dufaston zoladex danogen To the benign cervical condition belong all EXCEPT: Endometriosis dysplasia leukoplakia adenomatosis erythroplasia Why does endometriosis cause pain in some women? Endometriosis tissues cannot leave the body Endometriosis areas make chemicals that irritate pelvic tissues Endometriosis produces chemicals that are known to cause pain Developing adhesions E. * 668. A. B. C. D. * E. 669. A. B. C. D. E. * 670. A. B. * C. D. E. 671. A. B. C. * D. E. 672. A. B. * C. D. E. 673. A. * B. C. D. E. 674. A. B. C. * D. E. 675. All of the above What is one of the most common symptoms of endometriosis? Bloating Pelvic muscle spasm Diarrhea Infertility Heavy Bleeding The main symptom of endometriosis is uterine abscess formation Heavy Bleeding Hormonal imbalance Fever dysmenorrhea The main symptom of endometriosis is Uterine abscess formation Pain Heavy Bleeding Hormonal imbalance Fever Endometriosis affects women of reproductive age and is characterized by: Squamous cells over producing White spots in the vaginal canal Ectopic implantation of endometrial glands Uterus enlargement and unilateral severe pelvic pain Abdominal bloating, vomiting Which one is the pathogenesis of endometriosis? Epithelial hypoplasia Ectopic implantation of endometrial glands Endometrial glands overgrowth Over producing of epithelial cells Squamous cells over producing All of them are clinical findings of endometriosis except: Fatigue/muscle ache Dyschezia Chronic pelvic pain Dysmenorrhea Dyspareunia Immobile uterus, cervical motion tenderness, adnexal mass and posterior cul-de-sac are suggestive for? Mole presentation Ovarian cancer Endometriosis Vaginal cancer Metastasis breast cancer Which of the following is true about endometriosis? A. B. C. D. E. * 676. A. B. C. D. * E. 677. A. B. C. D. E. * 678. A. B. C. D. E. * 679. A. B. C. * D. E. 680. A. * B. C. D. E. 681. A. B. C. * D. E. 682. A. B. * C. Affects approximately 50% of women Affects mostly the age 5-25 years Rarely causes infertility Risk increased in menopause extremely painful (or disabling) menstrual cramps The most common symptom of a vaginal yeast infection is: Bleeding Discharge Fever Itching Infertility Which of the following is a possible symptom of sexually transmitted diseases (STD), EXCEPT? Bumps, sores, or warts near the mouth, anus, or vagina Painful urination Painful sex Infertility Ovarian apoplexy The bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis can cause all EXCEPT: Lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV) Cervicitis Urethritis Infertility Female organ prolapse Name a complication of Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), EXCEPT: Infertility Ectopic pregnancy Menopause Abscesses Long-term (chronic) pain Excretions from a vagina “cheese-like” arise up at: Vaginal candidosis Genital trichomoniasis Malignant tumors Menopause Puberty age Which localization of pain is typical for the inflammatory diseases of adnexa? in lower part of abdomen above a pubis in a right hypogastric area in lateral quadrants of lower part of abdomen in epigastrium in sacrum and lumbal region Thin-white discharge with fishy odor, no inflammation is suggestive for? Hormonal imbalance Bacterial vaginitis Candida vaginitis D. E. 683. A. B. C. D. E. * 684. A. B. C. * D. E. 685. A. B. C. * D. E. 686. A. * B. C. D. E. 687. A. B. * C. D. E. 688. A. B. C. * D. E. 689. A. B. C. * D. E. 690. Trichomoniasis Syphilis Thin-yellow/ green malodorous discharge with vaginal inflammation mostly indicates? Hormonal changes Candida vaginitis Cervicitis Bacterial vaginitis Trichomoniasis Genital warts (condylomata acuminata), is cause by? Candida Bacterial vaginitis Human papillomavirus (HPV) 6 and 11 Syphilis Trichomoniasis Choose the diagnostic testing method for chlamydia and gonorrhea in women: Skin testing Pap smear Nucleic-acid amplification testing Cytology Human papillomavirus (HPV) Choose the treatment of choice for the Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): Parenteral (iv) clindamycin + Gentamicin Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) thyroxine Birth control pills Clomiphene citrate Why chlamydia does not show organisms on culturing? It is weakly motile It is an obligate intracellular pathogen It has no color It is highly mobile It is strongly motile Choose criteria for the clinical diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis: Abnormal whitish-gray discharge Vaginal pH > 4.5 All of them Positive amine (whiff) test Clue cells comprise > 20% of epithelial cells on wet mount Choose best describe for Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): Inflammation of genital Inflammation of uterus and urethra Polymicrobial infection of the upper genital tract It is always caused by trachomatis Never causes lower abdominal pain If there are many WBCs and no organism on saline smear, then suspect: A. B. * C. D. E. 691. A. B. C. D. * E. 692. A. B. * C. D. E. 693. A. B. C. D. * E. 694. A. B. C. * D. E. 695. A. * B. C. D. E. 696. A. B. * C. D. E. 697. A. B. C. Candida Chlamydia Aerobes rods HSV Streptococcus B group Choose treatment of candida vaginitis: Azithromycin Amoxicillin Ceftriaxone Topical azole or fluconazole Low pH soap Choose the right treatment of Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): Methotrexate Ofloxacin or levofloxacin 14 days or metronidazole 14 days Estrogen Clomiphene citrate Progestin Choose the complication caused from Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): Infertility Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome Repeated episodes of infection All of them Chronic pelvic pain Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) presents with all of the following, EXCEPT? Lower abdominal pain Fever/ chills Night sweats Menstrual disturbances Purulent cervical discharge Choose the similar name for the “cervical motion tenderness”: Chandelier sign Cul-de-sac Poor negative reflect Fitz-Hugh-curtis Cervical os over-opening Which organism is responsible for toxic shock syndrome within 5 days after tampons use? Streptococcus B Staphylococcus aureus Chlamydia N. Gonorrhea Candida Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is causing chronic pelvic pain due to…….? Producing ulcers Hard nodules Tearing of ligaments D. * E. 698. A. * B. C. D. E. 699. A. B. * C. D. E. 700. A. B. C. * D. E. 701. A. B. C. D. E. * 702. A. B. * C. D. E. 703. A. B. C. D. * E. 704. A. B. * C. D. E. 705. Pelvic scarring Abscess rupture Which of the following is true about vaginitis? The most common presenting symptom is discharge Night sweats Headaches Mood changes Anxiety Which of the following is NOT the side effect of the combination oral contraceptives? Hypertension Diarrhea Nausea Bloating Breaking through bleeding Combined oral contraceptive can __________ risk of ovarian/ endometrial cancer. Unchanged Increase Decrease Rapidly increase Strongly increase Which of the following is an advantage of Combined oral contraceptive’s use, EXCEPT: Reliable with failure rate of <1% Decreases incidence of Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and ectopic pregnancy Makes menses more predictable and less painful Protective against ovarian and endometrial cancer sexually transmitted diseases (STD) protection Choose a disadvantage of Combined oral contraceptive’s use: Makes menses more predictable No sexually transmitted diseases (STD) protection Weight loss Anorexia Makes menses less painful Choose an alternative to Combined oral contraceptive’s: Withdrawal intercource Ovariectomy Hysterectomy Intrauterine device Sexual abstinence Contraceptive oral pills help in birth control by Killing of ova Preventing ovulation Killing of sperms Forming barrier between sperms and ova Decreasing libido Most important component of oral contraceptive agents is A. B. C. * D. E. 706. A. B. * C. D. E. 707. A. B. * C. D. E. 708. A. B. * C. D. E. 709. A. B. C. * D. E. 710. A. B. C. * D. E. 711. A. B. C. * D. E. 712. A. B. C. Thyroxine Luteinizing hormone(LH) Progestrone Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Gonadotrophin-releasing hormone (GnRH) Copper-T/ loop prevents Ovulation Fertilization Zygote formation Cleavage Reproduction Which of the following is a mechanical barrier used in birth control? Copper-T Diaphragm Loop Dalcon shield Combined oral contraceptive Oral contraceptive pills function by inhibiting Fertilization Ovulation Reproduction Implantation Libido Menopause is defined as: 2 or more irregular periods after age 40 The start of hot flashes No menstrual period for 12 consecutive months No menstrual period for 6 consecutive months An increase in mood swings The average age of menopause is: 60 55 51 45 40 The first step in the workup of primary or secondary amenorrhea is: Bimanual examination Ultrasound of abdomen/pelvic Pregnancy test Nucleic amplification test Mammography Choose the right period for menstruation/follicular phase Days 7-14 Days 14-21 Days 5-10 D. * E. 713. A. B. C. D. E. * 714. A. B. * C. D. E. 715. A. B. * C. D. E. 716. A. B. C. * D. E. 717. A. B. * C. D. E. 718. A. B. * C. D. E. 719. A. B. C. D. * E. 720. Days 1-13 Days 14-21 Choose the right period for ovulation: Day 5 Day 21 Day 28 Day 7 Day 14 Choose the right period for luteal phase: Days 3-14 Days 15-28 Days 5-10 Days 7-14 Days 10-14 Duration of proliferation phase in uterine cycle is: from 1 to 5 day from 5 to 14 day from 14 to 28day from 10 to 14 day from 15 to 20 day Duration of secretion phase in uterine cycle is: from 1 to 5 day from 5 to 14 day from 14 to 28day from 10 to 14 day from 15 to 20 day What is spaniomenorrhea? menstruations come in 6-8 weeks menstruations come 1 time per 4-6 monthes menstruations are absent quantity of menstrual blood less than 50ml duration of menstruation 1-2 days In climacteric age the medical treatment of dysfunctional uterine bleeding begin with: setting of estrogens diagnostic curettage of uterine cavity colposcopy setting of androgens setting of gestagens What appearance of the first menstruation in 17 years can testify about? About the presence of inflammatory disease of uterus About the presence of inflammatory disease of adnexa About the presence of abnormal position of uterus About the presence of genital infantilism About normal development of organism of girl Hypomenstrual syndrome includes: A. B. * C. D. E. 721. A. B. C. D. * E. 722. A. B. * C. D. E. 723. A. B. * C. D. E. 724. A. B. * C. D. E. 725. A. B. C. D. * E. 726. A. B. * C. D. E. 727. A. B. C. * Opsomenorrhea, polimenorrhea Oligomenorrhea, opsomenorrhea, hypomenorrhea Proyomenorrhea, hypomenorrhea Oligomenorrhea, hypermenorrhea Spaniomenorrhea, hypermenorrhea What appearance of the first menstruation in 14 years can testify about? about the presence of inflammatory disease of uterus about the presence of inflammatory disease of adnexa about the presence of abnormal position of uterus about normal development of organism of girl about the presence of of genius infantilism To hypothalamic amenorrhea does not belong: psychogenic amenorrhea amenorrhea at a syndrome Shikhane amenorrhea at false pregnancy amenorrhea at adipozogenital dystrophy amenorrhea at a syndrome Kiary-Frommel Menorrhagia is: acyclic uterine bleeding cyclic uterine bleeding in connection with menstruation cycle painfull and abundant menstruation pre- & post menstruation bloody allocation short period of menstruation cycle What is spaniomenorrhea? menstruations come in 6-8 weeks menstruations come 1 time per 4-6 monthes menstruations are absent quantity of menstrual blood less than 50ml duration of menstruation 1-2 days How is the state named, when less than 2 days proceed to menstruation? spaniomenorrhea hypomenorrhea proyomenorrhea oligomenorrhea opsomenorrhea What is the initial evaluation in case of secondary amenorrhea? Prolactin, TSH and FSH followed by B-hcG to exclude pregnancy B-hcG Prolactin level only Patient's BMI and level of cortisol Patient's age and level of gonadotropine Mean age for menopause is? 40 years 45 years 51 years D. E. 728. A. B. C. * D. E. 729. A. B. C. D. E. * 730. A. B. * C. D. E. 731. A. B. * C. D. E. 732. A. B. C. * D. E. 733. A. * B. C. D. E. 734. A. B. * C. D. E. 735. 48 years 39 years Which of the following is NOT a risk factor for the cervical cancer? Multiple or high risk sexual partners Tobacco use Being at menopausal age History of Sexual Transmitted Disease Hpv 16.18 Which of the following is true about granulosa cell tumor? Cells in rosette pattern Complex ovarian mass High estradiol and high inhibin Sex cord-stromal tumor All of them Which among these gynecologic neoplasms has the highest mortality rate? Uterine Ovarian Cervical Endometrial Vulvar Indicate the types of endometrial cancer: Benign endometroid – atypical endometrial Type 1, endometroid - Type 2, serous Type 1 serous – Type 2, endometroid Columnar - squamous Type A, fibroid, Type B, serous Indicate the risk factor of vulvar cancer: Alcoholism-down syndrome Sjogren syndrome HPV (16,18,31), lichen sclerosis, smoking Diabetes, allergy, high protein diet Stress(anxiety), anorexia nervosa Choose the frequency of female genital tract cancers: Endometrial>ovarian>cervical Ovarian>endometrial>cervical Cervical>ovarian>endometrial Endometrial>cervical>ovarian Ovarian>cervical>endometrial Choose the number of death rate with female genital tract cancers: Endometrial>ovarian>cervical Ovarian>endometrial>cervical Cervical>endometrial>ovarian Ovarian>cervical>endometrial Endometrial>cervical>ovarian Indicate which of the following best explains teratoma: A. B. C. D. E. * 736. A. * B. C. D. E. 737. A. * B. C. D. E. 738. A. B. C. D. * E. 739. A. B. C. D. * E. 740. A. B. C. * D. E. 741. A. B. * C. D. E. 742. A. B. C. * A tumor very soft, round, filled with clean pus A tumor very large, firm, filled in with blood An abscess with a pinkish surface An abscess covering the os of cervix A tumor made up of hair, muscle, bone Explain the term called, serous cystadenoma: Most common ovarian neoplasm, and is benign Most common ovarian neoplasm, highly aggressive Most common uterus neoplasm Cervical hyperplasia Large cyst under the one ovary What is a Brenner tumor? Group of ovarian neoplasm, majority benign Group of ovarian neoplasm, causing rapid metastasis This tumor is very common in young women The tumor is made up of muscle, hair and bone The tumor is firm-small in size <1cm Explain correctly the krukenberg tumor: Benign tumor of ovaries Benign tumor of uterus Benign tumor on labia major Malignancy in the ovary that metastasized from other site Malignancy in the cervix that metastasized from primary site Explain what the sertoli-leydig cell tumor is: A small tumor on labia minor A small tumor on posterior wall of vagina A tumor on the opening of the cervix Is an ovarian tumor that secrets testosterone Is an ovarian tumor with LH overproducing Thick cottage-cheese-like discharge and vaginal inflammation is suggestive of? Cancer Hormonal changes Candida vaginitis Bacterial vaginitis Trichomoniasis Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome (perihepatitis) mostly caused by: HBV Chlamydia and gonorrhea E.coli Candida Streptococci How can the Tanner Stages be defined? Emotional changes of the aging woman Thelarche Stages of adolescent physical development D. 748. Menarche Menopause What is correct about test tube baby? Fertilization inside female genital tract and grown in test tube Rearing of prematuraly born in incubator Fertilization outside and gestation inside womb of mother Both fertilization and development are effected outside the genital tract. Fertilization of only donation egg Which of the following represents a condition where the motility of sperms is highly reduced? Azospermia Polyspermy Oligospermia Asthenospermia Hyperspermy Oral contraceptive pills function by inhibiting: Fertilization Ovulation Reproduction Implantation Libido Which test is found positive during fertlity period of menstrual cycle, in which cervical mucus is slippery and can be drawn into a thread when stretched between two fingers: Spinnbarkeit test Shick test Ballottement test Pyroglobulin test Schiller's test Failure of testis to descend into the scrotum is called: Paedogenesis Castration Cryptorchidism Impotency Infertility After a sperm has entered on ovum, entry of other sperm is prevented by: A. B. C. D. * E. 749. A. B. C. D. * E. Condensation of the yolk Formation of pigment coat Development of viteline membrane Development of fertilization membrane Formation of chorion The site of fertilization in human is: Ovary Uterus Vagina Fallopian tube Cervix E. 743. A. B. C. * D. E. 744. A. B. C. D. * E. 745. A. B. * C. D. E. 746. A. * B. C. D. E. 747. A. B. C. * D. E. 750. C. D. * Gonads develop from embryonic: Ectoderm Endoderm Mesoderm Both mesoderm and endoderm Both ectoderm and endoderm Location and secretion of Leydig cells are: Liver-cholestrol Ovary-estrogen Testis-testosterone Pancreas-glucogen Ovary-progesteron Freshly released human egg has: One Y-chromosome One X-chromosome Two X-chromosome One X-chromosome and one Y-chromosome Two Y-chromosome In 28 day human ovarian cycle, ovulation occures on: Day 1 Day 5 Day 14 Day 28 Two days before mensis Part of sperm involved in penetrating egg membrane is: Tail Acrosome Allosome Autosome Plasma membrane Preparation of sperm before penetrating ovum is: Spermation Coition Insemination Capacitation E. 756. A. * B. C. D. E. 757. A. B. * Implantation Spermatozoa are nourished by: Sertoli cells Interstitial cells Connective tissue cells Adiposal tissue cells Hyaluronic acid Fertilized ovum is implanted in uterus after: 1 day 7 days A. B. C. * D. E. 751. A. B. C. * D. E. 752. A. B. * C. D. E. 753. A. B. C. * D. E. 754. A. B. * C. D. E. 755. A. B. C. B. 8 days 10 days 1 month Middle piece of human sperm contains: Nucleus Vacuoles Mitochondria Centriole Chorion Immediately after ovulation, the egg is covered by a membrane called: Chorion Zona pellucida Corona radiata Vitelline membarane Placenta Ovulation or release of ovum occures on the day of menstrual cycle: 8-10 12-14 14-18 Last two days of mensrtual cycle Mensis Sperms produce an enzymatic substance for dissolving egg coverings. It is called: Hyaluronic acid Hyaluronidase Androgamone Diastase Estogen Testes descent into scrotum for: Spermatogenesis Fertilization Development of sex organs Development of visceral organs Sexual life Choose the indications for cervical conization Cervicitis Uterine masses C. * D. E. 764. A. B. * C. D. E. Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grades 2 and 3 Ovarian torsion Vaginitis Indicate the risk factors for the pelvic organ prolapse: Lack of vitamins, obesity, Nulliparity Obesity, multiparity, hysterectomy, postmenopausal age Nulliparity, obesity, young age Alcohol abuse, aspirin intake Young age, diabetes, drug abuse D. E. 758. A. B. C. * D. E. 759. A. B. * C. D. E. 760. A. B. * C. D. E. 761. A. B. * C. D. E. 762. A. * B. C. D. E. 763. A. 765. D. E. * Choose the treatment of stress incontinence: Kegel exercises, surgery Fitness, diet Walking exercises, Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Warm compress Hot patches Choose the treatment of urge incontinence: Kegel exercises Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Anti-spasmotics, anti-cholinergics Beta blockers Muscle relaxants The two main anatomic divisions of the uterus are: corpus and fundus. cornu and fundus. cervix and isthmus . cervix and fundus . corpus and cervix. Which of the following doesn’t supply the uterus? uterine artery. ovarian artery. all above. nothing above. vaginal artery. Before puberty, the ratio of the length of the body of the uterus to the length of the cervix is approximately: 3:1. 4:1. nothing above. 1:1. 2:1. What part of the ovary comes to contain the developing follicles? medulla. inner par . membrane. nothing above. cortex. 771. A. B. C. D. E. * 772. A. What portions does the uterus tube consist of? isthmus. ampulla. infundibulum. ampulla and infundibulum all above. The wall of the uterus consists of: serous membrane and myometrium. A. * B. C. D. E. 766. A. B. C. * D. E. 767. A. B. C. D. E. * 768. A. B. C. D. E. * 769. A. B. C. D. * E. 770. A. B. C. B. C. * endometrium and myometrium endometrium and perimetrium perimetrium and myometrium perimetrium, myometrium, endometrium. What is the narrowest part of uterine tube? ampulla. infundibulum. all above ampulla and infundibulum isthmus. Duration of secretion phase in uterine cycle from 1 to 5 day from 5 to 14 day from 10 to 14 day. from 14 to 28day . from 15 to 20 day Duration of proliferation phase in uterine cycle from 1 to 5 day from 14 to 28day from 10 to 14 day from 15 to 20 day from 5 to 14 day The blood supply of the fallopian tubes is from the ovarian arteries the uterine arteries the tubal arteries the rectum arteries the ovarian and uterine arteries What quantity of blood is loss by a woman during normal menstruation? less than 40 ml. 60-80 ml. 250-300 ml. 200-250 ml. 50-150 ml. This is the site of fertilization Ureters Urethra Uterine tubes D. E. 779. A. B. * C. D. Ovaries Vagina This is the portion of the uterus that opens into the vagina Urethra Cervix Uterine tubes Inguinal canal C. D. E. * 773. A. B. C. D. E. * 774. A. B. C. D. * E. 775. A. B. C. D. E. * 776. A. B. C. D. E. * 777. A. B. C. D. E. * 778. A. B. E. 786. A. Ovaries Anterior to the vagina and urethral openings is the Labia majora Labia minora Mons pubis Cervical sphincter Labial frenulum Skene's glands secrete Estrogen Progesterone Testosterone Androgens Mucus Structures that produce estrogens? pituitary gland Luteal body growing follicles hypothalamus Germinal epithelium Progesteron is secreted by Thymus Thyroid Testis Corpus luteum Corpus albicans Bartholin’s gland of femal corresponds to gland in male Rectal Cowper’s Inguanal Prostate Nothing above The vagina is lined by: pseudo-stratified squamous non keratinised epithelium stratified cuboidal non keratinised endothelium stratified cuboidal non keratinised epithelium stratified squamous keratinised epithelium stratified squamous non keratinised epithelium What is produced by the ovaries? Primary oocytes, insulin and estrogen B. C. D. * E. 787. A. * Secondary oocytes, progesterone and cortisol Tertiary oocytes, insulin and estrogen Secondary oocytes, estrogen and progesterone Primary oocytes, estrogen and testosterone What is the narrowest part of uterine tube? isthmus . 780. A. B. C. D. E. * 781. A. B. C. D. E. * 782. A. B. C. * D. E. 783. A. B. C. D. * E. 784. A. B. * C. D. E. 785. A. B. C. D. E. * B. C. D. E. 788. A. B. C. D. E. * 789. A. * B. C. D. E. 790. A. B. C. D. E. * 791. A. * B. C. D. E. 792. A. B. C. * D. E. 793. A. B. C. * D. E. 794. A. B. C. ampulla infundibulum all above ampulla and infundibulum The uterus is supported by: the uterosacral ligaments the cardinal ligaments the round ligaments the broad ligaments all above Number of eggs typically produced in a 28 day menstrual cycle? one egg two eggs three eggs some eggs ten eggs What quantity of blood is lost by a woman during normal menstruation? less than 50 ml. 50-100 ml. 150-200 ml. 200-250 ml. 50-150 ml. Combined hormonal methods of contraception protect against: Endometrial/ovarian cancer Osteoporosis Mammary Paget disease Hypertension Sexually transmitted diseases Ovarian cancer is: Early to detect with the Pap smear Likely to carry a good prognosis once it is detected Frequently detected late in its course Early to detect with Human papillomavirus (HPV) tests Early to detect with An alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) tests Cancer prevention program for women include all of the following, EXCEPT: Smoking cessation Periodic screening Bone density index measurement Human papillomavirus (HPV) tests Pap tests Risk factors for uterine cancer include those factors that expose the endometrium to estrogen, including: Early menarche (before 12) Never having children Late menopause(after age 55) D. A. History of failure to ovulate All of them Risk factors for uterine cancer include those factors that expose the endometrium to estrogen, including: Infertility Diabetes Gallbladder disease Hypertension All of them Risk factors for uterine cancer include those factors that expose the endometrium to estrogen, including: Infertility Gallbladder disease Hypertension Obesity All of them Which of the following symptoms is seen in granulosa cell tumor? Thickened endometrium Postmenopausal bleeding Endometrial hyperplasia Large adnexal mass All of them Vaginal cancer located on upper 1/3 of the posterior vaginal wall. Squamous cell Columnar epithelial Multiple cells Clear cell adenocarcinoma Leiomyoma Vaginal cancer located on upper 1/3 of the anterior vaginal wall. Clear cell adenocarcinoma Squamous cell Multiple cells Cuboidal cells Columnar epithelial Choose the management of choice for the cervical intraepithelial neoplasia: Cervical conization Antibiotics Chemotherapy Radiotherapy Hormanal therapy Which of the following is NOT a risk factor for the cervical cancer? Multiple or high risk sexual partners B. C. * D. Tobacco use Being at menopausal age History of Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) E. * 795. A. B. C. D. E. * 796. A. B. C. D. E. * 797. A. B. C. D. E. * 798. A. * B. C. D. E. 799. A. * B. C. D. E. 800. A. * B. C. D. E. 801. E. D. * E. Hpv 16.18 Which of the following is true about granulosa cell tumor? Cells in rosette pattern Complex ovarian mass High estradiol and high inhibin Sex cord-stromal tumor All of them Which among these gynecologic neoplasms has the highest mortality rate? Uterine Ovarian Cervical Endometrial Vulvar Indicate the types of endometrial cancer: Benign endometroid – atypical endometrial Type 1, endometroid - Type 2, serous Type 1 serous – Type 2, endometroid Columnar - squamous Type A, fibroid, Type B, serous Indicate the risk factor of vulvar cancer: Alcoholism-down syndrome Sjogren syndrome HPV (16,18,31), lichen sclerosus, smoking Diabetes, allergy, high protein diet Stress(anxiety), anorexia nervosa Choose the frequency of female genital tract cancers: Endometrial>ovarian>cervical Ovarian>endometrial>cervical Cervical>ovarian>endometrial Endometrial>cervical>ovarian Ovarian>cervical>endometrial Choose the number of death rate with female genital tract cancers: Endometrial>ovarian>cervical Ovarian>endometrial>cervical Cervical>endometrial>ovarian Ovarian>cervical>endometrial Endometrial>cervical>ovarian Choose the ovarian tumor marker for epithelial tumor: An alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) CA-19 Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) CA-125 human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) 809. A. Choose the ovarian tumor marker for endometrial sinus tumor: CA-19 802. A. B. C. D. E. * 803. A. B. * C. D. E. 804. A. B. * C. D. E. 805. A. B. C. * D. E. 806. A. * B. C. D. E. 807. A. B. * C. D. E. 808. A. B. C. B. A. B. C. CA-125 human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) Inhibin An alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) Choose the ovarian tumor marker for embryonal carcinoma: An alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) CA-125 An alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) Inhibin Choose the ovarian tumor marker for choriocarcinoma: Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) CA-19 CA-125 Inhibin human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) Choose the ovarian tumor marker for the dysgerminoma: Inhibin CA-125 human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) An alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) Indicate which of the following best explains teratoma: A tumor very soft, round, filled with clean pus A tumor very large, firm, filled in with blood An abscess with a pinkish surface An abscess covering the os of cervix A tumor made up of hair, muscle, bone Explain the term called, serous cystadenoma: Most common ovarian neoplasm, and is benign Most common ovarian neoplasm, highly aggressive Most common uterus neoplasm Cervical hyperplasia Large cyst under the one ovary What is a Brenner tumor? Group of ovarian neoplasm, majority benign Group of ovarian neoplasm, causing rapid metastasis This tumor is very common in young women The tumor is made up of muscle, hair and bone The tumor is firm-small in size <1cm Explain correctly the krukenberg tumor: Benign tumor of ovaries Benign tumor of uterus Benign tumor on labia major D. * Malignancy in the ovary that metastasized from other site C. D. E. * 810. A. B. C. D. * E. 811. A. B. C. D. E. * 812. A. B. C. D. * E. 813. A. B. C. D. E. * 814. A. * B. C. D. E. 815. A. * B. C. D. E. 816. E. 817. A. B. C. D. * E. 818. A. B. * C. D. E. 819. A. B. C. * D. E. 820. A. B. C. * D. E. 821. A. * B. C. D. E. 822. A. B. C. * D. E. 823. A. * B. C. D. E. 824. Malignancy in the cervix that metastasized from primary site Explain what is the sertoli-leydig cell tumor: A small tumor on labia minor A small tumor on posterior wall of vagina A tumor on the opening of the cervix Is an ovarian tumor that secrets testosterone Is an ovarian tumor with Luteinising hormone (LH) overproducing Indicate one of the cause of secondary amenorrhea: Premature ovarian failure All of them Hypothalamus (neoplasm) Pituitary (adenoma) Asherman syndrome Menopause is defined as: 2 or more irregular periods after age 40 The start of hot flashes No menstrual period for 12 consecutive months No menstrual period for 6 consecutive months An increase in mood swings The average age of menopause is: 60 55 51 45 40 Choose the treatment of choice for the primary dysmenorrhea: Topical heat therapy, combined Oral contraceptive pills (OCPs), progestin Intrauterus device (IUD), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Topical cold therapy, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, muscle relaxants Corticosteroids Antibiotics therapy Non-combined Oral contraceptive pills (OCPs) and estrogen patch The first step in the workup of primary or secondary amenorrhea is: Bimanual examination Ultrasound of abdomen/pelvic Pregnancy test Nucleic amplification test Mammography Which of the following can NOT cause central hypogonadism? Hypernatremia Undernourishment Stress Central nerve system (CNS) tumor Hyperprolactinemia Luteinizing hormone (LH) surge triggers the: A. B. * C. D. E. 825. A. B. C. D. * E. 826. A. B. C. D. E. * 827. A. B. * C. D. E. 828. A. B. * C. D. E. 829. A. B. C. * D. E. 830. A. B. * C. D. E. 831. A. B. * C. D. Ovulation and initiates production of estrogen Ovulation and initiates production of progesterone Direct effect on production of growth hormone Stimulates production of estrogen Indirectly maintains the T4/T3 levels Choose the right period for menstruation/follicular phase Days 7-14 Days 14-21 Days 5-10 Days 1-13 Days 14-21 Choose the right period for ovulation: Day 5 Day 21 Day 28 Day 7 Day 14 Choose the right period for luteal phase: Days 3-14 Days 15-28 Days 5-10 Days 7-14 Days 10-14 Duration of proliferation phase in uterine cycle is: from 1 to 5 day from 5 to 14 day from 14 to 28day from 10 to 14 day from 15 to 20 day Duration of secretion phase in uterine cycle is: from 1 to 5 day from 5 to 14 day from 14 to 28day from 10 to 14 day from 15 to 20 day What is spaniomenorrhea? menstruations come in 6-8 weeks menstruations come 1 time per 4-6 monthes menstruations are absent quantity of menstrual blood less than 50ml duration of menstruation 1-2 days In climacteric age the medical treatment of dysfunctional uterine bleeding begin with: setting of estrogens diagnostic curettage of uterine cavity colposcopy setting of androgens E. 832. A. B. * C. D. E. 833. A. B. C. * D. E. 834. A. B. C. * D. E. 835. A. B. * C. D. E. 836. A. B. C. D. * E. 837. A. B. C. D. * E. 838. A. B. * C. D. E. setting of gestagens What causes dysfunctional uterine bleeding during adolescence? Abnormal periods Anovulatory cycles Poor diet Poor grades Social withdrawal What is the most visible sign of puberty? Social withdrawal Weight gain Enlargement of the breast bud Anger Increasing libido How can the Tanner Stages be defined Emotional changes of the aging woman Thelarche Stages of adolescent physical development Menarche Menopause What is the second phase of the normal menstrual cycle? Ovulation Secretory-luteal phase Menstruation Proliferative phase Follicular phase The corpus luteum regresses with decreases in estrogen and progestin, resulting in menstruation, when what does not occur? Ovulation Cysts Menarche Implantation Menopause What appearance of the first menstruation in 17 years can testify about? About the presence of inflammatory disease of uterus About the presence of inflammatory disease of adnexa About the presence of abnormal position of uterus About the presence of genital infantilism About normal development of organism of girl Deficiency of which hormone presents in case of dysfunctional uterine bleeding? Estrogen Progesterone Thyroxin Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Cortisol Назва наукового напрямку (модуля): Семестр: 12 Obstetrics and Gynecology КРОК Опис: 6 course, 12 term Перелік питань: 1. A. B. C. D. E. * 2. A. B. C. * D. E. 3. A. B. C. D. E. * 4. A. * B. C. D. E. 5. A. B. C. * D. E. A 52-year-old obese woman complains of bloody discharges from sexual organs during 4 days. Last normal menses were 2 years ago. At histological investigation adenomatous hyperplasia was revealed. What is reason of mentioned pathology ? Supersecretion of androgens by the cortex of paranephroses Hypersecretion of estrogens by tissues of the organism. Poor aromatization of preandrogens due to hypothyroidism The increased contents of follicle-stimulating hormone Excessive transformation of preandrogens from adipose tissues. A 40-year-old woman complains of yellow color discharges from the vagina. There are no pathological changes in bimanual examination. Bacterioscopy reveals Trichomonas vaginalis and mixed flora. There are two hazy fields on the front labium, with a negative Iodum probing at colposcopy. What is your tactics? Specific treatment of Trichomonas colpitis Diathermocoagulation of the cervix uteri Treatment of specific colpitis with the subsequent biopsy Cervix ectomy Cryolysis of cervix uteri A woman complains of having slight dark bloody discharges and mild pains in the lower part of abdomen for several days. Last menstrual perid were 7 weeks ago. The pregnancy test is positive. Uterine body is enlarged to 5-6 weeks of pregnancy, soft, painless. There is a retort-like formation, 7х5 cm large, mobile, painless in the region of the adnexa. What examination is necessary for detection of conceptus localization? Cystoscopy Hysteroscopy Hromohydrotubation Colposcopy Ultrasound A 24-year-old woman complains of amenorrhea at 13 month after cesarean section. Cesarian section was performed as a result of placenta abruption. The total amount of blood loss was 2000 ml due to coagulation disorders.Choose the most suitable investigation. Determination of the level of gonadotropin Ultrasound of organs of a small pelvis Progesteron test Computer tomography of the head Determination of the contents of testosteron-depotum in blood serum. 27-year-old patient complained of amenorrhea after Caesarian section at 15 month. Cesarean section was performed because of Placental Abruption. Choose the most suitable investigation: Progesteron test USI of small pelvis organs Estimation of gonadotropin rate Computer tomography of head Estimation of testosteron rate in blood serum 6. A. * B. C. D. E. 7. A. B. * C. D. E. 8. A. * B. C. D. E. 9. A. B. C. D. * E. 10. A. * B. C. D. E. 11. A. * B. C. D. E. In the woman of 24 years about earlier normal menstrual function, cycles became irregular, according to tests of function diagnostics - anovulatory. The contents of prolactin in blood is boosted. Choose the most suitable investigation: Computer tomography of the head Determination of the level of gonadotropins USI of organs of small pelvis Progesterone assay Determination of the contents of testosteron-depotum in blood serum A 29 year old patient underwent surgical treatment because of the benign serous epithelial tumour of an ovary. The postoperative period has elapsed without complications. What is it necessary to prescribe for the rehabilitational period: Antibacterial therapy and adaptogens Hormonotherapy and proteolytic enzymes Lasertherapy and enzymotherapy Magnitotherapy and vitamin therapy The patient does not require further care A 26 y.o. woman complains of sudden pains in the bottom of abdomen irradiating to the anus, nausea, giddiness, bloody dark discharges from sexual tracts for one week, the delay of menses for 4 weeks. Signs of the peritoneum irritation are positive. Bimanual examination: borders of the uterus body and its appendages are not determined because of sharp painfullness. The painfullness of the back and dextral fornixes of the vagina are evident. What is the most probable diagnosis? Ruptured tubal pregnancy Apoplexy of the ovary Acute right-side adnexitis Torsion of the crus of the ovary tumour Acute appendicitis At the gynaecological department there is a patient of 32 years with the diagnosis: "acute bartholinitis".Body temperature is 38,2 0C, leucocytes count 10,4*109/L, the ESR is 24 mm/hour. In the area of big gland of the vestibulum - the dermahemia, the sign of the fluctuation, sharp tenderness (pain). What is the most correct tactics of the doctor? Antibiotic therapy Antibiotics, Sulfanilamidums Surgical dissection, drainage of the abscess of the gland Surgical dissecting, a drainage of an abscess of the gland, antibiotics Antibiotics, detoxication and biostimulants. An onset of severe preeclampsia at 16 weeks gestation might be caused by: Hydatidiform mole Anencephaly Twin gestation Maternal renal disease Interventricular defect of the fetus Which of the methods of examination is the most informative in the diagnostics of a tubal infertility? Laparoscopy with chromosalpingoscopy Pertubation Hysterosalpingography Transvaginal echography Bicontrast pelviography 12. A. B. C. D. * E. 13. A. * B. C. D. E. 14. A. * B. C. D. E. 15. A. B. C. * D. E. 16. A. * B. C. A 26 y.o. woman complains of a mild bloody discharge from the vagina and pain in the lower abdomen. She has had the last menstruation 3,5 months ago. The pulse is 80 bpm. The blood pressure (BP) is 110/60 mm Hg and body temperature is 36,6 0C. The abdomen is tender in the lower parts. The uterus is enlarged up to 12 weeks of gestation. What is your diagnosis? Complete abortion Incipient abortion Incomplete abortion Inevitable abortion Disfunctional bleeding A18 y.o. woman complains of pain in the lower abdomen. Some minutes before she has suddenly appeared unconscious at home. The patient had no menses within last 3 months.On examination: pale skin, the pulse- 110 bpm, BP- 80/60 mm Hg. The Schyotkin's sign is positive. Hb- 76 g/L. The vaginal examination: the uterus is a little bit enlarged, its displacement is painful. There is also any lateral swelling of indistinct size. The posterior fornix of the vagina is tendern and overhangs inside. What is the most probable diagnosis? Ruptured ectopic Ovarian apoplexy Twist of cystoma of right uterine adnexa Acute salpingoophoritis Acute appendicitis In the gynecologic office a 28 y.o. woman complains of sterility within three years. The menstrual function is not impaired. There were one artificial abortion and chronic salpingo-oophoritis in her case history. Oral contraceptives were not used. Her husband's analysis of semen is without pathology. What diagnostic method will you start from the workup in this case of sterility? Hysterosalpingography Hormone investigation Ultra sound investigation Diagnostic scraping out of the uterine cavity Hysteroscopia A 28-year-old patient underwent endometrectomy as a result of incomplete abortion. Blood loss was at the rate of 900 ml. It was necessary to start hemotransfusion. After transfusion of 60 ml of erythrocytic mass the patient presented with lumbar pain and fever which resulted in hemotransfusion stoppage. 20 minutes later the patient's condition got worse: she developed adynamia, apparent skin pallor, acrocyanosis, profuse perspiration. t- 38,5 0C, Ps-110/min, AP- 70/40 mm Hg. What is the most likely diagnosis? Septic shock Hemorrhagic shock Hemotransfusion shock Anaphylactic shock DIC syndrome A 58-year-old female patient came to the antenatal clinic with complaints of bloody light-red discharges from the genital tracts. Menopause is 12 years. Gynaecological examination found externalia and vagina to have age involution; uterine cervix was unchanged, there were scant bloody discharges from uterine cervix, uterus was of normal size; uterine adnexa were not palpable; parametria were free. What is the most likely diagnosis? Uterine carcinoma Atrophic colpitis Abnormalities of menstrual cycle with climacteric character D. E. 17. A. B. * C. D. E. 18. A. * B. C. D. E. 19. A. B. * C. D. E. 20. A. * B. C. D. E. 21. A. B. * C. D. E. 22. Cervical carcinoma Granulosa cell tumor of ovary The results of a separate diagnostic curettage of the mucous of the uterus' cervix and body made up in connection with bleeding in a postmenopausal period: the scrape of the mucous of the cervical canal revealed no pathology, in endometrium - the highly differentiated adenocarcinoma was found. Metastases are not found. What method of treatment is the most correct? Surgical treatment and chemotherapy Surgical treatment and hormonotherapy Surgical treatment and radial therapy Radial therapy all are wrong A 27 y.o. woman complains of having the disoders of menstrual function for 3 months, irregular pains in abdomen. On bimanual examination: in the right adnexa of uterus there is an elastic spherical formation, painless, 7 cm in diameter. USI: in the right ovary - a fluid formation, 4 cm in diameter, unicameral, smooth. What method of treatment is the most preferable? Prescription of an estrogen-gestogen complex for 3 months with repeated examination Operative treatment Dispensary observation of the patient Anti-inflammatory therapy Chemotherapeutic treatment A 40 year old patient complains of yellowish discharges from the vagina. Bimanual examination revealed no pathological changes. The smear contains Trichomonas vaginalis and blended flora. Colposcopy revealed two hazy fields on the frontal labium, with a negative Iodine test. Your tactics: Diathermocoagulation of the cervix of the uterus Treatment of specific colpitis and subsequent biopsy Specific treatment of Trichomonas colpitis Cervix ectomy Cryolysis of cervix of the uterus A 48 year old female patient complains about contact haemorrhage. Speculum examination revealed hypertrophy of uterus cervix. It resembles of cauliflower, it is dense and can be easily injured. Bimanual examination revealed that fornices were shortened, uterine body was nonmobile. What is the most probable diagnosis? Cervical carcinoma Metrofibroma Endometriosis Cervical pregnancy Cervical papillomatosis Laparotomy was performed to a 54 y.o. woman on account of big formation in pelvis that turned out to be one-sided ovarian tumor along with considerable omental metastases. The most appropriate intraoperative tactics involves: Biopsy of omentum Ablation of omentum, uterus and both ovaries with tubes Biopsy of an ovary Ablation of an ovary and omental metastases Ablation of omentum and both ovaries with tubes A parturient complains about pain in the mammary gland. Palpation revealed a 3х4 cm large infiltration, soft in the centre. Body temperature is 38,5oC. What is the most probable diagnosis? A. * B. C. D. E. 23. A. B. C. D. * E. 24. A. * B. C. D. E. 25. A. B. C. D. E. * 26. A. * B. C. D. E. 27. A. B. Acute purulent mastitis Pneumonia Pleuritis Retention of milk Birth trauma A 43 y.o. patient complains of formation and pain in the right mammary gland, rise of temperature up to (37,20C) during the last 3 months. Condition worsens before the menstruation. On examination: edema of the right breast, hyperemia, retracted nipple. Unclear painful infiltration is palpated in the lower quadrants. What is the most probable diagnosis? Premenstrual syndrome Right-side acute mastitis Right-side chronic mastitis Cancer of the right mammary gland Tuberculosis of the right mammary gland A 14 year old girl complains of profuse bloody discharges from genital tracts during 10 days after suppresion of menses for 1,5 month. Similiar bleedings recur since 12 years on the background of disordered menstrual cycle. On rectal examination: no pathology of the internal genitalia. In blood: Нb - 70 g/l, RBC- 2,3*1012 l, Ht - 20. What is the most probable diagnosis? Juvenile bleeding, posthemorrhagic anemia Werlholf's disease Polycyst ovarian syndrome Hormonoproductive ovary tumor Incomplete spontaneous abortion A 33-year-old woman was urgently brought to clinic with complaints of the pain in the lower part of the abdomen, mostly on the right, irradiating to rectum, she also felt dizzy. The above mentioned complaints developed acutely at night. Last menses were 2 weeks ago. On physical exam: the skin is pale, Ps - 92 bpm, t- 36,6 0C, BP- 100/60 mm Hg. The abdomen is tense, slightly tender in lower parts, peritoneal symptoms are slightly positive. Hb- 98 g/L. What is the most probable diagnosis? Renal colic Acute appendicitis Intestinal obstruction Abdominal pregnancy Apoplexy of the ovary A 54-year-old female patient consulted a doctor about bloody discharges from the genital tracts after 2 years of amenorrhea. USI and bimanual examination revealed no genital pathology. What is the tactics of choice? Fractional biopsy of lining of uterus and uterine mucous membranes Styptic drugs Contracting drugs Estrogenic haemostasia Hysterectomy A 27 y.o. gravida with 17 weeks of gestation was admitted to the hospital. There was a history of 2 spontaneous miscarriages. On bimanual examination: uterus is enlarged to 17 weeks of gestation, uterus cervix is shortened, isthmus allows to pass the finger tip. The diagnosis is isthmico-cervical insufficiency. What is the doctor's tactics? To interrupt pregnancy To administer tocolytic therapy C. * D. E. 28. A. B. C. D. * E. 29. A. B. C. * D. E. 30. A. * B. C. D. E. 31. A. B. * C. D. E. 32. A. B. To place suture on the uterus cervix To administer hormonal treatment To perform amniocentesis A 27 y.o. woman turns to the maternity welfare centre because of infertility. She has had sexual life in marriage for 4 years, doesn't use contraceptives. She didn't get pregnant. On examination: genital development is without pathology, uterus tubes are passable, basal (rectal) temperature is one-phase during last 3 menstrual cycles. What is the infertility cause? Immunologic infertility Chronic adnexitis Abnormalities in genital development Anovular menstrual cycle Genital endometriosis A 43 y.o. woman complains of contact hemorrhages during the last 6 months. Bimanual examination: cervix of the uterus is enlarged, its mobility is reduced. Mirrors showed the following: cervix of the uterus is in the form of cauliflower. Chrobak and Schiller tests are positive. What is the most probable diagnosis? Cervical pregnancy Polypus of the cervis of the uterus Cancer of cervix of the uterus Nascent fibroid Leukoplakia A primagravida in her 20th week of gestation complains of pain in her lower abdomen, blood smears from the genital tracts. The uterus has an increased tonus, the patient feels the fetus movements. Bimanual examination revealed that the uterus size corresponded with gestation, the uterine cervix was contracted down to 0,5 cm, the external os was dilatated by 2 cm. The discharges were bloody and smeary. What is the most likely diagnosis? Incipient abortion Risk of abortion Abortion in progress Incomplete abortion Missed miscarriage A patient was admitted to the hospital with complaints of periodical pain in the lower part of abdomen that gets worse during menses, weakness, malaise, nervousness, dark bloody smears from vagina directly before and after menses. Bimanual examination revealed that uterus body is enlarged, appendages cannot be palpated, posterior fornix has tuberous surface. Laparoscopy revealed: ovaries, peritoneum of rectouterine pouch and pararectal fat have "cyanotic eyes". What is the most probable diagnosis? Polycystic ovaries Disseminated form of endometriosis Chronic salpingitis Tuberculosis of genital organs Ovarian cystoma A pregnant woman in her 8th week was admitted to the hospital for artificial abortion. In course of operation during dilatation of cervical canal of uterus by means of Hegar's dilator № 8 the doctor suspected uterus perforation. What is the immediate tactics for confirmation of this diagnosis? Laparoscopy Bimanual examination C. D. * E. 33. A. * B. C. D. E. 34. A. B. C. * D. E. 35. A. B. * C. D. E. 36. A. B. C. * D. E. 37. A. B. C. D. E. * US examination Uterine probing Metrosalpingography A 59 year old female patient applied to a maternity clinic and complained about bloody discharges from the genital tracts. Postmenopause is 12 years. Vaginal examination revealed that external genital organs had signs of age involution, uterus cervix was not erosive, small amount of bloody discharges came from the cervical canal. Uterus was of normal size, uterine appendages were unpalpable. Fornices were deep and painless. What method should be applied for the diagnosis specification? Separated diagnosic curretage Laparoscopy Puncture of abdominal cavity through posterior vaginal fornix Extensive colposcopy Culdoscopy A 25-year-old woman complains of profuse foamy vaginal discharges, foul, burning and itching in genitalia region. She has been ill for a week. Extramarital sexual life. On examination: hyperemia of vaginal mucous, bleeding on touching, foamy leucorrhea in the urethral area. What is the most probable diagnosis? Chlamydiosis Gonorrhea Trichomonas vaginitis Vagina candidomicosis Bacterial vaginosis A 13 year old girl consulted the school doctor on account of moderate bloody discharge from the genital tracts, which appeared 2 days ago. Secondary sexual characters are developed.What is the most probable cause of bloody discharge? Juvenile hemorrhage Menarche Haemophilia Endometrium cancer Werlhof's disease After examination a 46-year-old patient was diagnosed with left breast cancer T2N2M0, cl. gr.II-a. What will be the treatment plan for this patient? Operation + radiation therapy Operation only Radiation therapy + operation + chemotherapy Radiation therapy only Chemotherapy only During examination of a patient, masses in the form of condyloma on a broad basis are found in the area of the perineum. What is the tactics of the doctor? Antiviral treatment Cryodestruction of condyloms Surgical ablation of condyloms Chemical coagulator treatment To schgend a woman into dermatological and venerological centre 38. A. * B. C. D. E. 39. A. B. * C. D. E. 40. A. * B. C. D. E. 41. A. B. C. * D. E. 42. A. B. C. D. * E. A 28 year old woman has bursting pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation; chocolate-like discharges from vagina. It is known from the anamnesis that the patient suffers from chronic adnexitis. Bimanual examination revealed a tumour-like formation of heterogenous consistency 7х7 cm large to the left from the uterus. The formation is restrictedly movable, painful when moved. What is the most probable diagnosis? Endometrioid cyst of the left ovary Follicular cyst of the left ovary Fibromatous node Exacerbation of chronic adnexitis Tumour of sigmoid colon A 68-year-old patient consulted a doctor about a tumour in her left mammary gland.Objectively: in the upper internal quadrant of the left mammary gland there is a neoplasm up to 2,5 cm in diameter, dense, uneven, painless on palpation. Regional lymph nodes are not enlarged. What is the most likely diagnosis? Cyst Cancer Fibroadenoma Mastopathy Lipoma A 40-year-old female patient has been observing profuse menses accompanied by spasmodic pain in the lower abdomen for a year. Bimanual examination performed during menstruation revealed a dense formation up to 5 cm in diameter in the cervical canal. Uterus is enlarged up to 5-6 weeks of pregnancy, movable, painful, of normal consistency. Appendages are not palpable. Bloody discharges are profuse. What is the most likely diagnosis? Protruded submucous fibromatous node Abortion in progress Cervical carcinoma Cervical myoma Algodismenorrhea A 29-year-old patient complains of sterility. Sexual life is for 4 years being married, does not use contraception. There was no pregnancy before. On physical examination, genitals are developed normally. Uterine tubes are passable. Rectal temperature during three menstrual cycles is monophase. What is the most probable reason for sterility? Anomalies of genitals development Chronic adnexitis Anovulatory menstrual cycle Immunologic sterility Genital endometriosis A 45 y.o. woman complains of contact bleedings during 5 months. On speculum examination: hyperemia of uterus cervix, looks like cauliflower, bleeds on probing. On bimanual examination: cervix is of densed consistensy, uterus body isn't enlarged, mobile, nonpalpable adnexa. What is the most likely diagnosis? Cervical pregnancy Cancer of body of uterus uterine cancer Fibromatous node which is being born cervical cancer Polypose uterine cervix 43. A. * B. C. D. E. 44. A. B. C. D. * E. 45. A. B. C. D. E. * 46. A. * B. C. D. E. 47. A. * B. C. D. E. A 20 y.o. patient complains of amenorrhea. Objectively: hirsutism, obesity with fat tissue prevailing on the face, neck, upper part of body. On the face there are acne vulgaris, on the skin - striae cutis distense. Psychological and intellectual development is normal. Gynecological condition: external genitals are moderately hairy, acute vaginal and uterine hypoplasia. What diagnosis is the most probable? Itsenko-Cushing syndrome Turner's syndrome Stein-Levental's syndrome Shichan's syndrome Babinski-Froehlich syndrome A 27 y.o. woman suffers from pyelonephritits of the single kidney. She presents to the maternity centre because of suppresion of menses for 2,5 months. On examination pregnancy 11 weeks of gestation was revealed. In urine: albumine 3,3 g/L, leucocytes cover the field of vision. What is doctor's tactics in this case? Pregnancy interruption at 24-25 weeks Pregnancy interruption after urine normalization Maintenance of pregnancy till 36 weeks Immediate pregancy interruption Maintenance of pregnancy till delivery term A 24-year-old female patient complains of acute pain in the lower abdomen that turned up after a physical stress. She presents with nausea, vomiting, dry mouth and body temperature 36,6 0C. She has a right ovarian cyst in history. Bimanual examination reveals that uterus is dense, painless, of normal size. The left fornix is deep, uterine appendages aren't palpable, the right fornix is contracted. There is a painful formation on the right of uterus. It's round, elastic and mobile. It is 7х8 cm large. In blood: leukocytosis with the left shit. What is the most likely diagnosis? Extrauterine pregnancy Right-sided pyosalpinx Subserous fibromyoma of uterus Acute metritis Ovarian cyst with pedicle torsion A woman was hospitalised with full-term pregnancy. Examination: the uterus is tender, the abdomen is tense, fetal heart tone is. What is the most probable complication of pregnancy? Placental abruptio absent Premature labor Back occipital presentation Acute hypoxia of a fetus Hydramnion A pregnant woman in her 40th week of pregnancy undergoes obstetric examination: the cervix of uterus is undeveloped. The oxytocin test is negative. Examination at 32 weeks revealed: AP 140/90 mm Hg, proteinuria 1 g/l, peripheral edemata. Reflexes are normal. Choose the most correct tactics: Labour stimulation after preparation Absolute bed rest for 1 month Complex therapy of gestosis for 2 days Caesarian section immediately Complex therapy of gestosis for 7 days 48. A. * B. C. D. E. 49. A. B. * C. D. E. 50. A. B. C. D. * E. 51. A. B. * C. D. E. 52. A. * B. C. D. E. A 26 year old woman had the second labour within the last 2 years with oxytocin application. The child's weight is 4080 g. After the placent birth there were massive bleeding, signs of hemorrhagic shock. Despite the injection of contractive agents, good contraction of the uterus and absence of any cervical and vaginal disorders, the bleeding proceeds. Choose the most probable cause of bleeding: Atony of the uterus Injury of cervix of the uterus Hysterorrhexis Delay of the part of placenta Hypotonia of the uterus A woman is admitted to maternity home with discontinued labor activity and slight bloody discharges from vagina. The condition is severe, the skin is pale, consciousness is confused. BP is 80/40 mm Hg. Heartbeat of the fetus is not heard. There was a Cesarian section a year ago. Determine the diagnosis? Cord presentation Uterus rupture Placental presentation Expulsion of the mucous plug from cervix uteri Premature expulsion of amniotic fluid Rise in temperature up to 39 0С was registered the next day after a woman had labor. Fetal membranes rupture took place 36 hours prior to labors. The examination of the bacterial flora of cervix uteri revealed the following: haemolytic streptococcus of group A. The uterus tissue is soft, tender. Discharges are bloody, with mixing of pus. Establish the most probable postnatal complication. Infective contamination of the urinary system Thrombophlebitis of veins of the pelvis Infected hematoma Metroendometritis Apostatis of stitches after the episiotomy On the first day after labour a woman had the rise of temperature up to 39 0C. Rupture of fetal membranes took place 36 hours before labour. Examination of the bacterial flora of cervix of the uterus revealed hemocatheretic streptococcus of A group. The uterus body is soft, tender. Discharges are bloody, with admixtures of pus. Specify the most probable postnatal complication: Thrombophlebitis of veins of the pelvis Metroendometritis Infectious hematoma Infective contamination of the urinary system Apostasis of sutures after the episiotomy A woman of a high-risk group (chronic pyelonephritis in anamnesis) had vaginal delivery. The day after labour she complained of fever and loin pains, frequent urodynia. Specify the most probable complication: Infectious contamination of the urinary system Thrombophlebitis of veins of the pelvis Infectious hematoma Endometritis Apostasis of sutures after episiotomy 53. A. * B. C. D. E. 54. A. * B. C. D. E. 55. A. * B. C. D. E. 56. A. * B. C. D. E. 57. A. * B. C. D. E. 58. A. In 8 months after the first labor a 24-year-old woman complains of amenorrhea. Cesarian section was conducted as a result of abruption of placenta. Hemorrhage has made low fidelity of 2000 ml due to breakdown of coagulation of blood. Choose the most suitable investigation. Determination of the level of gonadotropin Ultrasound of organs of a small pelvis Progesteron test Computer tomography of the head Determination of the contents of testosteron-depotum in blood serum. A 34 y.o. woman in her 29-th week of pregnancy, that is her 4-th labor to come, was admitted to the obstetric department with complaints of sudden and painful bloody discharges from vagina that appeared 2 hours ago. The discharges are profuse and contain grumes. Cardiac funnction of the fetus is rhytmic, 150 strokes in the minute, uterus tone is normal. The most probable provisional diagnosis will be: Placental presentation Detachment of normally located placenta Vasa previa Bloody discharges Disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome A 34-year-old woman with 10-week pregnancy (the second pregnancy) has consulted gynaecologist to make a record in patient chart. There was a hydramnion previous pregnancy, the birth weight of a child was 4086 g. What tests are necessary first of all? The test for tolerance to glucose Determination of the contents of \alpha fetoprotein Bacteriological test of discharge from the vagina Fetus cardiophonography Ultrasound of the fetus A primagravida with pregnancy of 37-38 weeks complains of headache, nausea, pain in epigastrium. Objective: the skin is acyanotic. Face is hydropic, there is short fibrillar twitching of blepharons, muscles of the face and the inferior extremities. The look is fixed. AP- 200/110 mm Hg; sphygmus of 92 bpm, intense. Respiration rate is 32/min. Heart activity is rhythmical. Appreciable edemata of the inferior extremities are present. Urine is cloudy. What medication should be administered? Droperidolum of 0,25% - 2,0 ml Dibazolum of 1% - 6,0 ml Papaverine hydrochloride of 2% - 4,0 ml Hexenalum of 1% - 2,0 ml Pentaminum of 5% - 4,0 ml An onset of severe preeclampsia at 16 weeks gestation might be caused by: Hydatidiform mole Anencephaly Twin gestation Maternal renal disease Interventricular defect of the fetus A woman had the rise of temperature up to 38,5?С on the first day after labour. The rupture of fetal membranes took place 36 hours before labour. The investigation of the bacterial flora of cervix of the uterus revealed hemocatheretic streptococcus of group A. The uterus body is soft, tender. Discharges are bloody, mixed with pus. Specify the most probable postnatal complication: Apostatis of junctures after the episiotomy B. C. D. E. * 59. A. * B. C. D. E. 60. A. * B. C. D. E. 61. A. * B. C. D. E. 62. A. * B. C. D. E. 63. A. * B. C. Thrombophlebitis of pelvic veins Infected hematoma Infection of the urinary system Metroendometritis A pregnant woman may be diagnosed with hepatitis if it is confirmed by the presence of elevated: SGOT (ALT) Sedimentation rates WBCs Alkaline phosphatase BUN A pregnant woman (35 weeks), aged 25, was admitted to the hospital because of bloody discharges. In her medical history there were two artificial abortions. In a period of 28-32 weeks there was noted the onset of hemorrhage and USD showed a placental presentation. The uterus is in normotonus, the fetus position is transversal (Ist position). The heartbeats is clear, rhythmical, 140 bpm. What is the further tactics of the pregnant woman care? To perform a delivery by means of Cesarean section To perform the hemotransfusion and to prolong the pregnancy To introduct the drugs to increase the blood coagulation and continue observation Stimulate the delivery by intravenous introduction of oxytocin To keep the intensity of hemorrhage under observation and after the bleeding is controlled to prolong the pregnancy Condition of a parturient woman has been good for 2 hours after live birth: uterus is thick, globe-shaped, its bottom is at the level of umbilicus, bleeding is absent. The clamp put on the umbilical cord remains at the same level, when the woman takes a deep breath or she is being pressed over the symphysis with the verge of hand, the umbilical cord drows into the vagina. Bloody discharges from the sexual tracts are absent. What is the doctor's further tactics? To do manual removal of afterbirth To apply Abduladze method To apply Crede's method To do curettage of uterine cavity To introduct oxitocine intravenously The woman who has delivered twins has early postnatal hypotonic uterine bleeding reached 1,5% of her bodyweight. The bleeding is going on. Conservative methods to arrest the bleeding have been found ineffective. The conditions of patient are pale skin, acrocyanosis, oliguria. The woman is confused. The pulse is 130 bpm, BP– 75/50 mm Hg. What is the further treatment? Uterine extirpation Supravaginal uterine amputation Uterine vessels ligation Inner glomal artery ligation Putting clamps on the uterine cervix A 37 y.o. primigravida woman has been having labor activity for 10 hours. Labor pains last for 20-25 seconds every 6-7 minutes. The fetus lies in longitude, presentation is cephalic, head is pressed upon the entrance to the small pelvis. Vaginal examination results: cervix of uterus is up to 1 cm long, lets 2 transverse fingers in. Fetal bladder is absent. What is the most probable diagnosis? Primary uterine inertia Secondary uterine inertia Normal labor activity D. E. 64. A. * B. C. D. E. 65. A. B. C. D. * E. 66. A. * B. C. D. E. 67. A. * B. C. D. E. 68. A. * B. C. D. Discoordinated labor activity Pathological preliminary period A 26 y.o. woman complains of a mild bloody discharge from the vagina and pain in the lower abdomen. She has had the last menstruation 3,5 months ago. The pulse is 80 bpm. The blood pressure (BP) is 110/60 mm Hg and body temperature is 36,6 0C. The abdomen is tender in the lower parts. The uterus is enlarged up to 12 weeks of gestation. What is your diagnosis? Inevitable abortion Incipient abortion Incomplete abortion Complete abortion Disfunctional bleeding A 20 y.o. pregnant woman with 36 weeks of gestation was admitted to the obstetrical hospital with complains of pain in the lower abdomen and bloody vaginal discharge. The general condition of the patient is good. Her blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg. The heart rate of the fetus is 140 bpm, rhythmic. Vaginal examination: the cervix of the uterus is formed and closed. The discharge from vagina is bloody up to 200 ml per day. The head of the fetus is located high above the pelvis inlet. A soft formation was defined through the anterior fornix of the vagina. What is the probable diagnosis? Premature placental separation Uterine rupture Threatened premature labor Placental presentation Incipient abortion A 28-year-old parturient complains about headache, vision impairment, psychic inhibition. Objectively: AP- 200/110 mm Hg, evident edemata of legs and anterior abdominal wall. Fetus head is in the area of small pelvis. Fetal heartbeats is clear, rhythmic, 190/min. Internal examination revealed complete cervical dilatation, fetus head was in the area of small pelvis. What tactics of labor management should be chosen? Forceps operation Cesarean Embryotomy Conservative labor management with episiotomy Stimulation of labor activity A 25 year old woman had the third labour and born a girl with manifestations of anemia and progressing jaundice. The child's weight was 3 600 g, the length was 51 cm. The woman's blood group is B (III) Rh-, the father's blood group is A (III) Rh+, the child's blood group is B (III) Rh+. What is the cause of anemia? Rhesus incompatibility Antigen A incompatibility Antigen B incompatibility Antigen AB incompatibility Intrauterine infection A parturient complains about pain in the mammary gland. Palpation revealed a 3х4 cm large infiltration, soft in the centre. Body temperature is 38,5 0C. What is the most probable diagnosis? Acute purulent mastitis Pneumonia Pleuritis Retention of milk E. 69. A. * B. C. D. E. 70. A. * B. C. D. E. 71. A. * B. C. D. E. 72. A. * B. C. D. E. 73. A. * B. C. D. E. Birth trauma A secundipara has regular birth activity. Three years ago she had cesarean section for the reason of acute intrauterine hypoxia. During labor she complains of extended pain in the area of postsurgical scar. Objectively: fetus pulse is rhythmic - 140 bpm. Vaginal examination shows 5 cm cervical dilatation. Fetal bladder is intact. What is the tactics of choice? Cesarean section Augmentation of labour Obstetrical forceps Waiting tactics of labor management Vaginal delivery A primagravida in her 20th week of gestation complains about pain in her lower abdomen, blood smears from the genital tracts. The uterus has an increased tonus, the patient feels the fetus movements. Bimanual examination revealed that the uterus size corresponded the term of gestation, the uterine cervix was contracted down to 0,5 cm, the external orifice was open by 2 cm. The discharges were bloody and smeary. What is the most likely diagnosis? Incipient abortion Risk of abortion Abortion in progress Incomplete abortion Missed miscarriage A woman consulted a doctor on the 14th day after labour about sudden pain, hyperemy and induration of the left mammary gland, body temperature rise up to 39oC, headache. Objectively: fissure of nipple, enlargement of the left mammary gland, pain on palpation. What pathology would you think about in this case? Lactational mastitis Lacteal cyst with suppuration Fibrous adenoma of the left mammary gland Breast cancer Phlegmon of mammary gland A young woman applied to gynecologist due to her pregnancy of 4-5 weeks. The pregnancy is desirable. Anamnesis stated that she had rheumatism in the childhood. Now she has combined mitral heart disease with the priority of mitral valve deficiency. When will she need the inpatient treatment (what periods of pregnancy)? 8-12 weeks, 28–32 weeks, 37 weeks 6-7weeks, 16 weeks, 38 weeks 16 weeks, 34 weeks, 39-40 weeks 10-12 weeks, 24 weeks, 37-38 weeks 12-16 weeks, 27-28 weeks, 37-38 weeks A woman in the first half of pregnancy was brought to clinic by an ambulance. Term of pregnancy is 36 weeks. She complains of intensive pain in the epigastrium, had vomiting for 2 times. Pain started after the patient had eaten vinaigrette. Swelling of lower extremities. BP - 140/100 mm Hg. Urine became curd after boiling. What is the most probable diagnosis? Preeclampsia Nephropathy of the 3rd degree Food toxicoinfection Dropsy of pregnant women Exacerbation of pyelonephritis 74. A. * B. C. D. E. 75. A. * B. C. D. E. 76. A. * B. C. D. E. 77. A. * B. C. D. E. 78. A. * B. C. D. E. Immediately after delivery a woman had haemorrhage, blood loss exceeded postpartum haemorrhage rate and was progressing. There were no symptoms of placenta detachment. What tactics should be chosen? Manual removal of placenta and afterbirth Uterus tamponade Instrumental revision of uterine cavity walls Removal of afterbirth by Crede's method Intravenous injection of methylergometrine with glucose A 30 y.o. woman has the 2-nd labour that has been lasting for 14 hours. Hearbeat of fetus is muffled, arrhythmic, 100/min. Vaginal examination: cervix of uterus is completely opened, fetus head is in outlet from small pelvis. Saggital suture is in the straight diameter, small is near symphysis. What is the further tactics of handling the delivery? Use of obstetrical forceps Stimulation of labour activity by oxytocin Cesarean section Cranio-cutaneous (Ivanov's) forceps Use of cavity forceps In10 minutes after delivery a woman discharged placenta with a tissue defect 5х6 cm large. Discharges from the genital tracts were bloody profuse. Uterus tonus was low, fundus of uterus was located below the navel. Examination of genital tracts revealed that the uterine cervix, vaginal walls, perineum were intact. There was uterine bleeding with following blood coagulation. Your actions to stop the bleeding: To make manual examination of uterine cavity To apply hemostatic forceps upon the uterine cervix To introduce an ether-soaked tampon into the posterior fornix To put an ice pack on the lower abdomen To administer uterotonics On the 5th day after labor body temperature of a 24-year-old parturient suddenly rose up to 38,7 0C. She complains about weakness, headache, abdominal pain, irritability. Objectively: AP- 120/70 mm Hg, Ps- 92 bpm, t- 38,7 0C. Bimanual examination revealed that the uterus was enlarged up to 12 weeks of pregnancy, it was dense, slightly painful on palpation. Cervical canal dilated for two fingers, discharges are moderate, turbid, with foul smell. In blood: leykocytosis, lymphopenia, ESR 30 mm/h. What is the most likely diagnosis? Endometritis Parametritis Pelviperitonitis Metrophlebitis Lochiometra A 27 y.o. gravida with 17 weeks of gestation was admitted to the hospital. There was a history of 2 spontaneous miscarriages. On bimanual examination: uterus is enlarged to 17 weeks of gestation, uterus cervix is shortened, isthmus allows to pass the finger tip. The diagnosis is isthmico-cervical insufficiency. What is the doctor's tactics? To place suture on the uterus cervix To administer tocolytic therapy To interrupt pregnancy To administer hormonal treatment To perform amniocentesis 79. A. * B. C. D. E. 80. A. * B. C. D. E. 81. A. * B. C. D. E. 82. A. * B. C. D. E. 83. A. * B. C. D. E. Examination of a just born placenta reveals defect 2x3 cm large. Hemorrhage is absent. What tactic is the most reasonable? Manual exploration of uterine cavity Prescription of uterotonic medicines External uterus massage Parturient supervision Uterine curretage On the tenth day after discharge from the maternity house a 2-year-old patient consulted a doctor about body temperature rise up to 39єC, pain in the right breast. Objectively: the mammary gland is enlarged, there is a hyperemized area in the upper external quadrant, in the same place there is an ill-defined induration, lactostasis, fluctuation is absent. Lymph nodes of the right axillary region are enlarged and painful. What is the most likely diagnosis? Lactation mastitis Abscess Erysipelas Dermatitis Tumour A 28-years-old woman complains of nausea and vomiting about 10 times per day. She has been found to have body weight loss and xerodermia. The pulse is 100 bpm. Body temperature is 37,20C. Diuresis is low. USI shows 5-6 weeks of pregnancy. What is the most likely diagnosis? Moderate vomiting of pregnancy Mild vomiting of pregnancy I degree preeclampsia Premature abortion Food poisoning A 25 y.o. patient complains of body temperature rise up to 37 0С, pain at the bottom of her abdomen and vaginal discharges. Three days ago, when she was in her 11th week of pregnancy, she had an artificial abortion. Objectibely: cervix of uterus is clean, uterus is a little bit enlarged in size, painful. Appendages cannot be determined. Fornixes are deep, painless. Vaginal discharges are sanguinopurulent. What is the most probable diagnosis? Postabortion endometritis Hematometra Pelvic peritonitis Postabortion uterus perforation Parametritis A 25 y.o. pregnant woman in her 34th week was taken to the maternity house in grave condition. She complains of headache, visual impairment, nausea. Objectively: solid edemata, AP- 170/130 mm Hg. Suddenly there appeared fibrillary tremor of face muscles, tonic and clonic convulsions, breathing came to a stop. After 1,5 minute the breathing recovered, there appeared some bloody spume from her mouth. In urine: protein - 3,5 g/L. What is the most probable diagnosis? Eclampsia Epilepsy Cerebral hemorrhage Cerebral edema Stomach ulcer 84. A. * B. C. D. E. 85. A. * B. C. D. E. 86. A. * B. C. D. E. 87. A. * B. C. D. E. 88. A. * B. C. D. A primigravida woman appealed to the antenatal clinic on the 22.03.09 with complaints of boring pain in the lower part of abdomen. Anamnesis registered that her last menstruation was on the 4.01.03. Bimanual examination revealed that uterine servix is intact, external os is closed, uterus is enlarged up to the 9-th week of pregnancy, movable, painless. What complication can be suspected? Risk of abortion in the 9-th week of pregnancy Initial in the 9-th week of pregnancy Hysteromyoma Vesicular mole Pathological preliminary period An ambulance delivered a 21-year-old woman to the gynaecological department with complaints of colicky abdominal pain and bloody discharges from the genital tracts. Bimanual examination revealed that uterus was soft, enlarged to the size of 6 weeks of gestation, a gestational sac was palpated in the cervical canal. Uterine appendages weren't palpable. Fornices are free, deep and painless. Discharges from the genital tracts are bloody and profuse. What is the most likely diagnosis? Inavitable abortion Cervical pregnancy Threat of abortion Incipient abortion Interrupted fallopian pregnancy A woman is 34 years old, it is her tenth labor at full term. It is known from the anamnesis that the labor started 11 hours ago, labor was active, painful contractions started after discharge of waters and became continuous. Suddenly the parturient got knife-like pain in the lower abdomen and labor activity stopped. Examination revealed positive symptoms of peritoneum irritation, ill-defined uterus outlines. Fetus was easily palpable, movable. Fetal heartbeats wasn't auscultable. What is the most probable diagnosis? Rupture of uterus Uterine inertia Discoordinated labor activity Risk of uterus rupture II labor period Examination of placenta revealed a defect. An obstetrician performed manual investigation of uterine cavity, uterine massage. Prophylaxis of endometritis in the postpartum period should involve following actions: Antibacterial therapy Instrumental revision of uterine cavity Haemostatic therapy Contracting agents Intrauterine instillation of dioxine A pregnant woman was delivered to the gynecological unit with complaints of pain in the lower abdomen and insignificant bloody discharges from the genital tracts for 3 hours. Last menstruation was 3 months ago. Vaginal examination showed that body of womb was in the 10th week of gestation, a fingertip could be inserted into the external orifice of uterus, bloody discharges were insignificant. USI showed small vesicles in the uterine cavity. What is the most likely diagnosis? Molar pregnancy Abortion in progress Incipient abortion Threat of spontaneous abortion E. 89. A. * B. C. D. E. 90. A. * B. C. D. E. 91. A. B. * C. D. E. 92. A. * B. C. D. E. 93. A. * B. C. D. E. Incomplete abortion A 28 y.o. primagravida, pregnancy is 15-16 weaks of gestation, presents to the maternity clinics with dull pain in the lower part of the abdomen and in lumbar area. On vaginal examination: uterus cervix is 2,5 cm, external isthmus allows to pass the finger tip. Uterus body is enlarged according to the pregnancy term. Genital discharges are mucous, mild. What is the diagnosis? Threatened spontaneous abortion Spontaneous abortion which has begun Stopped pregnancy Hydatid molar pregnancy Placenta presentation A maternity house has admitted a primagravida complaining of irregular, intense labour pains that have been lasting for 36 hours. The woman is tired, failed to fall asleep at night. The fetus is in longitudinal lie, with cephalic presentation. The fetus heartbeat is clear and rhythmic, 145/min. Vaginal examination revealed that the uterine cervix was up to 3 cm long, dense, with retroflexion; the external orifice was closed; the discharges were of mucous nature. What is the most likely diagnosis? Pathological preliminary period Uterine cervix dystocia Primary uterine inertia Physiological preliminary period Secondary uterine inertia In the department of pathology of the pregnant woman was hospitalized with second 38 weeks pregnancy. The first ended in cesarean section due to cephalopelvic disproportion. The estimated fetal weight - 3200. What method of delivery will choose? Expect spontaneous onset of labor to make a vacuum - the extraction of the fetus Elective caesarean section Excitation of labor at 38 weeks, delivery lead conservative Expect spontaneous onset of labor, eliminate attempts by forceps Plan the delivery can only know the size of the pelvis By the end of the 1st period of physiological labor clear amniotic fluid came off. Contractions lasted 35-40 sec every 4-5min. Heartbeat of the fetus was 100 bpm. The BP was 140/90 mm Hg. What is the most probable diagnosis? Acute hypoxia of the fetus Premature labor Premature detachment of normally posed placenta Back occipital presentation Hydramnion Which gestational age gives the most accurate estimation of weeks of pregnancy by uterine size? Less that 12 weeks Between 12 and 20 weeks Between 21 and 30 weeks Between 31 and 40 weeks Over 40 weeks 94. A. * B. C. D. E. 95. A. * B. C. D. E. 96. A. * B. C. D. E. 97. A. * B. C. D. E. 98. A. * B. C. D. E. A 24 years old primipara was hospitalised with complaints about discharge of the amniotic waters. The uterus is tonic on palpation. The position of the fetus is longitudinal, it is pressed with the head to pelvic outlet. Palpitation of the fetus is rhythmical, 140 bpm, auscultated on the left below the navel. Internal examination: cervix of the uterus is 2,5 cm long, dense, the external os is closed, light amniotic waters out of it. Point a correct component of the diagnosis: Antenatal discharge of the amniotic waters Early discharge of the amniotic waters The beginning of the 1st stage of labour The end of the 1st stage of labour Pathological preterm labour A 36 year old woman in the 9th week of gestation (the second pregnancy) consulted a doctor of antenatal clinic in order to be registered there. In the previous pregnancy hydramnion was observed, the child's birth weight was 5000 g. What examination method should be applied in the first place? The test for tolerance to glucose Determination of the PAPP - protein Bacteriological examination of discharges from vagina .Determination of chorionic gonatotropin hormone US of fetus A pregnant woman (35 weeks), aged 25, was admitted to the hospital because of bloody discharges. In her medical history there were two artificial abortions. In a period of 28-32 weeks there was noted the onset of hemorrhage and USD showed a placental presentation. The uterus is in normotonus, the fetus position is transversal (Ist position). The heartbeats is clear, rhythmical, 140 bpm. What is the further tactics of the pregnant woman care? To perform a delivery by means of Cesarean section To perform the hemotransfusion and to prolong the pregnancy To introduct the drugs to increase the blood coagulation and continue observation Stimulate the delivery by intravenous introduction of oxytocin Spasmoletics prescription A woman consulted a doctor on the 14th day after labour about sudden pain, hyperemy and induration of the left mammary gland, body temperature rise up to 39oC, headache, indisposition. Objectively: fissure of nipple, enlargement of the left mammary gland, pain on palpation. What pathology would you think about in this case? Lactational mastitis Lacteal cyst with suppuration Fibrous adenoma of the left mammary gland Breast cancer Phlegmon of mammary gland Immediately after delivery a woman had hemorrhage, blood loss exceeded postpartum hemorrhage rate and was progressing. There were no symptoms of placenta detachment. What tactics should be chosen? Manual removal of placenta and afterbirth Uterus tamponade Instrumental revision of uterine cavity walls Removal of afterbirth by Crede's method Intravenous injection of methylergometrine with glucose 99. A. * B. C. D. E. 100. A. * B. C. D. E. 101. A. * B. C. D. E. 102. A. * B. C. D. E. 103. A. * B. C. D. E. Internal obstetric examination of a parturient woman revealed that the sacrum hollow was totally occupied with fetus head, ischiadic spines couldn't be detected. Sagittal suture is in the straight diameter, occipital fontanel is directed towards symphysis. In what plane of small pelvis is the presenting part of the fetus? Plane of pelvic outlet Wide pelvic plane Narrow pelvic plane Plane of pelvic inlet Over the pelvic inlet Vaginal inspection of a parturient woman revealed: cervix dilation is up to 2 cm, fetal bladder is intact. Sacral cavity is free, sacral promontory is reachable only with a bent finger, the inner surface of the sacrococcygeal joint is accessible for examination. The fetus has cephalic presentation. Sagittal suture occupies the transverse diameter of pelvic inlet, the small fontanel to the left, on the side. What labor stage is this? Cervix dilatation stage Preliminary stage Prodromal stage Stage of fetus expulsion Placental stage A parturient woman is 23 years old. Vaginal obstetric examination reveals full cervical dilatation. There is no fetal bladder. Fetal head is in the plane of pelvic inlet. Sagittal suture is in mesatipellic pelvis, anterior fontanel and posterior fontanee are presented. The fetal head diameter in such presentation will be: Suboccipito-bregmaticus Fronto-occipitalis recta Biparietal Suboccipitio-frontalis Mento-occipitalis After delivery and revision of placenta there was found the defect of placental lobule. General condition of woman is normal, uterus is firm, and there is moderate bloody discharge. Speculum examination of birth canal shows absence of lacerations and ruptures. What action is necessary? Manual exploration of the uterine cavity External massage of uterus Introduction of uterine contracting agents Urine drainage, cold on the lower abdomen Introduction of hemostatic medications A parturient woman is 25 years old, it is her second day of postpartum period. It was her first full-term uncomplicated labour. The lochia should be: Bloody Sanguino-serous Mucous Purulent Serous 104. A. * B. C. D. E. 105. A. B. C. * D. E. 106. A. * B. C. D. E. 107. A. B. * C. D. E. 108. A. * B. C. D. E. 109. A woman is 34 years old, it is her tenth labor at full term. It is known from the anamnesis that the labor started 11 hours ago, labor was active, painful contractions started after discharge of waters and became continuous. Suddenly the parturient got knife-like pain in the lower abdomen and labor activity stopped. Examination revealed positive symptoms of peritoneum irritation, ill-defined uterus outlines. Fetus was easily palpable, movable. Fetal heartbeats weren’t auscultable. What is the most probable diagnosis? Rupture of uterus Uterine inertia Discoordinated labor activity Risk of uterus rupture II labor period At which gestational age does multipara feel first fetal movements? Less that 12 weeks At 20 week At 18 week At 23 week At 30 week A 22-year-old woman is having interm labor continued for 5 hours. Light amniotic fluid came off. The fetus head is fixed to the orifice in the small pelvis. The probable fetal weight is 4000,0 g. Heartbeat of the fetus is normal. In vaginal examination – cervix is dilated to 1 cm, the fetal membranes are not present. In which stage of labor does the woman present? First, latent phase First, active phase First, spontaneous phase Second, active phase Third, latent phase A woman in her 40th week of pregnancy, the second labour, has regular birth activity. Uterine contractions take place every 3 minutes. What criteria describe the beginning of the II labor stage the most objective? Cervical dilatation by no less than 4 cm Cervical dilation to 10 cm Duration of uterine contractions over 30 seconds Presenting part is in the lower region of small pelvis Rupture of fetal bladder A woman in her 39-th week of pregnancy, the second labor, has regular birth activity. Uterine contractions take place every 3 minutes. All of the below indicate the beginning of the II stage of labor EXEPT: Cervical dilatation to .4 cm Cervical dilation to 9-10 cm Duration of uterine contractions more than 30 seconds Presenting part is in 0 station Rupture of membranes A 24 years old primipara was hospitalised with complaints about discharge of the amniotic waters. The uterus is tonic on palpation. The position of the fetus is longitudinal, it is pressed with the head to pelvic outlet. Palpitation of the fetus is rhythmical, 140 bpm, auscultated on the left below the navel. Internal examination: cervix of the uterus is 2,5 cm long, dense, the external os is closed, light amniotic waters out of it. Point a correct component of the diagnosis: A. * B. Antenatal discharge of the amniotic waters Early discharge of the amniotic waters The beginning of the 1st stage of labour The end of the 1st stage of labour Pathological preterm labour A 32 year old woman in the 12th week of gestation (the second pregnancy) consulted a doctor of antenatal clinic in order to be registered there. In the previous pregnancy hydramnion was observed, the child's birth weight was 5000 g. What examination method should be applied in the first place? The test for tolerance to glucose Determination of the contents of fetoproteinum Bacteriological examination of discharges from vagina A cardiophonography of fetus US of fetus At term of a gestation of 40 weeks height of standing of a uterine fundus is less then assumed for the given term. The woman has given birth to the child in weight of 2500 g, length of a body 53 cm, with an assessment on Apgar score of 4-6 points. Labor were fast. The cause of such state of the child was: Placental dysfunction Acute fetal distress Placental detachment Infection of a fetus Prematurity 41 years old woman, primigravida, with infertility in the medical history, on the 42-43 week of pregnancy. Labour activity is weak. Longitudinal lie of the fetus, I position, anterior variety. The head of the fetus is engaged to pelvic inlet. Fetus heart rate is 140 bmp,rhythmic. Cervix dilation is .6 cm. One hour before green colored amniotic fluid released. Cranial bones are dense, cranial sutures and small fontanels are diminished. What should be management delivery? Caesarean section Amniotomy, labour stimulation, fetal hypoxia treatment Fetal hypoxia treatment, in the ІІ period - forceps delivery Fetal hypoxia treatment, conservative delivery Medication sleep, amniotomy, labour stimulation Examination of a placenta after delivery reveals defect 3x5 cm large. Hemorrhage is absent. What management is the most appropriate? Manual exploration of uterine cavity Prescription of uterotonic medicines External uterus massage Observation for the patient Uterine curretage A woman consulted a doctor on the 21th day after labor about discharge from vagina. Objectively body temperature is normal. Pulse rate is 72 beats per minute, blood pressure 120/60mm.Hg. What character of the discharge should be normally at this day of postpartum period? Bloody Purulent C. D. * E. Bloody-serous Serous Serous-bloody B. C. D. E. 110. A. * B. C. D. E. 111. A. * B. C. D. E. 112. A. * B. C. D. E. 113. A. * B. C. D. E. 114. A. 115. A. B. C. D. * E. 116. A. B. C. D. E. * 117. A. * B. C. D. E. 118. A. * B. C. D. E. 21 years old woman consulted a doctor on the 2 day after labor about the examinations which she should pass at postpartum period. Objectively body temperature is normal. Pulse rate is 72 beats per minute, blood pressure is 120/60mm.Hg. All of the below examination the woman should pass before discharge from hospital EXEPT: Genaral blood analysis General urine analysis Bacterioscopic examionation of the vaginal discarge Analysis of the feces Ultrasonography of the uterus In 14 min after .delivery by a 22-year-old woman, the placenta was spontaneousely delivered and 50 ml of blood came out. Woman weight is 60kg, infant weight - 3100g, length - 52 cm. The uterus contracted. In 15 minutes the hemorrhage renewed and the total amount of blood loss is 250 ml. What amount of blood loss is physiologic for this woman? 400 ml 1000 ml 450 ml 650 ml 300 ml A pregnant woman was registered in a maternity clinic in her 10th week of pregnancy. She was being under observation during the whole term, the pregnancy course was normal. Choose the document which the doctor should give to the pregnant woman to authorize her hospitalization in maternity hospital? Exchange card Appointment card for hospitalization Individual prenatal record Medical certificate Sanitary certificate A 26 years old primapara with pelvis size 23-26-18-18 cm has active labor activity. Amniotic fluid gush occurs in full cervical dilation. Probable fetal weight is is 4200 g, the head is engaged to the small pelvis inlet. Vasten's sign is positive. Cervix of uterus is fully dilated. Amniotic sac is absent. The fetus heartbeat is clear, rhythmic, 136 bpm. Which complication occur in labor? Clinical contracted pelvis Acute fetal distress Chronic fetal distress Preterm releasing of amniotic fluid Uterine inertia Назва наукового напрямку (модуля): Семестр: 1 Акушерство та гінекологія Ситуаційні задачі Опис: 5 курс 10 семестр Перелік питань: 1. A. * B. C. D. E. 2. A. B. C. D. E. * 3. A. B. C. D. * E. 4. A. * B. C. D. E. 5. A. B. C. D. E. * 6. A. 29 years old woman is presented in first stage of the second labor. Uterine contractions are every 3 minutes by 25 seconds. In Leopold maneuvers you have palpated fetal head above the pelvis inlet and fetal buttocks in the uterine fundus. Which lie is determined by a doctor? Longitudinal Transverse Oblique Breech Cephalic 34 years old woman is presented in first stage of labor. Uterine contractions are every 4 minutes by 20 seconds. In Leopold maneuvers you have palpated fetal head above the pelvis inlet and fetal buttocks in the uterine fundus. Which presentation is determined by a doctor? Longitudinal Transverse Oblique Breech Cephalic 32 years old woman is presented in first stage of the labor. Uterine contractions are every 4 minutes by 20 seconds. In Leopold maneuvers you have palpated fetal buttocks above the pelvis inlet and fetal head in the uterine fundus. Which presentation is determined by a doctor? Longitudinal Transverse Oblique Breech Cephalic 42-years old patient is hospitalized to Pathologic Pregnancy Department at 38 week of gestation. During external obstetric examination transverse lie of the fetus was diagnosed. Fetal head is presented to the left uterine wall. Which fetal position is diagnosed in the patient? I II III IV V 42-years old patient is hospitalized to Pathologic Pregnancy Department at 39 week of gestation. During external obstetric examination transverse lie of the fetus is diagnosed. Fetal head is presented to the right uterine wall. Indicate the fetal presentation. Cephalic Breech Shoulder Knee Presented part is absent 42-years old patient is hospitalized to Pathologic Pregnancy Department at 38 week of gestation. During external obstetric examination transverse lie of the fetus is diagnosed. Fetal head is presented to the right uterine wall. Which fetal position is diagnosed in the patient? I B. * C. D. E. 7. A. B. * C. D. E. 8. A. B. * C. D. E. 9. A. * B. C. D. E. 10. A. B. * C. D. E. 11. A. * B. C. D. E. 12. II III IV V 38-years old patient is hospitalized to Pathologic Pregnancy Department at 40 week of gestation. During external obstetric examination fetal head is in the mother’s hip. Which fetal lie is diagnosed in the patient? Transverse Oblique Longitudinal Cephalic Breech 28-years old patient is hospitalized to Pathologic Pregnancy Department at 40 week of gestation. During external obstetric examination fetal head is in the mother’s hip. Which fetal lie is diagnosed in the patient? Transverse Oblique Longitudinal Cephalic Breech 42-years old patient is hospitalized to Pathologic Pregnancy Department at 38 week of gestation. During external obstetric examination transverse lie of the fetus is diagnosed. Fetal head is presented to the left uterine wall. Which fetal position is diagnosed in the patient? I II III IV V 22-years old patient is hospitalized to Pathologic Pregnancy Department at 37 week of gestation. During external obstetric examination fetal head is in the right mother’s hip. Which fetal position is diagnosed in the patient? I II III IV V 28-years old patient is hospitalized to Pathologic Pregnancy Department at 37 week of gestation. During external obstetric examination fetal head is in the left mother’s hip. Which fetal position is diagnosed in the patient? I II III IV V 27-years old patient is hospitalized to Pathologic Pregnancy Department at 40 week of gestation. During external obstetric examination fetal buttocks are in the mother’s hip. Which fetal lie is diagnosed in the patient? A. B. * C. D. E. 13. A. B. * C. D. E. 14. A. * B. C. D. E. 15. A. B. * C. D. E. 16. A. * B. C. D. E. 17. A. B. C. Transverse Oblique Longitudinal Cephalic Breech 22 years old woman is presented in first stage of the labor. Uterine contractions are every 5 minutes by 20 seconds. In Leopold maneuvers fetal buttocks are palpated to the right uterine wall and fetal head to the left. Which lie is determined by a doctor? Longitudinal Transverse Oblique Breech Cephalic Patient M. in 39 week of gestation is presented in the first stage of labor. In vaginal examination the cervix is effaced and 4cm dilated, fetal head is in the pelvic inlet. A sagittal suture is in the right oblique size, a small fontanel is to the right close to the sacral bone. Determine the position and the variety of the fetus? II position, the posterior variety I position, the anterior variety I position, the posterior variety II position, the anterior variety Cephalic position, anterior variety Patient N. in 38 week of gestation is presented in the first stage of labor. In vaginal examination the cervix is effaced and 5cm dilated, fetal head is in the pelvic inlet. A sagittal suture is in the right oblique size, a small fontanel is to the left anteriorly. Determine the position and the variety of the fetus? II position, the posterior variety I position, the anterior variety I position, the posterior variety II position, the anterior variety Cephalic position, anterior variety Patient F. in 38 week of gestation is presented in the first stage of labor. In vaginal examination the cervix is effaced and 6cm dilated, fetal head is in the pelvic inlet. A sagittal suture is in the left oblique size, a small fontanel is to the left close to a sacral bone. Determine the position and the variety of the fetus? I position, the posterior variety I position, the anterior variety II position, the posterior variety II position, the anterior variety Cephalic position, anterior variety Patient F. in 38 week of gestation is presented in the first stage of labor. In vaginal examination the cervix is effaced and 6cm dilated, fetal head is in the pelvic inlet. A sagittal suture is in the left oblique size, a small fontanel is to the right anteriorly. close to a sacral bone. Determine the position and the variety of the fetus? II position, the posterior variety I position, the anterior variety I position, the posterior variety D. * E. 18. A. * B. C. D. E. 19. A. B. * C. D. E. 20. A. * B. C. D. E. 21. A. * B. C. D. E. 22. A. * B. C. D. E. II position, the anterior variety Cephalic position, anterior variety Patient M. in 39 week of gestation is presented in the first stage of labor. In vaginal examination the cervix is effaced and 4cm dilated, fetal head is in the pelvic inlet. A sagittal suture is in the right oblique size, a small fontanel is to the right close to the sacral bone. Choose the place for the best fetal heart rate auscultation. From the right below the umbilicus From the left below the umbilicus On the level of umbilicus From the right above umbilicus From the left above umbilicus Patient N. in 38 week of gestation is presented in the first stage of labor. In vaginal examination the cervix is effaced and 5cm dilated, fetal head is in the pelvic inlet. A sagittal suture is in the right oblique size, a small fontanel is to the left anteriorly. Determine the position and the variety of the fetus? From the right below the umbilicus From the left below the umbilicus On the level of umbilicus From the right above umbilicus From the left above umbilicus Patient F. in 38 week of gestation is presented in the first stage of labor. In vaginal examination the cervix is effaced and 6cm dilated, fetal head is in the pelvic inlet. A sagittal suture is in the left oblique size, a small fontanel is to the right anteriorly. Determine the position and the variety of the fetus? From the right below the umbilicus From the left below the umbilicus On the level of umbilicus From the right above umbilicus From the left above umbilicus Patient F. in 38 week of gestation is presented in the first stage of labor. In vaginal examination the cervix is effaced and 6cm dilated, fetal head is in the pelvic inlet. A sagittal suture is in the left oblique size, a small fontanel is to the right anteriorly. close to a sacral bone. Determine the position and the variety of the fetus? From the right below the umbilicus From the left below the umbilicus On the level of umbilicus From the right above umbilicus From the left above umbilicus Patient N., II labor. The patient’ condition is satisfactory. Uterine contractions are active. Fetal head is palpated on the left side from umbilicus, fetal buttocks from the right side. Your initial diagnosis is: Transverse lie, first position Breech presentation Transverse position Sinciput vertex presentation Transverse lie, second position 23. A. B. C. D. E. * 24. A. B. C. * D. E. 25. A. B. C. D. * E. 26. A. B. * C. D. E. 27. A. B. C. * D. E. 28. A. * B. C. D. Patient S., II labor. The patient’ condition is satisfactory. Uterine contractions are active. Fetal head is palpated on the right side from umbilicus, fetal buttocks from the left side. Your initial diagnosis is: Transverse lie, first position Breech presentation Transverse position Sinciput vertex presentation Transverse lie, second position 33 years old patient is presented in the first stage of labor. Fetal head is on -2 station. Fetal back is to the left, buttocks are presented. Fetal heart rate is clear, rhythmic, 136 in 1min. Which lie is present in the patient? Transverse lie Oblique Longitudinal Breech Shoulder In vaginal examination of a multipara the cervix is 100% effaced and 5 cm dilated. Fetal buttocks are palpated in the level of pelvic inlet. The intertrochanteric diameter is in the right oblique size, the fetal sacrum is anteriorly. What is the diagnosis? I position, the posterior variety I position, the anterior variety II position, the posterior variety II position, the anterior variety Cephalic position, anterior variety In vaginal examination of a multipara the cervix is 100% effaced and 6 cm dilated. Fetal buttocks are palpated in -1 station. The intertrochanteric diameter is in the left oblique size, the fetal sacrum is anteriorly. What is the diagnosis? I position, the posterior variety I position, the anterior variety II position, the posterior variety II position, the anterior variety Cephalic position, anterior variety In vaginal examination of 41 years old patient the cervix is 100% effaced and 6 cm dilated. Fetal buttocks are palpated in -2 stations. The intertrochanteric diameter is in the left oblique size, the fetal sacrum is posteriorly. What is the diagnosis? I position, the posterior variety I position, the anterior variety II position, the posterior variety II position, the anterior variety Cephalic position, anterior variety In vaginal examination of 33 years old patient the cervix is 100% effaced and 7 cm dilated. Fetal buttocks are palpated in 0 station. The intertrochanteric diameter is in the right oblique size, the fetal sacrum is posteriorly. What is the diagnosis? I position, the posterior variety I position, the anterior variety II position, the posterior variety II position, the anterior variety E. 29. A. * B. C. D. E. 30. A. B. * C. D. E. 31. A. B. * C. D. E. 32. A. B. C. D. E. * 33. A. * B. C. D. E. Cephalic position, anterior variety Patient N., II labor. The patient’ condition is satisfactory. Uterine contractions are active. Fetal head is palpated on the right from umbilicus; fetal buttocks from the left. Uterine cervix is dilated to 3cm, amniotic membranes are absent. Your obstetric diagnosis: Transverse lie, right position Transverse lie, left position Oblique lie Breech presentation Cephalic position, anterior variety Patient N., II labor. The patient’ condition is satisfactory. Uterine contractions are active. Fetal head is palpated on the left from umbilicus; fetal buttocks from the right. Uterine cervix is dilated to 3cm, amniotic membranes are absent. Your obstetric diagnosis is: Transverse lie, right position Transverse lie, left position Oblique lie Breech presentation Cephalic position, anterior variety 36 years old patient is presented in the second stage of labor. Uterine contractions are every 2 minutes by 45-50 seconds. Fetal lie is longitudinal, cephalic presentation is diagnosed. Fetal heart rate is 136 beats per minute. Cervical dilation is 10cm, amniotic fluid is absent, fetal head is presented at 0 station at vaginal examination. What does 0 point of the measuring stake mean? Linea terminalis Ischial spines Promontory Ischial tubes Coccyx 27 years old patient is presented in labor. Uterine contractions are every 4 minutes by 25 seconds. Fetal lie is longitudinal, cephalic presentation is diagnosed. Fetal heart rate is 136 beats per minute. Cervical dilation is 10 cm, amniotic membranes are absent, top of the fetal head reaches 0 station. What does 0 point of the measuring stake mean? Crowning Top of fetal head reaches line terminalis Top of fetal head reaches ischial tubes Fetal head is floating Fetal head is engaged 31 years old patient is presented in labor. Pushing efforts are every 2 minutes by 55 seconds. Fetal lie is longitudinal, cephalic presentation is diagnosed. Fetal heart rate is 136 beats per minute. Cervical dilation is 10cm, amniotic membranes are absent, top of the fetal head reaches +3 station. What does +3 point of the measuring stake mean? Crowning Top of fetal head reaches linea terminalis Top of fetal head reaches ischial tubes Fetal head is floating Fetal head is engaged 34. A. B. C. D. * E. 35. A. * B. C. D. E. 36. A. B. C. D. E. * 37. A. B. * C. D. E. 38. A. B. 26 years old patient is presented in the second stage of labor. Uterine contractions are every 2 minutes by 45-50 seconds. Fetal lie is longitudinal, cephalic presentation is diagnosed. Fetal heart rate is 136 beats per minute. Cervical dilation is 10cm, amniotic fluid is absent, fetal head is presented at 0 station at vaginal examination. Sagittal suture is located in the right oblique diameter of the midpelvis, posterior fontanel to the left anteriorly. Which fetal position is diagnosed? Anterior Posterior Oblique First Second 40 years old patient is presented in the second stage of labor. Uterine contractions are every 2 minutes by 45-50 seconds. Fetal lie is longitudinal, cephalic presentation is diagnosed. Fetal heart rate is 136 beats per minute. Cervical dilation is 10cm, amniotic fluid are absent, fetal head is presented at 0 station at vaginal examination. Sagittal suture is located in the right oblique diameter of the midpelvis, posterior fontanel to the left anteriorly. Which fetal variety is diagnosed? Anterior Posterior Oblique First Second Patient N., 33 years old is presented in the first stage of labor. Uterine contractions are every 3 minutes by 35-40 seconds. Fetal lie is longitudinal, cephalic presentation is diagnosed. Fetal heart rate is 136 beats per minute. Cervical dilation is 4cm, amniotic membranes are intact, fetal head is presented at -2 station at vaginal examination. Sagittal suture is located in the left oblique diameter of the pelvic inlet; posterior fontanel is to the right anteriorly. Which fetal position is diagnosed? Anterior Posterior Oblique First Second Patient N., 33 years old is presented in the first stage of labor. Uterine contractions are every 3 minutes by 35-40 seconds. Fetal lie is longitudinal, cephalic presentation is diagnosed. Cervical dilation is 4cm, amniotic membranes are intact, fetal head is presented at -2 station at vaginal examination. Sagittal suture is located in the left oblique diameter of the pelvic inlet; posterior fontanel is to the right anteriorly. Fetal heart rate is 136 beats per minute. Which fetal variety is diagnosed? Anterior Posterior Oblique First Second 26 years old patient is presented in the second stage of labor. Uterine contractions are every 2 minutes by 45-50 seconds. Fetal lie is longitudinal, cephalic presentation is diagnosed. Fetal heart rate is 136 beats per minute. Cervical dilation is 10cm, amniotic fluid is absent, fetal head is presented at 0 station at vaginal examination. Sagittal suture is located in the right oblique diameter of the midpelvis, posterior fontanel is to the right posteriorly. Which fetal position is diagnosed? Anterior Posterior C. D. E. * 39. A. B. * C. D. E. 40. A. B. C. D. * E. 41. A. B. * C. D. * E. 42. A. * B. C. D. E. Oblique First Second 40 years old patient is presented in the second stage of labor. Uterine contractions are every 2 minutes by 45-50 seconds. Fetal lie is longitudinal, cephalic presentation is diagnosed. Fetal heart rate is 136 beats per minute. Cervical dilation is 10cm, amniotic fluid is absent, fetal head is presented at 0 station at vaginal examination. Sagittal suture is located in the right oblique diameter of the midpelvis, posterior fontanel is to the right posteriorly. Which fetal variety is diagnosed? Anterior Posterior Oblique First Second Patient N., 33 years old is presented in the first stage of labor. Uterine contractions are every 3 minutes by 35-40 seconds. Fetal lie is longitudinal, cephalic presentation is diagnosed. Fetal heart rate is 136 beats per minute. Cervical dilation is 4cm, amniotic membranes are intact, fetal head is presented at -2 station at vaginal examination. Sagittal suture is located in the left oblique diameter of the pelvic inlet; posterior fontanel is to the left posteriorly. Which fetal position is diagnosed? Anterior Posterior Oblique First Second Patient N., 33 years old is presented in the first stage of labor. Uterine contractions are every 3 minutes by 35-40 seconds. Fetal lie is longitudinal, cephalic presentation is diagnosed. Fetal heart rate is 136 beats per minute. Cervical dilation is 4cm, amniotic membranes are intact, fetal head is presented at -2 station at vaginal examination. Sagittal suture is located in the left oblique diameter of the pelvic inlet; posterior fontanel is to the left posteriorly. Which fetal variety is diagnosed? Anterior Posterior Oblique First Second 24 years old woman is presented in postpartum period after physiological delivery. At objective examination her temperature is 36, 8 0C, Ps - 72/min, BP - 120/80 mm Hg. Mammary glands are moderately swollen, nipples are clean without fissures. Lactation is characterized by colostrum. Abdomen is soft and painless. Uterine fundus height is 3 fingers below the umbilicus. Lochia are bloody, moderate. The most appropriate day for postpartum period would be: 3 day 2 day 1 day 5 day 4 day 43. A. B. C. D. * E. 44. A. B. * C. D. E. 45. A. B. * C. D. E. 46. A. * B. C. D. E. 47. A. B. * C. D. 28 years old woman is presented in postpartum period after physiological delivery. At objective examination her temperature is 36, 8 0C, Ps - 84/min, BP - 120/80 mm Hg. Mammary glands are moderately swollen, nipples are clean without fissures. Lactation is characterized by immature milk. Abdomen is soft and painless. Uterine fundus height is in the midway between symphysis and umbilicus. Lochia are bloody-serous, moderate. The most appropriate day for postpartum period would be: 3 day 2 day 1 day 5 day 4 day 22 years old woman is presented in postpartum period after physiological delivery. At objective examination her temperature is 36, 7 0C, Ps - 72/min, BP - 110/70 mm Hg. Mammary glands are moderately swollen, nipples are clean without fissures. Lactation is characterized by colostrum. Abdomen is soft and painless. Uterine fundus - 2 fingers below the umbilicus. Lochia are bloody, moderate. The most appropriate day for postpartum period would be: 3 day 2 day 1 day 5 day 4 day 25 years old woman is presented in postpartum period after physiological delivery. At objective examination her temperature is 36, 7 0C, Ps - 72/min, BP - 110/70 mm Hg. Mammary glands are soft, nipples are clean without fissures. Lactation is good. Abdomen is soft and painless. Uterine fundus is located 8cm above symphysis. The lochia should be: Bloody Bloody-serous Mucous Purulent Serous 22 years old woman is presented at postpartum period after physiological delivery. At objective examination her temperature is 36,7 0C, Ps - 72/min, BP - 110/70 mm Hg. Mammary glands are soft, nipples are clean without fissures. Lactation is good. Abdomen is soft and painless. Uterine fundus is located 6cm below umbilicus. The lochia should be: Bloody Bloody-serous Mucous Purulent Serous 19 years old woman is presented in postpartum period after physiological delivery At objective examination her temperature is 36,8 0C, Ps - 72/min, BP - 120/80 mm Hg. Mammary glands are normal, colostrum is presented. Abdomen is soft and painless. Uterine fundus height is 2 cm below the umbilicus. Lochia are bloody, moderate. The most appropriate day for postpartum period would be: 3 day 2 day 1 day 5 day E. 48. A. B. C. D. E. * 49. A. B. C. * D. E. 50. A. * B. C. D. E. 51. A. * B. C. D. E. 52. A. B. C. * D. 4 day 33 years old woman is presented in postpartum period after physiological delivery. At objective examination her temperature is 36, 8 0C, Ps - 84/min, BP - 120/80 mm Hg. Mammary glands are moderately swollen, nipples are clean without fissures. Lactation characterizes by immature milk. Uterine fundus height is 4 fingers below umbilicus. Lochia are bloody-serous, moderate. The most appropriate day for postpartum period would be: 3 day 2 day 1 day 5 day 4 day 35 years old woman is presented in postpartum period after physiological delivery. At objective examination her temperature is 36, 8 0C, Ps - 84/min, BP - 120/80 mm Hg. Mammary glands are normal without infiltration. Lactation characterizes by immature milk. Uterine fundus height is 4 fingers above symphysis. Lochia are bloody-serous, moderate. The most appropriate day for postpartum period would be: 3 day 2 day 6day 5 day 4 day 29 years old woman is presented in postpartum period after physiological delivery. At objective examination her temperature is 36, 8 0C, Ps - 84/min, BP - 120/80 mm Hg. Mammary glands are normal. Lactation is good. Uterine fundus height is 3 fingers above symphysis. Lochia are serous-bloody, moderate. The most appropriate day for postpartum period would be: 7 day 2 day 1 day 5 day 4 day 28 years old woman is presented in postpartum period after physiological delivery. At objective examination her temperature is 36, 8 0C, Ps - 84/min, BP - 120/80 mm Hg. Mammary glands are normal without infiltrations. Lactation is good. Uterine fundus height is 4cm above symphysis. Lochia are serous-bloody, moderate. The most appropriate day for postpartum period would be: 8 day 2 day 1 day 5 day 4 day 28 years old woman is presented in postpartum period after physiological delivery. At objective examination her temperature is 36, 8 0C, Ps - 84/min, BP - 120/80 mm Hg. Mammary glands are normal. Lactation is good. Uterine fundus height is 2cm above symphysis. Lochia are serous-bloody, moderate. The most appropriate day for postpartum period would be: 7 day 2 day 9 day 5 day E. 53. A. B. C. * D. E. 54. A. B. * C. D. E. 55. A. B. * C. D. E. 56. A. * B. C. D. E. 57. A. * B. C. D. E. 4 day 24 years old woman is presented in postpartum period after physiological delivery. At objective examination her temperature is 36, 8 0C, Ps - 84/min, BP - 120/80 mm Hg. Mammary glands are normal. Lactation is good. Lochia are serous in small amount. The most appropriate day for postpartum period would be: 7 day 2 day 10day 5 day 4 day 25 years old woman is presented in postpartum period after physiological delivery at objective examination her temperature is 36,7 0C, Ps - 72/min, BP - 110/70 mm Hg. Mammary glands are soft, nipples are clean without fissures. Lactation is good. Abdomen is soft and painless. Uterine fundus is located 8cm below umbilicus. The lochia should be: Bloody Bloody-serous Mucous Purulent Serous 25 years old woman is presented in postpartum period after physiological delivery. At objective examination her temperature is 36,7 0C, Ps - 72/min, BP - 110/70 mm Hg. Mammary glands are soft, nipples are clean without fissures. Lactation is good. Abdomen is soft and painless. Uterine fundus is located in the midway between umbilicus and xiphoid process. The lochia should be: Bloody Bloody-serous Mucous Purulent Serous 22 years old woman is presented at postpartum period after physiological delivery. At objective examination her temperature is 36,7 0C, Ps - 72/min, BP - 110/70 mm Hg. Mammary glands are soft, nipples are clean without fissures. Lactation is good. Abdomen is soft and painless. Uterine fundus is located 2cm below umbilicus. The lochia should be: Bloody Bloody-serous Mucous Purulent Serous 22 years old woman is presented at postpartum period. At objective examination her temperature is 36,7 0C, Ps - 72/min, BP - 110/70 mm Hg. Mammary glands are soft, nipples are clean without fissures. Lactation is good. Abdomen is soft and painless. Uterine fundus is located 4cm below umbilicus. The lochia should be: Bloody Bloody-serous Mucous Purulent Serous 58. A. B. C. * D. E. 59. A. B. C. D. E. * 60. A. B. * C. D. E. 61. A. B. C. * D. E. 62. A. * B. C. D. E. 18 years old woman is presented at postpartum period. At objective examination her temperature is 36,7 0C, Ps - 72/min, AP - 110/70 mm Hg. Mammary glands are soft, nipples are clean without fissures. Lactation is good. Abdomen is soft and painless. Uterine fundus is located 2cm below umbilicus. Routine postpartum care should include searching for all of the following EXEPT: Fever Anemia Diabetes Depression Thrombophlebitis 44 years old woman is presented at postpartum period after fifth physiological delivery. At objective examination her temperature is 36,7 0C, Ps - 72/min, BP - 110/70 mm Hg. Mammary glands are soft, nipples are clean without fissures. Lactation is good. Abdomen is soft and painless. Uterine fundus is located 6cm below umbilicus. Condition to consider before performing a postpartum sterilization include all of the following EXEPT: A signed permit Normal coagulogram Negative pap smear The infants’ well being The patient awareness of hormonal suppression therapy A patient is presented at 14 day of postpartum period after second physiological delivery. She is found to have spotting and increasing of the temperature. At objective examination her temperature is 38,7 0C, Ps - 100/min, BP - 110/70 mm Hg. Mammary glands are soft, nipples are clean without fissures. Lactation is good. Abdomen is soft and painful in the lover parts. In bimanual examination the uterus is enlarged and tender. The primary diagnosis would be: Pyelonephritis Endometritis Parametritis Mastitis Vaginitis A patient is presented at 12 day of postpartum period after first physiological delivery. She is found to have high temperature, pain in the left mammary gland. At objective examination her temperature is 39, 7 0C, Ps - 110/min, BP - 110/70 mm Hg. Left mammary gland is swollen, painful. Lactation is prominent. In bimanual examination the uterus is normal. The primary diagnosis would be: Pyelonephritis Endometritis Lactostasis Peritonitis Vaginitis A 20-year-old primapara is presented in labor for 14 hours. The probable fetal weight is 4200, 0 g. Fetal heart rate is normal. In vaginal examination the cervix is dilated to 4 cm, amniotic membranes are presented. The fetal head station is -1. Woman is exhausted. What is necessary to do firstly? Therapeutic rest Augmentation by oxytocin Fetal distress prevention Induction by prostaglandins Amniotomy 63. A. B. C. D. E. * 64. A. * B. C. D. E. 65. A. * B. C. D. E. 66. A. * B. C. D. E. 67. A. B. C. * D. A 22-year-old multipara is presented in labor for 6 hours. The probable fetal weight is 3800, 0 g. Fetal heart rate is normal. In vaginal examination the cervix is dilated to 4 cm, amniotic membranes are presented. The fetal head station is -1. Oligohydramnios is presented. What is necessary to do to prevent uterine inertia? Therapeutic rest Augmentation by oxytocin Fetal distress prevention Induction by prostaglandins Amniotomy 24 years old primipara is hospitalized with complaints of irregular painful uterine contractions which are presented for 7 hours hypertonic uterine dysfunction is presented. Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation is diagnosed during external objective examination. Fetal heart rate is rhythmic, 140 bpm. Uterine cervix is 2,5cm long, dense, the external os is closed in vaginal examination. What is the correct diagnosis: False labor First stage of labor Second stage of labor Discoordinative uterine activity Pathological preterm labor 29 years old primipara is hospitalized with complaints of irregular painful uterine contractions during 8 hours. Hypertonic uterine dysfunction is presented. Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation is diagnosed during external objective examination. Fetal heart rate is rhythmic, 140 bpm. Uterine cervix is 2,5cm long, dense, the external os is closed in vaginal examination. The most appropriate treatment would be: Therapeutic rest Induction by oxytocin Fetal distress prevention Induction by prostaglandins Amniotomy 28 years old primipara is hospitalized with complaints of regular uterine contractions every 4-5 minutes by 20 seconds. She is in labor for 10 hours. Uterine contractions become weaker. She is exhausted. Fetal lie is longitudinal, fetal head is fixated to pelvic inlet. Fetal heart rate is rhythmic, 140 bpm. In obstetric exam cervical dilation is 2 cm. Amniotic sac is intact. What is the adequate management of patient? Therapeutic rest Augmentation of labor by oxytocin Amniotomy Augmentation of labor by prostaglandins Fetal destroying operation 28 years old primipara is hospitalized with complaints of regular uterine contractions every 4-5 minutes by 20 seconds. She is in labor for 10 hours. Uterine contractions become weaker. She is exhausted. Fetal lie is longitudinal, fetal head is fixated to pelvic inlet. Fetal heart rate is rhythmic, 140 bpm. In obstetric exam cervical dilation is 2 cm. Amniotic sac is intact. Therapeutic rest is prescribed for her. What you should do firstly after patient awakening? Spasmolytics prescriptions Augmentation of labor by oxytocin Amniotomy Augmentation of labor by prostaglandins E. 68. A. B. * C. D. E. 69. A. * B. C. D. E. 70. A. * B. C. D. E. 71. A. * B. C. D. E. 72. A. B. C. D. Fetal destroying operation 28 years old primipara is hospitalized with complaints of regular uterine contractions every 4-5 minutes by 20 seconds. She is in labor for 10 hours. Uterine contractions become weaker. She is exhausted. Fetal lie is longitudinal, fetal head is fixated to pelvic inlet. Fetal heart rate is rhythmic, 140 bpm. In obstetric exam cervical dilation is 2 cm. Amniotic sac is intact. She undergo for therapeutic rest and amniotomy. What is the next step in your management? Spasmolytics prescriptions Augmentation of labor by oxytocin Tokolytics prescriptions Augmentation of labor by prostaglandins Fetal destroying operation 28 years old primipara is hospitalized with complaints of regular uterine contractions every 4-5 minutes by 20 seconds. She is in labor for 10 hours. Uterine contractions become weaker. She is exhausted. Fetal lie is longitudinal, fetal head is fixated to pelvic inlet. Fetal heart rate is rhythmic, 140 bpm. In obstetric exam cervical dilation is 2 cm. Amniotic sac is intact. She undergo for therapeutic rest and amniotomy. Which drug belongs to the first line medication for labor’ augmentation? Oxytocin Miphepristone Misoprostol Duphaston Carboprost 28 years old primipara undergoes labor augmentation as a result of primary uterine inertia. Fetal lie is longitudinal, fetal head is fixated to pelvic inlet after performed therapeutic rest and amniotomy. Fetal heart rate is rhythmic, 140 bpm. In obstetric exam cervical dilation is 2 cm and amniotic membranes are absent. What is the initial rate for intravenous oxytocin in labor’ augmentation? 6-8 drops per minute 10-14 drops per minute 18-20 drops per minute 2-24 drops per minute 28-30 drops per minute 28 years old primipara is hospitalized with complaints of regular uterine contractions every 4-5 minutes by 20 seconds. She is 14 hours in labor. Uterine contractions are weak. She is exhausted. Fetus is in longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation. Fetal heart rate is rhythmic, 140 bpm. Cervical dilation is 2 cm. Amniotic sac is presented. The initial diagnosis would be: Primary uterine inertia Secondary uterine inertia Pushing efforts inertia Precipitatous labor Discoordinative uterine activity 28 years old primipara undergoes augmentation by oxytocin as a result of primary uterine inertia. Fetal lie is longitudinal, fetal head is fixated to pelvic inlet after performed therapeutic rest and amniotomy. Fetal heart rate is rhythmic, 140 bpm. Which rate of oxytocin is the highest during augmentation? 16-18 drops per minute 20-22 drops per minute 28-30 drops per minute 30-32 drops per minute E. 73. A. * B. C. D. E. 74. A. B. C. D. E. * 75. A. * B. C. D. E. 76. A. * B. C. D. E. 77. A. * B. C. D. E. 38-40 drops per minute 50-year-old primapara is presented in labor for 15 hours. The probable fetal weight is 3200, 0 g. Fetal heart rate is normal. In vaginal examination the cervix is dilated to 5 cm, amniotic membranes are presented. The fetal head station is -2. Woman is exhausted. What is necessary to do firstly? Therapeutic rest Augmentation by oxytocin Fetal distress prevention Induction by prostaglandins Amniotomy 28-year-old multipara is presented in labor for 7 hours. In vaginal examination the cervix is dilated to 3 cm, amniotic membranes are presented. The fetal head station is - 2. Oligohydramnios is presented during ultrasonography. What is necessary to do to prevent uterine inertia? Therapeutic rest Augmentation by oxytocin Fetal distress prevention Induction by prostaglandins Amniotomy Patient F., 28 years old is hospitalized with complaints of irregular painful uterine contractions which have been presented for 10 hours. Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation is diagnosed in Leopold’s maneuvers. Fetal heart rate is rhythmic, 136 bpm. Uterine cervix is 3,5cm long, dense, the external os is closed in vaginal examination. What is the correct diagnosis: False labour First stage of labor Second stage of labor Discoordinative uterine activity Pathological preterm labour Patient M., 39 years old is hospitalized with complaints of irregular painful uterine contractions during11 hours. Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation is diagnosed. Fetal heart rate is rhythmic, 160 bpm. Uterine cervix is 3,0cm long, dense, the external os is closed in vaginal examination. The most appropriate treatment would be: Therapeutic rest Induction by oxytocin Fetal distress prevention Induction by prostaglandins Amniotomy 38 years old primipara is hospitalized with complaints of regular uterine contractions every 5-6 minutes by 10-15 seconds. She is in labor for 11 hours. Uterine contractions become weaker. She is exhausted. Fetal lie is longitudinal, fetal head is fixated to pelvic inlet. Fetal heart rate is rhythmic, 140 bpm. In obstetric exam cervical dilation is 1 cm. Amniotic sac is intact. What is the adequate management of patient? Therapeutic rest Augmentation of labor by oxytocin Amniotomy Augmentation of labor by prostaglandins Fetal destroying operation 78. A. B. C. * D. E. 79. A. B. * C. D. E. 80. A. * B. C. D. E. 81. A. * B. C. D. E. 82. A. * B. C. D. E. 83. 21 years old primipara is hospitalized with complaints of regular uterine contractions every 5-6 minutes by 20 seconds and general weakness. She is in labor for 9 hours. She is exhausted. Fetal lie is longitudinal, fetal head is fixated to pelvic inlet. Fetal heart rate is rhythmic, 140 bpm. In obstetric exam cervical dilation is 2 cm. Amniotic sac is presented. Therapeutic rest is prescribed for her. What you should do firstly after patient awakening? Spasmolytics prescriptions Augmentation of labor by oxytocin Amniotomy Augmentation of labor by prostaglandins Fetal destroying operation 28 years old primipara undergoes for therapeutic rest and amniotomy as a result of uterine inertia. What is the next step in your management? Spasmolytics prescriptions Augmentation of labor by oxytocin Tokolytics prescriptions Augmentation of labor by prostaglandins Fetal destroying operation 26 years old primipara is hospitalized with complaints of regular uterine contractions every 5-6 minutes by 20-25 seconds. She is in labor for 14 hours. She undergo for therapeutic rest and amniotomy. Which drug belongs to the first line medication for labor’ augmentation? Oxytocin Miphepristone Misoprostol Duphaston Carboprost 40 years old primapara is presented on 42-43 week of pregnancy. Uterine contractions are weak. Fetal head is arrested to pelvic inlet. Vasten sign is positive. Fetal heart rate is 140 bmp, rhythmic. Cervical dilation is 6 cm. Cranial bones are dense, sagittal suture is not palpated. What is the management of labor? Caesarean section Amniotomy Forceps delivery Labor induction Vacuum application 40 years old primapara is presented on 42-43 week of pregnancy. Uterine contractions are weak. Fetal head is arrested to pelvic inlet. Vasten sign is positive. Fetal heart rate is 140 bmp, rhythmic. Cervical dilation is 6 cm. Cranial bones are dense, sagittal suture is not palpated. Which complication is presented? Cephalo-pelvic disproportion Fetal distress Uterine inertia False labor Hypertonic uterine dysfunction 40 years old primapara is presented on 42-43 week of pregnancy. Uterine contractions are weak. Fetal head is arrested to pelvic inlet. Vasten sign is positive. Fetal heart rate is 140 bmp, rhythmic. Cervical dilation is 7 cm. Cranial bones are dense, sagittal suture is not palpated. What is the reason of labor complication? A. * B. C. D. E. 84. A. * B. C. D. E. 85. A. B. C. * D. E. 86. A. B. * C. D. E. 87. A. * B. C. D. Postterm pregnancy Deflexed presentation Breech presentation Multiple pregnancy Polyhydramnios 39 years old primapara at 40 week of pregnancy is admitted to the hospital with complaints of regular uterine contractions every 2- 3minutes by 45 seconds. Longitudinal fetal lie, cephalic presentation was diagnosed. Vasten sign is positive. Fetal heart rate is 142 in 1min, clear, rhythmic. The sizes of pelvis are normal. Probable fetal weight is 4200 g. Uterine cervix is dilated to 8 cm, edematous. Amniotic membranes are absent. Fetal head is above the pelvic inlet. Promontorium is not reached. What is the adequate management of labor? Immediate cesarean section Fetal destroying operation Medical treatment Augmentation of labor Spasmolytic prescription 39 years old primapara at 40 week of pregnancy is admitted to the hospital with complaints of regular uterine contractions every 2- 3minutes by 45 seconds. Longitudinal fetal lie, cephalic presentation were diagnosed. Vasten sign is positive. Fetal heart rate is 142 in 1min, clear, rhythmic. The sizes of pelvis are normal. Probable fetal weight is 4200 g. Uterine cervix is dilated to 8 cm, edematous. Amniotic membranes are absent. Fetal head is above the pelvic inlet. Promontorium is not reached. Which of the below pelvic sizes are considered to be normal for such woman? 20-22-24-29cm 22-22-24-28cm 25-28-30-20cm 28-28-30-20cm 23-24-25-26cm 37 years old primapara at 41 week of pregnancy is admitted to the hospital with complaints of regular uterine contractions every 2- 3minutes by 45 seconds. Longitudinal fetal lie, cephalic presentation were diagnosed. Vasten sign is positive. Fetal heart rate is 142 in 1min, clear, rhythmic. The sizes of pelvis are normal. Probable fetal weight is 4200 g. Uterine cervix is dilated to 8 cm, edematous. Amniotic membranes are absent. Fetal head is above the pelvic inlet. Promontorium is not reached. Positive Vasten sign suggest about: Adequate cervical dilation Cephalo-pelvic disproportion Uterine inertia Uterine rupture Hypertonic uterine dysfunction 39 years old primapara at 39 week of gestation is admitted with complaints of regular uterine contractions every 2- 3minutes by 45 seconds. Lie of the fetus is longitudinal, cephalic presentation. Vasten sign is positive. Fetal heart rate is 136 beats per minute, rhythmic. Pelvic sizes are normal. Probable fetal weight is 4100g. Uterine cervix is dilated to 9 cm, edematous. Amniotic membranes are absent. Fetal head is above the pelvic inlet. Promontorium is not reached. Which complication has been occurred in labor? Clinical contracted pelvis Uterine rupture Fetal distress Uterine inertia E. 88. A. * B. C. D. E. 89. A. B. C. D. * E. 90. A. B. * C. D. E. 91. A. B. C. D. E. * 92. A. * B. C. D. E. General contracted pelvis A 29 years old woman at 38 weeks of gestation complaints of regular contractions. Pelvic sizes: 25-28-30-21cm. The patient is found to have 100% effaced cervix and 3 cm cervical dilation. Diagonal conjugate has 13cm. Which type of the pelvis is presented in the patient? Normal pelvis General contracted pelvis Simple flat pelvis Flat rachitic pelvis Transverse contracted pelvis A 21 years old woman at 40 weeks of gestation woman presents with complaints of pain in the lower abdomen. Pelvic sizes: 26 – 26 – 30 - 21 cm. Uterine contractions are regular and last every 5 minutes by 20seconds. The patient is found to have 100 % effaced cervix for 1 cm dilated. Diagonal conjugate has 11cm. Which type of the pelvis is presented in this patient? Normal pelvis General contracted pelvis Simple flat pelvis Flat rachitic pelvis Transverse contracted pelvis 29 years old woman at 32 week of gestation woman presents with complaints of regular uterine contractions. Pelvic sizes: 23 – 25 – 29 - 18 cm. Uterine contractions are regular and last every 5 minutes by 20seconds. The patient is found to have 100 % effaced cervix for 2 cm dilated. Diagonal conjugate has 11cm. Which type of the pelvis is presented in this patient? Normal pelvis General contracted pelvis Simple flat pelvis Flat rachitic pelvis Transverse contracted pelvis 29 years old woman at 35 week of gestation woman presents with complaints of regular uterine contractions. Pelvic sizes: 23 – 25 – 29 - 18 cm. Solovjov index is 14 cm. Uterine contractions are regular and last every 5 minutes by 20seconds. The patient is found to have 100 % effaced cervix for 2 cm dilated. How many centimeters do obstetric conjugate have? 15cm 14cm 13cm 11cm 9cm 29 years old woman at 35 week of gestation woman presents with complaints of regular uterine contractions. Pelvic sizes: 23 – 25 – 29 - 18 cm. Solovjov index is 14 cm. Uterine contractions are regular and last every 5 minutes by 20seconds. The patient is found to have 100 % effaced cervix for 2 cm dilated. Which degree of pelvic contraction does the patient have? I II III IV V 93. A 21 years old woman at 40 weeks of gestation woman presents with complaints of pain in the lower abdomen. Pelvic sizes: 26 – 26 – 30 - 21 cm. Uterine contractions are regular and last every 5 minutes by 20seconds. Solovjov index is 15cm. The patient is found to have 100 % effaced cervix for 1 cm dilated. Diagonal conjugate has 13cm. How much centimeters does obstetric conjugate have? A. 15cm 14cm 13cm 11cm 9cm A 24 years old primipara was hospitalized with complaints of irregular painful uterine contractions. The uterus is tonic on palpation. The position of the fetus is longitudinal, fetal head is fixated to pelvic inlet. Fetal heart rate is rhythmic, 140 bpm. Vertical size of Michaelis rhomb has 11cm, and transverse has 10cm. In obstetric exam cervix of the uterus is 2,5 cm long, dense, the external cervical os is closed. How much centimeters does obstetric conjugate have? 11 10 8 7 6 A 24 years old primipara was hospitalized with complaints of irregular painful uterine contractions. The uterus is tonic on palpation. The position of the fetus is longitudinal, fetal head is fixated to pelvic inlet. Fetal heart rate is rhythmic, 140 bpm. Vertical size of Michaelis rhomb has 10cm, and transverse has 9cm. In obstetric exam cervix of the uterus is 2,5 cm long, dense, the external cervical os is closed. How much centimeters does obstetric conjugate have? 11 10 8 7 6 B. C. D. * E. 94. A. * B. C. D. E. 95. A. B. * C. D. E. 96. A. B. C. * D. E. 97. A. * B. C. N., 21 years old, primapara, 38 weeks of pregnancy. The labor started 5 hours ago. The membranes ruptured 2 hours ago. Pelvic sizes: 22,24,29,19 cm. Solovjov index is 14 cm. Fetal head rate 140 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. Per vaginum: the cervix is 6 cm dilated. The amniotic sac is absent. Diagonal conjugate is 10 cm. Fetal buttocks are palpated in the pelvic inlet. Which type of the pelvis does the woman have? Simple flat pelvis Flat rachitic pelvis General contracted pelvis Osteomalatic pelvis Transverse contracted pelvis K., 23 years old, primapara, 39 weeks of pregnancy. The labor started 5 hours ago. The membranes ruptured 2 hours ago. Pelvic sizes: 22,24,29,19 cm. Solovjov index is 14 cm. Fetal head rate 140 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. Cervix is 6 cm dilated in vaginal examination. The amniotic sac is absent. Diagonal conjugate is 10 cm. Fetal buttocks are palpated in the pelvic inlet. Which degree of pelvic contraction does the woman have? I II III D. E. 98. A. B. C. D. E. * 99. A. B. * C. D. E. 100. A. B. * C. D. E. 101. A. B. * C. D. E. 102. A. B. * C. IV Normal pelvic sizes N., 21 years old, primapara, 39 weeks of pregnancy. The labor has been started 6 hours ago. The membranes ruptured 2 hours ago. Pelvic sizes: 25,28,31,20 cm. Solovjov index is 14 cm. Fetal heart rate is 140 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. Cervix is 6 cm dilated in vaginal examination. The amniotic sac is presented. Diagonal conjugate is 13 cm. Fetal head is presented at – 1 station. Which type of the pelvis does the woman have? Simple flat pelvis Flat rachitic pelvis General contracted pelvis Osteomalatic pelvis Normal pelvis 39-years old primapara at 38 week of gestation complaints of regular uterine contractions every 3 minutes by 25 seconds. Fetal head is presented at – 2 station. Fetal head rate 140 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. Uterine cervix is 6 cm dilated in vaginal examination. The amniotic sac is presented. Diagonal conjugate is 13 cm. At the sacrococcygeal region 2cm exostosis is presented. What is management of labor? Spontaneous vaginal delivery Cesarean section Obstetric forceps Vacuum extraction Fetal destroying operation A woman with obliquely dislocated pelvis in her 40th week of pregnancy, first labor has regular birth activity. Uterine contractions are every 3 minutes by 25 seconds. Fetal head is presented at – 2 station. Fetal heart rate is 140 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. Cervix is 6 cm dilated in vaginal examination. The amniotic sac is presented. Diagonal conjugate has 13 cm. What is management of labor? Spontaneous vaginal delivery Cesarean section Obstetric forceps Vacuum extraction Fetal destroying operation A woman with obliquely contracted pelvis has regular birth activity. Uterine contractions take place every 3 minutes by 30 seconds. Fetal head is presented at – 2 station. Fetal heart rate is 140 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. Cervix is 7 cm dilated. The amniotic sac is present. Diagonal conjugate is 11 cm. What is management of labor? Spontaneous vaginal delivery Cesarean section Obstetric forceps Vacuum extraction Fetal destroying operation 25 years old woman at 38 week of gestation woman presents with complaints of regular uterine contractions. Pelvic sizes: 23 – 25 – 29 - 17 cm. Solovjov index is 14 cm. Uterine contractions are regular and last every 5 minutes by 20seconds. The patient is found to have 100 % effaced cervix for 4 cm dilated. Which degree of pelvic contraction does the patient have? I II III D. E. 103. A. B. C. * D. E. 104. A. B. C. * D. E. 105. A. B. * C. D. E. 106. A. B. * C. D. E. 107. A. B. C. IV V 21 years old woman at 40 week of gestation woman presents with complaints of regular uterine contractions. Pelvic sizes: 22 – 24 – 27 - 16 cm. Solovjov index is 14 cm. Uterine contractions are regular and last every 5 minutes by 20seconds. The patient is found to have 100 % effaced cervix for 5 cm dilated. Which degree of pelvic contraction does the patient have? I II III IV V 21 years old woman at 40 week of gestation woman presents with complaints of regular uterine contractions. Pelvic sizes: 22 – 24 – 27 - 16 cm. Solovjov index is 14 cm. Uterine contractions are regular and last every 5 minutes by 20seconds. The patient is found to have 100 % effaced cervix for 5 cm dilated. What is best management of labor? Vacuum extraction Forceps application Cesarean section Vaginal delivery Fetal destroying operation M., 28 years old, para 2. Full term of pregnancy. Initiation of labor was 8 hours ago. The membranes ruptured 20 minutes ago. Pelvic sizes: 25, 28, 31, 20 cm. Vasten sign is positive. Fetal heart rate is 132 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. Uterine cervix is is 9cm dilated in vaginal examination. The amniotic sac is absent. Fetal head is in in the pelvic inlet. The chin is palpated near sacral region. What is the best management of labor? Spontaneous vaginal delivery Cesarean section Obstetric forceps Vacuum extraction Fetal destroying operation F., 29 years old, para 2. Full term of pregnancy. Labor has been started 8 hours ago. The membranes ruptured 20 minutes ago. Pelvic sizes: 25, 28, 31, 20 cm. Fetal heart rate is 132 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. Vasten sign is positive. Uterine cervix is 9cm dilated. The amniotic sac is absent. Fetal head is in in the pelvic inlet. The chin is palpated near sacral region. Which complication is presented in the patient? General contracted pelvis Clinical contracted pelvis Fetal distress Primary uterine inertia Secondary uterine inertia F., 29 years old, para 2. Full term of pregnancy. Labor has been started 8 hours ago. The membranes ruptured 20 minutes ago. Pelvic sizes: 25, 28, 31, 20 cm. Fetal heart rate is 132 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. Vasten sign is positive. Uterine cervix is 9cm dilated. The amniotic sac is absent. Fetal head is in in the pelvic inlet. The chin is palpated near sacral region. What is the reason of cephalo-pelvic disproportion? General contracted pelvis Uterine inertia Cephalic presentation D. E. * 108. A. B. * C. D. E. 109. A. * B. C. D. E. 110. Breech presentation Face presentation M., 22 years old, nullipara. Full term of pregnancy. Labor has been started 8 hours ago. The membranes ruptured are intact. Pelvic sizes: 25,28,31,20 cm. Fetal heart rate is 140 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. Per vaginum: the cervix is 8 cm dilated. The amniotic sac is persent. Fetal head is in the plane of inlet. Face line is in the right oblique size, the chin is palpated near sacral region of the symphysis. Which complication is presented in the patient? General contracted pelvis Cephalopelvic disproportion Fetal distress Primary uterine inertia Secondary uterine inertia M., 25 years old, nullipara. Full term of pregnancy. Labor has been started 9 hours ago. The membrane is intact. Pelvic sizes: 25,28,31,20 cm. Vasten sign is positive. Fetal heart rate is 140 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. Cervix is 9 cm dilated in vaginal examination. The amniotic sac is presented. Fetal head is in the plane of inlet. Face line is in the right oblique size, the chin is palpated near sacral region of the symphysis. What is the reason of cephalopelvic disproportion? Face anterior presentation General contracted pelvis Face posterior presentation Sinciput vertex presentation Brow presentation Primipara N., 25 years old. Delivery at term. The labor started 6 hours ago. The membranes ruptured 1 hour ago. Pelvic sizes: 23,26,29,19 cm. Solovjov index is 15cm. Fetal heart rate is 140 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. Uterine contractions occur every 4-5 minutes. The probable fetal weight by Volskov is 4200 g. Uterine cervix dilatation is 7 cm. The amniotic sac is absent. Fetal head is -1 station. Sagittal suture is in the right oblique size. Small and large fontanels are palpated. The large fontanel is under the symphysis. Which degree of pelvic contraction is presented in woman? A. * B. C. I II III D. E. 111. IV V Primipara N., 25 years old. Delivery at term. The labor started 6 hours ago. The membranes ruptured 1 hour ago. Pelvic sizes: 23,26,29,19 cm. Solovjov index is 15cm. Fetal heart rate 140 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. Uterine contractions occur every 4-5 minutes. The probable fetal weight by Volskiy is 4200 g. Uterine cervix dilatation is 8 cm. The amniotic sac is absent. Fetal head is -1 station. Sagittal suture is in the right oblique size. Small and large fontanels are palpated. The large fontanel is under the symphysis. Which complication is presented in labor? Cephalopelvic disproportion Uterine inertia primary Uterine inertia secondary Uterine rupture Discoordinative uterine activity A. * B. C. D. E. 112. A. B. C. D. E. * 113. A. B. C. D. * E. 114. A. B. C. D. * E. 115. A. B. C. D. * E. 116. A. B. C. D. E. * Pregnant N., 25 weeks of pregnancy. During the last 2 months complains of general weakness, violation of taste, the promoted fragility of hair and nails. Uterine height is 20cm above the symphysis. Laboratory findings: erythrocytes - 2,8x10 12/ L, Hb - 98 G/L. The most common fetal complication would be: Macrosomia Avitaminosis Izoimmunisation Asphyxia Fetal growth retardation 26 years old patient is presented in the second stage of labor. Uterine contractions are every 2 minutes by 45-50 seconds. Fetal lie is longitudinal, cephalic presentation is presented. Fetal heart rate is 60 beats per minute. Cervical dilation is 10cm, amniotic fluid are absent, fetal head is presented at +2 station at vaginal examination. The most likely diagnosis is: Preterm labor Uterine inertia Preeclampsia Fetal distress Breech presentation 26 years old patient is presented in the second stage of labor. Uterine contractions are every 2 minutes by 45-50 seconds. Fetal lie is longitudinal, cephalic presentation is presented. Fetal heart rate is 60 beats per minute. Cervical dilation is 10cm, amniotic fluid are absent, fetal head is presented at +2 station at vaginal examination. The appropriate management is: Augmentation of labor Spasmolytics prescription Corticosteroids prescriptions Obstetric forceps application Cesarean section 28 years old patient is presented in the second stage of labor. Uterine contractions are every 1-2 minutes by 50-55 seconds. Fetal lie is longitudinal, cephalic presentation is presented. Fetal heart rate is 70 beats per minute. Cervical dilation is 10cm, amniotic fluid are absent, fetal head is presented at +3 station at vaginal examination. The appropriate management is: Augmentation of labor Spasmolytics prescription Corticosteroids prescriptions Vacuum application Cesarean section 32 years old patient is presented in the first stage of labor. Uterine contractions are every 4 minutes by 25-30 seconds. Fetal lie is longitudinal, cephalic presentation is presented. Fetal heart rate is 60 beats per minute. Cervical dilation is 2 cm, amniotic fluid is absent, fetal head is presented at -2 station at vaginal examination. The appropriate management is: Augmentation of labor Spasmolytics prescription Corticosteroids prescriptions Obstetric forceps application Cesarean section 117. A. B. C. D. * E. 118. A. B. C. D. * E. 119. A. B. C. D. * E. 120. A. B. C. D. E. * 121. A. * B. C. D. E. 36 years old patient is presented in the second stage of labor. Uterine contractions are every 2 minutes by 45-50 seconds. Fetal lie is longitudinal, cephalic presentation is presented. Fetal heart rate is 60 beats per minute. Cervical dilation is 10cm, amniotic fluid is absent, fetal head is presented at +1 station at vaginal examination. The most likely diagnosis is: Preterm labor Uterine inertia Preeclampsia Fetal distress Breech presentation 39 years old patient is presented in the second stage of labor. Uterine contractions are every 1-2 minutes by 50-55 seconds. Fetal lie is longitudinal, cephalic presentation is presented. Fetal heart rate is 70 beats per minute. Cervical dilation is 10cm, amniotic fluid is absent, fetal head is presented at +1 station at vaginal examination. The appropriate management is: Augmentation of labor Spasmolytics prescription Corticosteroids prescriptions Vacuum application Cesarean section 33 years old patient is presented in the second stage of labor. Uterine contractions are every 1-2 minutes by 50-55 seconds. Fetal lie is longitudinal, cephalic presentation is presented. Fetal heart rate is 70 beats per minute. What you should do firstly? Augmentation of labor Spasmolytics prescription Corticosteroids prescriptions Vaginal examination Cesarean section Patient F., 33 years old is admitted to Pathologic Pregnancy department at 36 week of gestation. She complaints of general weakness, dizziness, increasing of fetal activity. Uterine fundus height is situated at the level of the umbilicus. Fetal lie is longitudinal, cephalic presentation is diagnosed. Fetal heart rate is 124 beats per minute. The most likely diagnosis is: Multiple pregnancy Oligohydramnios Fetal hypoxia Fetal distress Fetal growth retardation Patient F., 33 years old is admitted to Pathologic Pregnancy department at 36 week of gestation. She complaints of general weakness, dizziness, increasing of fetal activity. Uterine fundus height is situated at the level of the umbilicus. Fetal lie is longitudinal, cephalic presentation is diagnosed. Fetal heart rate is 124 beats per minute. Appropriate studies to be performed would be: Biophysical profile, umbilical cord Doppler Fetal cells for karyotyping Fetal echocardiography Amniotic fluid alpha-fetoprotein Cervical culture 122. A. * B. C. D. E. 123. A. * B. C. D. E. 124. A. * B. C. D. E. 125. A. * B. C. D. E. 126. A. B. C. D. E. * Patient M., 35 years old is admitted to Pathologic Pregnancy department at 35 week of gestation. She complaints of general weakness, increasing of fetal activity. Uterine fundus height is situated 2 cm above umbilicus. Fetal lie is longitudinal, cephalic presentation is diagnosed. Fetal heart rate is 136 beats per minute. Biophysical profile test score is 10. Your Biophysical Profile is considered to be: Normal Decreased Abnormal Pathologic Equivocal Patient M., 35 years old is admitted to Pathologic Pregnancy department at 36 week of gestation. She complaints of general weakness, increasing of fetal activity. Uterine fundus height is situated 3 cm above umbilicus. Fetal lie is longitudinal, breech presentation is diagnosed. Fetal heart rate is 136 beats per minute. Biophysical profile test score is 9. Your Biophysical Profile is considered to be: Normal Decreased Abnormal Pathologic Equivocal Patient L., 30 years old is admitted to Pathologic Pregnancy department at 30 week of gestation. She complaints of general weakness, increasing of fetal activity. Uterine fundus height is situated 4 cm above umbilicus. Fetal lie is longitudinal, breech presentation is diagnosed. Fetal heart rate is 160 beats per minute. Biophysical profile test score is 8. Your Biophysical Profile is considered to be: Normal Decreased Abnormal Pathologic Equivocal Patient L., 30 years old is admitted to Pathologic Pregnancy department at 30 week of gestation. She complaints of general weakness, increasing of fetal activity. Uterine fundus height is situated 4 cm above umbilicus. Fetal lie is longitudinal, breech presentation is diagnosed. Fetal heart rate is 160 beats per minute. Biophysical profile test score is 8. Your Biophysical Profile is considered to be: Normal Decreased Abnormal Pathologic Equivocal Patient S., 34 years old is admitted to Pathologic Pregnancy department at 32 week of gestation. She complaints of weak fetal activity. Uterine fundus height is situated 4 cm above umbilicus. Fetal lie is transverse. Fetal heart rate is 160 beats per minute. Biophysical profile test score is 6. Your Biophysical Profile is considered to be: Normal Decreased Abnormal Pathologic Equivocal 127. A. B. C. D. E. * 128. A. B. C. * D. E. 129. A. B. C. * D. E. 130. A. B. C. * D. E. 131. A. B. C. * D. E. 132. Patient W., 29 years old is admitted to Pathologic Pregnancy department at 33 week of gestation. She complaints of weak fetal activity. Uterine fundus height is situated 4 cm above umbilicus. Fetal lie is transverse. Fetal heart rate is 160 beats per minute. Biophysical profile test score is 5. Your Biophysical Profile is considered to be: Normal Decreased Abnormal Pathologic Equivocal Patient W., 39 years old is admitted to Pathologic Pregnancy department at 34 week of gestation with moderate degree of preeclampsia. She complaints of weak fetal activity. Uterine fundus height is situated 4 cm above umbilicus. Fetal lie is longitudinal. Fetal heart rate is 160 beats per minute. Biophysical profile test score is 4. Your Biophysical Profile is considered to be: Normal Decreased Abnormal Pathologic Equivocal Patient K., 38 years old is admitted to Pathologic Pregnancy department at 35 week of gestation with moderate degree of preeclampsia. She complaints of weak fetal activity. Uterine fundus height is situated 5 cm above umbilicus. Fetal lie is longitudinal. Fetal heart rate is 160 beats per minute. Biophysical profile test score is 3. Your Biophysical Profile is considered to be: Normal Decreased Abnormal Pathologic Equivocal Patient A., 41 years old is admitted to Pathologic Pregnancy department at 36 week of gestation with severe degree of preeclampsia. She complaints of weak fetal activity. Uterine fundus height is situated 2 cm above umbilicus. Fetal lie is longitudinal. Fetal heart rate is 124 beats per minute. Biophysical profile test score is 2. Your Biophysical Profile is considered to be: Normal Decreased Abnormal Pathologic Equivocal Patient Z., 41 years old is admitted to Pathologic Pregnancy department at 36 week of gestation with severe degree of preeclampsia. She complaints of weak fetal activity. Uterine fundus height is situated 2 cm above umbilicus. Fetal lie is longitudinal. Fetal heart rate is 124 beats per minute. Biophysical profile test score is 1. Your Biophysical Profile is considered to be: Normal Decreased Abnormal Pathologic Equivocal Patient W., 39 years old is admitted to Pathologic Pregnancy department at 35 week of gestation with moderate degree of preeclampsia. She complaints of weak fetal activity. Uterine fundus height is situated 4 cm above umbilicus. Fetal lie is longitudinal. Fetal heart rate is 160 beats per minute. Biophysical profile test score is 4. Appropriate management of the patient is: A. B. C. * D. E. 133. A. B. C. * D. E. 134. A. B. C. * D. E. 135. A. B. C. * D. E. 136. A. B. C. D. * E. 137. A. B. Metabolic drugs prescription Corticosteroids prescription Immediate delivery Fetal heart rate monitoring Tocolytic prescription Patient K., 38 years old is admitted to Pathologic Pregnancy department at 35 week of gestation with moderate degree of preeclampsia. She complaints of weak fetal activity. Uterine fundus height is situated 5 cm above umbilicus. Fetal lie is longitudinal. Fetal heart rate is 160 beats per minute. Biophysical profile test score is 3. Appropriate management of the patient is: Metabolic drugs prescription Corticosteroids prescription Immediate delivery Fetal heart rate monitoring Tocolytic prescription Patient A., 41 years old is admitted to Pathologic Pregnancy department at 36 week of gestation with severe degree of preeclampsia. She complaints of weak fetal activity. Uterine fundus height is situated 2 cm above umbilicus. Fetal lie is longitudinal. Fetal heart rate is 124 beats per minute. Biophysical profile test score is 2. Appropriate management of the patient is: Metabolic drugs prescription Corticosteroids prescription Immediate delivery Fetal heart rate monitoring Tocolytic prescription Patient Z., 41 years old is admitted to Pathologic Pregnancy department at 36 week of gestation with severe degree of preeclampsia. She complaints of weak fetal activity. Uterine fundus height is situated 2 cm above umbilicus. Fetal lie is longitudinal. Fetal heart rate is 124 beats per minute. Biophysical profile test score is 1. Appropriate management of the patient is: Metabolic drugs prescription Corticosteroids prescription Immediate delivery Fetal heart rate monitoring Tocolytic prescription Patient S., 34 years old is admitted to Pathologic Pregnancy department at 35 week of gestation. She complaints of weak fetal activity. Uterine fundus height is situated 4 cm above umbilicus. Fetal lie is transverse. Fetal heart rate is 160 beats per minute. Biophysical profile test score is 6. Appropriate management of the patient is: Metabolic drugs prescription Corticosteroids prescription Immediate delivery Repeat test within 24hours Tocolytic prescription Patient W., 29 years old is admitted to Pathologic Pregnancy department at 36 week of gestation. She complaints of weak fetal activity. Uterine fundus height is situated 4 cm above umbilicus. Fetal lie is transverse. Fetal heart rate is 160 beats per minute. Biophysical profile test score is 5. Appropriate management of the patient is: Metabolic drugs prescription Corticosteroids prescription C. D. * E. 138. A. B. C. * D. E. 139. A. B. C. * D. E. 140. A. B. * C. D. E. 141. A. B. * C. D. E. 142. Immediate delivery Repeat test within 24hours Tocolytic prescription 33 Patient years old is admitted to Pathologic Pregnancy department at 36 week of gestation. She complaints of general weakness. Uterine fundus height is situated 2 fingers above umbilicus. Left occipital anterior presentation is diagnosed. Fetal heart rate is 110 beats per minute. Reversed blood flow is diagnosed at umbilical cord Doppler. Appropriate management of the patient is: Metabolic drugs prescription Corticosteroids prescription Immediate delivery Repeat umbilical cord Doppler within 2 days Tocolytic prescription 32 Patient years old is admitted to Pathologic Pregnancy department at 36 week of gestation. She complaints of general weakness. Uterine fundus height is situated 2 fingers above umbilicus. Left occipital anterior presentation is diagnosed. Fetal heart rate is 110 beats per minute. Blood flow is absent at umbilical cord Doppler. Appropriate management of the patient is: Metabolic drugs prescription Corticosteroids prescription Immediate delivery Repeat umbilical cord Doppler within 2 days Tocolytic prescription Patient Q., 32 years old is admitted to Pathologic Pregnancy department at 32 week of gestation. Signs of moderate preeclampsia are diagnosed in the patient. Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation is diagnosed. Fetal heart rate is 160 beats per minute. Bishop score cervical evaluation has 4 points. Blood flow is absent at umbilical cord Doppler during 3 days monitoring. Corticosteroids have been prescribed for her. Biophysical profile test score is 4. Appropriate management of the patient is: Metabolic drugs prescription Cesarean section immediately Vaginal delivery Repeat biophysical profile within 24hours Tocolytic prescription Patient X., 32 years old is admitted to Pathologic Pregnancy department at 32 week of gestation. Signs of moderate preeclampsia are diagnosed in the patient. Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation is diagnosed. Fetal heart rate is 160 beats per minute. Bishop score cervical evaluation has 4 points. Reversed blood flow is diagnosed at umbilical cord Doppler during 3 days monitoring. Corticosteroids have been prescribed for her. Biophysical profile test score is 3. Appropriate management of the patient is: Metabolic drugs prescription Cesarean section immediately Vaginal delivery Repeat biophysical profile within 24hours Tocolytic prescription Patient N., 33 years old is presented in the first stage of labor. Uterine contractions are every 3 minutes by 35-40 seconds. Fetal lie is longitudinal, cephalic presentation is diagnosed. Fetal heart rate is 100 beats per minute. During fetal heart rate monitoring pathological decelerations have been diagnosed. Cervical dilation is 4cm, amniotic membranes are intact, fetal head is presented at -2 station at vaginal examination. Sagittal suture is located in the left oblique diameter of the pelvic inlet; posterior fontanel is to the left posteriorly. Appropriate management of the patient is: A. B. * C. D. E. 143. A. * B. C. D. E. 144. A. B. * C. D. E. 145. A. B. C. * D. E. 146. A. B. C. D. * E. Metabolic drugs prescription Cesarean section immediately Vaginal delivery Biophysical profile Umbilical cord Doppler Patient N., 33 years old is presented in the first stage of labor. Uterine contractions are every 3 minutes by 35-40 seconds. Fetal lie is longitudinal, cephalic presentation is diagnosed. Fetal heart rate is 100 beats per minute. During fetal heart rate monitoring pathological decelerations have been diagnosed. Cervical dilation is 4cm, amniotic membranes are intact, fetal head is presented at -2 station at vaginal examination. Sagittal suture is located in the left oblique diameter of the pelvic inlet; posterior fontanel is to the left posteriorly. Your diagnosis: Fetal distress Fetal hypoxia Placental dysfunction Fetal growth retardation Placental insufficiency Patient Q., 42 years old is admitted to Pathologic Pregnancy department at 33 week of gestation with mild preeclampsia. Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation is diagnosed. Fetal heart rate is 100 beats per minute. Bishop score cervical evaluation has 4 points. Blood flow is absent at umbilical cord Doppler during 3 days monitoring. Corticosteroids have been prescribed for her. Biophysical profile test score is 6. Appropriate management of the patient is: Metabolic drugs prescription Cesarean section immediately Vaginal delivery Repeat umbilical cord Doppler within 24hours Tocolytic prescription Pregnant B, 20 years, complaints of weak fetal movement. Pregnancy 38 weeks. Uterine contractions are absent. The fetal heart rate is 170 bpm. The estimation of the biophysical profile of the fetus is 6 points. Appropriate management of the pregnant is: Fetal distress therapy Cesarean section immediately Hospitalisation, repeat the biophysical profile within 24 hours Amniocentesis Fetal heart rate monitoring Primapara C., is presented in the first stage of labor which has been started 10 hours ago. Suddenly she complains of releasing green colored amniotic fluid with meconium. Uterine contractions are every 3 minutes by 35 seconds. Longitudinal lie, breech presentation is diagnosed. Fetal heart rate is 90 beats per minute. Pathologic decelerations are presented during fetal heart rate monitoring. Cervix is dilated to 4 cm at vaginal examination. Buttocks are presented. Appropriate management of the patient is: Forceps application Vacuum extraction Breech extraction Cesarean section Fetal heart rate monitoring 147. A. B. C. * D. E. 148. A. B. C. D. E. * 149. A. B. C. * D. E. 150. A. * B. C. D. E. 151. A. * B. C. D. Multipara with pelvis sizes 25-28-31-20 cm is presented in labor. Pushing efforts are every 2 minutes by 45 seconds. Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation is diagnosed. The fetal hear rate is green colored, arrhythmic 80 bpm. At vaginal examination the cervix is totally dilated, Amniotic sac is absent. fetal head is presented in +2 station. Sagittal suture is in anteroposterior diameter of the pelvic outlet. What is the best management of this situation? Caesarean section Vacuum extraction of the fetus Obstetric forceps Conservative tactics of labor Stimulation of the labor activity 25 years old multipara woman is in the second labor for 12hours. Fetal lie is longitudinal, breech presentation is presented. Heartbeat of fetus is arrhythmic, 80beats per min. Cervix of uterus is completely dilated, fetal buttocks are on the pelvic floor. What is the best management of such obstetric situation? Use of obstetric forceps Augmentation of labor Cesarean section Vacuum extraction Breech extraction Pregnant C., 26 years, entered maternity department with regular uterine contractions. Term of pregnancy 39 weeks. Abdominal circumference - 126 cm, uterine fundus height – 41 cm. The fetal lie is longitudinal, breech presentation. Uterus in normal tonus. The fetal heart rate is 130 in 1 min, rhythmic. Vaginally: cervical dilatation is full, vagina is filled by an amniotic sac. During examination about 5 L of amniotic fluid came out, buttocks are in the pelvic cavity. Diagnosis? Large fetus. Breech presentation Multifetal pregnancy. Incomplete presentation of the I fetus Franc breech presentation. Polyhydramnion Polyhydramnion. Complete breech presentation Polyhydramnion A patient in a term 37 weeks of pregnancy was admitted to female dispensary. Patient feels the fetal motions in all abdomen. Abdomen is increased due to a pregnant uterus. Circumference of abdomen 122 cm, level of uterine fundus - 40 cm. 2 round and firm parts of the fetus is palpated [to the right at the level of umbilicus and in the uterine fundus]. Presenting part is mobile above the pelvic inlet. Fetal heart rate is listened to in many points, 140 in 1 min, rhythmic. What is most probable diagnosis? Multifetal pregnancy Hydramnion Pregnancy and myoma of uterus Molar pregnancy Large fetus Pregnant visited the doctor with complaints about the sharp increase of volume of abdomen after the acute infection. Abdominal circumference – 98 cm, uterine fundus height 36 cm. Fetal lie is longitudinal, the fetal head is -3 station, mobile. The fetal heart rate 120 in 1 min. What medical treatment is conducted? Medical treatment by antibiotics Medical treatment by diuretics Medical treatment is contraindicated Medical treatment bycardiac drugs E. 152. A. B. C. D. E. * 153. A. * B. C. D. E. 154. A. B. * C. D. E. 155. A. B. C. D. E. * 156. A. B. C. D. Medical treatment by hypotensive drugs Pregnancy A, multiple, 15-16 weeks of gestation. The table of contents of alpha-fetoprotein in the blood of pregnant exceeds a norm. How to interpret the anomalous level of alpha-fetoprotein in this case? Violation of osteogenesis. Defect of the fetal neural tube. Fetal anomalies. Necrosis of liver. The sign of multifetal pregnancy At a woman 28 years at the second labor a 3400 g girl was born with anemia and increasing icterus. Blood type at a woman B(ІІІ) Rh-, at the father of new-born B(ІІІ) Rh+, at newborn B(ІІІ) Rh+. What is the most credible diagnosis? Rh-izoimmunization. Conflict on an antigen A. Conflict on an antigen B. Conflict on an antigen AV. Infection The pregnant S. was admitted in pathologic of pregnant department. Pregnancy ІІ, 37 weeks. Complaints about the gradual enlargement of abdominal sizes after viral infection. Circumference of abdomen – 110 cm, uterine height – 36 cm. The fetal lie is longitudinal, cephalic presentation, head of the rounded shape, dense, above the pelvic inlet. The fetal heart rate is clear, rhythmic 130 in 1 min. The diagnosis: chronic polyhydramnion. Which antibiotics of the first line used for medical treatment? Doxycycline Erythromycin Amoxill Gentamycin Clyndamycin Patient in 37 weeks of pregnancy was presented in female dispensary. An abdomen is enlarged due to a pregnant uterus. Abdominal circumference - 122 cm, uterine height - 40 cm. Two great parts of fetus are palpated to the right and to the left at the level of umbilicus. Presenting part is not determined. The fetal heart rate is auscultating in many points at the level of umbilicus, 140 and 130 in 1 min, rhythmic. What is the diagnosis? Fetal macrosomia Polyhydramnion Pregnancy and uterine fibromioma Molar pregnancy Multifetal pregnancy 122. The pregnant Х. in 32 weeks of pregnancy visited the doctor of female dispensary with complaints about the increasing of abdominal volume after the acute infection a week ago. The patient’ condition is satisfactory, the edema are absent. The abdominal circumference is 98 cm, uterine fundus level – 36 cm. The fetal lie is longitudinal, the fetal head as in 32 weeks of pregnancy, above the pelvic inlet, mobile. The fetal heart rate 120 in 1 min. What pathology is presented? Multifetal pregnancy Chronic polyhydramnion Breech position of fetus Transversal position of fetus E. * 157. A. * B. C. D. E. 158. A. B. * C. D. E. 159. A. B. C. * D. E. 160. A. B. C. D. E. * 161. A. B. Acute polyhydramnion 133. Primipara F., 24 years old. Multiply pregnancy at term. The labor started 6 hours ago. The membranes are intact. Pelvic sizes: 25,28,31,21 cm. In Leopolds maneuvers – longitudinal lie of both fetuses, breech presentation of the first fetus and cephalic – of the second one. Fetal heart rates 140 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. Uterine contractions occur every 7-8 minutes. Per vaginum: the uterine cervix dilatation is 5 cm. The amniotic sac is absent. Buttocks of the first fetus is presented. Which type of breech presentation is presented? Multiply pregnancy. The frank breech presentation of the first fetus. Multiply pregnancy. Complete breech presentation of the first fetus. Multiply pregnancy. Complete foot-ling presentation of the first fetus. Multiply pregnancy. Incomplete foot-ling presentation of the first fetus. Multiply pregnancy. Knee-ling presentation of the first fetus. 134. Primipara F., 24 years old. Multiply pregnancy at term. The labor started 6 hours ago. The membranes are intact. Pelvic sizes: 25,28,31,21 cm. In Leopolds Maneuvers – longitudinal lie of both fetuses, breech presentation of the first fetus and cephalic – of the second one. Fetal heart rates 140 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. Uterine contractions occur every 7-8 minutes. Per vaginum: the uterine cervix dilatation is 5 cm. The amniotic sac is absent. Buttocks of the first fetus is presented. What is the management of labor? Manual aid by Tsovianov II Cesarean section Subtotal breech extraction Classic manual aid Total breech extraction The woman is admitted to the maternity home with discontinued uterine contractions and slight bloody discharges from the vagina. The condition is severe, skin is pale, and consciousness is confused. BP – 80/40 mm Hg. Fetal heart rate of the fetus is absent. Lover uterine segment is painful. There was a cesarean section one year ago. What is the clinical diagnosis: Placental abruption Placental presentation Uterine rupture Premature expulsion of the amniotic fluids Couveler uterus 25-years old pregnant woman at 32 weeks of gestation is admitted to the hospital with complaints of bloody discharge like spotting. Placenta previa is diagnosed during ultrasonography. The uterine tone is normal, fetal heart rate is 136 beats per minute. What is the best management of the pregnant woman? Induction of labor by prostaglandins Blood transfusion Induction of labor by oxytocin Cesarean section. Tranexamic acid prescription, female monitoring for the intensity of hemorrhage and fetal wellbeing, dexamethasone administration Pregnant N., 25 years is delivered in the maternity department with complaints of periodic pain in lower part of abdomen and lumbar region. Bloody discharge has appeared one hour before. Fetal heart rate is 136 in 1min. At vaginal examination: the uterine cervix is effaced, 6-7 cm dilated. Spongy tissue is palpated laterally. Blood loss is 250 ml and continues. Your management. Stimulation of labor Amniotomy C. D. E. * 162. A. B. C. * D. E. 163. A. B. C. * D. E. 164. A. B. C. * D. E. 165. A. * B. C. D. E. 166. A. B. C. D. * Obstetric forceps The fetal destroying operation Cesarean section Sharp pain in the uterine fundus with profuse bleeding has appeared in the in primapara during the first stage of labor. Uterus is in hypertonus. Fetal heart rate is 200 beats per minute. Uterine cervix is effaced, and 4 cm dilated on vaginal examination. Blood was presented in amniotic fluid during amniotomy. Your management. Labor induction Treatment of fetal distress Cesarean section immediately Tocolytics prescription Coagulants prescription Sharp pain in the uterine fundus with profuse bleeding has appeared in the in primapara during the first stage of labor. Uterus is in hypertonus. Fetal heart rate is 200 beats per minute. Uterine cervix is effaced, and 4 cm dilated on vaginal examination. Blood was presented in amniotic fluid during amniotomy. Your diagnosis. Low lying placenta Placenta previa Placenta abruption Hypertonic dysfunction DIC-syndrome Uterine contractions have stopped suddenly in 25 years old patient after excessive uterine contractions. Vasten sign is positive. Bloody excretions are presented. Fetal heart rate is absent. The condition of patient suddenly became worse, BP went down to 70 mm Hg, pulse 140 in a 1 minute, a skin is pale. What is the reason such condition? Threatened rupture of uterus Placenta abruption Uterine rupture Couveler uterus Placenta previa Postpartum patient 28 years. 3800 grams girl was born. Placenta was delivered as a result of active management of the placenta. Bleeding continues. Cervical and vaginal lacerations are absent. Ruptured vessels are presented during inspection of the placenta. What is the management of this situation? To perform manual exploration of uterine cavity Total hysterectomy Contractile drugs prescription External massage of uterus Antishock garment application 25 years old woman is admitted to the hospital on a 38 week of pregnancy with regular uterine contractions and bloody discharge from vagina. The uterine cervix is effaced and 4 cm dilated, soft spongy tissue is presented. Bleeding increased in vaginal examination. What is the reason of bleeding increasing? Amniotic fluid embolism Bleeding from the rupture of uterine cervix Premature removing of the normally located placenta Complete placenta previa E. 167. A. B. * C. D. E. 168. A. B. * C. D. E. 169. A. B. C. D. * E. 170. A. B. * C. D. E. 171. DIC - syndrome Patient at 39 week of gestation is admitted to the hospital with complaints of sudden acute pain in upper part of abdomen, dizziness, bleeding from vagina. The uterine contractions are regular. Skin and visible mucus membranes are pale, BP 80/50 mm Hg, pulse 126 per minute. Painful infiltrate is palpated in the fundal area. Fetal heart rate is 170, arrhythmic. At vaginal examination the uterine cervix is effaced and 5 cm dilated, amniotic membranes are presented, parts of placenta are not determined. Fetal head is at -2 station. Bloody discharges are visible. What is the most likely diagnosis? Uterine rupture Placenta abruption Placenta previa Hypotonic uterine contraction The uterine tetanus Patient at 39 week of gestation is admitted to the hospital with complaints of acute pain in lower abdomen, dizziness, and bloody discharge from vagina. The uterine contractions are regular every5 minutes by 40 seconds, amniotic membranes are intact. Objectively: skin and visible mucus membranes are pale, BP 80/50 mm Hg, pulse is 126 beats per minute. Uterus is dense. Painful infiltrate is determined on the fundus. Fetal heart rate is 170, arrhythmic. At vaginal examination: cervix is effaced and dilated to 4cm, amniotic membranes are presented, parts of placenta are not determined, fetal head of is at -2 station. Bleeding discharge without clots is presented. What is the management of this situation? Therapeutic rest Cesarean section Oxytocin prescription Fetal destroying operation Uterine curettage Multipara. Uterine contractions occur every 4-5 hours by 25 seconds. Bloody excretions began at once after appearance of contractions. Fetal heart rate is 100-110 beats per minute . Uterine cervix is effaced and dilated till 6 cm, placenta tissue is presented totally. Diagnosis? Threatening rupture of uterus. Couveler uterus Partial placenta previa Complete placenta previa. Placenta abruption Multipara. Uterine contractions occur every 4-5 hours. Bloody excretions began at once after appearance of contractions. Fetal heart rate 100-110 in min. At vaginal examination the uterine cervix is effaced and dilated till 6 cm. In the cervix placental tissue is determined. What will be adequate management? Therapeutic rest Cesarean section Oxytocin prescription Fetal destroying operation Uterine curettage Labor started at 39 weeks of pregnancy. There was one induced abortion, which was complicated by endometritis in the past. At active management of labor placenta doesn’t separated. Considerable bloody excretions appeared at an attempt to do the manual separation of placenta. The blood loss is 600 ml. An attempt of manual separation of placenta from the uterus was not successful. What is the doctor’ management? A. * B. C. D. E. 172. A. B. * C. D. E. 173. A. B. C. * D. E. 174. A. B. C. * D. E. 175. A. B. C. * D. E. 176. A. B. C. * D. E. 177. A. * Hysterectomy Uterine curettage To continue the manual separation of placenta Vasoconstrictors prescription Contractile drugs prescription Massive hypotonic uterine bleeding began after labor by dead child in postpartum period. The blood loss was reached to 1600ml. Venous bleeding was presented. Thrombocytes level was 80 x10 9/l. There were hemorrhages from the places of injections. Which stage of DIC-syndrome was developed at postpartum patient? I III II V IV The girl by 3100g weight was delivered in 35 years old patient. During active management of labor placenta doesn’t separated from uterine cavity. What is the most probable diagnosis? Hypertonus of uterus Placenta previa Placenta accreta Uterine rupture Uterine atony The boy by 3700g was delivered in 36 years old woman. During active management of labor placenta doesn’t separated from uterine cavity. What is the most probable diagnosis? Hypertonus of uterus Placenta previa Abnormal placenta adherence Uterine rupture Uterine atony The boy by 3300g was delivered in 36 years old woman. During active management of labor placenta doesn’t separated from uterine cavity. What is the most probable diagnosis? Hypertonus of uterus Placenta previa Placenta increta Uterine rupture Uterine atony The boy by 3300g was delivered in 36 years old woman. During active management of labor placenta doesn’t separated from uterine cavity. What is the most probable diagnosis? Hypertonus of uterus Placenta previa Placenta percreta Uterine rupture Uterine atony Widespread extravasation of blood into the uterine wall was revealed during cesarean section which was performed as a result of placenta abruption. The uterus is soft, hypotonic bleeding was presented. The uterus had a purplish appearance, owing to such extravasation of blood. Diagnosis? Couveler’s uterus B. C. D. E. 178. A. B. C. D. E. * 179. A. * B. C. D. E. 180. A. B. C. D. * E. 181. A. B. * C. D. E. 182. A. B. C. * D. E. Placenta previa Uterine atony Placenta abruption Inevitable abortion Widespread extravasation of blood into the uterine wall was revealed during cesarean section which was performed as a result of placenta abruption. The uterus is soft, hypotonic bleeding was presented. The uterus had a purplish appearance, owing to such extravasation of blood. Your initial management is: Total Hysterectomy Blood transfusion Subtotal hysterectomy Uterine curettage Pabal prescription, ligation of the a. iliac internal Widespread extravasation of blood into the uterine wall was revealed during cesarean section. The uterus is soft, hypotonic bleeding was presented. The uterus had a purplish appearance, owing to such extravasation of blood. What was the indication to cesarean section in the patient? Placenta abruption Ectopic pregnancy Low lying placenta Molar pregnancy Breech presentation Widespread extravasation of blood into the uterine wall was revealed during cesarean section which was performed as a result of placenta abruption. The uterus is soft, hypotonic bleeding was presented. The uterus had a purplish appearance, owing to such extravasation of blood. Which dose of pabal (Carbetocin) should be prescribed initially for the patient? 10 mkg 25 mkg 50 mkg 100mkg 1000 mkg 42 years old patient was admitted to the maternity hospital in 38 weeks of gestation with bloody discharge like spotting. Complete placenta previa was revealed at ultrasound. Uterine cervix is closed in vaginal examination. What is the adequate management of labor? Augmentation of labor Cesarean section Fetal destroying operation Obstetric forceps application Vacuum extraction 30-years old edematous patient is admitted to the hospital in the second stage of labor. Fetal head is in the pelvic outlet. Profuse hemorrhage have appeared suddenly. Fetal heart rate is 80 beats per minute. What is the adequate management of labor? Cesarean section Fetal heart rate monitoring Obstetric forceps Episiotomy Induction of labor 183. A. * B. C. D. E. 184. A. * B. C. D. E. 185. A. * B. C. D. E. 186. A. B. C. D. * E. 187. A. * B. C. D. E. 188. A. B. * C. D. 30-years old edematous patient is admitted to the hospital in the second stage of labor. Fetal head is in the pelvic outlet. Profuse hemorrhage have appeared suddenly. Fetal heart rate is 80 beats per minute. What is the most probable diagnosis? Placenta abruption Placenta previa Uterine atony Couveler uterus Placenta increta The bleeding began right after childbirth. The blood loss is 300 ml. In active management of third stage of labor placenta is nor separated. Signs of the placental separation are negative. What is the most probable diagnosis? Subtotal placenta adherens Total placenta adherens Couveler’s uterus Placenta previa Placenta abruption The bleeding began right after childbirth. The blood loss is 550 ml. What is the most appropriate management? Manual separation of placenta and exploration of the uterine cavity Prescription of contractile drugs Total hysterectomy Uterine curretage Uterine artery ligation On the 6 day of the postpartum period a 26 years-old woman complaints of profuse bleeding from vagina. Pelvic examination reveals 23-24 weeks increased uterus with clots inside. During examination bloody discharge increases. Diagnosis? Total placenta adherens Subtotal placenta adherens Couveler’s uterus Late postpartum hemorrhage Placenta previa On the 6 day of the postpartum period a 26 years-old woman complaints of profuse bleeding from vagina. Pelvic examination reveals 22-23 weeks increased uterus with clots inside. During examination bloody discharge increases. What is the most appropriate management of this situation? Uterine curettage Uterine artery ligation Total hysterectomy Manual exploration of the uterine cavity Prescription of contractile drugs 4500g infant was delivered in 42 years old patient. Placenta was delivered by active management. All membranes and parts of the placenta were presented during inspection. Blood loss was 350 ml. After 5 min bloody excretions increased. At external uterine massage uterus did not contract well, was soft and large. Diagnosis? Placental abruption Atonic bleeding Uterine rupture Couveler’s uterus E. 189. A. B. C. D. * E. 190. A. B. C. D. * E. 191. A. B. C. D. * E. 192. A. B. C. * D. E. 193. A. B. * C. D. Rupture of the cervix First pregnancy 35 week of gestation. Woman complaints of spotting from the vagina. Blood loss is 50 ml. Uterine tone is normal. Fetal heart rate is clear, rhythmic, 136 beats per minute. Head of the fetus is mobile above the pelvic inlet. Uterine cervix is closed. What is the initial management of the patient? Bed rest Cesarean section immediately Amniotomy Bed rest, hemostatic agents Bed rest, adequate tokolysis First pregnancy 32week of gestation. Woman complaints of spotting from the vagina. Blood loss is 50 ml. Uterine tone is normal. Fetal heart rate is clear, rhythmic, 136 beats per minute. Head of the fetus is mobile above the pelvic inlet. Uterine cervix is closed. What is the initial management of the patient? Bed rest Cesarean section immediately Amniotomy Bed rest, hemostatic, corticosteroids prescriptions Bed rest, adequate tokolysis First pregnancy 33 week of gestation. Woman complaints of spotting from the vagina. Blood loss is 50 ml. Uterine tone is normal. Fetal heart rate is clear, rhythmic, 136 beats per minute. Head of the fetus is mobile above the pelvic inlet. Uterine cervix is closed. What is the aim of corticosteroids prescription? Anti-inflammatory Hemostatic Sedative Prevention of respiratory distress syndrome Adequate tokolysis Massive postpartum bleeding has developed in 34 years old patient with twins. Placenta is intact. Vagina and perineum are without lacerations. Uterine fundus is 5cm above the umbilicus, soft. What is the most likely reason of bleeding? Couveler uterus Uterine rupture Uterine atony Placenta abruption DIC - syndrome Patient is admitted to the hospital with regular uterine contractions. During hospitalization the condition is satisfactory, pulse - 84 in 1 min, BP - 150/90 and 160/90 mm of Hg. Suddenly patient complains of severe pain in abdomen, general weakness, and dizziness. Pulse - 120 in min, AT 80/40 and 90/45 mm Hg. Uterus is tense, very painful. Fetal heart rate is not auscultated. Uterine cervix is effaced, 5 cm dilated at vaginal examination. Amniotic membrane is whole, tense. The head is in the pelvic inlet. Insignificant bloody discharge has appeared from vagina. What is the most likely diagnosis? Uterine rupture Placental abruption Amniotic fluid embolism Molar pregnancy E. 194. A. B. C. * D. E. 195. A. B. * C. D. E. 196. A. B. * C. D. E. 197. A. * B. C. D. E. 198. A. B. C. D. * E. 199. Placenta previa Considerable bloody discharge has appeared at 30week of gestation in 35 years old patient. Total placenta previa is diagnosed during ultrasonography. General blood loss is 500 ml and bleeding continues. What is the management? Tocolitics prescription Cervical cerclage Cesarean section immediately Hemostatics Vaginal delivery The bleeding began right after childbirth. The blood loss was 300 ml. In attempt to remove placenta during traction it did not separate. Doctors’ tactics. Cesarean section Manual removal of placenta Cerclage Total hysterectomy Ligation of uterine vessels 28 years old pregnant women complains of vaginal bleeding at 40 weeks. Fetal heart rate is 140 BPM. The results of the obstetrics examination: cervix is incompletely effaced, 3 cm dilated, the placental tissue is palpated. Diagnosis? Abnormal placenta adherence Complete placenta previa Uterine atony Uterine rupture Placental abruption 28 years old pregnant women complaints of vaginal bleeding at 40 week of gestation. Fetal heart rate is 140 BPM. The results of the obstetrics examination: cervix is incompletely effaced, 4 cm dilated, the placental tissue is palpated. Management? Cesarean section Manual removal of placenta Cerclage Total hysterectomy Ligation of ovarian vessels 29 years old woman at 39 weeks of pregnancy complaints of small amount of bloody discharge till 50 ml and regular uterine contractions which have been started 5 hours ago. Fetal head rate is 132 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. Cervix is dilated till 5 cm in obstetric examination The amniotic sac is present. Fetal head is in plane of pelvic inlet. The edge of the placenta lies adjacent to the internal os. Diagnosis? Abnormal placenta adherence Complete placenta previa Uterine atony Incomplete placenta previa Placental abruption 30 years old primapara at 39 week of pregnancy complaints of small amount of bloody discharge and regular uterine contractions which have been started 5 hours ago. Fetal head rate 132 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. At obstetric exam cervix is dilated till 2 cm. The amniotic sac is present. Fetal head is in plane of pelvic inlet. The edge of the placenta lies adjacent to the internal os. Blood loss is 300 ml and continues. What is the best management of labor? A. * B. C. D. E. 200. A. * B. C. D. E. 201. A. * B. C. D. E. 202. A. * B. C. D. E. 203. A. B. C. D. * E. 204. A. B. C. D. * E. Cesarean section Manual removal of placenta Amniotomy, oxytocin prescription Total hysterectomy Ligation of ovarian vessels 21 years old, primapara at 38 week of pregnancy complaints of profuse bleeding till 400ml. Contractions are regular. At obstetric exam cervix is dilated till 4 cm. The amniotic sac is present. Fetal head is in plane of pelvic inlet. The leading edge of the placenta is 2 cm from the internal cervical os. What is the best management of labor? Cesarean section Manual removal of placenta Amniotomy, oxytocin prescription Total hysterectomy Ligation of ovarian vessels 34 years old, primapara at 37 week of pregnancy complaints of small amount of bloody discharge. Contractions are irregular. Fetal heart rate is 132 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. At obstetric exam cervix is closed. The leading edge of the placenta is 1 cm from internal cervical os. What is the management of the pregnancy? Cesarean section Manual removal of placenta Amniotomy, oxytocin prescription Total hysterectomy Ligation of ovarian vessels What is the first step in postpartum hemorrhage treatment? Call for help Insert intravenous access Recognize circulatory problem. Administer for face oxygen mask Abdominal examination to confirm uterus well contracted Vaginal examination for laceration 30 years old undergoes spontaneous delivery of a 3900 g boy. 10 units of oxytocin were administered. After successful umbilical cord traction placenta was delivered. Placental tissue is expelled with umbilical cord, but vaginal hemorrhage ensues immediately thereafter. The placenta is clearly not intact. What are appropriate immediate interventions in this situation? Total hysterectomy Subtotal hysterectomy Uterine curettage Manual exploration of uterine cavity External uterine massage 30 years old undergoes spontaneous delivery of a 3900 g boy. 10 units of oxytocin were administered. After successful umbilical cord traction placenta was delivered. Placental tissue is expelled with umbilical cord, but vaginal hemorrhage ensues immediately thereafter. The placenta is clearly not intact. What is the most probable diagnosis? Placenta accreta Placenta increta Placenta percreta Retained placenta tissue Placenta previa 205. A. * B. C. D. E. 206. A. * B. C. D. E. 207. A. * B. C. D. E. 208. A. B. C. D. E. * 209. A. B. C. * D. E. 210. A 30-year-old pregnant was admitted to a maternity hospital with interm pregnancy. She complains of severe pain in the uterus that started 1 hour ago, nausea, vomiting, cold sweat. Cesarean section was performed 2 years ago. Uterine contractions have stopped. Skin and mucous membranes are pale. Heart rate is 100/min. BP is 90/60 mm Hg. Uterus is sharply painful. Fetal heart rate is not auscultated. Moderate bloody discharge from the uterus is observed. Uterus cervix is 4 cm open. Presenting part is not palpated. The most probably diagnosis is: Uterine rupture Placenta previa Placenta abruption Premature separation of normally localized placenta Compression of inferior pudendal vein Examination of a just delivered placenta reveals 2x3cm defect. Vaginal bleeding is presented. Your initial management: Manual exploration of uterine cavity Abduladze method Crede's method Uterine curettage Oxytocin intravenously Examination of a just delivered placenta reveals 2x3cm defect. Vaginal bleeding is absent. Your initial management: Manual exploration of uterine cavity Abduladze method Crede's method Uterine curettage Oxytocin intravenously Examination of a just delivered placenta reveals 2x3cm defect. Vaginal bleeding is presented. Manual exploration of the uterine cavity is indicated. Which method of anesthesia you would choose? You don’t need anesthesia Intrauterine Paravaginal Paracervical Intravenous 36 years old multipara at 41 week of pregnancy complaints of vaginal bleeding like spotting. Contractions are regular. At obstetric exam cervix is dilated till 5 cm. The amniotic sac is present. Fetal head is in the pelvic inlet. The leading edge of the placenta is 4 cm from the internal cervical os at ultrasonography. What is the best management of labor? Cesarean section Manual removal of placenta Amniotomy, oxytocin prescription Total hysterectomy Ligation of ovarian vessels 32 years old multipara at 40 week of pregnancy complaints of vaginal bleeding like spotting. Contractions are every 3-4 minutes by 30 seconds. Cervix is dilated to 6 cm during vaginal examination. Amniotic membranes are intact. Fetal head is in the pelvic inlet. The leading edge of the placenta is 3 cm from the internal cervical os at ultrasonography. What is the best management of labor? A. B. C. * D. E. 211. A. * B. C. D. E. 212. A. B. C. D. E. * 213. A. B. * C. D. E. 214. A. B. C. D. Cesarean section Manual removal of placenta Amniotomy, oxytocin prescription Total hysterectomy Ligation of ovarian vessels 29 years old primapara at 38 week of pregnancy is admitted to the hospital with complaints of bloody discharge, general weakness and regular uterine contractions which have been started 5 hours ago. In examination pulse is 100 beats per minute, BP – 100/60 and 95/55 mm of Hg. Uterus is tense, very painful in the fundal area. Fetal heart rate is not auscultated. Uterine cervix is effaced, 5 cm dilated at vaginal examination. Amniotic membranes are intact. The head is in the pelvic inlet. Blood loss reaches 1000ml. Which degree of hemorrhagic shock is presented in the patient? I II III IV V 29 years old primapara at 38 week of pregnancy is admitted to the hospital with complaints of bloody discharge, general weakness and regular uterine contractions which have been started 5 hours ago. In examination pulse is 100 beats per minute, BP – 100/60 and 95/55 mm of Hg. Uterus is tense, very painful in the fundal area. Fetal heart rate is not auscultated. Uterine cervix is effaced, 5 cm dilated at vaginal examination. Amniotic membranes are intact. The head is in the pelvic inlet. Blood loss reaches 1000ml.What is the general amount of infusion therapy should be prescribed? 500ml 1000ml 1500ml 2000ml 2500ml 34 years old primapara at 40 week of pregnancy is admitted to the hospital with profuse vaginal bleeding, loss of consciousness. In examination pulse is 120 beats per minute, BP – 80/60 and 75/55 mm of Hg. Uterus is tense, very painful in the fundal area. Fetal heart rate is not auscultated. Uterine cervix is effaced, 6 cm dilated at vaginal examination. Amniotic membranes are intact. The head is in the pelvic inlet. Blood loss reaches 1500ml. Which degree of hemorrhagic shock is presented in the patient? I II III IV V 34 years old primapara at 40 week of pregnancy is admitted to the hospital with profuse vaginal bleeding, loss of consciousness. In examination pulse is 120 beats per minute, BP – 80/60 and 75/55 mm of Hg. Uterus is tense, very painful in the fundal area. Fetal heart rate is not auscultated. Uterine cervix is effaced, 6 cm dilated at vaginal examination. Amniotic membranes are intact. The head is in the pelvic inlet. Blood loss reaches 1500ml. What is the general amount of infusion therapy should be prescribed? 500ml 1000ml 1500ml 2000ml E. * 215. A. B. C. D. * E. 216. A. * B. C. D. E. 217. A. B. C. * D. E. 218. A. B. C. * D. E. 219. A. B. C. D. * E. 220. 3000ml A primigravid client at 37 weeks' gestation has been hospitalized for several days with severe preeclampsia. While caring for the client, the physician observes that the client is beginning to have a seizure. Which of the following actions should the physician do first? Pad the side rails of the client's bed. Turn the client to the right side. Insert a padded tongue blade into the client's mouth. Call for immediate assistance in the client's room. Catheterize central vein The husband of a client, who at 24 weeks' gestation has been admitted to the hospital for preeclampsia, screams to the physician that his wife just had a seizure. The physician's immediate action should be to: Turn the client's head to the side Place an airway into the client's mouth Check the client for a spontaneous birth Assess the fetal heart rate for decelerations Monitor uterine contraction A 29-year-old multigravid client at 37 weeks' gestation is being treated for severe preeclampsia. She has magnesium sulfate infusing at 3 grams per hour. Before administering IV magnesium sulfate therapy the physician should assess the client's: Temperature and respirations Urinary glucose and specific gravity Urinary output and patellar reflexes Level of consciousness and funduscopic appearance Fetal heart rate and cervical dilatation A client with preeclampsia is admitted to the labor and birthing suite. Her blood pressure is 130/90 mm Hg, she has 2+ protein in her urine, and edema of the hands and face. As part of the admission history, the physician should ask the client about: Constipation, edema, visual problems, and headache Visual disturbances, headache, constipation, and bleeding Headache, visual disturbances, edema, and abdominal pain Leakage of amniotic fluid, bleeding, edema, and abdominal pain Increase urinary output, edema, and abdominal pain A 24-year-old primigravid client at 38 weeks' gestation is admitted to the labor and birthing suite. Her blood pressure is 170/130 mm Hg, she has 3+ protein in her urine, and edema of the hands and face. Severe preeclampsia was diagnosed and given an IV infusion of magnesium sulfate. The physician recognizes that magnesium sulfate is being given primarily because it is a: Hypotensive that relaxes smooth muscles Cholinergic that increases the release of acetylcholine Muscle relaxant that decreases the severity of uterine contractions Central nervous system depressant that blocks neuromuscular transmissions Source of microelements The physician on the high-risk unit assesses a 20-year-old primigravid client at 38 weeks' gestation admitted with severe preeclampsia. Her blood pressure is 190/140 mm Hg, she has 4+ protein in her urine, and edema of the hands and face. The client has audible crackles in the lower left lobe, slight blurring of vision in the right eye, and epigastric discomfort. Which sign or symptom would most likely indicate the potential for a seizure? A. B. C. * D. E. 221. A. B. C. * D. E. 222. A. B. C. * D. E. 223. A. * B. C. D. E. 224. A. B. C. D. * E. 225. A. B. Audible crackles Blurring of vision Epigastric discomfort Generalized facial edema Uterine contraction The labor of a pregnant woman with preeclampsia is going to be induced. Before initiating the Pitocin infusion, the physician reviews the woman's latest laboratory test findings that reveal a platelet count of 90,000, an elevated aspartate transaminase (AST) level, and a falling hematocrit. What is lab results are indicative for? Eclampsia Disseminated intravascular coagulation HELLP syndrome Idiopathic thrombocytopenia Thrombophilia A pregnant woman has been receiving a magnesium sulfate infusion for treatment of severe preeclampsia for 24 hours. On assessment, the physician finds the following vital signs: temperature of 37.3° C, pulse rate of 88 beats per minute, respiratory rate of 10 breaths per minute, blood pressure of 148/90 mm Hg, absent deep tendon reflexes, and no ankle clonus. The client complains, “I'm so thirsty and warm.” The physician: Calls for a stat magnesium sulfate level Administers oxygen Discontinues the magnesium sulfate infusion Prepares to administer hydralazine Measure level of proteinuria A woman with severe preeclampsia has been receiving magnesium sulfate by intravenous infusion for 8 hours for preeclampsia. The physician assesses the woman and documents the following findings: temperature of 37.1° C, pulse rate of 96 beats per minute, respiratory rate of 24 breaths per minute, blood pressure of 155/112 mm Hg, 3+ deep tendon reflexes, and no ankle clonus. Which prescriptions should be done? Hydralazine Magnesium sulfate bolus Diazepam Calcium gluconate Furosemide A woman at 39 weeks' gestation with a history of PIH is admitted to the labor and birth unit. She suddenly experiences increased contraction frequency of every 1 to 2 minutes, dark red vaginal bleeding, and a tense, painful abdomen. The physician suspects the onset of: Eclamptic seizure Rupture of the uterus Placenta previa Abruptio placentae Term delivery A client has been on magnesium sulfate for 20 hours for treatment of preeclampsia. She just delivered a viable infant girl 30 minutes ago. What uterine findings would you expect to observe/assess in this client? Absence of uterine bleeding in the postpartum period Fundus firm below the level of the umbilicus C. D. * E. 226. A. B. C. D. * E. 227. A. B. C. D. * E. 228. A. B. * C. D. E. 229. A. B. C. * D. E. 230. A. B. C. * D. E. 231. A. Scant lochia flow A boggy uterus with heavy lochia flow Prolong placenta separation A 17-year-old primigravida 36 weeks’ gestation has gained 1.9 kg since her last prenatal visit 2 weeks ago. Her blood pressure is 140/92. The most important action is to: caution her to avoid salty foods and to return in 2 weeks. advise her to cut down on fast foods that are high in fat. recommend she stay home from school for a few days to reduce stress. assess weight gain, location of edema, and urine for protein. perform vaginal examination and auscultation o fetal heart rate/ A 22-year-old primigravida 38 weeks’ gestation is admitted to the labor and birth unit. On assessment, the physician finds the following vital signs: temperature of 36.6° C, pulse rate of 90 beats per minute, respiratory rate of 16 breaths per minute, blood pressure of 180/135 mm Hg. A magnesium sulfate infusion for treatment of severe preeclampsia was prescribed. 2 hours late signs of magnesium sulfate toxyсity were diagnosed. Which medication should be prescribed Furosemide Hydralzine Nifedipine Calcium gluconate Diazepam Louise Perkins is admitted to the hospital at 32 weeks' gestation with a diagnosis of severe preeclampsia. Ms. Perkins receives intravenous infusion of 4 grams of magnesium sulfate. What is the purpose of magnesium sulfate for this client? to lower blood pressure to prevent seizures to inhibit labor to block dopamine receptors to stimulate labor Louise Perkins is admitted to the hospital at 32 weeks' gestation with a diagnosis of severe preeclampsia. Ms. Perkins receives intravenous infusion of 4 grams of magnesium sulfate. When assessing Mg s. Perkins's deep tendon reflexes (DTRs), the physician notes that they are 2+. What is the implication of this finding? The client needs a higher dose of magnesium sulfate. The client needs a lower dose of magnesium sulfate. A therapeutic level of magnesium sulfate has been reached. Magnesium sulfate should be discontinued. it is not influence on continuous if magnesium sulfate infusion A client at 32 weeks' gestation who has pregnancy-induced hypertension is attending the prenatal clinic for the routine checkup. The first sign of fluid retention suggestive of this complication is: Abdominal enlargement Facial swelling Sudden weight gain Swelling of the feet and ankles General edema A client at 36 weeks' gestation who has pregnancy-induced hypertension is present in the prenatal clinic. She has all the signs below. What is the most dangerous symptom? Diarrhea B. C. * D. E. 232. A. * B. C. D. E. 233. A. * B. C. D. E. 234. A. B. C. * D. E. 235. A. B. C. * D. E. 236. A. B. C. D. * E. Decreased urine output Blurred vision Backache Facial swelling The patient who is 28 weeks pregnant with chronic hypertension visit for routine checkup. What is the main recommendation physician should give her? Activity restriction Balanced nutrition Increased fluid intake to ensure adequate hydration Instruction about the effect of diuretics Increased nutrition A client at 36 weeks' gestation who has severe preeclampsia was prescribed intravenous magnesium sulfate infusion. Which assessment should be performed during this infusion? Count respirations and report a rate of less than 12 breaths per minute. Count respirations and report a rate of more than 20 breaths per minute. Check blood pressure and report a rate of less than 100/60. Monitor urinary output and report a rate of less than 100 ml per hour. Monitor reflexes and report increased reflexes At 32 weeks' gestation, a 15-year-old primgravida client who is 1.57 m tall has gained a total of 9 kg, with a 450g gain in the last 2 weeks. Urinalysis reveals negative glucose and a trace of protein. Which of the following factors increases this client's risk for preeclampsia? Total weight gain. Short stature. Adolescent age group. D. Proteinuria. E. Gestational age A 32-year-old multigravida returns to the clinic for a routine prenatal visit at 36 weeks' gestation. She has had a prior pregnancy with pregnancy induced hypertension. The assessments during this visit include BP 140/90, Ps 80, and + 2 edema of the ankles and feet. Based on the client's past history and current assessment, what further infor_mation should the physician obtain to determine if this client is becoming preeclamptic? Headaches. Blood glucose level. Proteinuria. Edema in lower extremities. Gestational age of previous pregnancy when preeclampsia was diagnosed A primigravid client's baseline blood pressure at her initial visit at 12 weeks' gestation was 110/70 mm Hg. During an assessment at 38 weeks' gestation, which of the following data would indicate mild preeclampsia? Blood pressure of 160/110 mm Hg on two separate occasions. Proteinuria, more than 5 g in 24 hours. Serum creatinine concentration of 1.4 ml/dl. Weight gain of 900g in the last week. Swelling of the feet and ankles 237. A. B. C. D. * E. 238. A. * B. C. D. E. 239. A. B. * C. D. E. 240. A. B. * C. D. E. 241. A. B. C. * D. E. 242. A. * B. During a routine checkup of a 16-year-old client at 34weeks' gestation diagnosed with mild preeclampsia, assessment reveals that the client has gained 900 g in the past week and her current blood pressure is 130/85 mm Hg. Which of the following assessment findings would provide further evidence to support the client's diagnosis? Pounding headache after reading. History of urinary tract infection. Frequent voiding in large amounts. Mild edema in hands and face. Blood pressure last week 140/85 mm Hg A 17-year-old client at 33 weeks' gestation diagnosed with mild preeclampsia is prescribed bed rest. The physician instructs the client to contact the nurse immediately if she experiences which of the following? Blurred vision. Ankle edema. Increased energy levels. Mild backache. General weakness One week after her prenatal visit, a primigravid client at 38 weeks' gestation diagnosed with mild preeclampsia calls the clinic physician complaining of a continuous headache for the past 2 days accompanied by nausea. The client does not want to take aspirin. Which of the following responses by the physician would be most appropriate? "Take two acetaminophen tablets. They aren't as likely to upset your stomach." "You should be examined today. Come to the clinic this morning." "You need to lie down and rest. Have you tried placing a cool compress over your head?" "Take aspirin with codeine.” "Don’t worry. Sometimes pregnant woman feels headache." When reviewing the prenatal records of a 16-year-old primigravid client at 37 weeks' gestation diagnosed with severe preeclampsia, the physician would interpret which of the following as most indicative of the client's diagnosis? Blood pressure of 138/94 mm Hg. Severe blurring of vision. Less than 2 g of protein in a 24-hour sample. Weight gain of 450 g in 1 week. Ankle edema The physician orders intravenous magnesium sul_fate for a primigravid client at 38 weeks' gestation diag_nosed with severe preeclampsia. Which of the following medications would the physician have readily available at the client's bedside? Diazepam. Hydralazine. Calcium gluconate. Oxytocin. Nifedipine For the 29-year-old multigravid client at 37 weeks' gestation who is receiving intravenous magnesium sulfate for severe preeclampsia, which of the following assessment findings would alert to suspect hypermagnesemia? Decreased deep tendon reflexes. Cool skin temperature. C. D. E. 243. A. B. * C. D. E. 244. A. B. C. D. * E. 245. A. B. C. * D. E. 246. A. * B. C. D. E. 247. A. B. C. * D. E. 248. Rapid pulse rate Tingling in the toes. Decrease of ankle edema A 28-year-old multigravid client at 37 weeks' gestation arrives at the emergency department via ambulance with a blood pressure of 160/104 mm Hg and +3 reflexes without clonus. The client, who is diagnosed with severe preeclampsia, asks the physician, "What is the cure for my high blood pressure?" Which of the following would the physician identify as the primary cure? Administration of glucocorticoids. Vaginal or cesarean delivery of the fetus. Sedation with anti-seizure medication. Reduction of fluid retention with thiazide diuretics. Administration of antihypertensive medication. Which of the following would the physician identify as the priority to achieve when developing the plan of care for a primigravid client at 38 weeks' gestation who is hospitalized with severe preeclampsia and receiving intravenous magnesium sulfate? Decreased generalized edema within 8 hours. Decreased urinary output during the first 24 hours Sedation and decreased reflex excitability within 48 hours. Absence of any seizure activity during the first 48 hours. Decreased breath movement less than 12 per minute When administering intravenous magnesium sulfate as ordered for a client at 34 weeks' gestation with severe preeclampsia, the physician would explain to the client and her family that this drug acts as which of the following? Peripheral vasodilator Antihypertensive. Central nervous system depressant. Sedative-hypnotic. Diuretic Soon after admission of a primigravid client at 38 weeks' gestation with severe preeclampsia, the physician orders a continuous intravenous infusion of 5% dextrose in Ringer's solution and 4 g of magnesium sulfate. While the medication is being administered, which of the following assessment findings should the physician report immediately? Respiratory rate of 12 breaths /minute Patellar reflex of+2. Blood pressure of 160/88 mm Hg. Urinary output exceeding intake. Increase of deep tendon reflexes As the physician enters the room of a newly admitted primigravid client diagnosed with severe preeclampsia, the client begins to experience a seizure. Which of the following should the physician do first? Insert an airway to improve oxygenation. Note the time when the seizure begins and ends. Call for immediate assistance. Turn the client to her left side. Catheterize central vein After administering hydralazine 5 mg intravenously as ordered for a primigravid client with severe preeclampsia at 39 weeks' gestation, the physician would be alert for which of the following? A. * B. C. D. E. 249. A. B. C. D. * E. 250. A. B. C. * D. E. 251. A. * B. C. D. E. 252. A. B. C. * D. E. 253. A. B. C. * D. E. Tachycardia. Bradypnea. Polyuria. Dysphagia. Constipation A primigravid client at 40 weeks' gestation with severe preeclampsia exhibits hyperactive, very brisk patellar reflexes with two beats of ankle clonus present. The physician documents the patellar reflexes as which of the following? 1+ 2+ 3+ 4+ 5+ A 16-year-old unmarried primigravid client at 37 weeks' gestation with severe preeclampsia is in early active labor. Her mother is at the bedside. The client's blood pressure is 164/110 mm Hg. Which of the following would alert the physician that the client may be about to experience a seizure? Decreased contraction intensity. Decreased temperature. Epigastric pain. Hyporeflexia. Increased ankle edema If a client at 36 weeks' gestation with eclampsia begins to exhibit signs of labor after an eclamptic seizure, for which of the following would the physician assess? Abruptio placentae. Transverse lie. Placenta accreta. Uterine atony. Placenta previa For a multigravid client at 39 weeks' gestation with suspected HELLP syndrome, the physician would immediately notify which of the following laboratory test results? Hyperfibrinogenemia. Decreased liver enzymes Thrombocytopenia. Hypernatremia. Anemia A 16-year-old primigravid client admitted at 38 weeks' gestation with severe pregnancy-induced hypertension is given intravenous magnesium sulfate and lactated Ringer's solution. Which of the following assessments should the physician prescribe? Urinary output even'8 hours. Deep tendon reflexes even' 4 hours. Respiratory rate every hour. Blood pressure every 6 hours. Uterine contraction every 4 hours 254. A. B. C. D. * E. 255. A. B. * C. D. E. 256. A. B. C. * D. E. 257. A. * B. C. D. E. 258. A. B. * C. D. E. 259. A. B. C. D. * A woman is using the basal body temperature method of contraception. She calls the clinic and tells the physician, “My period is due in a few days and my temperature has not gone up.” The physician's most appropriate response would be: “This probably means you are pregnant.” “Don't worry; it is probably nothing.” “Have you been sick this month?” “You probably did not ovulate during this cycle.” “You are pregnant.” A woman who has a seizure disorder and takes barbiturates and phenytoin sodium daily asks the physician about the pill as a contraceptive choice. The physician's most appropriate response would be: “This is a highly effective method, but it has some side effects.” “Your current medications will decrease the effectiveness of the pill.” “The pill will decrease the effectiveness of your seizure medication.” “This is a good choice for your age and personal history.” “This method is contraindicated for you” A woman who has just undergone a first trimester abortion will be using oral contraceptives. To be protected from pregnancy, she should be advised to: Avoid sexual contact for at least 10 days after starting the pill. Use condoms and foam for the first few weeks as backup. Use another method of contraception for one week after starting the pill. Begin sexual relations once vaginal bleeding has ended. Contraceptive pill start work after next period A woman was treated recently for toxic shock syndrome. She has intercourse occasionally and uses over-the-counter protection. Based on her history, what contraceptive method should she and her partner avoid? Cervical cap Condom Vaginal film Vaginal sheath Combine contraceptive pill An unmarried young woman visit to family planning center for consultation. She describes her sex life as “active” with “many” partners. She wants a contraceptive method that is reliable and does not interfere with sex. She requests an intrauterine device (IUD). The physician's most appropriate response would be: “The IUD does not interfere with sex.” “The risk of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) will be higher for you.” “The IUD will protect you from sexually transmitted infections.” “Pregnancy rates are high with the IUDs.” “The IUD is the best choice for you” A married couple is discussing male and female sterilization with the physician. Which of the following statements is most appropriate for the physician to make? “Male and female sterilization methods are 100% effective.” “A vasectomy may have a slight effect on sexual performance.” “Tubal ligation can be easily reversed if you change your mind in the future.” “Major complications after sterilization are rare.” E. 260. A. B. C. * D. E. 261. A. B. C. * D. E. 262. A. B. C. D. * E. 263. A. * B. C. D. E. 264. A. B. * C. D. E. 265. A. “A vasectomy is more preferable than tubal ligation” A woman had unprotected intercourse 36 hours ago and is concerned that she may become pregnant because it is her “fertile” time. She asks the physician about emergency contraception. The physician would tell her that: It is too late since she needed to begin treatment within 24 hours after intercourse. Prevent, an emergency contraceptive method, is 98% effective in preventing pregnancy. An over-the-counter antiemetic can be taken 1 hour prior to each contraceptive dose to prevent nausea and vomiting. The most effective approach is to use a progestin-only preparation. don’t worry you have additional 48 hour to make decision about taking the pill A client 34 years old with 14 years history of diabetes asks the physician for advice regarding methods of birth control. Which method of birth control is most suitable for the client with diabetes? Vaginal ring Oral contraceptives Diaphragm Contraceptive sponge Progestine only pill The adolescent client asks the physician why she has a 26-day cycle and her friend has a 29-day cycle? The physician's best response is: "The length of your menstrual cycle is individual and is controlled by hormones from the: Uterus and no other structure Ovaries and the uterus Pituitary gland and uterus Ovaries and pituitary gland Pituitary gland and no other structure A 22-year-old nulligravid client tells the physician that she and her husband have been considering using condoms for family planning. Which of the following instructions would the physician include about the use of condoms as a method for family planning? Using a spermicide with the condom offers added protection against pregnancy. Natural skin condoms protect against sexually transmitted diseases. The typical failure rate for couples using condoms is about 25%. Condom users commonly report penile gland sensitivity. It is not effective method for married couple A 32-year-old female client visit to family planning center for contraceptive counseling and selection. She is married and together with her husband makes decision about using diaphragm as family planning method. Which of the following would the physician include in the teaching plan for this client? Douching with an acidic solution after intercourse is recommended. Diaphragms should not be used if the client develops acute cervicitis. The diaphragm should be washed in a weak solution of bleach and water. The diaphragm should be left in place for 2 hours after intercourse. The diaphragm should be changed after each intercourse Garry, 36 years old male, visit to family planning center for contraceptive counseling and selection of effective contraceptive method. He is married, he has 3 kids and he thinks that rich desired family size. He thinks about vasectomy. When describing a vasectomy to Garry inquiring about this procedure, the physician would explain that which of the following is clamped or excised? Ejaculatory duct. B. C. D. * E. 266. A. B. * C. D. E. 267. A. B. C. * D. E. 268. A. B. C. D. * E. 269. A. B. C. * D. E. 270. A. B. C. D. * E. 271. Seminiferous tubules. Seminal vesicles. Vas deferens. Prostate gland A 23-year-old nulliparous client visiting the clinic for a routine examination tells the physician that she desires to use the basal body temperature method for family planning. The physician should instruct the client to do which of the following? Check the cervical mucus to see if it is thick and sparse. Take her temperature at the same time every morning before getting out of bed. Document ovulation when her temperature decreases at least 1°F. Avoid coitus for 10 days after a slight rise in temperature. you still infertile before rising temperature A multigravid client will be using medroxyprogesterone acetate (Depo-Provera) as a family planning method. After the physician instructs the client about this method, which of the following client statements indicates effective teaching? "This method of family planning requires monthly injections." "I should have my first injection during my menstrual cycle." "One possible adverse effect is absence of a menstrual period." "This drug will be given by subcutaneous injections." “I should massage injection site every day” Which of the following instructions should the physician expect to include in the teaching plan for a 30-year-old multiparous client who will be using an intrauterine device (IUD) for family planning? Amenorrhea is a common adverse effect of IUDs. The client needs to use additional protection for conception. IUDs are more costly than other forms of contraception. Severe cramping may occur when the IUD is inserted. The client needs to check displacement of IUD every week Carol LeBec, age 16, comes to the clinic for contraceptive counseling and selection. Before counseling Ms. LeBec, what should the physician do first? Obtain a complete health history. Perform a thorough physical examination. Evaluate personal beliefs about family planning. Determine why the client seeks counseling. Ask about menarche Sintia, age 20, comes to the clinic for contraceptive counseling and selection. The physician advises to teach Sintia about oral contraceptives because they are easy to use. How should the physician proceed? Review all contraceptive choices so that the client will understand the ease of taking one pill every day. Discuss barrier methods because the client may forget to take the pill every day. Ask the client which method she would like to learn about Check for contraindications and discuss methods that best fit the client's needs and life-style. Explain advantages of barrier method Laura Hunt, age 37, comes to the family planning clinic for contraceptive advice. Her history reveals frequent urinary tract infections. Which of the following contraceptive methods would be most appropriate for her? A. * B. C. D. E. 272. A. * B. C. D. E. 273. A. B. * C. D. E. 274. A. B. C. * D. E. 275. A. B. * C. D. E. 276. A. B. * C. D. E. 277. A. condom cervical cap contraceptive sponge diaphragm spermicide Neatha, age 32, comes to the family planning clinic for contraceptive advice. Her history reveals frequent urinary tract infections. Which of the following assessment findings would contraindicate an oral contraceptive for Ms. Hunt? history of a benign liver tumor 10 pounds under her ideal weight history of dysmenorrhea since age 15 family history of ovarian cancer monogamous relationship Terry, age 27, comes to the family planning clinic for contraceptive advice. Her history reveals frequent urinary tract infections. Terry inquires about the symptothermal contraceptive method. In this method, the client notes which of the following signs to help detect the fertile period? breast enlargement and tenderness clear, thin, elastic cervical mucus decreased libido weight gain of 2 to 3 pounds irregular period Betty, age 24, has been using an oral contraceptive for the past 5 years. Now she wants to become pregnant. What advice should the physician give Betty? Attempt to conceive as soon as possible after discontinuing the oral contraceptive. Discontinue the oral contraceptive and wait 1 month before attempting to conceive. Discontinue the oral contraceptive and wait 3 months before attempting to conceive. Attempt to conceive after a physical assessment confirms a return to normal hormone levels. You should visit to reproductologist for consultation. Two days ago Mary had intercourse during which her partner's condom broke. She has come to the clinic today for a morning-after contraceptive. Which of the following statements accurately describes this form of contraception? The morning-after contraceptive must be used within 24 hours of unprotected intercourse. The morning-after contraceptive may cause mild nausea for 1 to 2 days. The morning-after contraceptive creates a local, sterile inflammatory reaction in the uterus. The morning-after contraceptive has a relatively low effectiveness rate. The morning-after contraceptive is not used after broking of condom. Maria, age 26, married, calls the clinic because she has forgotten to take her oral contraceptive for the past 2 days. What advice should the physician give to Maria? Discard the rest of the pack and use another contraceptive method for the rest of the cycle. Take two pills for the next 2 days and use another contraceptive method for the rest of the cycle. Continue to take the remaining pills for the rest of the cycle. Take two pills immediately and then take one pill daily for the rest of the cycle. IUD should be placed during next 5 days The physician is teaching Sarah unmarried, age 24, about diaphragm use and care. Which of the following statements should be part of this teaching session? Use only petroleum jelly for vaginal lubrication, if needed. B. C. D. Check the diaphragm for tears or holes after each use. Have the diaphragm refitted after a loss or gain of 10 pounds or more. Store the diaphragm in its container in a cool, dry place. Continue to use diaphragm during the period Maria, age 18, has become pregnant as a result of a rape 10 weeks ago. She asks the physician about pregnancy interruption. The physician describes various procedures, including vacuum curettage and dilatation and curettage (D & C). How do they compare? D & C requires uterus scraping with a metal curette; vacuum curettage does not D & C is performed more frequently than vacuum curettage. D & C uses crushing instruments; vacuum curettage uses suction equipment D & C carries a higher risk of complications than vacuum curettage. D & C carries a lower risk of complications than vacuum curettage Donna, age 23, has become pregnant as a result of a rape 7 weeks ago. She asks the physician about pregnancy interruption. The physician describes various procedures, including vacuum curettage and dilatation and curettage (D & C). If Donna postpones the decision until she is 10 weeks pregnant, which method of pregnancy interruption is most likely to be used? dilatation and curettage dilatation and evacuation prostaglandin suppository RU-4S6 administration cesarean section Liz, age 28, has become pregnant as a result of a rape 10 weeks ago. She asks the physician about pregnancy interruption. The physician describes various procedures, including vacuum curettage and dilatation and curettage (D & C). After Liz undergoes a first-trimester pregnancy interruption, the physician provides postoperative care. Which of the following statements should be part of the postoperative teaching session? Wipe the perineum from front to back. Douche once a week until the follow-up visit Avoid sexual intercourse for 3 to 4 weeks. Expect the next menstrual period in about 3 weeks. Intrauterine Device (IUD) is a method of choice for you While pregnant with her fourth child, Anita discusses sterilization with her husband John. They ask the physician to tell them about tubal ligation and its effects. How does this procedure terminate fertility? It prevents ovulation and menstruation. It removes the entire uterus. It occludes the cervix. It blocks ova from the fallopian tubes. Suppress ovulation While pregnant with her fourth child, Olivia discusses sterilization with her husband Mike. They ask the physician to tell them about tubal ligation and its effects. Olivia decides to undergo sterilization after delivery while she is still in the hospital. Which procedure is most appropriate for her? minilaparotomy laparoscopy hysteroscopy hysterectomy E. colposcopy C. D. * E. 278. A. B. C. D. * E. 279. A. B. C. * D. E. 280. A. * B. C. D. E. 281. A. B. C. D. * E. 282. A. * B. 283. A. B. C. * D. E. 284. A. * B. C. D. E. 285. A. B. C. D. * E. 286. A. B. * C. D. E. 287. A. B. * C. D. E. 288. A. * B. C. Rick is scheduled for a vasectomy on Friday. His partner Anne asks the physician when they can begin having unprotected intercourse. What is the physician's best response? when desired because sterilization is immediate as soon as scrotal edema and tenderness disappear when the sperm count reflects sterilization after about 6 to 10 ejaculations after one month Rita is scheduled for a tubal ligation on Wednesday. Her partner John asks the physician when they can begin having unprotected intercourse. What is the physician's best response? when desired because sterilization is immediate as soon as wound edema and tenderness disappear after next menstrual period 6 month later you should use barrier method at least 2 weeks A 26-year-old woman is scheduled for a first trimester abortion in the morning. A laminaria tent is inserted as part of the vacuum aspiration procedure. The physician explains to the woman that laminaria is used to: Stimulate the uterus to contract. Prevent postabortion infection. Reduce pain by numbing the cervix. Dilate the cervix for easier insertion of the aspirator. Prevent postabortion hemorrhage A married 23 years old woman visit to family planning center for consultation. She uses the basal body temperature method of contraception. She describes her sexual life as mogamous with husband. She wants to use Basal Body Temperature as family planning method. She asks physician what does the Basal Body Temperature (BBT) chart tell about. Problems with ovulation Time of ovulation Time of next ovulation None of these Time of previous ovulation A married 23 years old woman visit to family planning center for contraceptive advice. She describes her sex life as “active” with “many” partners. She wants a contraceptive method that is reliable and does not interfere with sex. Which method of contraception will be most appropriate for this client: Vaginal rings Condoms Patches Progestin only pill Intrauterine device Mona, is a 23-year-old healthy, non-smoking woman without medical complications. She has no contraindications for the use of oral contraceptives. When during her cycle should BB begin her oral contraceptives? Take the first tablet on the first day of menses; this avoids the risk of early ovulation and the need to use alternative methods of contraception Take the first tablet on the first Sunday after the beginning of menstruation and use alternative method of contraception for the first 14 days. Take the first tablet on the first day of menses; and use alternative method of contraception for the first 14 days D. E. 289. A. B. * C. D. E. 290. A. B. * C. D. E. 291. A. B. * C. D. E. 292. A. B. C. D. E. * 293. A. B. Take the first tablet on the first Sunday after the beginning of menstruation this avoids the risk of early ovulation and the need to use alternative methods of contraception Take the first tablet days after visit; and use alternative method of contraception for the next cycle Nadia is a 30-year-old mother of three children. She has been exclusively breastfeeding her youngest child, who is 5 months old. Nadia is planning to begin supplementing her infant’s diet and weaning her baby next month. Today, she has come to clinic to make choice about family planning method. Which method of contraception will be most available for Nadia? Lactational amenorrhea Progestin only pill Sterilization Calendar method Basal body temperature method Nelly is a 26-year-old mother of two children. She has been exclusively breastfeeding her youngest child, who is 5,5 months old. Nelly is planning to begin supplementing her infant’s diet and weaning her baby next month. Today, she has come to clinic to make choice about family planning method. She wants to use combine oral contraceptives. What is the mechanism of action of this method? make the cervical mucus thin prevent the release of eggs from the ovaries stimulate peristaltic waves of fallopian tube destroy ovum decrease speed of sperm movement Ashley, a 23-year-old unmarried, comes for an initial visit to request birth control. She asks about birth control pills, but also wants information about the newer hormonal methods on the market. Vital signs: 1,68 m tall, 95 kg., BMI 33.9, Ps 76, RR 16, T 36,6.7 C, BP 142/88 mm Hg. What information do you NOT need prior to starting Ashley on hormonal contraception? Blood pressure Smoking history Pap smear and pelvic exam History of migraines with auras Family history of thrombotic disorders Olga, a 33-year-old unmarried, comes for an initial visit to request birth control. She asks about birth control pills, but also wants information about the newer hormonal methods on the market. Vital signs: 1,68 m tall, 95 kg., BMI 33.9, Ps 76, RR 16, T 36,6.7 C, BP 142/88 mm Hg. Olga should watch for all of the following side effects with an OCP EXCEPT headache nausea spotting breast tenderness amenorrhea Irma, a 26-year-old unmarried, comes for an initial visit to request birth control. She asks about birth control pills, but also wants information about the newer hormonal methods on the market. After listening to your instructions on how to use an oral contraceptive, Irma worries that she will not be reliable in taking the pill every day, and asks about other options. Physician recommends her depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA, Depo-Provera ® ). Her vital signs: 1,68 m tall, 95 kg., BMI 33.9, Ps 76, RR 16, T 36,6.7 C, BP 142/88 mm Hg. Which of the following side effects is Not true about depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA, Depo-Provera ® )? Irregular bleeding is uncommon during the first 6-9 months of use DMPA never causes amenorrhea C. Fertility may be delayed after discontinuation D. E. * 294. Weight gain is not a reported side effect DMPA affect bone mineral density Kanisha, a 35-year-old female comes to your clinic to ask about contraception. She and her husband have one child. She wants some type of birth control that she doesn't have to think about for as long as possible. She is otherwise healthy, and her only complaint is heavy periods. She is currently using the “rhythm method” and adding condoms during high-risk times. Which of the following contraceptives would you recommend? Tubal ligation Basal body temperature method Spermicides IUD (Intrauterine Device) Progestin only pill A woman's obstetric history indicates that she is pregnant for the fourth time and all her children from prior pregnancies are living. One was born at 39 weeks' gestation, twins at 34 weeks' gestation, and another at 35 weeks' gestation. What is her gravity and parity using the GTPAL system? 3-1-1-1-3 4-1-2-0-4 3-0-3-0-3 4-2-1-0-3 4-0-2-1-3 A woman is 6 weeks pregnant. She has had a previous spontaneous abortion at 14 weeks' gestation and a pregnancy that ended at 38 weeks with the birth of a stillborn girl. What is her gravity and parity using the GTPAL system? 2-0-0-1-1 2-1-0-1-0 3-1-0-1-0 3-0-1-1-0 3-2-1-1 Juanita has just moved to the United States from Mexico. She is 3 months pregnant and has arrived for her first prenatal visit. During her assessment interview, you discover that Juanita has not had any immunizations. Which of the following immunizations should Juanita receive at this point of her pregnancy? HIV Diphtheria Chickenpox Rubella Varicella Zoster Nancy is a 31-year-old woman who believes she may be pregnant. She took an over-the-counter pregnancy test one week after a missed period test that turned positive. During her assessment interview, the physician inquires about Nancy’s LMP and if she is taking any medications. Nancy states that she takes medicine for epilepsy. She has been under much stress lately at work and has not been sleeping well. She also has a history of irregular periods. Nancy’s physical exam does not indicate that she is pregnant. Nancy has an ultrasound that reveals she is not pregnant. What is the most likely cause for obtaining false-positive pregnancy test results? Nancy took the pregnancy test too early Nancy takes anticonvulsants A. B. C. D. E. * 295. A. B. * C. D. E. 296. A. B. C. * D. E. 297. A. B. * C. D. E. 298. A. B. * C. D. E. 299. A. * B. C. D. E. 300. A. B. C. D. * E. 301. A. * B. C. D. E. 302. A. B. C. * D. E. 303. A. B. C. * D. E. 304. A. B. Nancy has a fibroid tumor Nancy has been under much stress and has a hormone imbalance. Result of ultrasound is not valid Betty is in her 7th month of pregnancy. She has been complaining of nasal congestion and occasional epistaxis. The physician suspects that: This is a normal respiratory change in pregnancy due to elevated levels of estrogen. This is an abnormal cardiovascular change and the nosebleeds are an ominous sign. Betty is a victim of domestic violence and is being hit in the face by her partner. Betty has been using cocaine intranasally. Betty should be examined by laryngologist o rule out chronic synusitis Juanita has just moved to the United States from Mexico. She is 3 months pregnant and has arrived for her first prenatal visit. During her assessment interview, you discover that Juanita has not had any immunizations. Which of the following immunizations should Juanita receive at this point of her pregnancy? Herpes Simplex Type 3 Chickenpox Rubella Hepatitis B HIV A woman is in for a routine prenatal checkup. You are assessing her urine for proteinuria. You know that which of the following findings are considered normal? Dipstick assessment of trace to +1 > 300 mg/24 hours Dipstick assessment of +2 > 300 mg/24 hours It is impossible to use urine dipstick test A woman arrives at the clinic for a pregnancy test. Her last menstrual period (LMP) was February 14. Her expected date of birth (EDB) would be: September 17 November 7 November 21 December 17 May 7 A pregnant woman at 10 weeks’ gestation jogs three to four times per week. She is concerned about the effect of exercise on the fetus. The physician would inform her: “You do not need to modify your exercising any time during your pregnancy.” “Stop exercising because it will harm the fetus.” “You may find that you need to modify your exercise to walking later in your pregnancy around the seventh month.” “Jogging is too hard on your joints; switch to walking now.” Continue jogging to delivery time it is allows to decrease time of labour A woman who is 14 weeks pregnant tells the physician that she always had a glass of wine with dinner before she became pregnant. She has abstained during her first trimester and would like to know if it is safe for her to have a drink with dinner now. You would tell her: “Since you are in your second trimester, there is no problem with having one drink with dinner.” “One drink every night is too much. One drink three times a week should be fine.” C. D. * E. 305. A. B. * C. D. E. 306. A. B. C. D. * E. 307. A. * B. C. D. E. 308. A. B. C. D. * E. 309. A. B. C. * D. 310. A. * “Since you are in your second trimester, you can drink as much as you’d like.” “Because no one knows how much or how little alcohol it takes to cause fetal problems, it is recommended that you abstain throughout your pregnancy.” “One glass of wine three times a week will help make you delivery easier” A pregnant woman at 18 weeks’ gestation calls the clinic to report that she has been experiencing occasional backaches of mild to moderate intensity. The physician would recommend that she: Do Kegel exercises Do pelvic rock exercises Use a softer mattress Stay in bed for 24 hours Should do X-ray of spine In her work with pregnant women of various cultures, a physician has observed various practices that seemed strange or unusual. She has learned that cultural rituals and practices during pregnancy seem to have one purpose in common. Which of the following statements best describes that purpose? To promote family unity To ward off the “evil eye” To appease the gods of fertility To protect the mother and fetus during pregnancy To have desired sex of the baby Juanita has just moved to the United States from Mexico. She is 3 months pregnant and has arrived for her first prenatal visit. During her assessment interview, you discover that Juanita has not had any immunizations. Which of the following immunizations should Juanita receive at this point of her pregnancy? Tetanus Chickenpox Rubella Cytomegalovirus Herpes Simplex type I A 22-year-old pregnant woman with a single fetus has a preconception body mass index (BMI) of 24. When she was seen in the clinic at 14 weeks’ gestation, she had gained 1.8 kg since conception. How would the physician interpret this? This large weight gain indicates possible pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH). This small weight gain indicates that her infant is at risk for intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR). It is impossible to evaluate this weight gain until the woman has been observed for several more weeks. The woman’s weight gain is appropriate for this stage of pregnancy. The weight gain is not important during pregnancy A pregnant woman’s diet consists almost entirely of whole grain breads and cereals, fruits, and vegetables. The physician would be least concerned about this woman’s intake of: Calcium Protein Vitamin B12 Folic acid A pregnant woman reports that she is still playing tennis at 32 weeks’ gestation. The physician would be most concerned whether this woman consumes which of the following during and after tennis matches? Several glasses of fluid B. C. D. E. 311. A. B. C. * D. E. 312. A. B. C. D. * E. 313. A. B. C. D. * E. 314. A. * B. C. D. E. 315. A. B. C. * D. E. 316. A. Extra protein sources such as peanut butter Salty foods to replace lost sodium Easily digested sources of carbohydrate Avoid food 2 hours after match A 27-year-old pregnant woman had a preconceptal BMI of 18.0. The physician would be aware that this woman’s total recommended weight gain during pregnancy should be at least: 20 kg (44 lb) 16 kg (35 lb) 12.5 kg (27.5 lb) 10 kg (22 lb) 8 kg (17,5 lb) A woman in her 34th week of pregnancy reports that she is very uncomfortable because of heartburn. The physician would suggest that the woman: Substitute other calcium sources for milk in her diet. Lie down after each meal. Decrease the amount of fiber that she consumes. Eat five small meals daily. Should be examined by gastroenterologist A woman who has come to the clinic for preconception counseling because she wants to start trying to get pregnant in 3 months can expect the following advice: “Discontinue all contraception now.” “Lose weight so that you can gain more during pregnancy.” “You may take any medications that you have been taking regularly.” “Make sure you include adequate folic acid in your diet.” “Start to do additional exercise like jog” After you complete your nutritional counseling for a pregnant woman, you ask her to reiterate your instructions to assess her understanding of the instructions given. What statement below would indicate that she understands the role of protein in her pregnancy? “Protein will help my baby grow.” “Eating protein will prevent me from becoming anemic.” “Eating protein will make my baby have strong teeth after he is born.” “Eating protein will prevent me from being diabetic.” “Eating protein will prevent excessive blood lost in postpartum period” Your client reports “unusual food cravings”. When you inquire about the specifics, she reports eating laundry detergent and dirt. You know that this type of craving is known as ___. anorexia bulimia pica vomiting emesis A woman arrives at the clinic seeking confirmation that she is pregnant. The following information is obtained: She is 24 years old with a BMI of 17.5. She admits to having used cocaine “several times” during the past year and drinks alcohol occasionally. Her blood pressure is 108/70 mm Hg, her pulse rate is 72 beats per minute, and her respiratory rate is 16 breaths per minute. Family history is positive for diabetes mellitus and cancer. Her sister recently gave birth to an infant with a neural tube defect. Which characteristics place the woman in a high-risk category? Blood pressure, age, BMI B. C. D. * E. 317. A. * B. C. D. E. 318. A. * B. C. D. E. 319. A. B. * C. D. E. 320. A. B. C. * D. E. 321. A. B. C. D. * E. 322. Drug/alcohol use, age, family history Family history, blood pressure, BMI Family history, BMI, drug/alcohol abuse Blood pressure, family history, BMI A 39-year-old primigravida thinks that she is about 8 weeks pregnant, although she has had irregular menstrual periods all of her life. She has a history of smoking approximately one pack of cigarettes a day, but tells you that she is trying to cut down. Her laboratory data are within normal limits. Which of the following diagnostic techniques could be employed with this pregnant woman at this time? Ultrasound examination Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein screening Amniocentesis Nonstress test Biophysical profile The physician sees a woman for the first time when she is 30 weeks pregnant. The woman has smoked throughout the pregnancy, and now fundal height measurements are suggestive of growth restriction in the fetus. In addition to ultrasound to measure fetal size, what would be another tool useful in confirming the diagnosis? Doppler blood flow analysis Contraction stress test Amniocentesis Daily fetal movement counts Vaginal examination A 41-week pregnant multigravida presents in the labor and delivery unit after a nonstress test indicated that her fetus could be experiencing some difficulties in utero. Which diagnostic tool would yield more detailed information about the fetus? Ultrasound for fetal anomalies Biophysical profile Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein screening Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling Daily fetal movement counts At 35 weeks of pregnancy, a woman experiences preterm labor. Although tocolytics are administered and she is placed on bed rest, she continues to experience regular uterine contractions and her cervix is beginning to dilate and efface. What would be an important test for fetal well-being at this time? Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling Ultrasound for fetal size Amniocentesis for fetal lung maturity Nonstress test Vaginal examination A 40-year-old woman is 10 weeks pregnant. Which diagnostic tool would be appropriate to suggest to her at this time? Biophysical profile Amniocentesis Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein Transvaginal ultrasound Vaginal examination A 30-year-old 3-2-0-0-2 is at 18 weeks' gestation. At this time, what screening test should be suggested to her? A. B. C. * D. E. 323. A. B. * C. D. E. 324. A. * B. C. D. E. 325. A. * B. C. D. E. 326. A. B. C. * D. E. 327. A. B. * C. D. E. Biophysical profile Chorionic villi sampling Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein screening Screening for diabetes mellitus Speculum examination A maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein test indicates an elevated level. It is repeated and again is reported as higher than normal. What would be the next step in the assessment sequence to determine the well-being of the fetus? Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling Ultrasound for fetal anomalies Biophysical profile for fetal well-being Amniocentesis for genetic anomalies Doppler velocimetry Karen is undergoing a nipple-stimulated contraction stress test. She is having contractions that occur every three minutes. The fetal heart rate has a baseline of approximately 120 bpm without any decelerations. The interpretation of this test is said to be: Negative Positive Satisfactory Unsatisfactory Normal A pregnant woman’s biophysical profile score is 8. She asks the physician to explain the results. The physician’s best response is: “The test results are within normal limits.” “Immediate delivery by cesarean birth is being considered.” “Further testing will be performed to determine the meaning of this score.” “An obstetric specialist will evaluate the results of this profile and, within the next week, will inform you of your options regarding delivery.” ”You should repeat this test again after 3 days” A primigravid client visiting the antepartal clinic at 8 weeks' gestation tells the physician that she wants an amniocentesis because there is a history of hemophilia A in her family. The physician instructs the client that newer techniques now allow amniocentesis to be performed as early as which of the following? 8 weeks'gestation. 10 weeks'gestation. 12 weeks' gestation. 14 weeks' gestation. 16 weeks' gestation. A 40-year-old gravida 4 client at 10 weeks' gestation and her husband are coming into the clinic to discuss tests that are available during the first or early second trimester to diagnose an abormality of the fetus. Which of the following tests are appropriate? Electrocardiogram. Chorionic villus sampling (CVS). External fetal monitoring (EFM). Nonstress test Auscultation of fetal heart rate 328. A. B. C. * D. E. 329. A. B. C. D. * E. 330. A. B. * C. D. E. 331. A. B. C. D. * E. 332. A. B. C. * D. E. 333. A. B. C. A 40-year-old gravida 4 client at 10 weeks' gestation and her husband are coming into the clinic to discuss tests that are available during the first or early second trimester to diagnose an abnormality of the fetus. Which of the fol¬lowing tests are appropriate? Electrocardiogram. External fetal monitoring (EFM). Amniocentesis. Nonstress test Vaginal examination A primigravid adolescent client at approximately 15 weeks' gestation who is visiting the prenatal clinic with her mother is to undergo alphafetoprotein (AFP) screen¬ing. When developing the teaching plan for this client, the physician should include which of the following pieces of in¬formation? Ultrasonography usually accompanies AFP testing. Results are usually very accurate until 20 weeks' gestation. A clean-catch midstream urine specimen is needle Increased levels of AFP are associated with neural tube defects. Elevated level of alphafetoprotein is responsible for preterm labour A 40-year-old client at 8 weeks' gestation has a 3-year-old child with Down syndrome. The physician is dis_cussing amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling as genetic screening methods for the expected baby. The physician is confident that her teaching has been understood when the client states which of the following? “Each test identifies a different part of the infant's genetic makeup.” ”Chorionic villus sampling can be performed earlier in pregnancy.” “The test results take the same length of time to be complete” “Amniocentesis is a more dangerous procedure for the fetus.” “Amniocentesis is the most safe procedure for the fetus sex” A 27-year-old primigravid client with insulin-dependent diabetes at 34 weeks' gestation undergoes a nonstress test, the results of which are documented as reactive. The physician tells the client that the test results indicate which of the following? A contraction stress test is necessary. The nonstress test should be repeated Chorionic villus sampling is necessary. There is evidence of fetal well-being. This is indication to emergency Cesarean section A primigravid client with insulin-dependent diabetes tells the physician that the contraction stress test performed earlier in the day was suspicious. The physician interprets this test result as indicating that the fetal heart rate pattern showed which of the following? Frequent late decelerations Decreased fetal movement Inconsistent late decelerations Lack of fetal movement Late acceleration A 34-years-old woman at 36 week’s gestation has been scheduled for a biophysical profile. She asks the physician why the test needs to be performe. The physician would tell her that the test: Determines how well her baby will breathe after born Evaluates the response of her baby’s heart to uterine contractions Measures her baby’s head and length D. * E. 334. A. B. * C. D. E. 335. A. B. C. * D. E. 336. A. * B. C. D. E. 337. A. B. C. D. E. * 338. A. B. C. * D. E. 339. A. Observes her baby’s activities to ensure that her baby is getting enough oxygen Identify lung maturation A 40-year-old woman at 18 week’s of gestation is having Triple Marked test performed. She is obese and her health history reveals that she is Rh negative. The primary purpose of this test is screen for Spina bifida Down syndrome Gestational diabetes Rh antibody Pregnancy induced hypertension During a contraction stress test, four contractions lasting 45 to 55 seconds were recorded in a 10 minute period. A late deceleration was noted during the third contraction. The physician conducting the test would document which of the following result negative positive Suspicious Unsatisfactory Normal Patient S., labor first, at term. Uterine contractions on 45-50 sec, every 2-3 min. Fetal heart rate is rhythmic, 144 bpm, a head is in the pelvic inlet. Vaginally: cervix is effaced, opening 7 cm, amniotic membrane is absent. What is the stage of labor? First. Second. Preliminary. Finishing. Third. Pregnant 24 years, the first pregnancy, I labor. Regular uterine contractions. At vaginal examination: the cervical opening is 4 cm, an amniotic sac is whole, the fetal head is fixed in the pelvic inlet. Sagittal suture is in a transversal size, the small fontanel is in the center of pelvis to the left. What is the moment of the labor biomechanism? The V moment of the labor biomechanism The ІІ moment of the labor biomechanism The ІІІ moment of the labor biomechanism The IV moment of the labor biomechanism I moment of the labor biomechanism The first delivery, II period. The fetal lie is longitudinal. The head presents, that it can't be determinate by external maneuvers. In internal examination: the uterine cervix is effaced, dilatation is full, membranes are absent. The sagittal suture is in a direct size, small fontanel is under the pubis. In the pushing the fetal head appears from a vulva. What area of pelvis a fetal head occupies? Pelvic inlet That is pressed to pelvic inlet plane The area of pelvic outlet The area of wide part of a cavity of a small pelvis The area of narrow part of a cavity of a small pelvis Patient S., labor first, at term. Uterine contractions on 45-50 sec, after 2-3 min.. Fetal heart rate is rhythmic, 144 in 1 min, a head is in the pelvic inlet. Vaginally: cervix is effaced, dilating is full, amniotic membrane is absent. What is period of labor? First. B. * C. D. E. 340. A. B. * C. D. E. 341. A. B. * C. D. E. 342. A. B. * C. D. E. 343. A. B. C. * D. E. 344. A. B. C. D. E. * Second. Preliminary. Finishing. Third. Primapara N., 20 years, II pregnancy, I labor. The fetal lie is longitudinal, the fetal back is anteriorly. The fetal heart rate is clear, rhythmic. Vaginal examination: the cervix is effaced, opening is full, an amniotic sac is absent. Head of fetus in the plane of pelvic outlet. Sagittal suture is in a direct size, small fontanel is under the pubis. What moment of the labor biomechanism at the anterior type of occipital presentation is ended? The І moment of the labor biomechanism II moment of the labor biomechanism The ІІІ moment of the labor biomechanism The IV moment of the labor biomechanism The V moment of the labor biomechanism The patient is admitted to delivery department. In examination longitudinal lie, I position, posterior variety of the fetus is exposed. What is the leading point at the posterior type of occipital presentation? Small fontanel The middle of sagittal suture Large fontanel Chin Subtongue bone Patient II, labor first, at term. The patient’ condition is satisfactory. The new-born is just delivered. The umbilical cord hangs down from a vagina and increases in its length. Bleeding is not present. Uterus is in normal tonus. How do you called this positive sign of placenta separation? Dovshenko sign Alfeld sign Shreder' sign Pupil sign Hehar sign Patient 30 years, labor at term. A girl with the Apgar score 8 was born. The umbilical vessels do not pulsate, the cord is clammed. Bloody excretions from the vagina are absent. What period of labor this patient is found in? Cervical Pelvic Placental Puerperal period Preliminary period Pregnant N., 25 years is delivered in the maternity department with complaints about periodic pains in lower part of abdomen and lumbal region during 7 hours. Amniotic fluid did not released. Fetal heart rate is 136 in 1min. Vaginal examination: the cervix is effaced, opening 10 cm, the amniotic membrane is whole. What is the doctor’ tactic? Cesarean section Stimulation of labor Obstetric forceps Conservative conducting of labor Amniotomy 345. A. * B. C. D. E. 346. A. B. C. D. E. * 347. A. B. C. D. * E. 348. A. * B. C. D. E. 349. A. 350. A. * Woman with full-term pregnancy. Uterine contractions occur every 4-5 minutes and lasts 30-35 seconds. Vaginal examination: cervix is totally effaced, dilation to 4 cm, fetal head is on -2 station. Sagittal suture is in right oblique diameter of the pelvic inlet, posterior fontanel under the symphysis. Amniotic sac is present. Diagnosis? Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation, I position, anterior. First stage of labor Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation, I position, posterior. First stage of labor Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation, II position, anterior. First stage of labor Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation, II position, anterior. Second stage of labor Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation, I position, anterior. Second stage of labor Woman with full-term pregnancy. Uterine contractions occur every 4-5 minutes and lasts 30-35 seconds. Vaginal examination: cervix is totally effaced, dilation to 4 cm, fetus head is on -2 station. Sagittal suture is in left oblique diameter of the pelvic inlet, posterior fontanel near sacral region. Amniotic sac is present. Diagnosis? Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation, I position, anterior. First stage of labour Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation, II position, posterior. First stage of labour Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation, II position, anterior. First stage of labour Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation, II position, anterior. Second stage of labour Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation, I position, posterior. First stage of labour Primapara R., 21 eyars old, primapara. Full term of pregnancy. The labor started 8 hours ago. The membranes ruptured 15 minutes ago. Pelvic sizes: 25,28,31,20 cm. Fetal head rate 140 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. Per vaginum: the cervix is dilated to 5 cm. The amniotic sac is absent. Fetal head is palpated in plane of pelvic inlet. Which stage of labor? Third Second Latent stage of first Active stage of first Fourth Primipara F., 25 years old. Pregnancy at term. The labor started 6 hours ago. The membranes ruptured one hour ago. Pelvic sizes: 23,25,29,18 cm. Fetal head rate 140 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. Uterine contractions occur every 7-8 minutes. Per vaginum: the uterine cervix dilatation is 2 cm. The amniotic sac is absent. One fetal foot is palpated in the vagina. Buttocks are in the pelvic inlet. Which stage of labor? Latent stage of first stage Active stage of first stage Second stage Third Fourth M., 25 years old, multipara. Full term of pregnancy. Initiation of labor was 7 hours ago. The membranes ruptured 40 minutes ago. Pelvic sizes: 25,28,31,20 cm. Fetal heart rate is 132 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. Per vaginum: the cervix is completely dilated. The amniotic sac is absent. Fetal head is in the plane of the greatest diameter of the true pelvis. The face line is in the right oblique size. The chin is palpated under the symphysis. What is the moment of labor biomechanism? A woman in her 40th weeks of pregnancy, the second labour, has regular labour activity. Uterine contractions take place every 3 minutes. All of criteria describe the beginning of the II labor stage EXEPT: Cervical dilatation by no less than 4 cm B. C. D. E. 351. A. B. C. D. * E. 352. A. B. C. D. E. * 353. A. B. C. D. E. * 354. A. * B. C. Cervical dilation to 10 cm Duration of uterine contractions over 30 seconds Presenting part is in the lower region of small pelvis Rupture of fetal bladder A 17 year-old G0 sexually active woman presents to the emergency room with acute right lower quadrant pain and nausea for 12 hours. Her periods have always been irregular, with her last one 6 weeks ago. She is otherwise completely healthy. She appears in mild distress. Physical examination: temperature 100.2°F (37.9°C); blood pressure 110/60; heart rate 108 beats/min. She has moderate abdominal tenderness with right greater than left pelvic tenderness. Pelvic exam reveals normal external genitalia and pink-tinged discharge is noted on speculum examination. Bimanual/rectovaginal exam confirms mild cervical motion tenderness and fullness in the right adnexa with moderate tenderness and some voluntary guarding. What is the single most important test to obtain? Pelvic ultrasound CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis GC and chlamydia DNA probe Beta-hCG CBC with differential An 18 year-old woman comes to the office due to vaginal spotting for the last two weeks. Her menstrual periods were regular until last month, occurring every 28-32 days. Menarche was at age 13. She started oral contraceptives 3 months ago. On pelvic examination, the uterus is normal in size, slightly tender with a mass palpable in the right adnexal region. No adnexal tenderness is noted. Which of the following tests is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient? Endometrial biopsy Coagulation studies Pelvic sonography Abdominal CT scan Urine pregnancy test A 26-year-old G0 woman presents to the emergency room with 8 hours of severe right lower quadrant pain associated with nausea. She has a history of suspected endometriosis, which was diagnosed 2 years ago, based on severe dysmenorrhea. She has been using NSAIDs with her menses to control the pain. She is not sexually active. She is otherwise in good health. Her menstrual cycles are normal every 28 days and her last menstrual period was 3 weeks ago. She has no history of sexually transmitted infections. Her blood pressure is 145/70; pulse is 100; temperature is 99.2°F. She appears uncomfortable. On abdominal exam, she has moderate tenderness to palpation in the right lower quadrant. On pelvic exam, she has no lesions or discharge. A complete bimanual exam was difficult to perform due to her discomfort. Labs: BHCG MRI of the pelvis Doppler pelvic ultrasound CAT scan of the pelvis Begin oral contraceptives Surgical exploration A 29 years old woman with a history of pelvic inflammatory disease presents to emergency with severe left lower quadrant crampy pain, spotting and amenorrhea for the past two cycles. There is a left adnexal mass with tenderness to palpation. The B-hcG is elevated. Further studies would most likely reveal an implantation at which of the following locations in the fallopian tube? Ampula Fimbriae Isthmus D. E. 355. A. B. C. D. * E. 356. A. B. C. D. * E. 357. A. B. * C. D. E. 358. A. B. C. D. E. * 359. A. B. C. * Infundibulum Uterine segment A 35 years old sexually active woman visits her gynecologist complaining of mild, right-sided, lower abdominal pain but no other symptoms, there are no peritoneal signs, her surgical history is significant for an appendectomy at age 10, her last period occurred 14 days ago, which of the following endometrial changes corresponds to this stage of the patient's menstrual cycle? Apical movement of secretions in the glandular cells Tissue expansion by cellular hypertrophy Degeneration of the glandular structures Growth of the spinal arteries Glandular glycogen accumulation in the functionalism A 35 years old woman comes to the emergency with a sudden onset of severe right lower abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting. Ultrasound shows enlarged ovary with decreased or absent blood flow, the diagnosis might be? PID Ectopic pregnancy Cyst rupture Ovarian torsion Endometriosis Name a complication of PID, presents with fever, abdominal pain and a complex multiloculated adnexal mass with thick walls and internal debris. Mole Tubo-ovarian abscess Cervicitis Bacterial vaginitis Ovarian cancer A 37-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of a 3-day history of increasingly severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Twelve years ago, she had a hysterectomy because of severe dysfunctional uterine bleeding. Her temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), blood pressure is 106/70 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 12/min. Examination shows a distended, tympanic abdomen with diffuse tenderness but no guarding; bowel sounds are hypoactive. Her leukocyte count is 10,000/mm3, and hematocrit is 44%. An x-ray of the abdomen is shown. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial step in management? Laparotomy Nasogastric intubation Esophagogastroduodenoscopy Intravenous neostigmine therapy CT scan of the abdomen A 25-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department 1 hour after she fainted. She has had mild intermittent vaginal bleeding, sometimes associated with lower abdominal pain, during the past 3 days. She has had severe cramping pain in the right lower abdomen for 12 hours. She has not had a menstrual period for 3 months; previously, menses occurred at regular 28-day intervals. Abdominal examination shows mild tenderness to palpation in the right lower quadrant. Bimanual pelvic examination shows a tender walnut-sized mass in the right parametrium. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? Appendicitis Cancer of the ovary Ectopic pregnancy D. E. 360. A. * B. C. D. E. 361. A. B. C. * D. E. 362. A. * B. C. D. E. 363. A. * B. C. D. E. 364. A. * B. C. D. E. Endometriosis Ovarian cyst A 23.y.old woman presents with fever and abdominal pain of 2 days duration. She has a positive chandelier sign. Antibiotics are started. What is the next step in management? Pelvic ultrasonography to rule out tubo-ovarian abscess Laparoscopic investigation Higher dose of antibiotics after 10 days Lower dose of antibiotics after 48 hours Emergency surgery A 25-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department 1 hour after she fainted. She has had mild intermittent vaginal bleeding, sometimes associated with lower abdominal pain, during the past 3 days. She has had severe cramping pain in the right lower abdomen for 12 hours. She has not had a menstrual period for 3 months; previously, menses occurred at regular 28-day intervals. Abdominal examination shows mild tenderness to palpation in the right lower quadrant. Bimanual pelvic examination shows a tender walnut-sized mass in the right parametrium. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? Appendicitis Cancer of the ovary Ectopic pregnancy Endometriosis Ovarian cyst Women, 39 year admitted to the gynecology department with complaints of severe abdominal pain, occurring after physiological activity. In bimanual examination found sharply painful swelling in the pelvis, the positive symptoms of peritoneal irritation on the side of the tumor. Your diagnosis? torsion of ovary cancer stem spontaneous miscarriage acute salpingoophoritis dysfunctional uterine bleeding none of the above In the gynecology department admitted a woman 23 year with complaints of sudden onset of pain in one of the iliac regions, radiating pain in the shoulder, nausea, and vomiting, delayed menstruation for 3 weeks. Pregnancy test is positive. Your diagnosis? an ectopic pregnancy, the type of rupture of the uterine tube torsion of ovary cancer stem spontaneous miscarriage acute salpingoophoritis dysfunctional uterine bleeding In 27 years old woman you suspect tubal abortion (without significant intra-abdominal bleeding). With which diseases you would differentiate: a miscarriage of small time dysfunctional uterine bleeding acute salpingoophoritis Endometriosis PID Cyst rupture 365. A. B. C. D. E. * 366. A. B. C. * D. E. 367. A. * B. C. D. E. 368. A. B. C. D. E. * Woman, aged 22 years was admitted to gynecologic department with complaints on pains in the lower abdomen, elevation of body temperature to 39,5*C. Objectively: heart beat rate – 108 beats/min, arterial pressure – 120/180 mm Hg., abdomen is bloated moderately, sharply painful in the hypogastric area. Signs of peritoneal irritation are positive in the hypogastric area. Vaginal examination: uterus and appendages are not palpable due to tension of the anterior abdominal wall, posterior fornix overhangs, sharply painful. What is the most probable diagnosis? Ovarian apoplexy acute salpingoophoritis Acute endometritis Ectopic pregnancy Pelvic peritonitis Urgent admission of a patient with complaints on pain in the lower abdomen with irradiation to the rectum, blood-tinged discharge from genital passages, dizziness. Complaints appeared suddenly. Last menses was 2 weeks ago. Skin integuments are pale, pulse – 102 beats/min., arterial pressure – 90/60 mm Hg. Abdomen is tense, somewhat painful in the lower areas, symptoms of irritation of the peritoneum are slightly positive. What is the most probable diagnosis? Intestinal obstruction. Fibroid, which is being born. Ovarian apoplexy. Ectopic pregnancy. Setting out abortion. Woman, aged 26 years was admitted to admission department with complaints on sudden pain in the lower abdomen, malaise, loss of consciousness at home. Previous menses was absent. Hb – 106 g/l, pulse rate – 120 beats/min, arterial pressure – 80-50 mm Hg., tenderness and symptoms of peritoneal irritation are in the bottom in the right side. What diagnosis is the most probable? Interrupted uterine pregnancy. Acute appendicitis. Right-sided acute salpingoophoritis Torsion of the ovarian pedicle. Intestinal obstruction Patient, aged 20 years was admitted to gynecologic unit with complaints on acute sudden pain in the lower abdomen in the lumbar area, moderate blood-tinged discharge from reproductive ways. Delay of menses – 2 weeks. On bimanual examination: uterine cervix is of 3,5 cm length, soft, cyanotic, through external os tip of the fingers passes. Uterine body is of ovoid form, large one, of softened consistency. In the left a soft formation, movable, painful on palpation is palpable. Discharge is blood-tinged, insignificant. Arterial pressure – 95/60 mm Hg., pulse rate – 100 beats/min. What diagnosis is the most probable? Incipient abortion. Threatened abortion. Abortion in progress. Uterine body leiomyoma. Ectopic pregnancy. 369. A. * B. C. D. E. 370. A. B. C. D. * E. 371. A. B. * C. D. E. 372. A. B. * C. D. E. Patient P., aged 37 years appealed to gynecologic unit complaining of pain in the lower abdomen, which becomes worse during 24 day period, nausea, elevation of body temperature to 38,5*C. Patient fell ill 15 days ago after surgery for artificial abortion. Objectively: T- 38,5*C, pulse rate – 100 beats/min. Tongue is dry, abdomen is tense in the lower portions, signs of peritoneal irritation are is positive. On bimanual examination: sharp pain develops in replacement of uterine body, contours of the uterus and appendage are not defined clearly because of tension of the anterior abdominal wall. In the right side through the crypt, pole of formation of ovoid form is determined, painful on palpation. Vaginal discharge is pus-like. What diagnosis is the most probable? Pelvic peritonitis. Acute salpingoophoritis. Acute appendicitis. Parametritis. Gonorrhea pelvic peritonitis. Patient was admitted to gynecologic unit complaining of menstruation delay during 2 weeks, staining blood-tinged discharge from reproductive passages, pain in the lower abdomen more expressed in the left side, nausea, vomiting, weakness. In the past history: chronic adnexitis. On bimanual examination: uterus body is slightly enlarged in sizes, softened, appendages in the left are enlarged, painful on palpation, uterine cervix is conical in shape, external os is closed. Posterior crypt hangs over, very painful. Reaction to chorionic gonadotropin is positive, By ultrasonic examination: in the uterine cavity a fetal ovum is not determined. What diagnosis is the most probable? Secondary amenorrhoe. Exacerbation of chronic salpingoophoritis. Shtein-Leventhal’s syndrome. Ectopic pregnancy. Endometriosis. Patient, aged 20 years was admitted to the hospital with sharp pains in the lower abdomen in the left. The last normal menstruation was 2 weeks ago, in time. Arterial pressure – 100/70 mm Hg., pulse rate – 90 beats/min., body temperature is 36,9*C, patient is pale. Abdomen is painful in the lower portions. Blumberg-Schyotkin’s symptom is slightly positive. On vaginal examination: uterine cervix is of conical shape, external os is closed. Uterine is not enlarged, sensitive. Appendages on the right are not palpable. On the left something painful appendages are palpable. Crypts hang over, painful ones. What diagnosis is the most probable? Uterine leiomyoma. Apoplexy of the ovary. Ectopic pregnancy. Inflammation of the uterine appendages. Acute appendicitis. Patient, aged 28 years was admitted to the in-patient unit complaining of sharp pains in the lower abdomen which developed 2 hours ago and of blood-tinged staining discharge from reproductive ways. Last menstruation began 2 months ago. On bimanual examination: uterine body is somewhat enlarged. Displacement along the uterine cervix is sharply painful. Uterine appendages in the left are enlarged, painful. In the blood: Hb – 102 g/l, ESR – 32, leucocytes – 6,5x109/l, diastase – 8g/hour l. Signs of peritoneal irritation are positive. What is the most probable diagnosis? Uterine leiomyoma. Disturbed uterine pregnancy. Acute appendicitis. Progressive ectopic pregnancy. Abortion in progress. 373. A. B. C. * D. E. 374. A. * B. C. D. E. 375. A. B. C. D. * E. 376. A. * B. C. D. E. 377. A. Patient B., 22 years of age complains of aching pains in the right iliac area, lasting during a week, nausea in the morning, gustatory changes. In the past history: menstruation delay – 3 weeks. Objectively: arterial pressure: 110/70 mm Hg., pulse rate – 78 beats/min., body temperature – 37*C. On bimanual examination: uterine is slightly enlarged, softened, movable, painless. Appendages: in the left side a painful formation of 3x4 cm, dense-elastic consistency, limitedly movable is palpable. What diagnosis should be made? Cyst of the right ovary. Disturbed uterine pregnancy. Progressive uterine pregnancy. Uterine pregnancy. Acute appendicitis. Ambulance delivered a patient complaining of short-term loss of consciousness, dizziness, sharp pain in the right lower abdomen, last menstruation was 2 weeks ago. Skin integuments are pale. Pulse rate – 110 beats/min., pulse is thread, Hb - 76 g/l, body temperature – 36,8*C, blood pressure – 80/60 mm Hg., abdomen falls behind on respiration in the lower portions, palpation of the abdomen on the bottom is painful. On examination: uterine cervix is within the norm, cervical canal is closed. Uterine body is not enlarged, on palpation insignificant tenderness is noted. Appendages in the right side on palpation are painful, ovary is enlarged. Posterior fornix of the vagina hangs over. What is the most probable diagnosis? Ruptured ectopic pregnancy. Acute appendicitis. Apoplexy of the ovary. Acute salpingoophoritis. Torsion of the cystoma of the right uterine appendages. Woman, aged 28 years appealed for doctor’s advice complaining of acute pain in the left iliac area, no menstruation delay. By the data of ultrasonic examination 2 months ago ovarian cyst in the left was revealed. Patient refused from hospitalization. On vaginal examination: in the left side tumor-like formation, sizes of 5x7 cm., painful one, very movable is determined. What is the most probable diagnosis? Ectopic pregnancy. Apoplexy of the ovaries. Threatening abortion. Torsion of the ovarian cyst. Hydatid mole. Patient K. aged 19 years, 3 hours ago after physical culture lesson developed pain in the lower abdomen in the left, dryness in the mouth. Menstruation was 2 weeks ago. Pulse rate – 92 beats/min., rhythmic one. Arterial pressure – 95/55mm Hg. Tongue is dry and coated. Abdomen “breathes”, but painful in the right iliac area and suprapubic junction, doubtful symptoms of peritoneal irritation are noted. What diagnosis should be made? Apoplexy of the ovary. Acute appendicitis. Acute salpingoophoritis. Disturbed uterine pregnancy. Renal colic in the left. Patient S., aged 41years appealed for doctor’s advice complaining of periodic pains in the lower abdomen, painful profuse, prolonged menstruation. On bimanual examination: uterine was enlarged to 9 weeks of pregnancy, along the posterior wall a node, sizes 3x3 cm is palpable, uterine body is movable, painful, appendages are without peculiarities. What disease should be thought of? Ovarian tumor. B. C. D. E. * 378. A. * B. C. D. E. 379. A. B. * C. D. E. 380. A. * B. C. D. E. 381. A. B. C. Adenomyosis. Uterine pregnancy. Chronic endometritis. Ischemia of fibromatous node. Woman, aged 30 years was admitted to gynecologic unit for planned surgical intervention because of tumor-like formation in the area of the right appendages, sizes 9x8 cm., of dense-elastic consistency, movable, painless. While performing physical work, severe pain developed, woman lost consciousness. During surgical intervention a thin-walled formation on the long pedicle, containing hair and teeth was removed. What diagnosis should be made? Torsion of the dermoid ovarian cyst. Uterine leiomyoma. Ovarian cancer. Hydrosalpinx. Pyo-ovarium. Patient, aged 28 years complains of pain in the lower abdomen, loss of consciousness developed at home. Menstruation is in time. Skin is pale, pulse rate – 110 beats/min., Hb. – 76 g/l., arterial pressure is 80/60. Signs of peritoneal irritation are positive. On vaginal examination: uterine body is not enlarged, painful on ectopia, appendages are not palpable. Posterior fornix of the vagina hangs over, painful. On abdominal paracentesis through the posterior crypt, bright blood, which coagulates was obtained. What is the most probable diagnosis? Disturbed ectopic pregnancy. Ovarian apoplexy. Torsion of the cystoma of the right uterine appendages. Acute salpingoophoritis. Acute appendicitis. Patient, aged 23 years, married. Menstruation has been since 16 years, regular one. Last menstruation was 7 weeks ago. Regular sexual life. Patient does not use means of contraception. In the past history: chronic adnexitis,, patient is followed up at the prenatal center, received treatment several times due to exacerbation of the inflammatory process of the small pelvis organs. By the data of ultrasonic examination, a formation, sizes - 7x3x4 cm in the area of the right appendages was revealed. Diagnosis of hydrosalpinx was made. On her way to work patient experienced sharp pain in the lower abdomen, lost consciousness. She was delivered to gynecologic unit by an ambulance in a severe state. Skin and mucous membranes are pale, arterial pressure – 75/40 mm Hg. Pulse rate is 116 beats/min., body temperature – 38*C, symptom of irritation of the peritoneum is positive. What is the most probable diagnosis? Ruptured ectopic pregnancy. Abortion in progress. Rupture of the ovarian cyst. Pelvioperitonitis. Perforating gastric ulcer. Patient with uterine fibromyoma (first revealed 4 years ago). During observation uterine sizes are stable (correspond to 8-9 weeks of pregnancy. Patient appealed for doctor’s advice, complaining of sharp pains in the lower abdomen. On examination: sharply positive symptoms of irritation of the peritoneum, high leucocytosis. On vaginal examination: uterine is enlarged to 9 weeks of pregnancy term at the expense of fibromatous nodes, one of them is movable, sharply painful. Appendages are not palpable. Discharge is mucous, moderate one. What is treatment tactics? Urgent surgical intervention (laparotomy). Observation and spasmolytic therapy. Fractional diagnostic curettage of uterine walls. D. * E. 382. A. B. * C. D. E. 383. A. B. C. * D. E. 384. A. B. C. D. * E. 385. A. * B. C. D. E. 386. A. * B. Surgical laparoscopy. Observation and therapy with antibiotics. Patient, aged 28 years was admitted to the gynecologic unit complaining of sharp pain in the lower portions of the abdomen, pain developed suddenly on the 4-th week of menstruation delay. Skin integuments are pale, pulse rate – 110 beats/min., arterial pressure – 90/60. Abdomen is sharply painful on palpation in the lower portions, positive symptom of irritation of the peritoneum. On vaginal examination: uterine is enlarged, deviated to the right, on the left – oblong formation, painful on palpation is revealed, posterior fornix is sharply painful, hangs over. What is the most informative method of investigation? Diagnostic laparoscopy. Paracentesis of the posterior fornix. Test for chorionic gonadotropin. Ultrasonic investigation. Dynamics of total blood analysis. Patient, aged 43 years complains of constant dull pains in the lower abdomen, mostly in the left side, elevation of body temperature up to 38*C. During the last 5 years patient is followed up due to subserous uterine fibromyoma. On bimanual examination: uterine is enlarged to 10 weeks of gestation term, solid, tuberous one. In the left side of the uterine, formation coming out of the uterine, size 6x8 cm., of elastic consistency, sharply painful on palpation is observed. What is the most probable diagnosis? Pyosalpinx. Extrauterine pregnancy. Necrosis of myomatous node. Cyst of the left ovary, which became suppurated. Uterine sarcoma. Patient, aged 37 years was admitted to the gynecologic unit complaining of intensive cramp-like pains in the lower abdomen, bleeding from reproductive passages. Over the period of the last 4 years patient experienced profuse menstruation, sometimes transitory into bleeding. Patient was not followed up at gynecologist. On bimanual examination: uterine cervix is smoothened, external os is opened up to 4 cm., in the cervical canal a dense tumor-like formation is palpable. Uterine is enlarged, dense. What is the most probable diagnosis? Necrosis of fibromatous node. Abortion in progress. Hydatid mole. Protruding myoma. Uterine cancer. A patient with acute pelvic pain has a low grade fever, nontender uterus and negative beta hCG test. The most probable diagnosis would be: Salpingitis Appendicitis Missed abortion Ectopic pregnancy Rupted ovarian cyst At the vaginal examination of the patient you revealed the following: the exernal os of cervix is closed, the uterus is slightly enlarged, soft, the right of the appendages is soft and painful. There is pain with movement of the cervix. Possible diagnosis: progressive tubal pregnancy. apoplexy of the right ovary. C. D. E. 387. A. B. C. D. * E. 388. A. B. C. * D. E. 389. A. * B. C. D. E. 390. A. B. C. * chronic inflammation of the right adnexa. Appendicitis. All answers are correct. Patient 29 years, delivered by the emergency, complains about acute pains in lower parts of an abdomen. Pains arose up suddenly, at getting up of weight. The last menstruation was 10 days ago, in the term. Labors — 2, abortions — 2. The last time visited gynecologist half-year ago, ovarian cyst was definite. Pulse - 100 in a minute, rhythmic, breathing 22 in a minute. Abdomen is tense, acutely painful, especially on the left. Objectively: the uterine cervix is cylinder, deformed by old postnatal ruptures, clean. The uterine body is not determined due to tension of abdominal wall. Right adnexa not palpated. A tumor without clear contours is palpated in the region of the left adnexa, elastic consistency; the mobile is limited, painful. Parametriums are free. What most reliable diagnosis? The ruptured ectopic pregnancy. Torsion of pedicle of ovarian cyst. Apoplexy of ovary. Rupture the cysts of ovary. Appendicitis The patient 36 years complains on pain in lower parts of abdomen on the left side, which arose up suddenly. Objectively: external genital organs without pathology, the uterine cervix is cylindric, clean. The body of uterus is enlarged to 12—13 weeks of pregnancy, the mobile is limited. One of fibroids on the left near a fundus acutely painful. Adnexa are not determined, its region is unpainful. Parametrium is free. Excretions serous. Blood test: Haemoglobin — 120 g/l, leucocytes — 12x109 /л. What is the most reliable diagnosis? Chorionepithelioma. Spontaneous rupture of pregnant uterus. Necrosis of fibroid. The interrupted pregnancy in the interstitsial region of fallopian tube. Destructive form of the molar pregnancy. The patient 36 years complains about pain in lower parts of abdomen, that reminds the labor contractions, weakness. The menstruations last 2 years are more abundant, of long duration. The last menstruation began 2 days ago. Objectively: A skin and mucous membranes are pale, pulse 88 in 1 min. Abdomen is soft, unpainful. Gynecological status: external genital organs without pathology, the uterine cervix is cylinder, a canal freely skips 2 fingers. From a cervix a tumor 3x6 cm hangs down to the vagina, pedicle by thickness to 1 cm enters to the cavity of uterus. The tumor is a dark-purple color, at contact bleeds. The body of uterus is enlarged to 7-8 weeks of pregnancy, unequal surface, mobile, not painful. Adnexa are not determined. What is the most reliable diagnosis? The protruding fibroid Endophytic growth of cancer of uterine cervix Chorionepithelioma, metastasis in the uterine cervix Inevitable abortion in 7-8 weeks of pregnancy Exophytic growth of cancer of uterine cervix In the gynecological department a woman 25 years appealed with complaints about the rise of temperature of body to 38,60С, pain in lower parts of abdomen, dysuria. Became ill 3 days to that, when the indicated complaints appeared after artificial abortion. At gynecological examination: the uterine cervix is cylinder, external os is closed. Body of uterus a few enlarged, painful, soft. The adnexa of uterus are not palpated. Excretions festering-bloody. In the blood test leycocytosis with displacement of formula of blood to the left, speed-up ESR. What diagnosis is most credible? Acute endocervicitis Acute salpingoophoritis Acute endometritis D. E. 391. A. B. C. D. * E. 392. A. B. * C. D. E. 393. A. B. C. * D. E. 394. A. B. * C. D. E. Acute cystitis Piosalpinx Patient delivered in the gynecological department by the emergency. Two hours ago suddenly the acute pain in an abdomen, nausea, vomits began. The last menstruation was two weeks ago. Patient is pale, pulse 116, soft, AP 70/40 mm Hg. An abdomen does not take part in breathing. Vaginally: the posterior fornix of vagina is painful, uterus of normal sizes, mobile, painful at palpation. Adnexa are not palpated through the tension of abdominal wall. Blood test: leucocytes 8x109/l. A pregnancy test is negative. Diagnosis? Acute appendicitis The ruptured ectopic pregnancy Necrosis of subserosal fibroid Ovarian apoplexy Acute bilateral adnexitis Patient D., 30 years, delivered with complaints about pain in lower parts of abdomen of periodic character which arose up suddenly, irradiate in sacrum and anus, and also on spotting bloody excretions. The last menstruation - 6 weeks ago. In anamnesis there are 1 labor, 2 abortions. After the last abortion - acute bilateral adnexitis. Objectively: the patient’ condition is satisfactory, t-36,8o. The symptoms of irritation of peritoneum are not exposed. Vaginal examination: uterine cervix of cyanotic, the uterus is enlarged in sizes, sensible at palpation; right adnexa - without changes. In the projection of the left adnexa – tumor which mobile is limited, consistency elastic, shape egg-like by sizes 4х4х5 cm, acutely painful at palpation; discharges are bloody, moderate. Diagnosis? Cyst of the left ovary with violation of blood supply The ruptured left-side ectopic pregnancy Acute left-side adnexitis Subserosal leyomyoma with violation of blood supply Apoplexy of the left ovary A woman, 26 years, appealed to the doctor of female dispensary with complaints about absence of menstruation (delay on 26 days) and feeling of nausea, mostly in the morning. A test on pregnancy is positive. Earlier a menstrual cycle was regular. Pregnancies were not present before. It is set at the objective inspection: mucous membrane the cervix is cyanotic, uterine consistency is soft, some enlarged in uterine sizes is present. Ultrasonography – a fetal sac in the uterine cavity is not exposed. The most credible diagnosis? Violation of menstrual cycle Uterine pregnancy Unruptured ectopic pregnancy Ruptured ectopic pregnancy Ovarian insufficiency Patient 34 years. The uterine myoma is exposed 2 years ago. Growth is not present. There is pain in lower parts of abdomen. Leucocytosis 17х109 /L. The symptoms of irritation of peritoneum are positive. At vaginal examination: the uterus is enlarged to 10 weeks of pregnancy, one of fibroids is mobile, painful. Excretions are mucous. Diagnosis? Cyst of ovary Fibroid’ torsion Acute adnexitis Rupture of piosalpinx Acute appendicitis 395. A. * B. C. D. E. 396. A. * B. C. D. E. 397. A. * B. C. D. E. 398. A. B. C. D. E. * 399. A. * B. C. D. E. Women, 39 year admitted to the gynecology department with complaints of severe abdominal pain, occurring after physiological activity. In bimanual examination found sharply painful swelling in the pelvis, the positive symptoms of peritoneal irritation on the side of the tumor. Your diagnosis? torsion of ovary cancer stem spontaneous miscarriage acute salpingoophoritis dysfunctional uterine bleeding none of the above In the gynecology department admitted a woman 23 year with complaints of sudden onset of pain in one of the iliac regions, radiating pain in the shoulder, nausea, and vomiting, delayed menstruation for 3 weeks. Pregnancy test is positive. Your diagnosis? an ectopic pregnancy, the type of rupture of the uterine tube torsion of ovary cancer stem spontaneous miscarriage acute salpingoophoritis Uterine pregnancy In 27 years old woman you suspect tubal abortion (without significant intra-abdominal bleeding). With which diseases you would differentiate: a miscarriage of small time acute salpingoophoritis Ovarian apoplexy Acute appendicitis All answers are correct Patient 22 years, complains about absence of pregnancy during 5 years of marriage. For the last 3 years conducted medical and resort treatment. Two months ago metrosalpingography was done — tubes’ permeability is normal. The last menstruation was with the delay on 2 weeks, painful. 2 days ago bloody excretions in a small amount and pain in lower parts of abdomen appeared again. Objectively: the uterine cervix is cyanotic, external os is closed. The uterus in normal position, enlarged to 5 weeks of pregnancy, is soft, mobile. Right adnexa are not determined. The left adnexa are enlarged in sizes to 6x3 cm, painful at palpation. Parametriums are free. Discharges are bloody, in a little quantity. Blood test: Haemoglobin — 90g/l, red cells — 3,0 h 10 /l, leucocytes— 8,6 h 10 /l. What is the most reliable diagnosis? Pregnancy 6-5 weeks. Initial abortion. Cyst of the left ovary. Pyosalpinx after metrosalpingography The molar pregnancy Violation of menstrual cycle Ectopic pregnancy, tubal abortion A 23 years old primigravida presents with abdominal pain, syncope and vaginal spotting, assessment reveals that she has an ectopic pregnancy, the most common site of pregnancy is: Ampula Isthmus Fimbrial end Abdomen Cervix 400. A. B. * C. D. E. 401. A. * B. C. D. E. 402. A. B. C. D. * A 31-year-old woman comes to the physician for follow-up after an abnormal Pap test and cervical biopsy. The patient's Pap test showed a high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HGSIL). This was followed by colposcopy and biopsy of the cervix. The biopsy specimen also demonstrated HGSIL. The patient was counseled to undergo a loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP). Which of the following represents the potential long-term complications from this procedure? Abscess and chronic pelvic inflammatory disease Cervical incompetence and cervical stenosis Constipation and fecal incontinence Hernia and intraperitoneal adhesions Urinary incontinence and urinary retention A 40-year-old woman comes to the physician for an annual examination. She has no complaints. She has menses every 28-30 days that last for 3 days. She has no intermenstrual bleeding. She has asthma, for which she uses an occasional inhaler. She had a tubal ligation 10 years ago. She has no known drug allergies. Examination is unremarkable, including a normal pelvic examination. One of her friends was recently diagnosed with endometrial cancer, and the patient wants to know when and if she needs to be screened for this. Which of the following is the most appropriate response? Screening for endometrial cancer is not cost effective or warranted Screening is with endometrial biopsy and starts at age 40 Screening is with endometrial biopsy and starts at age 50 Screening is with ultrasound and starts at age 40 Screening is with ultrasound and starts at age 50 A 21-year-old G0 woman has her first Pap smear, and it shows a high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL.) Colposcopy is performed, and three biopsies and an endocervical curettage are obtained. The biopsy and endocervical curettage were read as normal. Which of the following would be the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient? Pap smear in 6 months Colposcopy with directed biopsies in 3-6 months Cryotherapy Cervical conization E. 403. Treat for presumed infection and repeat Pap in 4-6 weeks An 88 year-old G2P2 nursing home resident is brought in for evaluation of blood found in her diapers. She has a long-standing history of incontinence. This is the first time that her caregivers have noted blood. They describe it as “quarter size.” Her nurses think that she may have been itching, as they frequently find her scratching through the diaper. On review of her medical record, biopsy documented lichen sclerosus of the vulva was diagnosed fifteen years ago. She has not been on any therapy for this condition for years. Examination of the external genitalia reveals an elevated, firm irregular lesion arising from the left labia. The lesion measures 2.5 cm in greatest dimension. The remainder of the external genitalia shows evidence of excoriation of thin, white skin with a wrinkled parchment appearance. The vagina and cervix are atrophic. No masses are noted on bimanual or rectovaginal exam and a sample of her stool is negative for blood. No nodularity is noted in her groin. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient? A. B. C. * D. E. Begin steroids for her lichen sclerosis Benadryl and xylocaine jelly for symptomatic relief Biopsy the lesion Exam under anesthesia with colposcopy and CO2 laser ablation Complete vulvectomy and lymph node dissection 404. A. B. * C. D. E. 405. A. B. * C. D. E. 406. A. B. C. D. E. * 407. A. * B. C. D. E. 408. A. B. C. D. * E. A 57 year-old G2P2 woman is seen for a routine visit. She states she and her 75 year-old husband stopped having sexual intercourse 3 years ago when he had an operation for prostate cancer. Menopause occurred at age 50 and she denies taking hormones. Her husband now wishes to resume intercourse and is able to get an erection with sildenafil (Viagra). Attempts at intercourse have been unsuccessful due to the pain she experiences when insertion is attempted. Examination is normal except for a narrowed vagina with atrophic mucosa. Which of the following is the most appropriate recommendation at this time? Progesterone cream Estrogen cream Oral estrogen testosterone cream Vaginal dilators A 39 year-old G1P1 woman comes to see you because of increased bleeding due to her known uterine fibroids, especially during her menses. She reports that her bleeding is so heavy that she has to miss two days of work every month. She has been using oral contraceptives and NSAIDs. Her most recent hematocrit was 27%. She is undecided about having more children. You discuss with her short and long-term options to decrease her bleeding. What is the next best step in the management of this patient? Blood transfusion Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists Endometrial ablation Hysterectomy Uterine artery embolization A 28-year-old G0 woman has her first abnormal Pap, which was read as high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL.) She has no complaints. She smokes one pack of cigarettes per day. Her pelvic exam is normal. Colposcopy is performed. The cervix is noted to have an ectropion and there is abundant aceto-white epithelium. Mosaicism, punctations and several disorderly, atypical vessels are noted. Several biopsies are obtained and sent to pathology. Which of the findings on this patient’s colposcopy is most concerning? Ectropion Acetol-white epithelium Mosaicism Punctations Disorderly, atypical vessels The patient K, 48 years old, came for regular check-up. Which process the type I does reflects in Pap smear test? Normal epithelium. Moderate dysplasia. Cancer. Inflammation. Malignization suspect. The patient C, 38 years old, complains on excessive with odor discharge from the vagina lately. Which process does the type IIA reflect in Pap smear test? Normal epithelium. Moderate dysplasia. Cancer. Inflammation. Malignization suspect. 409. A. B. * C. D. E. 410. A. B. * C. D. E. 411. A. B. * C. D. E. 412. A. * B. C. D. E. A 76-year-old G3P3 presents to the office with worsening stress urinary incontinence for the last 3 months. She reports an increase in urinary frequency, urgency and nocturia. On exam, she has a moderate size cystocele and rectocele. A urine culture is negative. A post-void residual is 50 cc. A cystometrogram shows two bladder contractions while filling. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient? Genuine stress incontinence Urge incontinence Overflow incontinence Functional incontinence Continuous incontinence An 81 year-old G3P3 woman presents to your office with a history of light vaginal spotting. She states this has occurred recently and in association with a thin yellow discharge. She never experienced any vaginal bleeding since menopause at the age of 52, and denies ever having been on hormone replacement therapy. She is otherwise reasonably healthy, except for osteoporosis, well-controlled hypertension, and diabetes. She is physically active and still drives to all her appointments. She is no longer sexually active since the death of her husband 2 years ago. On examination, she is noted to have severe atrophic changes affecting her vulva and vagina. A small Pederson speculum allows for visualization of a normal multiparous cervix, and the bimanual examination is notable for a small, mobile uterus. Rectovaginal exam confirms no suspicious adnexal masses or nodularity. Which of the following is the most appropriate management for this patient? Pelvic transvaginal ultrasound Office endometrial biopsy Reassurance and observation for further bleeding Vaginal estrogen therapy Dilation and curettage A 35 year-old G3P3 comes to the office to discuss tubal ligation as she desires permanent sterilization. What are the non-contraceptive health benefits of female sterilization? Reduced risk of endometriosis Reduced risk of ovarian cancer Protection against endometrial cancer Reduction in menstrual blood flow Reduced risk of sexually transmitted infections A 38 year-old G1P1 woman comes to the office for an annual exam. She has noticed some urinary frequency over the past month. She has no dysuria, hematuria, urgency or incontinence. She has normal cycles, no history of abnormal Pap smears or sexually transmitted infections and is sexually active, with 1 partner. She smokes a quarter of a pack of cigarettes daily, and drinks one glass of wine per day. Her mother had breast cancer at age 30. Her general examination is normal. On pelvic exam, she has normal external genitalia; vagina and cervix are without lesions. Her uterus is normal size, anteverted and nontender. Her left adnexa is normal, right adnexa has a mobile, slightly tender 4 cm mass. Laboratory results show a normal urinalysis, a negative urine pregnancy test and a normal Pap smear. What is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient? Perform a transvaginal ultrasound Perform a diagnostic laparoscopy Recommend a CT-guided drainage of the mass Order a KUB plain film Perform an exploratory laparotomy 413. A. B. C. * D. E. 414. A. B. C. D. * E. 415. A. * B. C. D. E. 416. A. * B. C. D. E. 417. A. B. C. * D. E. A 52 year-old nulliparous woman presents with long-standing vulvar and vaginal pain and burning. She has been unable to tolerate intercourse with her husband because of introital pain. She had difficulty sitting for prolonged periods of time or wearing restrictive clothing because of worsening vulvar pain. She recently noticed that her gums bleed more frequently. She avoids any topical over-the-counter therapies because they intensify her pain. Her physical examination is remarkable for inflamed gingiva and a whitish reticular skin change on her buccal mucosa. A fine papular rash is present around her wrists bilaterally. Pelvic examination reveals white plaques with intervening red erosions on the labia minora as shown in picture below. A speculum cannot be inserted into her vagina because of extensive adhesions. The cervix cannot be visualized. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient? Squamous cell hyperplasia Lichen sclerosus Lichen planus Genital psoriasis Vulvar cancer You are collecting data from a 37-year-old client who you suspect may have fibroid tumors. You expect her subjective data to include which of the following symptoms? Urinary urgency Difficult defecation Cyclic migraine headaches Deep pelvic paindyspareunia All of the above History of obesity, nulliparity, chronic anovulation, irregular intermenstrual bleeding, non tender uterus in 47-year-old woman gives indication for? Endometrial cancer/ hyperplasia Hormonal changes Sexual transmitted disease Pelvic Inflammatory disease Fibroids A 52-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 1-month history of headache, weakness, tingling of her extremities, muscle cramping, and fatigue. Her blood pressure is 170/110 mm Hg. Physical examination shows no other abnormalities. Laboratory studies show a decreased serum potassium concentration, metabolic alkalosis, and decreased plasma renin activity; serum sodium concentration is within the reference range. Urine catecholamine concentrations are within the reference range. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? Adrenal adenoma Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis Hypothalamic tumor Juxtaglomerular cell tumor Renal artery stenosis A twenty year old is found to have moderate dysplasia (high grade SIL) on a routine PAP. Moderate inflammation is noted on the PAP. The next appropriate step in management is? repeat PAP in 3 months treat inflammation and repeat PAP in 3 months colposcopy and biopsies wire loop excision of the transformation zone cold knife conization 418. A. * B. C. D. E. 419. A. B. C. D. * E. 420. A. * B. C. * D. E. 421. A. B. C. * D. E. Which treatment is followed by a 40 years patient with cervical dysplasia with the deformation of the cervical canal: diatermoconization of cervix diathermocoagulation of cervical laser treatment by solkovagin hysterectomy without appendages A 29-year-old woman comes to the physician for follow-up of a right breast lump. The patient first noticed the lump 4 months ago. It was aspirated at that time, and cytology was negative, but the cyst recurred about 1 month later. The cyst was re-aspirated 2 months ago and, again, the cytology was negative. The lump has recurred. Examination reveals a mass at 10 o'clock, approximately 4 cm from the areola. Ultrasound demonstrates a cystic lesion. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management? Mammography in 1 year Ultrasound in 1 year Tamoxifen therapy Open biopsy Mastectomy A 43-year-old African American woman comes to the physician because of her concern regarding breast cancer. She has no complaints at present. In past years, she had noted bilateral breast tenderness prior to her menses, but this has since abated. She has no medical problems. She had two cesarean deliveries, but no other surgeries. She takes a low-dose oral contraceptive pill and has no known drug allergies. She does not smoke, and her family history is negative. Physical examination is normal. All mammograms (yearly since age 40) have been negative to date. She wants to know whether BRCA1 and BRCA2 screening would be appropriate for her. Which of the following is the correct response? BRCA1 and 2 screening is not recommended BRCA1 and 2 screening should be performed after age 50 BRCA1 and 2 screening should be performed if breast pain recurs BRCA1 screening is recommended BRCA2 screening is recommended A 50 year-old G4P4 woman presents for her yearly checkup. She states her menses are of normal flow every 32 days, with minimal cramping and 5-day duration. Review of systems is negative. She has no medical problems. She had a bilateral tubal ligation following her last child, and a laparoscopic cholecystectomy 5 years ago. She has a history of LGSIL Pap smear with colposcopy and cryotherapy 15 years ago; her Paps have been normal since then. She does not smoke, drink alcohol or use any drugs. She is sexually active with one partner with no problems. Her general exam, including a breast exam and pelvic exam, is normal. In addition to performing a Pap smear, which of the following is the most appropriate screening test for this patient? Pelvic ultrasound Endometrial biopsy 1% C. 94% D. 2% E. Mammogram DEXA scan Colposcopy 422. A. B. * C. D. E. 423. A. B. C. D. * E. 424. A. * B. C. D. E. 425. A. B. C. D. * E. 426. A. B. C. * D. A 25 year-old G1P1 comes to the office due to left breast pain and fever. She is breast feeding her 2 1/2- week old infant. The symptoms began earlier in the day and are not relieved by acetaminophen. Blood pressure 120/60; pulse 64; temperature 99.9° F, 37.7° C. On exam, she has erythema on the upper outer quadrant of the left breast, which is tender to touch; there are no palpable masses. In addition to starting oral antibiotics, what is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient? Discontinue breastfeeding Add ibuprofen for pain relief Obtain a breast ultrasound Use a topical antifungal Admission to the hospital A 23 year-old G1P1 delivered her first baby two days ago after an uncomplicated labor and vaginal delivery. She wants to breast feed and has been working with the lactation team. Prior to discharge, her temperature was 100.4°F, 38°C (other vitals were normal). She denies urinary frequency or dysuria and her lochia is mild without odor. On examination, her lungs are clear, cardiac exam normal, and abdomen and uterine fundus are nontender. Her breasts are firm and tender throughout, without erythema and nipples are intact. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her fever? Endomyometritis Septic pelvic thrombophlebitis Mastitis Breast engorgement Vaginitis A 61 years old woman comes to the office because of an enlarging breast mass. Exam reveals a firm, fixed, 3 cm mass in the right upper outer quadrant, the biopsy of mass reveals loss of cell differentiation and lack of tissue organization, which if the following term best corresponds to this finding? Anaplasia Desmoplasia Dysplasia Hyperplasia Metaplasia A 67 years old woman with advanced metastatic breast cancer comes to the clinic for follow-up visit, her chief complaint at this time is weight loss and a reduced appetite. Which of the following is thought to be a major contributor to her chief complaint? Clathrin Histamin Interferon Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) Interleukin 45 years old woman presents with blood tinged discharge from the right nipple. The nipple appears slightly retracted and subareolar nodule can be felt on palpation. Mammographic exam shows linear shadows attributable to calcification. The lesion consists of dilated ducts and are surrounded by fibrosis and chronic inflammation, focal calcium deposition is present, which of the following is the diagnosis? Mondor disease Adenocarcinoma Mammary duct Eurasia Fat necrosis E. 427. A. B. C. D. * E. 428. A. B. C. D. E. * 429. A. B. C. D. * E. 430. A. B. * C. D. E. 431. A. B. * C. D. E. Abscess A 61 years old woman comes to the office because of an enlarging breast mass. Exam reveals a firm, fixed, 3 cm mass in the right upper outer quadrant, the biopsy of mass reveals loss of cell differentiation and lack of tissue organization, which if the following term best corresponds to this finding? Metaplasia Hyperplasia Dysplasia Anaplasia Desmoplasia A 67 years old woman with advanced metastatic breast cancer comes to the clinic for follow-up visit, her chief complaint at this time is weight loss and a reduced appetite. Which of the following is thought to be a major contributor to her chief complaint? Clathrin Histamin Interferon Interleukin-2 Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) A 30 years old woman complains of breast tenderness that becomes worse during the premenstrual period, multiple small masses are appreciable on palpation, cytologic exam of a fine needle aspirate reveals no malignant cells, biopsy shows multifocal cyst formation, areas of fibrosis, calcification and apocrine metaplasia, this condition is associated with an increased risk of cancer if: Apocrine Metaplasia is marked Calcification is prominent Cysts are larger than 0.5 cm Epithelial hyperplasia is florid Fibrosis is predominant An 18 years old girl whose grandmother was recently diagnosed with breast cancer discovers a large, round, movable nodule in her left breast, she visits the physician with concern about the nodule. Which of the diagnosis should rank highest on the physician’s differential? Cystosarcoma phyllodes Fibroadenoma Infiltrating ductal carcinoma Intraductal papilloma Fibrocystic breast disease You are counseling a 40-year-old client who has come to the clinic because she fund a “lump” in her breast last night. She is frantic because she believes she has cancer. The clinical breast examination reveals firm, smooth, discrete masses in both breast. You reinforce the physicisn’s impression that she is feeling is most likely a noncancerous “lump” and that she should have which of the following evaluation procedures first? Lumpectomy Mammogram Excisional biopsy Stereotactic biopsy All of the above 432. A. B. C. D. E. * 433. A. B. C. D. E. * 434. A. B. C. * D. E. 435. A. * B. C. D. E. 436. A. B. * C. D. E. 437. A. A 19-year-old woman noticed a mass in her left breast 2 weeks ago while doing monthly breast self-examination. Her mother died of metastatic breast cancer at the age of 40 years. Examination shows large dense breasts; a 2-cm, firm, mobile mass is palpated in the upper outer quadrant of the left breast. There are no changes in the skin or nipple, and there is no palpable axillary adenopathy. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? Lobular carcinoma Intraductal papilloma Infiltrating ductal carcinoma Fibrocystic changes of the breast Fibroadenoma 39 year old woman has been sent to the lab for evaluation of CA-125 level, this onco-marker is to indicate? Colon cancer Cervical cancer Vaginal cancer Metastasis from lung cancer Ovarian carcinoma The patient C, 45 years old, complains on dull abdominal pain, weakness, loss of appetite and weight loss for the last 5 months. Which process does the type V reflect in Pap smear test? Normal epithelium Moderate dysplasia. Cancer. Inflammation. Malignization suspect. You are completing the chief complaint interview with a client who states that she has a continuous dysmenorrhea. Based on her subjective data, you suspect which of the following medical diagnoses? Cervical cancer Hypermenorrhea Pelvic relaxation Polycystic ovary disease Moderate dysplasia. The patient C, 55 years old, complains on dull abdominal pain, weakness, bloody-serous, such as "meat slops"discharge from the vagina. Which additional diagnostic methods should be applied to refine the diagnosis of cancer of uterine body? An ultrasound scan. Endometrectomy. Colposcopy. Laparoscopy. Pap smear test A 45-year-old G4P3 woman presents with vaginal bleeding. Last week, she performed a home pregnancy test that was positive. She thinks her last menstrual period was four months ago. The last time she saw her doctor was 8 years ago, with the birth of her last child. She has no serious medical problems, has smoked a pack of cigarettes a day since the age of 20, occasionally has a beer and does not exercise. Her vitals are normal. Abdominal examination reveals a soft abdomen and the fundus palpable just below the umbilicus. Pelvic ultrasound reveals a fundal placenta and a fetus measuring 18 weeks with normal cardiac activity. Vaginal examination reveals a 3-centimeter lesion arising off the posterior lip of the cervix. It easily bleeds with palpation and is hard in consistency. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the bleeding? Trauma B. C. D. * E. 438. A. B. C. * D. E. 439. A. B. C. * D. E. 440. A. * B. C. D. E. 441. A. B. C. * Cervicitis Threatened abortion Cervical cancer Nabothian cyst A 16-year-old nulligravid woman comes to the emergency department because of heavy vaginal bleeding. She states that she normally has heavy periods every month but missed a period last month and this period has been unusually heavy with the passage of large clots. She has no medical problems, has no history of bleeding difficulties, and takes no medications. Her temperature is 37 C (98.6 F), blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, pulse is 96/minute and respirations are 12/minute. Pelvic examination shows a moderate amount of blood in the vagina, a closed cervix, and a normal uterus and adnexae. Hematocrit is 30%. Urine hCG is negative. Which of the following is the most appropriate management? Expectant management. Hysteroscopy Oral contraceptive pills Laparoscopy Laparotomy A 12-year-old female comes to the physician because of a vaginal discharge. The discharge started about 2 months ago and is whitish in color. There is no odor. The patient has no complaints of itching, burning, or pain. The patient started breast development at 9 years of age and her pubertal development has proceeded normally to this point. She has not had her first menses and she is not sexually active. She has no medical problems. Examination is normal for a 12-year-old female. Microscopic examination of the discharge shows no evidence of pseudohyphae, clue cells, or trichomonas. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? Bacterial vaginosis Candida vulvovaginitis Physiologic leucorrhea Syphilis Trichomoniasis A 34-year-old woman comes the physician because of lower abdominal cramping. The cramping started 2 days ago. Examination is unremarkable except for a pelvic examination that reveals a 10-week sized uterus. Urine hCG is positive, and pelvic ultrasound reveals a 10-week intrauterine pregnancy with a fetal heart rate of 160. The patient states that she is not sure whether to keep the pregnancy. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management? Counsel the patient or refer to an appropriate counselor Notify the patient's parents Notify the patient's partner Schedule a termination of pregnancy Tell the patient that she is likely to have a miscarriage A 67-year-old woman comes to the physician because of pain with urination and frequent urination. She has hypertension for which she takes a beta-blocker, but no other medical problems. She states that she is not sexually active. She does not smoke and drinks cranberry juice daily. Examination shows mild suprapubic tenderness and genital atrophy but is otherwise unremarkable. Urinalysis shows 50 to 100 leukocytes/high powered field (hpf) and 5 to 10 erythrocytes/hpf. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the infection? Cardiac disease Cranberry juice ingestion Hypoestrogenism D. E. 442. A. B. C. * D. E. 443. A. B. C. D. * E. 444. A. B. C. D. * E. 445. A. B. C. D. * Nephrolithiasis Sexual intercourse A 14-year old G0 adolescent reports menarche six months ago, with increasingly heavy menstrual flow causing her to miss several days of school. Three months ago, her pediatrician started her on oral contraceptives to control her menstrual periods, but she continues to bleed heavily. Her previous medical history is unremarkable. The patient has a normal body habitus for her age. Appropriate breast and pubic hair development is present. Her hemoglobin is 9.1 mg/dl, hematocrit 27.8%, urine pregnancy test negative. Which of the following etiologies for menorrhagia is most likely the cause of her symptoms? Uterine leiomyoma Thyroid disorder Coagulation disorder Endometrial hyperplasia Chronic Endometritis A 32 year-old G0 presents with amenorrhea for the last 3 months. She has a long history of irregular cycles, 26 to 45 days apart, for the last two years. She is otherwise in good health and is not taking any medications. She is sexually active with her husband and uses condoms for contraception. She is 5 feet 4 inches tall and weighs 140 pounds. On exam, she has a slightly enlarged, non-tender uterus. There are no adnexal masses. What is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient? Perform a pelvic ultrasound Check a TSH level Check progesterone and estrogen levels Perform a urine pregnancy test Check FSH and LH levels A 20-year-old G1P0 woman has vaginal spotting and mild cramping for the last 3 days. She had her last normal menstrual period approximately 6-1/2 weeks ago. She had a positive home pregnancy test. Her medical and gynecologic histories are negative and non-contributory. On physical exam: blood pressure 120/72; pulse 64; respirations 18; temperature 98.6°F (37°C). On pelvic exam, she has scant old blood in the vagina, with a normal appearing cervix and no discharge. On bimanual exam, her uterus is nontender and small, and there are no adnexal masses palpable. Pertinent labs: Quantitative Beta-hCG is 750 mIU/ml 48 hours ago; today, the level is 760 mIU/ml; progesterone level = 3.2 ng/ml; hematocrit is 37%. Transvaginal ultrasound shows a fluid collection in the uterus and no fetal pole, no masses and no free fluid in the pelvis. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient? Exploratory surgery Treat with Methotrexate Treat with Mifepristone Dilatation and Curettage Repeat hCG level in one week An obese 30 year-old G3P1 Asian woman undergoes an uncomplicated dilation and curettage for a first trimester miscarriage. Pathology reveals a molar pregnancy. The patient’s medical history is significant for chronic hypertension. She has a history of a previous uncomplicated term pregnancy, and termination of a pregnancy at 16 weeks gestation for trisomy 18. What aspect of the patient’s history places her at increased risk for a molar pregnancy? Obesity Previous history of fetal aneuploidy Chronic hypertension Asian race E. Prior term pregnancy 446. A 17 year-old G0 presents with a 3-year history of severe dysmenorrhea shortly after menarche at age 14. Her menstrual cycles are regular with heavy flow. She has been treated with NSAIDs and oral contraceptives for the last year without significant improvement. She misses 2-3 days of school each month due to her menses. She has never been sexually active. Physical examination is remarkable for Tanner: Stage IV breasts and pubic hair. Pelvic examination is normal, as is a pelvic ultrasound. Both the patient and her mother are concerned. What is the next best step in the management of this patient? Empiric treatment with GnRH agonist CT scan of the pelvis Diagnostic laparoscopy MRI of the pelvis Hysterosalpingography A 22-year old G0 presents with 5 months of amenorrhea since discontinuing her oral contraceptive pills. She had been on the pill for the last 6 years and had normal menses every 28 days while taking them. She is in good health and not taking any medications. She is 5 feet 4 inches tall and weighs 140 pounds. Her examination, including a pelvic examination, is normal. Which of the following history elements would be most useful in determining the cause of amenorrhea in this patient? Age at first intercourse History of sexually transmitted infections Parity Recent history of weight loss History of oligo-ovulatory cycles A 15 year-old G0 presents with severe menstrual pain for the past 12 months. The pain is severe enough for her to miss school. The pain is not relieved with ibuprofen 600 mg every 4 hours. She is not sexually active and the workup reveals no pathology. The most appropriate next step in the management of this patient is to begin combination oral contraceptives. How do oral contraceptives relieve primary dysmenorrhea? Creating endometrial atrophy Decreasing inflammation Increasing prolactin levels Decreasing inhibin levels Thickening cervical mucous A 18 year-old woman, married, has regular unprotected sex, presents with low appetite, insomnia and amenorrhea for 3 months. What is the most likely diagnose and how to confirm it? Hypothyroidism/Free T4 level Hypethyroidism/TsH level Cervical cancer/PAP Smear test Syphylis/VDRL Pregnancy/BhcG A woman who recently gave birth has elevated prolactin levels, the gland responsible for secretion of this hormone is derived from which of the following structures? Anterior Pituitary Cerebral vesicles Infundibulum Neurohypophysis Proctodeum A. B. C. * D. E. 447. A. B. C. D. E. * 448. A. * B. C. D. E. 449. A. B. C. D. E. * 450. A. * B. C. D. E. 451. A 55 year old woman stopped menstruating about 3 months ago, worried that she may be pregnant, she decided to have a pregnancy test, the result is negative, which of the following series of test results will confirm that the woman is postmenopausal? A. Increased LH, increased FSH, increased estrogen Decreased LH, decreased FSH, increased estrogen Decreased LH, increased FSH, decreased estrogen Increased LH, decreased FSH, decreased estrogen Increased LH, increased FSH, decreased estrogen Crampy lower abdominal and back pain during menses in 21 year old woman and normal examination would suggest? Trauma Cancer Primary dysmenorrhea Fibrosis PID Choose the most exact method for determination of pathological reason for uterine bleeding in woman 35 years old: measurement of the basal temperature of the body diagnostic curettage of the mucous membrane of the uterus hysteroscopy measurement of the concentration of estrogens in the blood serum Measurement of the concentration of progesterone in the blood serum You are counseling a perimenopausal client regarding prevention of osteoporosis. You recommend that she increase her dietary intake of which of the following? Milk and iron Calcium and vitamin D Magnesium and vitamin C Magnesium and phosphorus All of the above You are completing the chief complaint interview for a 17-year-old with dysmenorrhea. You will assess for which of the following symptoms? Food cravings Heart palpitations Abnormal bleeding Duration of her pain All of the above You are explaining the intervention strategies for PMS to a 28-year-old client. You recommend that during the latter part of her cycle she limit which of the following? Exercise Fluid intake Fruits and vegetables Salt and caffeine intake All of the above B. C. D. E. * 452. A. B. C. * D. E. 453. A. B. * C. D. E. 454. A. B. * C. D. E. 455. A. B. C. D. * E. 456. A. B. C. D. * E. 457. A. * B. C. D. E. 458. A. * B. C. D. E. 459. A. * B. C. D. E. 460. A. * B. C. D. E. A 42-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 1-year history of vaginal bleeding for 2 to 5 days every 2 weeks. The flow varies from light to heavy with passage of clots. Menses previously occurred at regular 25- to 29day intervals and lasted for 5 days with normal flow. She has no history of serious illness and takes no medications. She is sexually active with one male partner, and they use condoms inconsistently. Her mother died of colon cancer, and her maternal grandmother died of breast cancer. She is 163 cm (5 ft 4 in) tall and weighs 77 kg (170 lb); BMI is 29 kg/m2. Her temperature is 36.6°C (97.8°F), pulse is 90/min, respirations are 12/min, and blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg. The uterus is normal sized. The ovaries cannot be palpated. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Test of the stool for occult blood is negative. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in diagnosis? Endometrial biopsy Barium enema Progesterone challenge test Colposcopy Cystoscopy A 14-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her mother because of a 2-month history of heavy vaginal bleeding during menstrual periods. She has had episodes of excessive periodontal bleeding while brushing her teeth and easy bruising for 6 years. She also had an episode of extended bleeding after a tooth extraction 4 years ago. Her mother and brother have had similar symptoms. Physical examination shows patchy ecchymosis over the upper and lower extremities. Laboratory studies show: Platelet count 234,000/mm3 Bleeding time 17 min Prothrombin time 12 sec (INR=1) Partial thromboplastin time 46 sec Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? von Willebrand disease Factor X (Stuart factor) deficiency Factor XII (Hageman factor) deficiency Hemophilia A Vitamin K deficiency A 36-year-old woman has been trying to conceive for the past 2 years. Her menses occur every 19 to 45 days. She has a past history of some type of sexually transmitted disease, but says she was treated and cured. She is 163 cm (5 ft 4 in) tall and weighs 109 kg (240 lb); BMI is 41 kg/m2. Physical examination including a pelvic examination is unremarkable. An endometrial biopsy is performed based on the menstrual history and a negative pregnancy test. The biopsy shows stromal breakdown associated with proliferative glands. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her infertility? Anovulation Chronic endometritis Endometrial polyps Endometriosis All of the above Patient, aged 22 years complains of delay of menses during 2 months. Taste qualities changed. Nullipara, no abortions in the past history. Vaginal examination: mucous membrane and uterine cervix are cyanotic, uterus of ovoid form, enlarged to 7-8 weeks of pregnancy, soften consistency. Appendages are without peculiarities. Isthmus of the uterus is softened. Crypts of the vagina are free. What diagnosis is the most probable? Uterine pregnancy. Uterine leiomyoma. Disorder of ovarian-menstrual cycle. Hydatid mole. Choryonepithelioma. 461. A. * B. C. D. E. 462. A. * B. C. D. E. 463. A. B. C. * D. E. 464. A. * B. C. D. E. 465. A. * B. C. D. E. 466. A 48-year-old patient was delivered to a hospital in-patient unit with uterine bleeding that occurred after the 2-week-long delay of menstruation. Anamnesis states single birth. Examination of the uterine cervix with mirrors revealed no pathologies. On bimanual examination: uterus is of normal size, painless, mobile; uterine appendages have no changes. Discharge is bloody and copious. What primary hemostatic measure should be taken in the given case? Fractional curettage of uterine cavity Hormonal hemostasis Hemostatics Uterine tamponade Uterotonic A 13-year-old girl was admitted to the gynecology department for having a signifi-cant bleeding from the genital tract for 10 days. The patient has a history of irregular menstrual cycle since menarche. Menarche occurred at the age of 11. Recto-abdominal examination revealed no pathology. What is the provisional diagnosis? Juvenile uterine bleeding Adenomyosis Injury of the external genitalia Werlhof’s disease Endometrial polyp A 20-year-old female consulted a gynecologist about not having menstrual period for 7 months. History abstracts: early childhood infections and frequent tonsillitis, menarche since 13 years, regular monthly menstrual cycle of 28 days, painless menstruation lasts 5-6 days. 7 months ago the patient had an emotional stress. Gynecological examination revealed no alterations in the uterus. What is the most likely diagnosis? Algomenorrhea Primary amenorrhea Secondary amenorrhea Spanomenorrhea Cryptomenorrhea A 28-year-old patient complains of infertility. The patient has been married for 4 years, has regular sexual life and does not use contraceptives but has never got pregnant. Examination revealed normal state of the genitals, tubal patency. Basal body temperature recorded over the course of 3 consecutive menstrual cycles appeared to have a single phase. What is the most likely cause of infertility? Anovulatory menstrual cycle Immunological infertility Genital endometriosis Chronic salpingoophoritis Ovulatory menstrual cycle 3 months after the first labor a 24- year-old patient complained of amenorrhea. Pregnancy ended in Caesarian section because of premature detachment of normally positioned placenta which resulted in blood loss at the rate of 2000 ml due to disturbance of blood clotting. Choose the most suitable investigation: Estimation of gonadotropin rate US of small pelvis Progesteron assay Computer tomography of head Estimation of testosteron rate in blood serum A 28-year old woman presents with secondary amenorrhea of six month duration. After a history and physical and after pregnancy has been excluded, the next step should be: A. * B. C. D. E. 467. A. * B. C. D. E. 468. A. B. * C. D. E. 469. A. * B. C. D. E. 470. A. * B. C. D. E. 471. A. B. C. D. E. * Measurement of a TSH and prolactin and administer progestational challenge Measurement of gonadotropin assay and progestational challenge Measurement of gonadotropin assay followed by a 21-day cycle of estrogen and progestin Measurement of chromosomes and gonadotropin level Measurement of gonadotropins and a coronal CT scan A 22-year-old patient complains of 8-month delay of menstruation. Anamnesis: menarche since the age of 12,5. Since the age of 18 menstruations are irregular. No pregnancies. Mammary glands have normal development; when the nipples are pressed, milk drops are discharged. On gynecological examination: moderate uterus hypoplasia. On hormonal examination: prolactin level exceeds the norm two times. On computed tomogram of the sellar region: a space-occupying lesion 4 mm in diameter is detected. The most likely diagnosis is: Pituitary tumor Lactation amenorrhea Stein-Leventhal syndrome Sheehan’s syndrome Cushing’s disease A 24 year-old G0 presents with a one-year history of introital and deep thrust dyspareunia. She also has a 2- year history of severe dysmenorrhea, despite the use of oral contraceptives. She underwent a diagnostic laparoscopy 6 months ago that showed minimal endometriosis with small implants in the posterior cul de sac only, which were ablated with a CO2 laser. On further questioning, she reports significant urinary frequency, urgency and nocturia. A recent urine culture was negative. What is the most likely diagnosis in this patient? Acute cystitis 5% Interstitial cystitis Acute urethral syndrome Acute urethritis Salpingitis Pain peaks before menses, dyspareunia and infertility in 22 year old woman are the signs of? Endometriosis Sexually Transmitted Disease Pelvic congestion Malignancy Fibrosis Dysmenorrhea, pelvic pain, menorrhea (bulky, globular, tender uterus) in 25 year old woman are indicative of? Adenomyosis Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Malignancy Fibrosis None of them Dull and ill-defined pelvic ache that worsens with standing plus dyspareunia in 35 year old woman are indications for? Endometriosis Cancer Vaginitis Cervicitis Pelvic congestion 472. A 33 year old woman comes to the clinic on examination, there is an immobile uterus and posterior cul-de-sac, the patient has suffered from a chronic pelvic pain as well, the diagnosis might be: A. B. C. D. * E. 473. Vaginitis Mittelschmerz Cervical cancer Endometriosis Ovarian cyst A 36-year-old nulligravid woman with primary infertility comes for a follow-up examination. She has been unable to conceive for 10 years; analysis of her husband's semen during this period has shown normal sperm counts. Menses occur at regular 28-day intervals and last 5 to 6 days. She is asymptomatic except for severe dysmenorrhea. An endometrial biopsy specimen 5 days before menses shows secretory endometrium. Hysterosalpingography 1 year ago showed normal findings. Pelvic examination shows a normal vagina and cervix. Bimanual examination shows a normal-sized uterus and no palpable adnexal masses. Rectal examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? Endometriosis Tubal obstruction Male factor Intrauterine synechiae Anovulation A 28-year-old woman has bursting pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation; chocolate-like discharges from vagina are observed. It is known from the anamnesis that the patient suffers from chronic adnexitis. Bimanual examination revealed a tumour-like formation of heterogenous consistency 7х7 cm large to the left from the uterus. The formation is restrictedly movable, painful when moved. What is the most probable diagnosis? Endometrioid cyst of the left ovary Follicular cyst of the left ovary Fibromatous node Exacerbation of chronic adnexitis Tumour of sigmoid colon A 28-year-old female patient has been admitted to the gynecology department for abdominal pain, spotting before and after menstruation for 5 days. The disease is associated with the abortion which she had 2 years ago. Anti-inflammatory treatment had no effect. Bimanual examination findings: the uterus is enlarged, tight, painful, smooth. Hysteroscopy reveals dark red holes in the fundus with dark blood coming out of them. What diagnosis can be made on the grounds of these clinical presentations? Inner endometriosis Polymenorrhea Hypermenorrhea Submucous fibromatous node E Dysfunctional uterine bleeding A 35-year-old woman addressed a gynecological in-patient department with complaints of regular pains in her lower abdomen, which increase during menstruation, and dark-brown sticky discharge from the genital tracts. On bimanual examination: the uterine body is slightly enlarged, the appendages are not palpated. Mirror examination of the uterine cervix reveals bluish spots. What diagnosis is most likely? Cervical endometriosis Cervical erosion A. * B. C. D. E. 474. A. * B. C. D. E. 475. A. * B. C. D. E. 476. A. * B. C. D. E. 477. A. B. * C. D. E. 478. A. B. C. D. * E. 479. A. B. C. * D. E. 480. A. * B. C. D. Cervical polyp Cervical cancer Cervical fibroid A 16-year-old female comes to the physician because of an increased vaginal discharge. She developed this symptom 2 days ago. She also complains of dysuria. She is sexually active with one partner and uses condoms intermittently. Examination reveals some erythema of the cervix but is otherwise unremarkable. A urine culture is sent which comes back negative. Sexually transmitted disease testing is performed and the patient is found to have gonorrhea. While treating this patient's gonorrhea infection, treatment must also be given for which of the following? Bacterial vaginosis Chlamydia Herpes Syphilis Trichomoniasis A 23 year-old G0 reports having a solitary, painful vulvar lesion that has been present for three days. This lesion has occurred twice in the past. She states that herpes culture was done by her doctor during her last outbreak and was negative. She is getting frustrated in that she does not know her diagnosis. She has no significant previous medical history. She uses oral contraceptives and condoms. She has had four sexual partners in her lifetime. On physical examination, a cluster of three irregular erosions with a superficial crust is noted on the posterior fornix. Urine pregnancy test is negative. You suspect recurrent genital herpes. How do you explain the negative culture? Cultures were taken too early The more definitive test would be serum herpes antibody testing The cultures were refrigerated prior to transport to the lab Herpes cultures have a 10-20% false negative rate The herpes virus cannot be recovered with recurrent infections A 22 year-old P0 presents with a one-month history of profuse vaginal discharge with mild odor. She has a new sexual partner with whom she has had unprotected intercourse. She reports mild to moderate irritation, pruritus and pain. She thought she had a yeast infection, but had no improvement after using an over-the counter antifungal cream. She is concerned about sexually transmitted infections. Her medical history is significant for lupus and chronic steroid use. Pelvic examination shows normal external genitalia, an erythematous vagina with a copious, frothy yellow discharge and multiple petechial on the cervix. Vaginal pH is 7. Saline wet mount reveals motile, flagellated organisms and multiple white blood cells. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for this patient? Clindamycin Azithromycin Metronidazole Ampicillin Doxycycline A 26 year-old G2P2 reports that she is sexually active with a new male partner. She is using oral contraception for birth control and, as such, did not use a condom. She reports the new onset of vulvar burning and irritation. She thought she had a cold about 10 days ago. Given her history, which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient? Herpes simplex virus Primary syphilis Secondary syphilis Human immunodeficiency virus E. Trichomonas 481. A 39 year-old G0 presents to the clinic reporting non-tender spots on her vulva for about a week. No pruritus or pain is present. She also notes a brownish rash on the palms of her hands. She admits to IV drug abuse. She was diagnosed as HIV-positive two years ago, but has not been compliant with suggested treatment. On examination, three elevated plaques with rolled edges are noted on the vulva. They are non-tender. A brown macular rash is noted on the palms of her hands and the soles of her feet. What is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient? Obtain a treponemal-specific test Biopsy of the lesion Colposcopic evaluation of the vulvar lesions Culture the base of the lesion Perform a wet prep A 20 year old woman presents with a 2-day history of dysuria and increased urinary frequency, she is recently married and was not sexually active prior to the marriage, gynecologic exam reveals no evidence of discharge, vaginitis or cervicitis, urinalysis reveals 14 white blood cells per high-powered field with many gram-negative rods, which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy? Trimethropim-Sulfamethoxazole Ceftriaxone Fluconazole Gentamicin Metronidazole Woman with large, deep ulcers on genital with gray/yellow exudate, the ulcers are well-demarcated borders and soft, the patient also has severe lymphadenopathy, which of the following could be the case? Haemophilus (chancroid) HSV-vesicles Lymphogranuloma venerum HPV (wart) None of them A 37 years old woman has been examined and a fishy-odor discharge is noted, itching/ burning and inflamed vagina not to see, what is the diagnosis? Candida vaginitis Cancer Bacterial vaginosis Cervicitis HPV The chief complaint interview on a client reveals vaginal discharge with itching and burning. The client also reveals she experiences dyspareunia. If her diagnosis is monilial vulvovaginitis, you would expect the wet mount slide to contain which of the following? Bacteria Clue cells Trichomonads Budding hyphae All of the above A. * B. C. D. E. 482. A. * B. C. D. E. 483. A. * B. C. D. E. 484. A. B. C. * D. E. 485. A. B. C. D. * E. 486. A. * B. C. D. E. 487. A. B. C. D. E. * 488. A. * B. C. D. E. 489. A. * B. C. D. E. 490. A. B. * C. D. E. 491. A. B. C. D. * A 20.y.old woman is diagnosed with trichomonas and prescribed an antibiotic. She calls her physician complaining of the flushing, nausea, and emesis. What antibiotic was the patient prescribed and what should she have been warned of? Metronidazole - alcohol Metronidazole - sunlight Metronidazole – smoking Azithromycin – spicy food Azithromycin – oral contraceptive The patient complains of feeling of itching, pain in the vagina, large selection of white disharge. On examination: vaginal mucosa edematous flushed, in the lateral fornices - the accumulation of white layers, similar to the chees. What is the previous diagnosis? Trichomonas colpitis chlamydial colpitis urogenital mycoplasmosis bacterial vaginosis candidiasis vaginitis The patient D, 22 years old was diagnosed Trichomonas colpitis. Select a product for the treatment of this patient tinidozol ciprofloxacin ampicillin Biseptol Diflucan A 27 year-old G0 woman comes to the clinic as she has been unable to conceive for the last year. She is in good health and has not used any hormonal contraception in the past. She had normal cycles in the past every 28 days until about 6 months ago. At that time, she began to have irregular menses every 2-3 months, with some spotting in between. She is not taking any medications. She has no history of abnormal Pap smears or sexually transmitted infections. Her physical examination is normal. Laboratory tests show: Results Normal Values TSH 10 mIU/ml 0.5-4.0 mIU/ml Free T40.2 ng/dl 0.8-1.8 ng/dl Prolactin 40 ng/ml Begin combined oral contraceptive Begin bromocriptine Order a Clomid ovulation challenge test Obtain a brain MRI Order a thyroid gland ultrasound 25 year old woman comes to the physician for the regular check-up, during meeting, she asks the physician about the direct role of hcG in pregnancy, which of the following is the best reply? Egg producing Maintenance of the corpus luteum Uterine contraction Ovaries relaxant Maintenance of placenta A 35-year-old woman is considered infertile after ____ of trying to conceive 1 month 2 months 4 months 6 months E. 12 months 492. Patient 22 years, complains about absence of pregnancy during 5 years of marriage. For the last 3 years conducted medical and resort treatment. Two months ago metrosalpingography was done — tubes’ permeability is normal. The last menstruation was with the delay on 2 weeks, painful. 2 days ago bloody excretions in a small amount and pain in lower parts of abdomen appeared again. Objectively: the uterine cervix is cyanotic, external os is closed. The uterus in normal position, enlarged to 5 weeks of pregnancy, is soft, mobile. Douglas punch isn’t painfull. Right adnexa are not determined. The left adnexa are enlarged in sizes to 6x3 cm, painful at palpation. Parametriums are free. Excretions are bloody, in a little quantity. Blood test: Haemoglobin — 90g/l, red cells — 3,0 h 10 /l, leucocytes— 8,6 h 10 /l. What is the most reliable diagnosis? Pregnancy 6-5 weeks. Abortion, that began. Cyst of the left ovary. Pyosalpinx after metrosalpingography The molar pregnancy Violation of menstrual cycle Ectopic pregnancy, that was ruptured on the type of tube abortion The patient 25 years old, diagnosed with endocrine form of infertility. Which drug stimulates ovulation of patients with endocrine form of infertility? progesterone Clomiphene Citrate androkur femoston dufaston The patient 29 years old, complains of infertility. Sexual life has been leading in marriage for 4 years, hasn’t been preventing pregnancy. She didn’t have any pregnancy yet. An examination of women is established: the development of genital organs were normal; The fallopian tubes are passable. Basal [rectal] temperature for three menstrual cycles had single phase. The most probable cause of infertility? Anovulatory menstrual cycle Chronic adnexitis Anomalies of genital organs Immunological infertility Genital endometrioses The patient complains about infertility. Menstruations started at 16 years, are not regular, 5-6 days after 28-35 days, to marriage - painful. Sexual life during 4 years. Did not use contraceptives, become not pregnant. In childhood was ill on a measles, scarlet fever. Vaginally: the uterus is of normal size, mobile, unpainful, adnexa are not palpated. In speculum: the uterine cervix is normal. Analysis of sperm of husband - 55 mln of spermatozoa in 1 ml, 75% of them are mobile. Shuvarscy test is positive. A basal temperature during 2 cycles is monotonous. Diagnosis? Infertility I, tubal genesis Infertility I, tubal-peritoneal genesis Infertility I, anovulatory cycles Infertility I, masculine genesis Infertility I, anomaly of development of privy parts The woman, suffering from infertility came to the gynecologist with complain of delayed menstruation. Which pregnancy test will be the most reliable in the early stages? Measurement of human chorionic gonadotropin in the blood Immune hemagglutination inhibition test. Reaction Galey Maynini A. * B. C. D. E. 493. A. B. * C. D. E. 494. A. * B. C. D. E. 495. A. B. C. * D. E. 496. A. * B. C. D. E. 497. A. B. C. * D. E. 498. A. B. C. D. E. * 499. A. B. C. * D. E. 500. A. B. * C. D. E. 501. A. * B. C. D. E. 502. A. * B. C. Measurement of the concentration of estrogen in the blood Measurement of concentration of progesterone in the blood While discussing reproductive health with a group of female adolescents, one of the adolescents asks the doctor, "Where is the ovum fertilized?" The doctor responds by stating that fertilization normally occurs at which of the following sites? Uterus. Vagina. Fallopian tube. Cervix. Ovary A female patient, aged 25, suffers endocrine form of infertility for 5 years. What should be included in investigations of this patient? Ultrasonic monitoring of growth of follicles during the menstrual cycle. Measuring basal temperature. Determine the level of hormones in the blood. Smears on the "hormonal mirror." All answers are correct. A couple visiting the infertility clinic for the first time asks the doctor, "What causes infertility in a woman?" Which of the following would the doctor include in the response as one of the most common factors? Absence of uterus. Overproduction of prolactin. Anovulation. Immunologic factors. Genetic factors. 25-year-old patient notes the absence of pregnancy within 5 years. Operations were performed twice at the tubal pregnancy. What method can solve the problem of the generative function in this woman? Correction factors of ovarian In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) and embryo transplantation Intrauterine artificial insemination Intracervical artificial insemination Insemination sperm donor What is not included in the complex examination of patients with endocrine form of infertility? definition of the Fallopian tubes basal body temperature determine the level of hormones in the blood smears on the "hormonal mirror" ultrasound control the growth of follicles during the menstrual cycle A 26-year-old woman has attended maternity center complaining of her inability to become pregnant despite 3 years of regular sex life. Examination revealed the following: increased body weight; male-type pubic hair; excessive pilosis of thighs; ovaries are dense and enlarged; basal body temperature is monophasic. The most likely diagnosis is: Ovaries sclerocystosis Inflammation of uterine appendages Adrenogenital syndrome D. E. 503. A. * B. C. D. E. 504. A. * B. C. D. E. 505. A. B. C. * D. E. 506. A. * B. C. D. E. 507. A. B. C. * D. E. Premenstrual syndrome Gonadal dysgenesis A 31-year-old female patient complai-ns of infertility, amenorrhea for 2 years after the artificial abortion that was complicated by endometritis. Objectively: examination of the external genitalia revals no pathology, there is female pattern of hair distribution. According to the functional tests, the patient has biphasic ovulatory cycle. What form of infertility is the case? Uterine Ovarian Pituitary Hypothalamic Immunologica The patient 29 years old, complains of infertility. Sexual life has been leading in marriage for 4 years, hasn’t been preventing pregnancy. She didn’t have any pregnancy yet. An examination of women is established: the development of genital organs were normal; The fallopian tubes are passable. Basal [rectal] temperature for three menstrual cycles had single phase. The most probable cause of infertility? Anovulatory menstrual cycle Chronic adnexitis Anomalies of genital organs Immunological infertility Genital endometriosis The patient complains about infertility. Menstruations started at 16 years, are not regular, 5-6 days after 28-35 days, to marriage - painful. Sexual life during 4 years. Did not use contraceptives, become not pregnant. In childhood was ill on a measles, scarlet fever. Vaginally: the uterus is of normal size, mobile, unpainful, adnexa are not palpated. In speculum: the uterine cervix is normal. Analysis of sperm of husband - 55 mln of spermatozoa in 1 ml, 75% of them are mobile. Shuvarscy test is positive. A basal temperature during 2 cycles is monotonous. Diagnosis? Infertility I, tubal genesis Infertility I, tubal-peritoneal genesis Infertility I, anovulatory cycles Infertility I, masculine genesis Infertility I, anomaly of development of privy parts The woman, suffering from infertility came to the gynecologist with complain of delayed menstruation. Which pregnancy test will be the most reliable in the early stages? Measurement of human chorionic gonadotropin in the blood Immune hemagglutination inhibition test. Reaction Galey Maynini Measurement of the concentration of estrogen in the blood Measurement of concentration of progesterone in the blood A client is scheduled to have in vitro fertilization (IVF) as an infertility treatment. Which of the following client statements about IVF indicates that the client understands this procedure? "IVF requires supplemental estrogen to enhance the implantation process." "The pregnancy rate with IVF is higher than that with gamete intrafallopian transfer." "IVF involves bypassing the blocked or absent fallopian tubes." "Both ova and sperm are instilled into the openened of a fallopian tube." Nothing of the above 508. A. B. C. D. E. * 509. A. B. * C. D. E. 510. A. B. C. D. * E. 511. A. B. * C. D. E. 512. A. * B. C. D. E. A female patient, aged 25, suffers endocrine form of infertility for 5 years. What should be included in investigations of this patient? Ultrasonic monitoring of growth of follicles during the menstrual cycle. Measuring basal temperature. Determine the level of hormones in the blood. Smears on the "hormonal mirror." All answers are correct. 25-year-old patient notes the absence of pregnancy within 5 years. Operations were performed twice at the tubal pregnancy. What method can solve the question of the generative function in this woman? Correction factors of ovarian In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) and embryo transplantation Intrauterine artificial insemination Intracervical artificial insemination Insemination sperm donor A 19-year-old Hispanic woman who is a regular patient comes to the office for her annual physical examination and cervical cytology. She tells you that she has not had a menstrual period for the past 6 months. She is a college student who is in good health, has not had any medical illnesses or surgery, and has never been pregnant. She is currently sexually active and uses barrier contraception. She reports that during the past year her menses had become very irregular prior to complete cessation 6 months ago. She also notes that she has gained about 9 kg in the past 6 months and has had an increasing problem with acne and a troublesome growth of hair on her thighs and abdomen. She has been somewhat depressed about this, and her grades have declined. She reports that one of her sisters also had this problem prior to getting married. Physical examination shows a mildly obese young woman who has scattered facial acne, mild male pattern hair growth on the abdomen, and an essentially normal pelvic examination except for slight enlargement of the uterus and both ovaries. This patient's history is most consistent with which of the following? Androgen-producing ovarian tumor. Cushing syndrome. Hypothyroidism. Polycystic ovarian syndrome. Prolactinoma. An obese patient with Body Mass Index (BMI) of 38 is diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome, what is the very first-line treatment of choice? Protein diet Weight loss Warm bath Aspirin Laxatives A 60 years old woman comes to the office with complaints of vaginal bleeding, pelvic pressure on examination, the vulvovaginal dryness, irritation, pruritus to mention the mucosa is pale with low elasticity and low rugae. What might be the diagnosis? Genitourinary syndrome of menopausal Candida vaginitis Dermatitis Bacterial vaginitis Vaginal cancer 513. A. B. C. D. * E. 514. A. * B. C. D. E. 515. A. B. * C. D. E. 516. A. B. C. D. E. * 517. A. B. * C. D. E. 518. A. B. C. D. * E. Massive hemorrhage complicated with hypotension, low prolactin, fatigue, bradycardia, vaginal atrophy, are suggestive for? Bacterial vaginitis Ovarian torsion Ovarian cancer Sheehan syndrome Cancer A 22 years old first time mother 9 days after delivery develops inability to void or small-volume voids, incomplete bladder emptying and dribbling of urine, what might be the diagnosis? Postpartum urinary retention Cervicitis Vaginitis UTI Sheehan syndrome A 56 y.old woman presents with complaints of insomnia, vaginal dryness and lack of menses for 13 months. What is the most likely diagnosis? Sheehan syndrome Menopause Hypothyroidism Hyperthyroidism Ovarian cancer A 16 y.old girl presents with low appetite, insomnia and amenorrhea for 3 months. What is the most likely diagnosis and how will you confirm it? Hypothyroidism/Free T4 levels Hyperthyroidism/TSH level Cervical cancer/Pap smear test Syphilis/VDRL Pregnancy/BhcG You are counseling a perimenopausal client regarding prevention of osteoporosis. You recommend that she increase her dietary intake of which of the following? Milk and iron Calcium and vitamin D Magnesium and vitamin C Magnesium and phosphorus Calcium and iron You are explaining the intervention strategies for PMS to a 28-year-old client. You recommend that during the latter part of her cycle she limit which of the following? Exercise Fluid intake Fruits and vegetables Salt and caffeine intake Alcohol 519. A. B. * C. D. E. 520. A. * B. C. D. E. 521. A. * B. C. D. E. 522. A. B. C. D. * E. 523. A. B. C. A 62-year-old woman comes to the physician for a routine health maintenance examination. On questioning, she has had fatigue, constipation, and a 9-kg (20-lb) weight gain during the past year. She receives estrogen replacement therapy. Serum lipid studies were within the reference range 5 years ago. She is 157 cm tall and weighs 77 kg; BMI is 31 kg/m2. Physical examination shows no other abnormalities. Serum lipid studies today show: Total cholesterol 269 mg/dL, HDL-cholesterol 48 mg/dL, LDL-cholesterol 185 mg/dL, Triglycerides 180 mg/dL. Which of the following is the most likely cause? Thiazide diuretic therapy Hypothyroidism Estrogen replacement therapy Estrogen deficiency Diabetes mellitus A 28.y.old woman comes to clinic for a wellness exam. She describes that approximately 2 weeks after her menses, she experiences intense, sharp lower quadrant abdominal pain that lasts couple of hours. The pain varies from the right to the left side each cycle. What is the name of this phenomenon? Mittelschmerz Ovarian cancer Polycystic ovarian syndrome None of them Pelvic Inflammatory Disease A 15-year-old girl who is a ballet dancer has not had a menstrual period for the past 3 months. Menses were previously regular at 29-day intervals. She has lost weight over the past year; her weight is 70% of that expected for her height. She is afebrile and has purpuric lesions on her extremities and trunk. Platelet, absolute neutrophil, and lymphocyte counts are below the reference range. She has macrocytic anemia. The most likely cause of these symptoms is a deficiency of which of the following nutrients? Folic acid Iron Linoleic acid Magnesium Niacin A 16-year-old girl has hirsutism, deepening of the voice, and cessation of menses. She swims in competitions. Which of the following drugs is most likely to have caused these findings? Ethinyl estradiol Leuprolide Medroxyprogesterone Nandrolone Tamoxifen 22-year-old woman appealed to the doctor complaining of a two-year increase in body hair growth and weight gain of 3.2 kg. Menarche from 15 years, irregular menstruation in the range of 4 - to 6 months from the time. Not treated. Objectively: height - 160 cm, weight - 74 kg. Body mass index 29 kg / m. Blood pressure, pulse, respiratory rate and temperature within normal limits. In the study revealed hirsutism and strongly pigmented skin on the neck and axillary area. What is the correct diagnosis? Edison disease hypothyroidism punched hymen D. * E. 524. A. * B. C. D. E. 525. A. * B. C. D. E. 526. A. * B. C. D. E. 527. A. * B. C. D. E. 528. A. * B. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome Syndrome of premature ovarian failure 28-year-old woman complains of increased intermenstrual periods up to 2 months, hirsutism. Gynecological examination revealed that the ovaries were enlarged, painless, and compact, uterus had no peculiarities. Pelvic ultrasound revealed that the ovaries were 4-5 cm in diameter and had multiple enlarged follicles on periphery. X-ray of skull base showed that sellar region was dilated. What is the most probable diagnosis? Stein-Leventhal syndrome (Polycystic ovary syndrome) Algodismenorrhea Sheehan’s syndrome Premenstrual syndrome Morgagni-Stewart syndrome A woman consulted a therapeutist about fatigability, significant weight loss, weakness, loss of appetite. She has been having amenorrhea for 8 months. A year ago she delivered a full-term child. Hemorrhage during labor made up 2 She got blood and blood substitute transfusions. What is the most probable diagnosis? Sheehan’s syndrome Stein-Leventhal syndrome Shereshevsky-Turner’s syndrome Homological blood syndrome Vegetovascular dystonia A 22-year-old patient complains of 8-months-long delay of menstruation. Anamnesis: menarche since the age of 12,5. Since the age of 18 menstruations are irregular. No pregnancies. Mammary glands have normal development; when the nipples are pressed, milk drops are discharged. On gynecological examination: moderate uterus hypoplasia. On hormonal examination: prolactin level exceeds the norm two times. On computed tomogram of the sellar region: a space-occupying lesion 4 mm in diameter is detected. The most likely diagnosis is: Pituitary tumor Lactation amenorrhea Stein–Leventhal syndrome (Polycystic ovary syndrome) Sheehan’s syndrome Cushing’s disease A 30-year-old woman complains of infertility during her 10-year-long married life. Menstruations occur since she was 14 and are irregular, with delays up to a month and longer. Body mass is excessive. Hirsutism is observed. On bimanual examination: uterine body is decreased in size; ovaries are increased in size, dense, painless, and mobile. The most likely diagnosis is: Stein–Leventhal syndrome (Polycystic ovary syndrome) Follicular cyst of ovaries Genital endometriosis Genital tuberculosis Inflammatory tumor of ovaries A 39-year-old female patient complains of dyspnea when walking, palpitation, edema in the evening. The patient’s height is 164 cm, weight - 104 kg. Objectively: overnutrition. Heart sounds are weak, and tachycardia is present. The menstrual cycle is not broken. Blood sugar is 5,6 mmol/l, ACTH-response tests revealed no alterations. X-ray of the Turkish saddle revealed no pathology. What disease is it? Alimentary obesity Climax C. D. E. 529. A. * B. C. D. E. 530. A. * B. C. D. E. 531. A. * B. C. D. E. 532. A. B. C. D. * E. 533. A. B. C. D. * E. Pituitary obesity Diabetes mellitus Cushing’s syndrome (primary hypercortisizm) An 18-year-old girl complains of breast pain and engorgement, headaches, irritability, swelling of the lower extremities. These symptoms have been observed since menarche and occur 3-4 days before the regular menstruation. Gynecological examination revealed no pathology. Make a diagnosis: Premenstrual syndrome Neurasthenia Renal disease Mastopathy Cardiovascular disorder A 25-year-old female presented to a women’s welfare clinic and reported the inability to get pregnant within 3 years of regular sexual activity. Examination revealed increased body weight, male pattern of pubic hair growth, dense enlarged ovaries, monophasic basal temperature. What is the most likely diagnosis? Polycystic ovarian syndrome Adnexitis Adrenogenital syndrome Premenstrual syndrome Gonadal dysgenesis A 49-year-old female patient complains of itching, burning in the external genitals, frequent urination. The symptoms have been present for the last 7 months. The patient has irregular menstruation, once every 3-4 months. Over the last two years she has had hot flashes, sweating, sleep disturbance. Examination revealed no pathological changes of the internal reproductive organs. Complete blood count and urinalysis showed no pathological changes. Vaginal smear contained 20-25 leukocytes per HPF, mixed flora. What is the most likely diagnosis? Menopausal syndrome Cystitis Trichomonas colpitis Vulvitis E Bacterial vaginosis A 35-year old woman presents with no menses for six months. Her serum prolactin is normal. She does not have withdrawal bleeding after progesterone. She does have bleeding after a combined estrogen and progestin treatment and her serum FSH is 100. The most likely diagnosis is Outflow tract obstruction Asherman’s Syndrome Hyperprolactinemia Premature menopause Hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism A 18-year old presents with primary amenorrhea. Physical exam reveals a lack of secondary sex characteristics and the presence of a uterus. Which of the following is NOT a possible diagnosis? Sawyer’s Syndrome 17 hydroxylase deficiency Turner’s Syndrome Rokitansky Custer Hauser Syndrome Pure XY gonadal dysgenesis 534. A. * B. C. D. E. 535. A. * B. C. D. E. 536. A. B. C. D. * E. 537. A. B. * C. D. E. An 18-year-old woman complains of mammary glands swelling, headaches, tearfulness, abdominal distension occurring the day before menstruation. The symptoms disappear with the beginning of menstruation. Menstruations are regular, last for 5-6 days with interval of 28 days in between. Gynecological examination revealed no changes of internal genitals. What is your diagnosis? Premenstrual syndrome Sheehan syndrome Stein-Leventhal syndrome Asherman’s syndrome Adrenogenital syndrome A 25-year-old woman complains of menstruation retention lasting for 3 years. The patient explains it by a difficult childbirth complicated with profuse hemorrhage, weight loss, brittleness and loss of hair, loss of appetite, depression. Objective examination reveals no pathologic changes of uterus and uterine appendages. What pathogenesis is characteristic of this disorder? Decreased production of gonadotropin Hyperproduction of estrogen Hyperproduction of androgen Decreased production of progesterone Hyperproduction of prolactin A 15-year-old girl is brought to the office by her mother because of abdominal pain and constipation for the past several weeks. Her mother says, "She is getting almost all A's in school and she is on the track team." You ask the patient about her diet and she responds, "I'm kind of a picky eater." She requests a laxative to help with her constipation. She is 158 cm tall and weighs 43 kg; BMI is 18 kg/m2. Pulse is 65/min. Specific additional history should be obtained regarding which of the following? Color, caliber, and frequency of bowel movements Exposure to sexually transmitted diseases. Family history of irritable bowel syndrome. Menstrual history. Use of illicit drugs. An 18 year-old college student is seen in the emergency room, claiming she was raped by a 29 year-old janitor in her dorm 4 hours ago. He threatened her with a knife and she did not resist. She appears calm and has a flattened affect when the history is taken. Currently, she is sexually active with a fellow student and is taking birth control pills. The alleged attacker used a condom, which she helped him put on. The student is 173cm tall and weighs 82kg. She is a cheerleader for the college football team. Examination reveals no bruising and gynecologic examination reveals no apparent injuries. Which of the following statements is the most likely explanation for this patient’s presentation? The attack was not emotionally traumatic The student is in shock The attack never happened The student cooperated with the attacker The student suffers from chronic depression 538. A. B. * C. D. E. 539. A. * B. C. D. E. 540. A. * B. C. D. E. 541. A. * B. C. D. E. 542. A 32 year-old G0 woman comes to the office due to the inability to conceive for last two years. She reports having been on oral contraceptives for 8 years prior. She had menarche at age 14 and has had irregular cycles about every 3 months until she started oral contraceptives, which regulated her cycles. In the last year, she has had about 5 cycles in total; her last menstrual period was 6 weeks ago. She is otherwise in good health and has not had any surgeries. She has no history of abnormal Pap smears or sexually transmitted infections. She is 176cm and weighs 90kg. On general appearance, she seems to be hirsute on the face and the abdomen. The rest of her exam is otherwise normal. Which of the following is most likely to help identify the underlying cause of this woman’s infertility? Lutenizing hormone levels Testosterone levels Follicle stimulating hormone levels Thyroid function tests Progesterone levels A 34 year-old woman comes to you for a chief complaint of hirsutism. She states that this has been present since menarche, but has gotten worse in the past two years. Her menses have become more irregular, now every 28-45 days apart. She states that she quit smoking and gained approximately thirty pounds in the past three years. Her mother is obese, diabetic and has hirsutism. There is no hair seen on her chin, but she shaves every few days. TSH, prolactin, 17-hydroxyprogesterone and DHEAS are normal. Testosterone is mildly elevated. Which of the following is the most likely etiology of her hirsutism? Polycystic ovarian syndrome Ovarian neoplasm Diabetes Cushing’s syndrome Adrenal tumor A 52 year-old G3P3 woman presents to your office with severe hot flashes and vaginal dryness for 6 months. Her last menstrual period was 15 months ago. After discussing the risks and benefits of hormone therapy with this patient, she decides to begin treatment. This patient is most likely to stop hormone therapy secondary to what side effect? Vaginal bleeding Development of breast cancer Hirsutism Nausea Relief of menopausal symptoms A 22 year-old G0 college student returns for follow-up of mood swings and difficulty concentrating on her schoolwork the week before her menses for the past 12 months. Her past medical history is unremarkable and physical examination is normal. Which of the following would be an appropriate treatment option for this patient? Oral contraceptive pills Reassurance and observation Methylphenidate (Ritalin Gabapentin Ginkgo A 16 year-old girl comes to the doctor to discuss contraception. She recently became sexually active and states she has never had a menstrual cycle. She regularly attends school and participates in the band. On physical examination, she is 175cm and weighs 84kg. She has no secondary sexual characteristics with normal appearing external genitalia. The physician suspects Kallmann syndrome. Which of the following diagnostic tests will help confirm the diagnosis? A. B. * C. D. E. 543. A. B. * C. D. E. 544. A. B. * C. D. E. 545. A. B. * C. D. E. 546. A. B. C. D. * E. An MRI of the pituitary Olfactory challenge Measurement of testosterone levels Pelvic ultrasound Cortisol levels An 18 year-old G0 comes in for an annual exam with her mother. Her mother comments that she had severe PMS symptoms in her twenties and thirties. She would like to know if her daughter will inherit this as well. Which of the following has the strongest association with premenstrual syndrome? Obesity Positive family history Insulin dependent diabetes mellitus History of early menarche Vitamin K deficiency A 28 year-old G1P1 presents to your office. She delivered 4 days ago and tearfully reports that yesterday and the day before she had trouble sleeping, felt anxious and was irritable. She feels somewhat better today, but is still concerned. What is the most likely diagnosis? Hypothyroidism Blues Depression Normal postpartum state Anxiety A 24 year-old woman comes to her physician for help with her premenstrual syndrome symptoms. She complains of “not being herself” for 3 to 4 days before her period and has episodes of crying and irritability. She denies depressive symptoms and notes she is a stay-at-home mother for her three children. After a complete history and physical examination, the patient is prescribed a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor but, after three months, she returns as there is no change in her symptoms. Upon further discussion, the patient admits that her husband has a bad temper at times. Physical examination is normal with the exception of some bruising on the patient’s arms. She claims that she fell and that she is often clumsy. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient? Report the injuries to the police Offer domestic violence resources to the patient Refer the patient for a psychiatric consultation Arrange for a home visit by a women’s shelter counselor Arrange for security to escort her to a women’s shelter A mother brings her 16 year-old daughter to the doctor because she has not begun menses and has not kept up in growth with her friends. She performs well in school and participates in extracurricular activities. On physical examination, she is171cm tall, 78kg and has Tanner stage 1 breast and pubic hair growth. Her breast nipples are widely spaced with a shield chest and neck is thickened. No genital tract abnormalities are noted on exam. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her delayed sexual maturation? Partial deletion of the long arm of the X chromosome Mullerian agenesis Down Syndrome Turner syndrome Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser Syndrome 547. A. * B. C. D. E. 548. A. B. C. D. * E. 549. A. B. * C. D. E. 550. A. B. C. * D. E. 551. A. B. C. D. * E. A 21 year-old woman comes to the office because of acne, irregular menses and hirsutism. She initially was evaluated 6 months ago. At that time, she was diagnosed with idiopathic hirsutism. She was started on oral contraceptive pills to improve her symptoms. Menstrual periods now occur every month, but her hirsutism has not significantly improved. In addition to the oral contraceptives, which of the following would be an appropriate treatment for hirsutism? Spironolactone Lupron Danazol Depo-Provera Steroids Postmenopausal woman should be routinely screened after age 65 for which of the following: Cirrhosis Ovarian cancer Small cell carcinoma Osteoporosis Dementia A 56 year-old woman presents with complains of insomnia, vaginal dryness and amenorrhea for 13 months. What is the most likely diagnose? Sheehan syndrome Menopause Hypothyroidism Hypethyroidism Ovarian cancer A 90-year-old G7P7 woman presents with severe vaginal prolapse. The entire apex, anterior and posterior wall are prolapsed beyond the introitus. She cannot urinate without reduction of the prolapse. Hydronephrosis was noted on ultrasound of the kidneys and it is thought to be related to the prolapse. She has a long-standing history of diabetes and cardiac disease. She is not a candidate for general or regional anesthesia. She has failed a trial of pessaries. Which of the following is the next best step in the management of this patient? Do nothing and observe. Anterior and posterior repair Colpocleisis Sacrospinous fixation Sacrocolpopexy A 48-year-old G0 woman comes to the office for a health maintenance exam. She is healthy and not taking any medications. She has no history of abnormal Pap smears or sexually transmitted diseases. She is not currently sexually active. Her menstrual cycles are normal and her last cycle was three weeks ago. She smokes one pack of cigarettes per day. Her mother was diagnosed with endometriosis and had a hysterectomy and removal of the ovaries at age 38. She is 5 feet 4 inches tall and weighs 130 pounds. On pelvic examination, the patient had a palpable left adnexal mass. An ultrasound was obtained, which showed a 4 cm complex left ovarian cyst and a 2 cm simple cyst on the right ovary. What is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient? CAT scan of the abdomen and pelvis MRI of the pelvis Abdominal hysterectomy and bilateral salpingoophorectomy (TAH/BSO) Repeat ultrasound in 2 months Oral contraceptives 552. A. B. C. * D. E. 553. A. B. C. D. E. * 554. A. B. C. D. E. 555. A. B. C. D. E. * 556. A. B. C. A 45 year-old G5P5 premenopausal woman was initially seen in your office for work-up and evaluation of a FIGO grade 2 endometrial cancer that was diagnosed by her gynecologist. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for this patient? Total laparoscopic hysterectomy with bilateral salpingoophorectomy Vaginal hysterectomy with bilateral salpingoophorectomy Total abdominal hysterectomy, bilateral salpingoophorectomy, bilateral pelvic and paraaorticlymphadenectomy, pelvic washings Supracervical abdominal hysterectomy with ovarianpreservation Megace (megestrol acetate) A 31 year-old G0 woman has been diagnosed with uterine fibroids. A fluid contrast ultrasound confirmed the presence of two intramural fibroids measuring 5 x 6 cm and 2 x 3 cm that appear to be distorting the patient’s uterine cavity. The patient has a two-year history of infertility. She has had a thorough infertility work up. No etiology for her infertility has been identified. Which of the following treatments is most appropriate for this patient? Hysteroscopy Uterine curettage Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist Uterine artery embolization Myomectomy A 72 year-old G3P2 postmenopausal woman is referred to your office by her internist after a work-up for abdominal bloating revealed a large pelvic mass on transvaginal ultrasound and an elevated CA-125. She has no significant medical history and only a prior appendectomy. The CT scan showed a large heterogenous pelvic mass measuring 20 x 13 x 10 cm. There was a moderate amount of ascites and likely “omental caking.” There was no significant pelvic or abdominal lymphadenopathy, and the chest x-ray showed only a small right pleural effusion. On pelvic examination, there is minimal cul-de-sac nodularity and the mass is readily palpable and somewhat mobile. There is an obvious fluid wave. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient? Thoracentesis Exploratory laparotomy and tumor debulking (cytoreduction) Paracentesis Diagnostic laparoscopy and tissue biopsies Neoadjuvant chemotherapy Which of the following is the risk factor for vesicovaginal fistula? Child birth trauma Prolonged labour Pelvic irradiation Pelvic surgery All of them A previously healthy 27-year-old nulligravid woman comes to the emergency department because of a 2-day history of moderate-to-severe pain and swelling of the left labia. She is sexually active and uses condoms inconsistently. Her temperature is 37.2°C (99°F), pulse is 92/min, respirations are 18/min, and blood pressure is 115/75 mm Hg. Pelvic examination shows a 4 x 3-cm, tender, fluctuant mass medial to the left labium majus compromising the introital opening. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management? Vulvectomy Ultrasound-guided needle aspiration of the mass Administration of intravenous penicillin G D. E. 557. A. * B. C. D. E. 558. Administration of intravenous metronidazole Incision and drainage 26 years old patient has formed formation of purulent inflammation of the appendages of the uterus. What would you recommend? puncture through the posterior vaginal vault, draining pus cavity and the introduction of antibiotics into it surgery pirogenal therapy electrophoresis of zinc Nothing above Woman I., aged 38 years was admitted to gynecologic department with complaints on cramp-like pains in the lower abdomen and moderate blood-tinged discharge from vagina. In past-history: labor 1, medical abortions – 2. Patient notes delay of menstruation, instantaneous loss of consciousness. Objectively: skin integuments are pale, covered with cold perspiration. Arterial pressure – 90/50 mm Hg., pulse rate – 120 beats/min. On vaginal examination: somewhat enlarged uterine, in the right – movable formation of ovoid form, soft consistency is palpable. What treatment should be carried out? A. * B. C. D. Surgical intervention. Treatment with estrogens. Treatment with androgens. Symptomatic treatment. E. 559. Treatment with gestagens. Patient, aged 32 years was admitted to gynecologic department with complaints on sharp pain in the lower abdomen. Menses were 2 weeks ago, timely. On bimanual vaginal examination: vagina and uterine cervix are without peculiarities. Examination of the uterine body and appendages is impossible to perform due to tenderness and tension of the anterior abdominal wall. Posterior fornix overhangs, painful. Apoplexy of the ovary is suspected. What should be done to precise diagnosis? To perform bimanual examination again under narcosis. Paracentesis of the abdominal cavity through posterior fornix of vagina. Ultrasonic investigation. Symptomatic treatment Hysteroscopic examination. Patient, aged 23 years was admitted to the gynecologic unit complaining of pain in the lower abdomen, general weakness, collaptoid state, blood-tinged discharge from the reproductive passages. In the past history: patient had chronic adnexitis; last 2 months – no menstruation, sometimes bloody discharge was noted. Objectively: skin and mucous membranes are pale. Arterial pressure – 90/60, pulse rate – 100 beats/min. Abdomen is swelled a little, painful in the lower portions. Shchyotkin’s symptom is positive. Vaginal examination: uterine is enlarged up to 5-6 weeks, soft, painful one on palpation. Appendages are not palpable clearly due to a sharp tension of the anterior abdominal wall. Posterior fornix hangs over, painful one. Dark blood-tinged discharge continues. What method of investigation is the most informative? Hysteroscopy. Laparoscopy. Ultrasonic investigation. Abdominal paracentesis. Dopplerometry. A. B. * C. D. E. 560. A. B. C. D. * E. 561. A. * B. C. D. E. 562. A. B. C. * D. E. 563. A. * B. C. D. E. 564. A. * B. C. D. E. 565. A. B. * C. D. E. A 30-year-old woman complains of irregular copious painful menstruations, pain irradiates to the rectum. Anamnesis states 10- year-long infertility. On bimanual examination: uterus is of normal size; uterine appendages on the both sides are corded, with rectricted mobility, painful; there are dense nodular painful growths detected in the posterior fornix. A doctor suspects endometriosis. What method allows to verify this diagnosis? Laparoscopy Diagnostic curettage of uterine cavity Paracentesis of posterior fornix Uterine probing Hysteroscopy Which treatment is followed by a 48 years patient with severe cervical dysplasia and ovarian cyst: diatermokonization of cervix diathermocoagulation of cervix hysterectomy with appendages treatment by solkovagin hysterectomy without appendages Patient 22 years. Complains about pain in a right labia pudenda majora, rise of body temperature to 38.0°C. At the review of genital organs the considerable increasing of right large sexual lip definites, especially in the lower third. Erythema, edema, at palpation acutely painful, fluctuation is determined. To conduct vaginal examination due to acute pain is impossible. Blood test: Leucocytes — 10,0 x 109 per cu mm. What method is main? The dissection and drainage of abscess. To withdraw a bartolin gland within the limits of healthy tissue. To appoint physical therapy procedures. To appoint compresses with liniment. To expect a spontaneous regeneration of abscess. 26 years old patient has formed formation of purulent inflammation of the appendages of the uterus. What would you recommend? puncture through the posterior vaginal vault, draining pus cavity and the introduction of antibiotics antibiotics into it surgery pirogenal therapy electrophoresis of zinc A 16-year-old female comes to the physician because of an increased vaginal discharge. She developed this symptom 2 days ago. She also complains of dysuria. She is sexually active with one partner and uses condoms intermittently. Examination reveals some erythema of the cervix but is otherwise unremarkable. A urine culture is sent which comes back negative. Sexually transmitted disease testing is performed and the patient is found to have gonorrhea. While treating this patient's gonorrhea infection, treatment must also be given for which of the following? Bacterial vaginosis Chlamydia Herpes Syphilis Trichomoniasis 566. A. B. C. D. * E. 567. A. B. C. * D. E. 568. A. * B. C. D. E. 569. A. * B. C. D. E. A 23 year-old G0 reports having a solitary, painful vulvar lesion that has been present for three days. This lesion has occurred twice in the past. She states that herpes culture was done by her doctor during her last outbreak and was negative. She is getting frustrated in that she does not know her diagnosis. She has no significant previous medical history. She uses oral contraceptives and condoms. She has had four sexual partners in her lifetime. On physical examination, a cluster of three irregular erosions with a superficial crust is noted on the posterior fornix. Urine pregnancy test is negative. You suspect recurrent genital herpes. How do you explain the negative culture? Cultures were taken too early The more definitive test would be serum herpes antibody testing The cultures were refrigerated prior to transport to the lab Herpes cultures have a 10-20% false negative rate The herpes virus cannot be recovered with recurrent infections A 22 year-old P0 presents with a one-month history of profuse vaginal discharge with mild odor. She has a new sexual partner with whom she has had unprotected intercourse. She reports mild to moderate irritation, pruritus and pain. She thought she had a yeast infection, but had no improvement after using an over-the counter antifungal cream. She is concerned about sexually transmitted infections. Her medical history is significant for lupus and chronic steroid use. Pelvic examination shows normal external genitalia, an erythematous vagina with a copious, frothy yellow discharge and multiple petechial on the cervix. Vaginal pH is 7. Saline wet mount reveals motile, flagellated organisms and multiple white blood cells. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for this patient? Clindamycin Azithromycin Metronidazole Ampicillin Doxycycline A 26 year-old G2P2 reports that she is sexually active with a new male partner. She is using oral contraception for birth control and, as such, did not use a condom. She reports the new onset of vulvar burning and irritation. She thought she had a cold about 10 days ago. Given her history, which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient? Herpes simplex virus Primary syphilis Secondary syphilis Human immunodeficiency virus Trichomonas A 39 year-old G0 presents to the clinic reporting non-tender spots on her vulva for about a week. No pruritus or pain is present. She also notes a brownish rash on the palms of her hands. She admits to IV drug abuse. She was diagnosed as HIV-positive two years ago, but has not been compliant with suggested treatment. On examination, three elevated plaques with rolled edges are noted on the vulva. They are non-tender. A brown macular rash is noted on the palms of her hands and the soles of her feet. What is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient? Obtain a treponemal-specific test Biopsy of the lesion Colposcopic evaluation of the vulvar lesions Culture the base of the lesion Perform a wet prep 570. A. * B. C. D. E. 571. A. * B. C. D. E. 572. A. B. C. * D. E. 573. A. B. C. D. * E. 574. A. * B. C. D. E. 575. A. B. C. A 20 year old woman presents with a 2-day history of dysuria and increased urinary frequency, she is recently married and was not sexually active prior to the marriage, gynecologic exam reveals no evidence of discharge, vaginitis or cervicitis, urinalysis reveals 14 white blood cells per high-powered field with many gram-negative rods, which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy? Trimethropim-Sulfamethoxazole Ceftriaxone Fluconazole Gentamicin Metronidazole Woman with large, deep ulcers on genital with gray/yellow exudate, the ulcers are well-demarcated borders and soft, the patient also has severe lymphadenopathy, which of the following could be the case? Haemophilus (chancroid) HSV-vesicles Lymphogranuloma venerum HPV (wart) None of them A 37 years old woman has been examined and a fishy-odor discharge is noted, itching/ burning and inflamed vagina not to see, what is the diagnosis? Candida vaginitis Cancer Bacterial vaginosis Cervicitis HPV The chief complaint interview on a client reveals vaginal discharge with itching and burning. The client also reveals she experiences dyspareunia. If her diagnosis is monilial vulvovaginitis, you would expect the wet mount slide to contain which of the following? Bacteria Clue cells Trichomonads Budding hyphae All of the above A 20.y.old woman is diagnosed with trichomonas and prescribed an antibiotic. She calls her physician complaining of the flushing, nausea, and emesis. What antibiotic was the patient prescribed and what should she have been warned of? Metronidazole - alcohol Metronidazole - sunlight Metronidazole – smoking Azithromycin – spicy food Azithromycin – oral contraceptive The patient complains of feeling of itching, pain in the vagina, large selection of white disharge. On examination: vaginal mucosa edematous flushed, in the lateral fornices - the accumulation of white layers, similar to the chees. What is the previous diagnosis? Trichomonas colpitis chlamydial colpitis urogenital mycoplasmosis D. E. * 576. A. * B. C. D. E. 577. A. * B. C. D. E. 578. A. B. C. D. * E. 579. A. * B. C. D. E. 580. A. * B. C. D. E. 581. A. B. C. * D. E. bacterial vaginosis candidiasis vaginitis The patient D, 22 years old was diagnosed Trichomonas colpitis. Select a product for the treatment of this patient tinidozol ciprofloxacin ampicillin Biseptol Diflucan When performing a clinical breast examination on a client, a physician palpates a thickened area where the skin folds under the breast. What is the physician’s best action? Proceed with the examination. Determine if the thickness is bilateral. Ask the client how long the thickness has been present. Attempt to elicit the same response with the client in a different position. Schedule for MRI The client who has discovered a lump in one breast is very upset when calling to schedule a mammogram. What is the physician’s best response? “It is a good thing you called. All lumps are considered cancerous until proven otherwise.” “Unless you have a relative with breast cancer, this lump is most likely benign.” “Diagnosing cancer at this early stage is most likely to result in a cure.” “Many women have breast lumps, and 90% of the lumps are benign.” “Routine mammogram allows you rule out cancer” During the visit for a school physical, the 13-year old girl being examines questions the asymmetry of her breasts. The best response is One breast may grow faster than the other during development I will give you a referral for a mammogram You will probably have fibrocystic disease when you are older This may be an indication of hormonal imbalance. We will check again in 6 month It is first symptom of cancer This is the first visit for a woman, age 38. The physician instructs her that a baseline mammogram is recommended for woman between the age of 35 and 39 and that the clinical exam schedule would be based on age. The recommendation for women 40 to 49 is: every year every 2 years twice a year only the baseline exam is needed unless the woman has symptoms woman of this age have no any need in mammogram examination The client is 45 years old and has just been diagnosed with fibrocystic breast disease. She asks what this means in terms of her health. What is the physician’s best response? “This problem greatly increases your risk for breast cancer, so be sure to schedule yearly mammograms.” “This problem progressively increases as you age, especially if you have never been pregnant.” “This problem will probably diminish with menopause if you don't take replacement hormones.” “This problem is genetic and you should teach your daughters about it.” “This first symptom od cancer” 582. A. * B. C. D. E. 583. A. B. C. D. * E. 584. A. B. C. * D. E. 585. A. B. C. D. * E. 586. A. B. C. * D. E. 587. A. B. C. * D. E. The client who has just been diagnosed with invasive infiltrating ductal carcinoma asks what this means. What is the physician’s best response? “The cancer has spread from the breast ducts into surrounding breast tissue.” “The cancer has spread from the breast into local lymph nodes and channels.” “The cancer has spread from the breast into surrounding tissues and organs.” “The cancer has spread from the breast into distant tissues and organs.” “The cancer has spread from the breast into the ducts from surrounding breast tissue Which comment made by the client with breast cancer indicates correct understanding regarding cancer causes and prevention? “I will cure my cancer by eating a low-fat diet from now on.” “If I had breast-fed my children, this would not have happened to me.” “I hope this doesn't increase my risk for bone cancer or lung cancer.” “I will have regular mammograms on my other breast to detect cancer early.” “Regular physical exercise is good method of prevention of cancer in future” The client frequently finds lumps in her breasts, especially around her period. Which info should the physician teach the client about breast self care? This is a benign process that does not need follow up. Eliminate chocolate and caffeine from diet. Practice breast self exam monthly. This is how breast cancer starts and she needs surgery. Do additional physical exercise to decrease size of lump The physician is teaching a class on breast health to a group of ladies at the senior center. Which is the most important risk factor to emphasize to this group? Find out about family history of Breast Cancer Men at this age can get breast cancer and should also be screened Monthly self-exam is the key to early detection. The older a woman gets, the greater the chance of developing Breast Cancer. Men and women have same chance to have Breast Cancer if they are married While the physician is obtaining a nursing history from a 52-year-old patient who has found a small lump in her breast, which question is most pertinent? "Do you currently smoke cigarettes?" "Have you ever had any breast injuries?" "Is there any family history of fibrocystic breast changes?" "At what age did you start having menstrual periods?" “Do you know somebody who have breast cancer A 62-year-old patient complains to the physician that mammograms are painful and a source of radiation exposure. She says she does breast self-examination (BSE) monthly and asks whether it is necessary to have an annual mammogram. The physician's best response to the patient is: "If your mammogram was painful, it is especially important that you have it done annually." "An ultrasound examination of the breasts, which is not painful or a source of radiation, can be substituted for a mammogram." "Because of your age, it is even more important for you to have annual mammograms." "Unless you find a lump while examining your breasts, a mammogram every 2 years is recommended after age 60." "If you will have two normal result of mammogram you can stop to do this procedure" 588. A. B. * C. D. E. 589. A. B. C. * D. E. 590. A. B. * C. D. E. 591. A. B. * C. D. E. 592. A. B. * C. D. E. 593. A patient with a small breast lump is advised to have a fine needle aspiration biopsy. The physician explains that an advantage to this procedure is that only a small incision is necessary, resulting in minimal breast pain and scarring. if the specimen is positive for malignancy, the patient can be told at the visit. if the specimen is negative for malignancy, the patient's fears of cancer can be put to rest. fine needle aspiration is guided by a mammogram, ensuring that cells are taken from the lesion. after this procedure there are no any risk for septic complication A 33-year-old patient tells the physician that she has fibrocystic breasts but reducing her sodium and caffeine intake and other measures have not made a difference in the fibrocystic condition. An appropriate patient outcome for the patient is calls the mammologist if any lumps are painful or tender. states the reason for immediate biopsy of new lumps. monitors changes in size and tenderness of all lumps in relation to her menstrual cycle. has genetic testing for BRCA-1 and BRCA-2 to determine her risk for breast cancer. increases your physical activity A 20-year-old student comes to the student health center after discovering a small painless lump in her right breast. She is worried that she might have cancer because her mother had cervical cancer. The physician's response to the patient is based on the knowledge that the most likely cause of the breast lump is fibrocystic complex. fibroadenoma. breast abscess. adenocarcinoma. Lactostasis A 51-year-old woman at menopause is considering the use of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) but is concerned about the risk of breast cancer. When discussing this issue with the patient, the physician explains that HRT does not appear to increase the risk for breast cancer unless there are other risk factors. She and her health care provider must weigh the benefits of HRT against the possible risks of breast cancer. HRT is a safe therapy for menopausal symptoms if there is no family history of BRCA genes. Alternative therapies with herbs and natural drugs are as effective as estrogen in relieving the symptoms of menopause. Additional physical exercises are as effective as estrogen in relieving the symptoms of menopause At a routine health examination, a woman whose mother had breast cancer asks the physician about the genetic basis of breast cancer and the genes involved. The physician explains that her risk of inheriting BRCA gene mutations is small unless her mother had both ovarian and breast cancer. changes in BRCA genes that normally suppress cancer growth can be passed to offspring, increasing the risk for breast cancer. because her mother had breast cancer, she has inherited a 50% to 85% chance of developing breast cancer from mutated genes. genetic mutations increase cancer risk only in combination with other risk factors such as obesity. Avoiding caffeine and fatty food allows to decrease risk of breast cancer related to inheriting BRCA gene mutations When assessing a patient for breast cancer risk, the physician considers that the patient has a significant family history of breast cancer if she has a A. B. * C. D. E. 594. A. B. * C. D. E. 595. A. B. C. * D. E. 596. A. B. * C. D. E. 597. A. * B. C. D. E. 598. A. B. C. D. * E. 599. A. * B. C. cousin who was diagnosed with breast cancer at age 38. mother who was diagnosed with breast cancer at age 42. sister who died from ovarian cancer at age 56. grandmother who died from breast cancer at age 72. daughter who was diagnosed lung cancer at age 16 A 32-week-pregnant client is upset and thinks she has breast disease because she has a yellowish discharge coming from her breasts. What can the physician say or do for this client? Refer the client for a mammogram This is normal toward the end of pregnancy and is called colostrum. Notify the mammologist Ask history questions about previous breast infections. Refer the client for a sonography The physician notes the presence of gynecomastia in a 15-year-old client. The physician knows: This is an abnormal finding for a client at this age. This condition is abnormal if it is of recent onset. This is a temporary condition in puberty. The client may be at increased risk for the development of breast cancer. This is a normal finding for a client at this age. The physician is planning a focused breast/axillae interview and wants to include a general health question. Which of the following questions would fit these criteria? "Has your mother or sister had breast cancer?" "Are you still menstruating?" "Have you ever had a mammogram?" "Have you had any breast trauma? "When was your last visit to gynecologist?" A 14-year-old female client is upset because her breast development is not equal. What can the physician say to this client? "It is normal for breast tissue development to be unequal during puberty. It will even out as you get older." "Don't worry; most girls have breasts that are slightly unequal in size." "Did your mother experience the same thing when she was your age?" "Your breasts appear equal in size." "You should do sonography to rule out breast cancer" A 65-year-old female client wants to know if she still should continue to perform self breast assessments. The most appropriate response by the physician is: "Women can stop breast self exams after menopause." "Self exam is not necessary if you get yearly mammograms." "After age 60, it is not really necessary." "Breast cancer can still develop when you get older." "In your age self breast assessments should be performed 2 times per month" When gathering breast history information on a client, the client states that she has noticed a few drops of clear discharge from her nipples over the past few months. Which of the following actions is most appropriate in this situation? Ask additional history questions about the discharge and medications she is currently taking. Refer the client for a mammogram. Notify the mammologist. D. E. 600. A. B. * C. D. E. 601. A. B. * C. D. E. 602. A. B. * C. D. E. 603. A. B. C. * D. E. 604. A. B. C. * D. E. 605. A. B. * C. D. E. Document the presence of the discharge. Refer the client for a sonography. A 20-year-old client with benign breast disease says she has increased breast pain and tenderness with menses. What should the physician do in this situation? Discuss the relationship of benign breast disease to breast cancer. Discuss how reducing caffeine and salt intake and wearing a support bra might help. Explain that a breast biopsy may be indicated. Tell the client that this condition will soon go away Explain that the additional physical exercises can reduce this pain The physician is performing a breast examination. Which of the following reflect abnormal findings during the inspection phase of breast examination? A woman whose left breast is slightly larger than her right A woman whose nipples are pointing in different directions A woman whose skin is marked with linear striae A pregnant woman whose breasts have a fine blue network of veins visible under the skin A woman who wear bra size 3 A client asks the physician, "Why do I need to examine my underarms when I perform my breast exam?" Which of the following is the most appropriate response for the physician to make to this client? This is the least likely area for breast cancer to occur. Breast tissue extends into the axilla. This is the hardest area to feel for changes. It is easier to detect abnormalities in this area than in the breast tissue. There are no any another need to examine this area Physician is teaching a client who suspects that she has a lump in her breast. The physician instructs the client that a diagnosis of breast cancer is confirmed by: breast self-examination. mammography. fine needle aspiration. chest X-ray. sonography Physician is teaching a group of women to perform breast self-examination. The physician should explain that the purpose of performing the examination is to discover: cancerous lumps. areas of thickness or fullness. changes from previous self-examinations. fibrocystic masses. mastitis Physician is speaking to a group of women about early detection of breast cancer. The average age of the women in the group is 47. Following the American Cancer Society guidelines, the physician should recommend that the women: perform breast self-examination annually. have a mammogram annually. have a hormonal receptor assay annually. have a physician conduct a clinical examination every 2 years. visit to gynecologist annually 606. A. Physician is providing breast cancer education at a community facility. The American Cancer Society recommends that women get mammograms: yearly after age 40. after the birth of the first child and every 2 years thereafter. after the first menstrual period and annually thereafter. every 3 years between ages 20 and 40 and annually thereafter. in menopause A 34-year-old female client is requesting information about mammograms and breast cancer. She isn’t considered at high risk for breast cancer. What should the physician tell this client? She should have had a baseline mammogram before age 30. She should eat a low-fat diet to further decrease her risk of breast cancer. She should perform breast self-examination during the first 5 days of each menstrual cycle. When she begins having yearly mammograms, breast self-examinations will no longer be necessary. She should do additional physical exercise Nina, an oncology educator, is speaking to a women’s group about breast cancer. Questions and comments from the audience reveal a misunderstanding of some aspects of the disease. Various members of the audience have made all of the following statements. Which one is accurate? Mammography is the most reliable method for detecting breast cancer. Breast cancer is the leading killer of women of childbearing age. Breast cancer requires a mastectomy. Men can develop breast cancer. Breast self examination is the first step in an early detection of Brest cancer Physician is instructing a premenopausal woman about breast self-examination. The physician should tell the client to do her self-examination: at the end of her menstrual cycle. at the same day each month. at the 1st day of the menstrual cycle. immediately after her menstrual period. Any time when remind Gio, a community health physician, is instructing a group of female clients about breast self-examination. The physician instructs the client to perform the examination: At the onset of menstruation Every month during ovulation Weekly at the same time of day 1 week after menstruation begins Any time during the cycle A 70 year old woman has a palpable lesion on clinical breast examination done during a physical examination. The hard, painless left breast mass measures approximately 5 cm. The patient has no palpable abnormalities of the contralateral breast or either axilla, and has no additional symptoms (such as bone pain or weight loss). It has been just over a year since the patient had a screening mammogram. Of the following options, which is the best first step in further evaluation of this patient’s breast lesion? no further work-up is required B. C. * D. E. CT of the breast diagnostic mammography MR imaging of both breasts Sonography of both breasts A. * B. C. D. E. 607. A. B. * C. D. E. 608. A. B. C. D. * E. 609. A. B. C. D. * E. 610. A. B. C. D. * E. 611. 612. A. * B. C. D. E. 613. A. B. C. D. * E. 614. A. B. C. D. * E. 615. A. * B. C. D. E. 616. A. B. C. D. * E. GK is a 46-year-old woman who presents to your office for a well-woman examination. She informs you that her 51-year-old friend was diagnosed with breast cancer one month ago and that she is worried about getting breast cancer. On further inquiry, you learn that she delivered her only child when she was 32 years of age and has no family history for breast cancer. She does not perform breast self-examinations and has never had a mammogram. GK asks for your advice on breast cancer screening. Which one of the following options is best for this patient? Discuss the harms and benefits of screening, and offer screening because she is older than age 40. Do not offer screening because she is younger than age 50. Offer screening to obtain a baseline examination, and begin routine screening at age 50. Discuss the harms and benefits of screening, and offer screening because she is older than age 40; continue screening every one to two years until age 70. Screening is not indicated because she is at low risk for developing breast cancer. GK is a 46-year-old woman who presents to your office for a well-woman examination. She informs you that her 51-year-old friend was diagnosed with breast cancer one month ago and that she is worried about getting breast cancer. On further inquiry, you learn that she delivered her only child when she was 32 years of age and has no family history for breast cancer. She does not perform breast self-examinations and has never had a mammogram. GK asks for your advice on breast cancer screening. Which one of the following strategies is best to screen for breast cancer? Monthly breast self-examinations combined with an annual clinical breast examination. Monthly breast self-examinations and mammography every one to two years. Clinical breast examination every one to two years. Mammography with or without clinical breast examination every one to two years. Routine breast self-examinations and mammography with or without clinical breast examinations every one to two years. A dilatation and curettage (D&C) is scheduled for a primigravid client admitted to the hospital at 10 weeks' gestation with abdominal cramping, bright red vaginal spotting, and passage of some of the products of conception. What is the most appropriate diagnosis? recurrent abortion threatened abortion septic abortion incomplete abortion complete abortion Patient S., labor first, at term. Uterine contractions on 45-50 sec, every 2-3 min. Fetal heart rate is rhythmic, 144 bpm, a head is in the pelvic inlet. Vaginally: cervix is effaced, opening 7 cm, amniotic membrane is absent. What is the stage of labor? First. Second. Preliminary. Finishing. Third. A primigravid client admitted to the hospital at 10 weeks' gestation with abdominal cramping, bright red vaginal spotting, and passage of some of the products of conception. What is the most appropriate tactic in this situation? Hemostatic drugs Blood transfusion Spasmolytic A dilatation and curettage (D&C) Bed rest and Vitamin supplements 617. A. A 22-year-old Gravida 2, Para 2 client who has disseminated intravascular coagulation after delivering a dead fetus. Which of the following laboratory or assessment findings are the highest priority to report? Activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) of 30 seconds. Hemoglobin of 11.5g/dl. Urinary output of 25 ml in the past hour Platelets at 149,000/mm. Hematocrite 0,37 A 24-year old client, G 3, P 1, at 32 weeks' gestation, is admitted to the hospital because of vaginal bleeding. After reviewing the client's history, which of the following factors might lead the physician to suspect placentae abruptio? Several hypotensive episodes. Previous low transverse cesarean delivery. One induced abortion. History of cocaine use. Chronic hypertension On arrival at the emergency department, a client tells that she suspects that she may be pregnant but has been having a small amount of bleeding and has severe pain in the lower abdomen. The client's blood pressure is 70/50 mm Hg and her pulse rate is 120 bpm. which of the following is suspected? Ectopic pregnancy. placentae abruptio. Gestational trophoblastic disease. Complete abortion. Hydatiform mole A multigravid client seen in the emergency department complaining of sharp abdominal pain and vaginal spotting is diagnosed with an ectopic pregnancy. What is the most common site of implantation of fertilized egg outside the uterus? Fallopian tube. Intestine. Interstitial lining. Ovary. Uterine cervix Pregnant 24 years, the first pregnancy, I labor. Regular uterine contractions. At vaginal examination: the cervical opening is 4 cm, an amniotic sac is whole, the fetal head is fixed in the pelvic inlet. Sagittal suture is in a transversal size, the small fontanel is in the center of pelvis to the left. What is the moment of the labor biomechanism? The V moment of the labor biomechanism The ІІ moment of the labor biomechanism The ІІІ moment of the labor biomechanism The IV moment of the labor biomechanism I moment of the labor biomechanism A multigravid client at 8 weeks' gestation is admitted with a diagnosis of probable ectopic pregnancy. Before surgery to remove an ectopic pregnancy and the fallopian tube, which of the following would alert to the possibility of tubal rupture? Amount of vaginal bleeding and discharge. B. C. * Falling hematocrit and hemoglobin levels. Slow, bounding pulse rate of 80 bpm. A. B. C. * D. E. 618. A. B. C. D. * E. 619. A. * B. C. D. E. 620. A. * B. C. D. E. 621. A. B. C. D. E. * 622. D. E. 623. A. B. C. * D. E. 624. A. B. C. * D. E. 625. A. B. C. * D. E. 626. A. B. C. * D. E. 627. A. B. C. D. * E. 628. A. Marked abdominal edema. Uterine cramping The first delivery, II period. The fetal lie is longitudinal. The head presents, that it can't be determinate by external maneuvers. In internal examination: the uterine cervix is effaced, dilatation is full, membranes are absent. The sagittal suture is in a direct size, small fontanel is under the pubis. In the pushing the fetal head appears from a vulva. What area of pelvis a fetal head occupies? Pelvic inlet That is pressed to pelvic inlet plane The area of pelvic outlet The area of wide part of a cavity of a small pelvis The area of narrow part of a cavity of a small pelvis A multigravid client diagnosed with a probable ruptured ectopic pregnancy is scheduled for emergency surgery. In addition to monitoring the client's blood pressure before surgery, which of the following would the nurse assess? Uterine cramping. Abdominal distention. Hemoglobin and hematocrit. Pulse rate. Vaginal discharge A 36-year-old multigravid client is admitted to the hospital with possible ruptured ectopic pregnancy. When obtaining the client's history, which of the following would the most important to identify as a predisposing factor? Urinary tract infection. Marijuana use during pregnancy. Episodes of pelvic inflammatory disease. Use of estrogen-progestin contraceptives. Constipation A multigravid client is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy. The nurse antidotes that, because the client's fallopian tube has not yet ruptured, which of the following may be ordered? Progestin contraceptives Medroxyprogesterone (Depo-Provera). Methotrexate. Betamethasone Oxytocin A pregnant client at 15 weeks' gestation is admitted with dark brown vaginal bleeding and continuous nausea and vomiting. Her blood pressure is 142/98 mm Hg and fundal height is 19 cm. Based on these findings, the client is most likely suffering from which obstetrical problem? Preeclampsia. Ectopic pregnancy. Hyperemesis gravidarum. Hydatidiform mole. Multiple pregnancy A 38-year-old client at about 14 weeks' gestation is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of complete hydatidiform mole. Which of the following signs and symptoms would the physician assesses for? Pregnancy-induced hypertension. B. C. D. * E. 629. A. B. * C. D. E. 630. A. B. * C. D. E. 631. A. B. * C. D. E. 632. A. B. * C. D. E. 633. A. * B. C. D. E. 634. Gestational diabetes. Hypothyroidism. Polycythemia. Thrombophilia After a dilatation and curettage (D&C) to evacuate a molar pregnancy, assessing the client for signs and symptoms of which of the following would be most important? Urinary tract infection. Hemorrhage. Abdominal distention. Chorioamnionitis. Vaginal infection When preparing a multigravid client who has undergone evacuation of a hydatidiform mole for discharge, the physician explains the need for follow-up care because this the client is at risk for developing which of the following? Ectopic pregnancy. Choriocarcinoma. Multifetal pregnancies. Infertility. Septic abortion Patient S., labor first, at term. Uterine contractions on 45-50 sec, after 2-3 min.. Fetal heart rate is rhythmic, 144 in 1 min, a head is in the pelvic inlet. Vaginally: cervix is effaced, dilating is full, amniotic membrane is absent. What is period of labor? First. Second. Preliminary. Finishing. Third. After suction and evacuation of a complete hydatidiform mole, the 28-year-old multigravid client asks the nurse when she can become pregnant again. The nurse would advise the client not to become pregnant again for at least which of the following time spans? 6 months. 12 months. 18 months. 24 months. 30 months Upon assessment the physician found the following: fundus at 2 fingerbreadths above the umbilicus, last menstrual period (LMP) 4 months ago, fetal heart beat (FHB) not appreciated. Which of the following is the most possible diagnosis of this condition? Hydatidiform mole Missed abortion Pelvic inflammatory disease Ectopic pregnancy Multifetal pregnancy A woman presents to the emergency department complaining of bleeding and cramping. Initial history is significant for a last menstrual period 6 weeks ago. On sterile speculum examination, the physician finds that the cervix is closed. The anticipated plan of care for this woman would be based on a probable diagnosis of which type of spontaneous abortion? A. B. C. * D. E. 635. A. B. C. * D. E. 636. A. B. * C. D. E. 637. A. B. C. D. * E. 638. A. B. C. * D. E. 639. A. B. C. D. * E. 640. A. * B. C. D. Incomplete Inevitable Threatened Septic Recurrent A woman arrives for evaluation of her symptoms, which include: a missed period, adnexal fullness, tenderness, and dark red vaginal bleeding. Upon examination, the physician notices an ecchymotic blueness around the woman’s umbilicus. The physician recognizes this assessment finding as: Normal integumentary changes associated with pregnancy Turner sign associated with appendicitis Cullen’s sign associated with a ruptured ectopic pregnancy Chadwick sign associated with early pregnancy Ortner's sign associated with cholecystitis A woman who is 9 weeks pregnant is experiencing heavy bleeding and cramping. She reports passing some tissue. Cervical dilation is noted on examination. This woman most likely had: An inevitable abortion An incomplete abortion A complete abortion A missed abortion A recurrent abortion A woman who is 8 weeks pregnant becomes concerned when she has light vaginal bleeding accompanied by abdominal pain. An ectopic pregnancy is confirmed by ultrasound. The statement that indicates that the woman understands the explanation of an ectopic pregnancy is: The chorionic villi develop vesicles within the uterus. The placenta develops in the lower part of the uterus. The fetus dies in the uterus during the first half of the pregnancy. The embryo is implanted in the fallopian tube. The cervical os is not closed well. The 28-year-old primigravid client admitted to the hospital because she thinks that she is pregnant. Which of the following findings on a prenatal visit at 10 weeks might suggest a hydatidiform mole? Complaint of frequent mild nausea Blood pressure of 120/80 Fundal height measurement of 18 cm History of bright red spotting for 1 day weeks ago Low abdominal cramping A 32-year-old primigravida is admitted with a diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy. Management is based on the knowledge that: bed rest and analgesics are the recommended treatment. she will be unable to conceive in the future. a D&C will be performed to remove the products of conception. hemorrhage is the major concern. urinary tract infection is the main predisposing factor for development of this problem A primigravida at 10 weeks' gestation reports mild uterine cramping and slight without passage of tissue. When she is examined, no cervical dilation is noted. The physician would: Sent the woman home and placed on bed rest with instructions to avoid stress or orgasm Prepare the woman for a dilation and curettage Notify a grief counsellor to assist the woman with the imminent loss of her fetus Tell the woman that cerclage performing help her maintain her pregnancy E. 641. A. B. * C. D. E. 642. A. B. * C. D. E. 643. A. B. * C. D. E. 644. A. * B. C. D. E. 645. A. B. C. D. * E. 646. A. B. C. Prepare the woman for a methotrexate therapy Primapara N., 20 years, II pregnancy, I labor. The fetal lie is longitudinal, the fetal back is anteriorly. The fetal heart rate is clear, rhythmic. Vaginal examination: the cervix is effaced, opening is full, an amniotic sac is absent. Head of fetus in the plane of pelvic outlet. Sagittal suture is in a direct size, small fontanel is under the pubis. What moment of the labor biomechanism at the anterior type of occipital presentation is ended? The І moment of the labor biomechanism II moment of the labor biomechanism The ІІІ moment of the labor biomechanism The IV moment of the labor biomechanism The V moment of the labor biomechanism Jill Pangborn, age 20, has just had an incomplete abortion. While caring for her, the physician withholds ergot products until the uterus is empty. Why? to prevent intrauterine infection to avoid placental fragment retention to reduce the risk of hypertension to allow hormone levels to return to normal to avoid future infertility The patient is admitted to delivery department. In examination longitudinal lie, I position, posterior variety of the fetus is exposed. What is the leading point at the posterior type of occipital presentation? Small fontanel The middle of sagittal suture Large fontanel Chin Mid fontanel Katherine Holden is admitted to the hospital with suspected ectopic pregtancy. Which health history finding places Ms. Holden at risk for an ectopic pregnancy? history of pelvic inflammatory disease grand multiparity (five or more births) use of an intrauterine device for 1 year use of an oral contraceptive for 5 years use of an condoms for 3 years Katherine Holden is admitted to the hospital with suspected ectopic pregnancy. The physician assesses Ms. Holden for signs and symptoms of ectopic pregnancy. What is the most common finding associated with this antepartum complication? temperature elevation vaginal bleeding nausea and vomiting abdominal pain uterine enlargement Katherine Holden is admitted to the hospital with suspected ectopic pregnancy. The physician orders diagnostic tests for Ms. Holden. Which three tests typically are ordered to identify ectopic pregnancy? serum test for beta-hCG, ultrasonography, and amniocentesis serum test for progesterone, laparoscopy, and culdocentesis serum test for estrogen, ultrasonography, and nitrazine paper test D. * serum test for beta-hCG, ultrasonography, and laparoscopy E. 647. serum test for beta-hCG, nitrazine paper test, and colposcopy Denise Sorley comes to the prenatal clinic for a routine visit. She is 12 weeks pregnant, but the size of her uterus approximates that in an 18-to 20 week pregnancy. She is diagnosed as having gestational trophoblastic disease. For Ms. Sorley, what ultrasonography findings should the physician expect to see? empty gestational sac grapelike clusters severely malformed fetus ectopic pregnancy two babies Sixteen weeks pregnant, Nicole Evans sees her physician for a regular prenatal visit. Although Ms. Evans reports no pain or uterine contractions, the physician detects cervical dilation of 1 cm during the physical assessment. What is the most appropriate diagnosis? cervical incompetence preterm delivery spontaneous abortion premature rupture of the membranes placenta previa The physician uses nitrazine paper when examining Sarah Wilder, age 24, for premature rupture of the membranes (PROM). If Ms. Wilder has PROM, the paper will have which the color? pink blue yellow green red Jessica Arnold, 28 weeks pregnant, is admitted to the labor and delivery area in preterm labor. The physician prescribes an I.V. infusion of the tocolytic drug ritodrine. The physician monitors Ms. Arnold for adverse effects of ritodrine. Which of the following is a common adverse effect of ritodrine? tachycardia pohuria hypertension hyporeflexia hypotermia Patient II, labor first, at term. The patient’ condition is satisfactory. The new-born is just delivered. The umbilical cord hangs down from a vagina and increases in its length. Bleeding is not present. Uterus is in normal tonus. How do you called this positive sign of placenta separation? Dovshenko sign Alfeld sign Shreder' sign Pupil sign Hehar sign Robert Crane, 11 weeks pregnant, is admitted with hyperemesis gravidarum. She characterizes her condition by saying she has never known anyone to have such severe morning sickness. What is the cause of hyperemesis gravidarum? neurotogic disorders A. B. * C. D. E. 648. A. * B. C. D. E. 649. A. B. * C. D. E. 650. A. * B. C. D. E. 651. A. B. * C. D. E. 652. A. B. C. * D. E. 653. A. B. * C. D. E. 654. A. B. C. * D. E. 655. A. B. C. * D. E. 656. A. B. * C. D. E. 657. A. * B. C. D. E. inadequate nutrition unknown cause hemolysis of fetal RBCs pure nutrition A woman's obstetric history indicates that she is pregnant for the fourth time and all her children from prior pregnancies are living. One was born at 39 weeks' gestation, twins at 34 weeks' gestation, and another at 35 weeks' gestation. What is her gravity and parity using the GTPAL system? 3-1-1-1-3 4-1-2-0-4 3-0-3-0-3 4-2-1-0-3 4-0-2-1-3 A woman is 6 weeks pregnant. She has had a previous spontaneous abortion at 14 weeks' gestation and a pregnancy that ended at 38 weeks with the birth of a stillborn girl. What is her gravity and parity using the GTPAL system? 2-0-0-1-1 2-1-0-1-0 3-1-0-1-0 3-0-1-1-0 3-2-1-1 Patient 30 years, labor at term. A girl with the Apgar score 8 was born. The umbilical vessels do not pulsate, the cord is clammed. Bloody excretions from the vagina are absent. What period of labor this patient is found in? Cervical Pelvic Placental Puerperal period Preliminary period Nancy is a 31-year-old woman who believes she may be pregnant. She took an over-the-counter pregnancy test one week after a missed period test that turned positive. During her assessment interview, the physician inquires about Nancy’s LMP and if she is taking any medications. Nancy states that she takes medicine for epilepsy. She has been under much stress lately at work and has not been sleeping well. She also has a history of irregular periods. Nancy’s physical exam does not indicate that she is pregnant. Nancy has an ultrasound that reveals she is not pregnant. What is the most likely cause for obtaining false-positive pregnancy test results? Nancy took the pregnancy test too early Nancy takes anticonvulsants Nancy has a fibroid tumor Nancy has been under much stress and has a hormone imbalance. Result of ultrasound is not valid Betty is in her 7th month of pregnancy. She has been complaining of nasal congestion and occasional epistaxis. The physician suspects that: This is a normal respiratory change in pregnancy due to elevated levels of estrogen. This is an abnormal cardiovascular change and the nosebleeds are an ominous sign. Betty is a victim of domestic violence and is being hit in the face by her partner. Betty has been using cocaine intranasally. Betty should be examined by laryngologist o rule out chronic synusitis 658. Juanita has just moved to the United States from Mexico. She is 3 months pregnant and has arrived for her first prenatal visit. During her assessment interview, you discover that Juanita has not had any immunizations. Which of the following immunizations should Juanita receive at this point of her pregnancy? A. B. Herpes Simplex Type 3 Chickenpox Rubella Hepatitis B HIV A woman is in for a routine prenatal checkup. You are assessing her urine for proteinuria. You know that which of the following findings are considered normal? Dipstick assessment of trace to +1 > 300 mg/24 hours Dipstick assessment of +2 > 300 mg/24 hours It is impossible to use urine dipstick test A woman arrives at the clinic for a pregnancy test. Her last menstrual period (LMP) was February 14. Her expected date of birth (EDB) would be: September 17 November 7 November 21 December 17 May 7 A pregnant woman at 10 weeks’ gestation jogs three to four times per week. She is concerned about the effect of exercise on the fetus. The physician would inform her: “You do not need to modify your exercising any time during your pregnancy.” “Stop exercising because it will harm the fetus.” “You may find that you need to modify your exercise to walking later in your pregnancy around the seventh month.” “Jogging is too hard on your joints; switch to walking now.” Continue jogging to delivery time it is allows to decrease time of labour A woman who is 14 weeks pregnant tells the physician that she always had a glass of wine with dinner before she became pregnant. She has abstained during her first trimester and would like to know if it is safe for her to have a drink with dinner now. You would tell her: “Since you are in your second trimester, there is no problem with having one drink with dinner.” “One drink every night is too much. One drink three times a week should be fine.” “Since you are in your second trimester, you can drink as much as you’d like.” “Because no one knows how much or how little alcohol it takes to cause fetal problems, it is recommended that you abstain throughout your pregnancy.” “One glass of wine three times a week will help make you delivery easier” Pregnant N., 25 years is delivered in the maternity department with complaints about periodic pains in lower part of abdomen and lumbar region during 7 hours. Amniotic fluid did not released. Fetal heart rate is 136 in 1min. Vaginal examination: the cervix is effaced, opening 10 cm, the amniotic membrane is whole. What is the doctor’ tactic? Cesarean section Stimulation of labor Obstetric forceps C. D. * E. 659. A. * B. C. D. E. 660. A. B. C. * D. E. 661. A. B. C. * D. E. 662. A. B. C. D. * E. 663. A. B. C. D. 664. A. B. * C. D. E. 665. A. * B. C. D. E. 666. A. B. C. D. * E. 667. A. * B. C. D. E. 668. A. B. C. D. * E. 669. A. * Conservative conducting of labor A pregnant woman at 18 weeks’ gestation calls the clinic to report that she has been experiencing occasional backaches of mild to moderate intensity. The physician would recommend that she: Do Kegel exercises Do pelvic rock exercises Use a softer mattress Stay in bed for 24 hours Should do X-ray of spine Woman with full-term pregnancy. Uterine contractions occur every 4-5 minutes and lasts 30-35 seconds. Vaginal examination: cervix is totally effaced, dilation to 4 cm, fetal head is on -2 station. Sagittal suture is in right oblique diameter of the pelvic inlet, posterior fontanel under the symphysis. Amniotic sac is present. Diagnosis? Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation, I position, anterior. First stage of labor Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation, I position, posterior. First stage of labor Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation, II position, anterior. First stage of labor Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation, II position, anterior. Second stage of labor Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation, I position, anterior. Second stage of labor In her work with pregnant women of various cultures, a physician has observed various practices that seemed strange or unusual. She has learned that cultural rituals and practices during pregnancy seem to have one purpose in common. Which of the following statements best describes that purpose? To promote family unity To ward off the “evil eye” To appease the gods of fertility To protect the mother and fetus during pregnancy To have desired sex of the baby Juanita has just moved to the United States from Mexico. She is 3 months pregnant and has arrived for her first prenatal visit. During her assessment interview, you discover that Juanita has not had any immunizations. Which of the following immunizations should Juanita receive at this point of her pregnancy? Tetanus Chickenpox Rubella Cytomegalovirus Herpes Simplex type I A 22-year-old pregnant woman with a single fetus has a preconception body mass index (BMI) of 24. When she was seen in the clinic at 14 weeks’ gestation, she had gained 1.8 kg since conception. How would the physician interpret this? This large weight gain indicates possible pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH). This small weight gain indicates that her infant is at risk for intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR). It is impossible to evaluate this weight gain until the woman has been observed for several more weeks. The woman’s weight gain is appropriate for this stage of pregnancy. The weight gain is not important during pregnancy A pregnant woman reports that she is still playing tennis at 32 weeks’ gestation. The physician would be most concerned whether this woman consumes which of the following during and after tennis matches? Several glasses of fluid B. C. D. E. 670. A. B. C. * D. E. 671. A. B. C. D. * E. 672. A. B. C. D. E. * 673. A. B. C. D. * E. 674. A. B. C. D. * E. 675. Extra protein sources such as peanut butter Salty foods to replace lost sodium Easily digested sources of carbohydrate Avoid food 2 hours after match A 27-year-old pregnant woman had a preconceptal BMI of 18.0. The physician would be aware that this woman’s total recommended weight gain during pregnancy should be at least: 20 kg (44 lb) 16 kg (35 lb) 12.5 kg (27.5 lb) 10 kg (22 lb) 8 kg (17,5 lb) A woman in her 34th week of pregnancy reports that she is very uncomfortable because of heartburn. The physician would suggest that the woman: Substitute other calcium sources for milk in her diet. Lie down after each meal. Decrease the amount of fiber that she consumes. Eat five small meals daily. Should be examined by gastroenterologist Woman with full-term pregnancy. Uterine contractions occur every 4-5 minutes and lasts 30-35 seconds. Vaginal examination: cervix is totally effaced, dilation to 4 cm, fetus head is on -2 station. Sagittal suture is in left oblique diameter of the pelvic inlet, posterior fontanel near sacral region. Amniotic sac is present. Diagnosis? Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation, I position, anterior. First stage of labour Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation, II position, posterior. First stage of labour Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation, II position, anterior. First stage of labour Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation, II position, anterior. Second stage of labour Longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation, I position, posterior. First stage of labour A woman who has come to the clinic for preconception counseling because she wants to start trying to get pregnant in 3 months can expect the following advice: “Discontinue all contraception now.” “Lose weight so that you can gain more during pregnancy.” “You may take any medications that you have been taking regularly.” “Make sure you include adequate folic acid in your diet.” “Start to do additional exercise like jog” Primapara R., 21 eyars old, primapara. Full term of pregnancy. The labor started 8 hours ago. The membranes ruptured 15 minutes ago. Pelvic sizes: 25,28,31,20 cm. Fetal head rate 140 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. Per vaginum: the cervix is dilated to 5 cm. The amniotic sac is absent. Fetal head is palpated in plane of pelvic inlet. Which stage of labor? Third Second Latent stage of first Active stage of first Fourth After you complete your nutritional counseling for a pregnant woman, you ask her to reiterate your instructions to assess her understanding of the instructions given. What statement below would indicate that she understands the role of protein in her pregnancy? A. * B. C. D. E. 676. A. B. C. * D. E. 677. A. B. C. D. * E. 678. A. * B. C. D. E. 679. A. * B. C. D. E. 680. A. B. * C. “Protein will help my baby grow.” “Eating protein will prevent me from becoming anemic.” “Eating protein will make my baby have strong teeth after he is born.” “Eating protein will prevent me from being diabetic.” “Eating protein will prevent excessive blood lost in postpartum period” Your client reports “unusual food cravings”. When you inquire about the specifics, she reports eating laundry detergent and dirt. You know that this type of craving is known as ___. anorexia bulimia pica vomiting emesis A woman arrives at the clinic seeking confirmation that she is pregnant. The following information is obtained: She is 24 years old with a BMI of 17.5. She admits to having used cocaine “several times” during the past year and drinks alcohol occasionally. Her blood pressure is 108/70 mm Hg, her pulse rate is 72 beats per minute, and her respiratory rate is 16 breaths per minute. Family history is positive for diabetes mellitus and cancer. Her sister recently gave birth to an infant with a neural tube defect. Which characteristics place the woman in a high-risk category? Blood pressure, age, BMI Drug/alcohol use, age, family history Family history, blood pressure, BMI Family history, BMI, drug/alcohol abuse Blood pressure, family history, BMI A 39-year-old primigravida thinks that she is about 8 weeks pregnant, although she has had irregular menstrual periods all of her life. She has a history of smoking approximately one pack of cigarettes a day, but tells you that she is trying to cut down. Her laboratory data are within normal limits. Which of the following diagnostic techniques could be employed with this pregnant woman at this time? Ultrasound examination Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein screening Amniocentesis Nonstress test Biophysical profile The physician sees a woman for the first time when she is 30 weeks pregnant. The woman has smoked throughout the pregnancy, and now fundal height measurements are suggestive of growth restriction in the fetus. In addition to ultrasound to measure fetal size, what would be another tool useful in confirming the diagnosis? Doppler blood flow analysis Contraction stress test Amniocentesis Daily fetal movement counts Vaginal examination A 41-week pregnant multigravida presents in the labor and delivery unit after a nonstress test indicated that her fetus could be experiencing some difficulties in utero. Which diagnostic tool would yield more detailed information about the fetus? Ultrasound for fetal anomalies Biophysical profile Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein screening D. E. 681. A. * B. C. D. E. 682. A. B. C. * D. E. 683. A. B. C. D. * E. 684. A. B. C. * D. E. 685. A. B. * C. D. E. 686. A. * B. Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling Daily fetal movement counts Primipara F., 25 years old. Pregnancy at term. The labor started 6 hours ago. The membranes ruptured one hour ago. Pelvic sizes: 23,25,29,18 cm. Fetal head rate 140 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. Uterine contractions occur every 7-8 minutes. Per vaginum: the uterine cervix dilatation is 2 cm. The amniotic sac is absent. One fetal foot is palpated in the vagina. Buttocks are in the pelvic inlet. Which stage of labor? Latent stage of first stage Active stage of first stage Second stage Third Fourth At 35 weeks of pregnancy, a woman experiences preterm labor. Although tocolytics are administered and she is placed on bed rest, she continues to experience regular uterine contractions and her cervix is beginning to dilate and efface. What would be an important test for fetal well-being at this time? Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling Ultrasound for fetal size Amniocentesis for fetal lung maturity Nonstress test Vaginal examination A 40-year-old woman is 10 weeks pregnant. Which diagnostic tool would be appropriate to suggest to her at this time? Biophysical profile Amniocentesis Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein Transvaginal ultrasound Vaginal examination A 30-year-old 3-2-0-0-2 is at 18 weeks' gestation. At this time, what screening test should be suggested to her? Biophysical profile Chorionic villi sampling Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein screening Screening for diabetes mellitus Speculum examination A maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein test indicates an elevated level. It is repeated and again is reported as higher than normal. What would be the next step in the assessment sequence to determine the well-being of the fetus? Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling Ultrasound for fetal anomalies Biophysical profile for fetal well-being Amniocentesis for genetic anomalies Doppler velocimetry Karen is undergoing a nipple-stimulated contraction stress test. She is having contractions that occur every three minutes. The fetal heart rate has a baseline of approximately 120 bpm without any decelerations. The interpretation of this test is said to be: Negative Positive C. D. E. 687. A. * B. C. D. E. 688. A. B. C. * D. E. 689. A. B. * C. D. E. 690. A. B. C. * D. E. 691. A. 692. A. * Satisfactory Unsatisfactory Normal A pregnant woman’s biophysical profile score is 8. She asks the physician to explain the results. The physician’s best response is: “The test results are within normal limits.” “Immediate delivery by cesarean birth is being considered.” “Further testing will be performed to determine the meaning of this score.” “An obstetric specialist will evaluate the results of this profile and, within the next week, will inform you of your options regarding delivery.” ”You should repeat this test again after 3 days” A primigravid client visiting the antepartal clinic at 8 weeks' gestation tells the physician that she wants an amniocentesis because there is a history of hemophilia A in her family. The physician instructs the client that newer techniques now allow amniocentesis to be performed as early as which of the following? 8 weeks'gestation. 10 weeks'gestation. 12 weeks' gestation. 14 weeks' gestation. 16 weeks' gestation. A 40-year-old gravida 4 client at 10 weeks' gestation and her husband are coming into the clinic to discuss tests that are available during the first or early second trimester to diagnose an abormality of the fetus. Which of the following tests are appropriate? Electrocardiogram. Chorionic villus sampling (CVS). External fetal monitoring (EFM). Nonstress test Auscultation of fetal heart rate A 40-year-old gravida 4 client at 10 weeks' gestation and her husband are coming into the clinic to discuss tests that are available during the first or early second trimester to diagnose an abnormality of the fetus. Which of the fol¬lowing tests are appropriate? Electrocardiogram. External fetal monitoring (EFM). Amniocentesis. Nonstress test Vaginal examination M., 25 years old, multipara. Full term of pregnancy. Initiation of labor was 7 hours ago. The membranes ruptured 40 minutes ago. Pelvic sizes: 25,28,31,20 cm. Fetal heart rate is 132 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. Per vaginum: the cervix is completely dilated. The amniotic sac is absent. Fetal head is in the plane of the greatest diameter of the true pelvis. The face line is in the right oblique size. The chin is palpated under the symphysis. What is the moment of labor biomechanism? A woman in her 40th weeks of pregnancy, the second labour, has regular labour activity. Uterine contractions take place every 3 minutes. All of criteria describe the beginning of the II labor stage EXEPT: Cervical dilatation by no less than 4 cm B. C. D. E. 693. A. B. C. D. * E. 694. A. B. * C. D. E. 695. A. B. * C. D. E. 696. A. B. C. D. * E. 697. A. B. C. * D. E. Cervical dilation to 10 cm Duration of uterine contractions over 30 seconds Presenting part is in the lower region of small pelvis Rupture of fetal bladder A primigravid adolescent client at approximately 15 weeks' gestation who is visiting the prenatal clinic with her mother is to undergo alphafetoprotein (AFP) screen¬ing. When developing the teaching plan for this client, the physician should include which of the following pieces of in¬formation? Ultrasonography usually accompanies AFP testing. Results are usually very accurate until 20 weeks' gestation. A clean-catch midstream urine specimen is needle Increased levels of AFP are associated with neural tube defects. Elevated level of alphafetoprotein is responsible for preterm labour Woman with in-time pregnancy. Bears down during 40-45 seconds with intervals 1-2 minutes. The rupture of the membrane has occurred 10 minutes ago. Vaginal examination: fetal head is on the pelvic floor. Sagittal suture is in anterior-posterior diameter of pelvic outlet. Amniotic sac is absent. What is the stage of labor? Cervical Pelvic Cranial Early postpartum Placental A 40-year-old client at 8 weeks' gestation has a 3-year-old child with Down syndrome. The physician is dis_cussing amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling as genetic screening methods for the expected baby. The physician is confident that her teaching has been understood when the client states which of the following? “Each test identifies a different part of the infant's genetic makeup.” ”Chorionic villus sampling can be performed earlier in pregnancy.” “The test results take the same length of time to be complete” “Amniocentesis is a more dangerous procedure for the fetus.” “Amniocentesis is the most safe procedure for the fetus sex” A 27-year-old primigravid client with insulin-dependent diabetes at 34 weeks' gestation undergoes a nonstress test, the results of which are documented as reactive. The physician tells the client that the test results indicatw which of the following? A contraction stress test is necessary. The nonstress test should be repeated Chorionic villus sampling is necessary. There is evidence of fetal well-being. This is indication to emergency Cesarean section A primigravid client with insulin-dependent diabetes tells the physician that the contraction stress test performed earlier in the day was suspicious. The physician interprets this test result as indicating that the fetal heart rate pattern showed which of the following? Frequent late decelerations Decreased fetal movement Inconsistent late decelerations Lack of fetal movement Late acceleration 698. A. B. C. D. * E. 699. A. B. * C. D. E. 700. A. B. C. * D. E. 701. A. B. C. D. * E. 702. A. B. C. D. E. * 703. A. B. C. D. * E. A 34-years-old woman at 36 week’s gestation has been scheduled for a biophysical profile. She asks the physician why the test needs to be performe. The physician would tell her that the test: Determines how well her baby will breathe after born Evaluates the response of her baby’s heart to uterine contractions Measures her baby’s head and length Observes her baby’s activities to ensure that her baby is getting enough oxygen Identify lung maturation A 40-year-old woman at 18 week’s of gestation is having Triple Marked test performed. She is obese and her health history reveals that she is Rh negative. The primary purpose of this test is screen for Spina bifida Down syndrome Gestational diabetes Rh antibody Pregnancy induced hypertension During a contraction stress test, four contractions lasting 45 to 55 seconds were recorded in a 10 minute period. A late deceleration was noted during the third contraction. The physician conducting the test would document which of the following result negative positive Suspicious Unsatisfactory Normal Primapara. At vaginal examination: opening of cervix is 8 cm, sagittal suture in a transversal size of the pelvic inlet, small fontanel is palpated as a leading point. For which type of presentation is it typical? The brow presentation The vertex presentation. The face presentation The anterior occiput presentation. The posterior occiput presentation Postpartum patient. A girl was born by mass 3800 g. In pressing above the symphysis umbulical cord doesn't change it length. How do you call this sign of placenta separation? Positive Shreder sign Positive Alfeld sign Positive Vasten sign Positive Chukalov-Kustner sign Negative Chukalov-Kustner sign Pregnant D. admitted to the maternity hospital with pregnancy at term and regular uterine contractions during 6 hours. This pregnancy is first. Pelvic sizes: 25-26-31-20 cm. Fetal heart rate 136 in 1 min. What is the doctor’ conclusion about the pelvic sizes? Normal pelvis The true conjugate decreased The external conjugate decreased Distantia cristarum decreased Distantia spinarum decreased 704. A. B. * C. D. E. 705. A. B. C. * D. E. 706. A. B. * C. D. E. 707. A. * B. C. D. E. 708. A. B. C. * D. E. 709. A. B. C. * D. E. The doctor is measuring the patient’ pelvic size between the anterior spines of the os ileum. Which size is measuring by the doctor? Distantia cristnarum Distantia spinarum Distantia trochanterica Conjugata externa Conjugata vera The last menstrual period of patient was 22.12. 2017.What is the exposed term of labor on the Negele’ formula? 15.09.18 29.08.18 29.09.18 22.09.18 22.10.18 The pregnant C. was admitted in the pathology’pregnancy department. Pregnancy ІІ, 39 weeks. Circumference of abdomen – 110 cm, height of the uterine fundus – 36 cm. The fetal lie is longitudinal, cephalic presentation. What is the exposed fetal weight by Volskov’ method? 3700 g 3960 g 4200 g 2880 g 3270 g The neonatologist is measuring the sizes of the newborn head. The baby is at term, weight 3200 g. One of the fetal head size is 9.5 cm, circumference 32 cm. Which size is measured? Small obligue (suboccipitobregmatic) Middle obligue (suboccipitofrontal) Large obligue (occipitomental) Biparietal Bitemporal The external conjugate of patient is 21 cm. Solovjov’s index 15cm. What is the average of the true conjugate? 11 cm 10 cm 12 cm 13 cm 14 cm M., 28 years old, para 2. Full term of pregnancy. Initiation of labor was 8 hours ago. The membranes ruptured 20 minutes ago. Pelvic sizes: 25,28,31,20 cm. Fetal heart rate is 132 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. Per vaginum: the cervix is completely dilated. Fetal head is in outlet plane of pelvic. The chin is palpated under the symphysis. Which moment of biomechanism? First Second Third Fourth Fifth 710. A. * B. C. D. E. 711. A. B. * C. D. E. 712. A. B. * C. D. E. 713. A. B. C. D. * E. 714. A. * B. C. D. E. 715. A. * B. M., 22 years old. According to gestational age 40 weeks of gestation. Complaints of regular uterine contractions for 5 hours. Fetal heart rate is 140 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. Per vaginum: the cervix is dilated for 4 cm. The amniotic sac is presented. Fetal head is in plane of pelvic inlet. Sagittal suture and small fontanel is palpated. Indicate stage of labor. Active phase of cervical stage Latent phase of cervical stage Passive stage Active phase of pelvic stage Latent phase of pelvic stage M., 22 years old. According to gestational age 40 weeks of gestation. Complaints of regular uterine contractions for 3 hours. Fetal heart rate is 140 per minute with satisfactory characteristics. Per vaginum: the cervix is dilated for 2 cm. The amniotic sac is presented. Fetal head is in plane of pelvic inlet. Sagittal suture and small fontanel is palpated. Indicate stage of labor. Active phase of cervical stage Latent phase of cervical stage Passive stage Active phase of pelvic stage Latent phase of pelvic stage 199. Just after delivery of placenta in 60 kg woman 35years old woman after delivery 4000g boy 400ml blood appeared from the vagina. After uterine palpation through abdominal wall softness of uterus was revealed. What is the physiological blood loss for this patient? 250 ml 300 ml 600ml 400 ml 200 ml Woman 40y.o. weight 80 kg, delivered 4200g baby. Just after delivery of placenta 400ml blood appeared from the vagina. What is the physiological blood loss for this patient? 250 ml 300 ml 600ml 400 ml 200 ml A woman at 39th week of pregnancy, the second labor, has regular birth activity. Uterine contractions take place every 3 minutes. What criteria describe the beginning of the II labor stage the most precisely? Cervical dilatation by no less than 4 cm Cervical effacement over 90% Duration of uterine contractions over 30 seconds Presenting part is in the lower region of small pelvis Rupture of fetal bladder In 10 min after childbirth by a 22-year-old woman, the placenta was spontaneously delivered and 100 ml of blood came out. Woman weight - 84 kg, infant weight - 4100 g, length - 53 cm. The uterus contracted. In 10 minutes the hemorrhage renewed and the amount of blood is about 300 ml. What amount of blood loss is permissible for this woman? 420 ml 1000 ml C. D. E. 716. A. * B. C. D. E. 717. A. * B. C. D. E. 718. A. * B. C. D. E. 719. A. * B. C. D. E. 720. A. B. C. D. * E. 500 ml 650 ml 300 ml Vaginal inspection of a parturient woman revealed: cervix dilation is up to 2 cm, fetal bladder is intact. Sacral cavity is free, sacral promontory is reachable only with a bent finger, the inner surface of the sacrococcygeal joint is accessible for examination. The fetus has cephalic presentation. Sagittal suture occupies the transverse diameter of pelvic inlet, the small fontanel to the left, on the side. What labor stage is this? Cervix dilatation stage Preliminary stage Prodromal stage Stage of fetus expulsion Placental stage After delivery and revision of placenta there was found the defect of placental lobule. General condition of woman is normal, uterus is firm, and there is moderate bloody discharge. Speculum inspection of birth canal shows absence of lacerations and raptures. What action is necessary? Manual exploration of the uterine cavity External massage of uterus Introduction of uterine contracting agents Urine drainage, cold on the lower abdomen Introduction of hemostatic medications A 22-year-old woman is having interm labor continued for 5 hours. Light amniotic fluid came off. The fetus head is fixed to the orifice in the small pelvis. The probable fetal weight is 4000,0 g. Heartbeat of the fetus is normal. In vaginal examination – cervix is dilated to 1 cm, the fetal membranes are not present. The head is in 2-st plane of the pelvis. In which stage of labor does the woman present? First, latent phase First, active phase First, spontaneous phase Second, active phase Third, latent phase A woman, primagravida, consults a gynecologist on 05.03.2018. A week ago she felt the fetus movements for the first time. Last menstruation was on 10.01.2018. When should be the day of delivery according Neegle rule? 17 October .25 July 22 August 11 July 5 September 33 years old woman, multipara, consults a gynecologist on 25.02.2018. A week ago she felt the fetus movements for the first time. Last menstruation was on 11.12.2018. When should be the day of delivery according Neegle rule? 17 October .25 July 22 August 18 September 5 September 721. A. B. C. * D. E. 722. A. B. C. D. E. * 723. A. B. * C. D. E. 724. A. B. * C. D. E. 725. A. B. * C. D. E. 726. A. * B. In 10 min after delivery by a 32-year-old woman, the placenta was spontaneously delivered and 150 ml of blood came out. Woman weight is 90kg, infant weight - 3800 g, length - 52 cm. The uterus contracted. In 10 minutes the hemorrhage renewed and the total amount of blood loss is 350 ml. What amount of blood loss is physiologic for this woman? 400 ml 1000 ml 450 ml 650 ml 300 ml In 14 min after delivery by a 22-year-old woman, the placenta was spontaneously delivered and 50 ml of blood came out. Woman weight is 60kg, infant weight - 3100g, length - 52 cm. The uterus contracted. In 15 minutes the hemorrhage renewed and the total amount of blood loss is 250 ml. What amount of blood loss is physiologic for this woman? 400 ml 1000 ml 450 ml 650 ml 300 ml In 18 min after delivery by a 28-year-old woman, the placenta was spontaneously delivered and 80 ml of blood came out. Woman weight is 64kg, infant weight - 03100g, length - 50 cm. The uterus contracted. In 10 minutes the hemorrhage renewed and the total amount of blood loss is 300 ml. What amount of blood loss is physiologic for this woman? 400 ml 320 ml 450 ml 650 ml 300 ml In 20 min after delivery by a 19-year-old woman, the placenta was spontaneousely delivered and 60 ml of blood came out. Woman weight is 76kg, infant weight - 3500g, length - 50 cm. The uterus contracted. In 15 minutes the hemorrhage renewed and the total amount of blood loss is 250 ml. What amount of blood loss is physiologic for this woman? 400 ml 380 ml 450 ml 650 ml 300 ml A couple presented with infertility since last 2 years. Husband’s semen analysis was advised. What is WHO criterion – for minimum sperm count in normal semen? 10 million 20 million 30 million 70 million 40 million A 23- year old primagravidara presents with abdominal pain, syncope and vaginal spotting. Assessment reveals that she has an ectopic pregnancy. The most common site of pregnancy is: Ampulla Istmus C. D. E. 727. A. B. C. D. E. * 728. A. * B. C. D. E. 729. A. B. C. D. * E. 730. A. * B. C. D. E. 731. A. B. * C. D. E. 732. A. B. C. D. * E. Fimbrial part Abdomen Cervix Second degree of uterovaginal prolapse is characterized by: Complete protrusion of uterus outside introitus Descent of genital tract within vagina Descent of genital tract up to introitus Descent of genital tract outside the introitus Descent of cervix below the ischial spine A 63- year old lady presents with abdominal mass and weight loss, was diagnosed as having an ovarian tumor. The most common ovarian tumor in this woman would be: Epithelial tumor Germ tumor Stromal tumor Sex cord tumor Trophoblastic tumor A young girl, 23- year old is presented with complaints of abdominal pain, menorrhagia and 18 weeks size mass arising from hypogastrium. The most likely diagnosis is: Endometriosis Pelvic inflammatory disease Ovarian cyst Uterus fibroid Mesenteric cyst A 25-year old school teacher Para 1 wants to use oral contraceptive pills for contraception. She asking about the mode of action of oral contraceptivepills. The mechanism of action of oral contraceptive pills is: Inhibiting ovulation by suppression of serum FSH Inducing endometrial atrophy Increasing cervical mucous hostility Inducing endometritis Inhibiting prolactin Women complaining of milky whitish discharge with fishy odor. No history of itching. Most likely diagnosis is: Trichomoniasis Bacterial vaginosis Candidiasis Malignancy Urinary tract infection A medical student has come to you with complaints of oligomenorrhea, hirsutism and weight gain, ultrasound reveals bulky ovaries with sub-cupsular cysts. Most likely diagnosis is: Ovarian cancer Pelvic inflammatory desease Cushing’s syndrome Polycystic ovarian disease Uterus fibroid 733. A. B. C. D. * E. 734. A. B. C. * D. E. 735. A. B. C. D. * E. 736. A. * B. C. D. E. 737. A. B. C. D. E. * 738. A. B. C. * D. E. 739. A. A 43 year old woman has come to you with complaints of heavy but regular menstrual bleeding with flooding and clots. There is no anatomical reason for heavy flow. The most effective remedy for reducing her menstrual flow is: Dilatation and curettage Misoprostol Ergometrine maleate Tranexemic acid Progesterone acetate A 28 year old woman has 14 weeks size irregular uterus. She does not complain of abdominal pain or menorrhagia. Her Pap smear is normal. The best next step in her management would be: Continued observation Endometrial biopsy Pelvic ultrasonography Hysterectomy Laparoscopy The most effective treatment of pruritis vulve associated with atrophic vulvitis is: Antihistamines Hydrocortisone Alcohol injections Topical estrogen therapy Tranquilizers A 40-year old mulptiparous woman complains of involuntary loss of urine associated with coughing, laughing, lifting or standing. The history is most suggestive of: Stress incontinence Fistula Urge incontinence Urethral diverticulum Urinary tract infection A 28-year old G3, P2, has presented with comlaints of brownish vaginal discharge, passage of vesicles and excessive vomiting. Ultrasound scan shows snowstorm appearance in uterus with no fetus. The most likely diagnosis is: Septic induced abortion Fibroid utrus Twin pregnancy Ectopic pregnancy Gestational trophoblastic disease A 28-year old patient complains of amenorrhea after having dilatation and curettage. The most likely diagnosis is: Kallman’s syndrome Turner’s syndrome Asherman’s syndrome Pelvic inflammatory disease Anorexia nervosa A large cystic ovarian tumor is detected in a woman on routine antenatal check up. The most common complication she can encounter is: Infection B. C. D. * E. 740. A. B. C. D. * E. 741. A. B. C. D. * E. 742. A. B. C. D. * E. 743. A. B. C. D. * E. 744. A. B. C. * D. E. 745. A. B. C. D. * E. Rupture Haemorrhage Torsion Degeneration A 20-year old medical student presents with five years history of weight gain, irregular periods and worsening fascial hair. What is the most likely diagnosis? Hypothyrodism Obesity Cushing’s syndrome Polycystic ovarian disease Nephrotic syndrome 28-year old woman with previous history of having baby with Down’s syndrome is now 12 weeks pregnant. Which of the following would you suggest to her: Obstetric ultrasound Fetal blood sampling Amniocentesis Chorionic villus sampling Wait till eighteen weeks for detailed ultrasound A newly married girl comes to gynae OPD with history of dysuria, burning, micturition and sore perineum. What is your likely diagnosis: Trichomonas infection Trauma due to coitus Candida infection Honey moon cystitis Genital herpes infection The most likely cause of abnormal uterine bleeding in 13-year old girl is: Uterine cancer Ectopic pregnancy Trauma Anovulation Uterus fibroid A 58-year old woman has presented with complaints of postmenopausal bleeding for the past two weeks. The most essential investigation would be: Colposcopy Pap smear D&C Hysteroscopy Ultrasound examination A 56 year old woman has come to you with the complaints of hot flushes irritability, joint pains with lack of sleep. Most appropriate treatment would be: Vitamins Phytooestrogens Selective estrogen receptor modulators Combined estrogen, progesterone preparations Hysterectomy 746. A. * B. C. D. E. 747. A. B. C. D. E. * 748. A. * B. C. D. E. 749. A. * B. C. D. E. 750. A. * B. C. D. E. In the 30years old primapara intensive uterine contractions with an interval of 1-2 min, duration 50 sec have begun. In time of the fetal head delivery the patient complaints on severe pain in the perineum. The perineum is 5 cm, its skin become pale. What is it necessary to perform: Perineotomy Episiotomy. Protection of the perineum. Vacuum - extraction of the fetus. Waiting tactics. The primapara 24 is admitted in to the hospital due to high body temperature – 38,7 0, 1 stage of labor, regular uterine contractions. Sizes of pelvis: 25-28-30-20 cm. Abdominal circumference is 100 cm, level of uterine fundus 28 cm, presenting part is absent. Right side the fetal head is palpated, left – the breech, fetal heart sounds are absent. Vaginal examination: the uterine cervix is fully dilated, amniotic membrane is whole. What is the tactic of labor conducting? Cesarean section after full dilatation Cesarean section immediately External version of the fetus on a head Stimulation of uterine contractions Classic obstetric version of the fetus In patient 25 year, labor III. The pelvic sizes: 24-27-30-19 cm. After stormy uterine contractions and pushing at a highly standing fetal head and positive Vasten’ sign uterine contractions were stopped suddenly, bloody excretions from a vagina appeared, fetal heart rate is not listened. The condition of patient suddenly became worse, blood pressure went down to 70 mm Hg, pulse 140 in a 1 minute, the skin is pale. Reason of the shock condition? Uterine rupture Threatened rupture of uterus Abruption placentae Syndrome of squeezing of lower hollow vein Placenta previa A 30 years old woman has the 2-nd labour that has been lasting for 14 hours. Hearbeat of fetus is muffled, arrhythmic, 100/min. Vaginal examination: cervix of uterus is completely opened, fetus head is at the pelvis outlet. Saggital suture is in the straight diameter, small fontanel is near symphysis. What is the further tactics of handling the delivery? Applying obstetric forceps Stimulation of labor activity by oxytocin Cesarean section Antihypoxic drugs Use of mid forceps A woman is 34- year old, it is her tenth labor at full term. It is known from the anamnesis that the labor started 11 hours ago, labor was active, painful contractions started after discharge of waters and became continuous. Suddenly the parturient got knife-like pain in the lower abdomen and labor activity stopped. Examination revealed positive symptoms of peritoneum irritation, ill-defined uterus outlines. Fetus was easily palpable, movable. Fetal heartbeat is not auscultable. What is the most probable diagnosis? Rupture of uterus Uterine inertia Discoordinated labor activity Risk of uterus rupture II stage of labor 751. A. * B. C. D. E. 752. A. B. C. * D. E. 753. A. B. C. D. * E. 754. A. B. * C. D. E. 755. A. B. * C. D. E. Multipara, the second stage of delivery, fetal head is in the pelvic cavity. Contractions last for 60 seconds in 2 minutes. Fetal heart beat slowed to 100 per min. What is the management? Applying obstetric forceps Oxytocin stimulation of uterus activity Perform a classic podalic version C-section nothing above The woman is admitted to the maternity home with discontinued uterine contractions and slight bloody discharges from the vagina. The condition is severe, the skin is pale, consciousness is confused. BP – 80/40 mm Hg. The heart rate of the fetus is not determined. In anamnesis there was a cesarean section a year ago. Establish the diagnosis: Placental presentation Placenta previa Uterine rupture Premature gush of the amniotic fluids Nothing above In the primapara, 30 years, intensive uterine contractions with an interval of 1-2 min, duration 50 sec have begun. In vaginal examination cervical dilation is complete. Amniotic sac is intact. Fetal head is present in 0 station. What is it necessary to perform: Vacuum - extraction of the fetus. Protection of the perineum. Episiotomy. Amniotomy Nothing Pregnant N., 25 years is delivered in the maternity department with complaints of periodic pains in lower part of abdomen and lumbal region, during 7 hours and bloody excretions from a vagina, which appeared 1 hour ago. Amniotic fluid is present. Pregnancy 4, labor is first, previous 3 pregnancies ended by artificial abortion. Fetal heart rate is 136 in 1min. At vaginal examination: the uterine cervix is effaced, opening 6-7 cm, from one side soft spongy tissue is palpated before the presenting head, the amniotic membrane is whole. Blood loss is 50 ml. What is the doctor’ tactic? Stimulation of labor Amniotomy Obstetric forceps Fetal destroying operation Cesarean section Patient 23 years. Pregnancy 39-40 weeks, position the fetus is longitudinal, cephalic presentation. Sizes of pelvis: 24-25-29-18 cm. The uterine contractions proceed 10 hours, last 2 hours are very painful, patient behaves very uneasily. Amniotic fluid released 2 hours ago. At the external examination a contractile ring is palpated on 2 fingers higher than umbilicus, Vasten’ sign is positive. Fetal heart rate 160 in 1 min. At internal examination: amniotic membrane is absent, opening of uterine cervix 8 cm, head presentation, large fontanel is palpated. The fetal head is in the plane of the pelvic inlet. What is the probable diagnosis? The rupture of uterus is completed Threatening rupture of uterus Dyscoordinative uterine contractions Placental abruption Tetanus of uterus 756. A. B. C. * D. E. 757. A. * B. C. D. E. 758. A. B. C. * D. E. 759. A. * B. C. D. E. 760. A. B. C. * D. E. Primapara in I period of labor acute pain in the region of uterine fundus appeared suddenly, insignificant bloody excretions from a vagina. Uterus is firm. Fetal heart rate – 175. In anamnesis: acutening of chronic pyelonephritis during pregnancy. At vaginal examination: the uterine cervix is effaced, opening of uterine cervix 4 cm. Amniotomy is conducted. Amniotic fluid released with blood. What is the doctor’ tactic? Stimulation of labor. Treatment of fetal hypoxia Cesarean section immediately. To appoint tocolitics To appoint coagulants Patient C., 26 year old, 18 hours are found in labor: pushing appeared hour ago – on 30 sec. in 3-4 minutes. Fetal heart rate is arhythmical, to 100 in 1 min. It is definite at vaginal examination, that a head is found in narrow part of small pelvis. What is your subsequent obstetric tactic? Obstetrical forceps The cardiomonitoring supervision Cesarean section. To perform perineotomy. Conservative management of labor Patient N., 33 years, labor I, term gestation 42 weeks. Position of the fetus is longitudinal, cephalic presentation. Amniotic fluid released, were colored by meconium. Auscultation: fetal heart rate arhythmical, to 170 in 1 min. Uterine contractions on 20-25 sec. after 4-5 min. At vaginal examination: cervix is immature. What tactic of conduct of labor? Obstetric forceps The cardiomonitoring supervision Cesarean section. Perineotomy. Vaginal delivery Patient 28 years with the expressed edema is found in a maternity hall, in the ІІ period of labor. Head of fetus in narrow part of small pelvis. Head pains began, twinkling of “spots” before eyes, contractions of muscles of the face. BP - 170/110 mm Hg. What is tactic of conduct of labor? Obstetric forceps Conservative conduct of labor Vacuum-extraction of the fetus Labor stimulation Cesarean section In patient 25 years (labor III) after excessive uterine contractions and pushing at a highly standing head and positive Vasten’ sign. Uterine contractions was stopped suddenly, bloody excretions from a vagina appeared, fetal heart rate was not listened. The condition of patient suddenly became worse, BP went down to 70 mm Hg, pulse 140 in a 1 minute, a skin is pale-grey. Reason of the shock condition? Threatened rupture of uterus Placentae abruption Uterine rupture Syndrome of squeezing of lower hollow vein Placenta previa 761. A. * B. C. D. E. 762. A. B. C. D. E. * 763. A. B. * C. D. E. 764. A. * B. C. D. E. 765. A. B. * C. D. E. 766. A. B. * C. D. Postpartum patient 28 years. A girl was born by mass 3800 g., by length 52 cm. Placenta was delivered in 15 minutes and 300 ml of blood was discharged. Bleeding proceeds. At the review of cervix and vagina the traumas of them are not found. At the review of placenta – vessels pass to the edge of placenta on membranes and are ruptured. What is the subsequent tactic? To perform the manual exploration of uterus cavity Total hysterectomy. Uterotonics To conduct the external massage of uterus. Uterine tamponade At postpartum patient 30 years at the manual removal of placenta and examination of uterus the rupture of uterine cervix is exposed in the right side with transition on a lower segment. Blood lost is arrives at 1300 ml and continues. Tactic of doctor? Subtotal hysterectomy External massage of uterus Tampon with ether in a posterior fornix Oxytocin 10 units intramuscularly Total hysterectomy Patient K. 24- year old has II delayed delivery, II period lasts 2 hours. Fetal head is fixed to the pelvic inlet. Pelvic dimensions 24, 26, 29, 18cm. Half an hour ago, fetal heartbeat disappeared. Tactics of the doctor? Immediate cesarean Fetal destroying operation Apply forceps Conduct induction of labor Make podalic version In women with pelvic contraction II degree diagnosed transverse fetus lie and fetal death. Doctor decided to perform fetal destroying operation. Which of these operations is carried out in such situation? Decapitation Amniotomy Craniotomy Thoracotomy Perforation of subsequent head Due to the presence of a dead fetus and clinically contracted pelvis was decided to perform the fetal destroying operation. Breech presentation. Which of the following operations can be applied? Craniotomy Perforation of following head Decapitation Evisceration Vacuum extraction At birth in the mixed breech presentation fell pulsing umbilical cord loops. Dilatation of cervical os is 8cm. Pelvic dimensions: 26,27 ,31, 17cm.Fetus heart rate is120/min. Make a plan of delivery Immediate extraction of the fetus at the end of the pelvic Urgent C-section Continue conservative management of labor Make an external version of the fetus E. 767. A. B. * C. D. E. 768. A. * B. C. D. E. 769. A. B. C. D. * E. 770. A. * B. C. D. E. 771. A. * B. C. D. E. Keep labor conservative, intervene only when there will be fetal distress In patient K. 24 years II delayed delivery, the second period lasts for 2 hours. Fetal head fixed to the pelvis inlet. Pelvic size are 24, 26, 29, 18cm. Half of hour ago ceased heartbeat of the fetus. Tactics of doctor? Immediately hysterotomy Fetal destroying operation Apply obstetric forceps Conduct stimulation uterus activity Make podalic version and extraction of the leg At patient on the 5th day of postpartum period suddenly there was an increasing of the temperature. The body temperature is 38,5oС, mammary glands are normal, lactation is satisfied. Signs of perotoneal irritation are abcent. In pelvic examination purulent excretions from the uterus are present, uterus is soft in painfull in palpation. The uterus is increased, soft, painful in palpation.What is the most probable diagnosis? Endometritis Mastitis Lochiometra Pelvioperitonitis Peritonitis At patient on the 7th day of puerperal period suddenly there was a hallucinatory syndrome: patient is not oriented in space and time, does not recognize neighbors. The temperature of body rose to 38,5oС, purulent excretions from the uterus appeared. At vaginal examination: the uterus is increased, soft, painful at palpation, the uterine cervix freely skips 1 finger. What reason of psychical violations, that arose up at postpartum patient? Psychical diseases in anamnesis Negative emotional influence of labor on patient Astenic-vegetative syndrome Puerperal infection Manifestation of postpartum blue A woman consulted a doctor on the 14th day after labour about sudden pain, hyperemia and induration of the left mammary gland, body temperature rised up to 39oC, headache, indisposition. Objectively: fissure of nipple, enlargement of the left mammary gland, pain during palpation. What pathology would you think about in this case? Lactational mastitis Lacteal cyst with suppuration Fibrous adenoma of the left mammary gland Breast cancer Phlegmon of mammary gland Examination of placenta revealed a defect. An obstetrician performed manual investigation of uterine cavity, uterine massage. Prophylaxis of endometritis in the postpartum period should involve following actions: Antibacterial therapy Instrumental revision of uterine cavity Haemostatic therapy Contracting agents Intrauterine instillation of dioxine 772. A. B. * C. D. E. 773. A. B. C. D. * E. 774. A. B. * C. D. E. 775. A. B. C. D. E. * In the woman of the first day after labor the rise of temperature up to 39oС was registered. The rupture of the fetal membranes has taken place 36 hours prior to labor. The investigation of the bacterial flora of cervix of the uterus revealed – hemolytic streptococcus of a group A. The uterine body is soft, tender. Discharges are bloody, with a pus. Establish the most probable postnatal complication. Thrombophlebitis of veins of the pelvis Metroendometritis Infected hematoma Infective contamination of the urinary system Endometritis Postpartum patient., 26 years, transferred from the department of physiological obstetrics in observative on a 4 day of puerperal period. Labor are second, coursed normally. Perineal rupture of the ІІ degree sutured by cetgut and silk stitches. A postnatal period during the first two days was without complications. At the end of the third day the body temperature increased to 37,30С, head ache appeares, pain in the area of perineum and vagina. Breasts are not tense, hyperemia is not present. Abdomen is soft, uterine fundus on 3 transversal fingers below the umbilicus, an uterus is firm, unpainful. Lochia rubra, in normal amount. Stitches on a perineum are covered by a purulent discharges, surrounding tissue are edematic, hyperemia present, painful at palpation. What is the complication of puerperal period ? Puerperal parametritis Puerperal endometritis Trombophlebitis of veins of pelvis Postpartum ulcer Mastitis On a 4 day after the first labor by a fetus with a mass 4200 g postpartum patient complaints of pain in the area of vagina, T-36,9oC, AT – 115/70 mm Hg. At examination: in lower third of right lateral wall of vagina the wound surface to 2 cm in a diameter is exposed, covered by a purulent discharge. A wound bleeds, in surrounded tissue edema and erythema are present. Diagnosis? Puerperal endometritis Puerperal ulcer of vagina Haematoma of vagina Parametritis Puerperal ulcer of perineum Labor are at term, first, amniotic membrane ruptured before beginning of the uterine contractions 12 hours ago. Duration of labor 10 hours. On the 4th day after labor a temperature increased to 38-39oC, tahicardiya, chill appeared. Pulse is 96 in 1 min, rhythmic. BT 105-70 mm Hg. Skin is pinky color. Breasts without pathology. Uterine body on 2 cm below the umbilicus, soft consistency, painful at palpation. Lochia rubra with an odor. Diagnosis? Parametritis Metrotrombophlebitis Pelvioperitonitis Postpartum ulcer of perineum Acute puerperal endometritis 776. A. * B. Patient 23 years. Pregnancy 39-40 weeks, position the fetus is longitudinal, cephalic presentation. Sizes of pelvis: 24-25-29-18 cm. The uterine contractions proceed 10 hours, at last 2 hours very painful, patient behaves very uneasily. Amniotic fluid released 2 hours ago. At the external examination a contractile ring is palpated on 2 fingers higher than umbilicus, Vasten’ sign is positive. Fetal heart rate 160 in 1 min. At internal examination: amniotic membrane is absent, opening of uterine cervix 8 cm, head presentation, large fontanel is palpated. The fetal head is in the plane of the pelvic inlet. What is the probable diagnosis? The rupture of uterus is completed Threatening rupture of uterus Dyscoordinate uterine contractions Placental abruption Tetanus of uterus Primapara in I period of labor acute pain in the region of uterine fundus appeared suddenly, insignificant bloody excretions from a vagina. Uterus in hypertonus. Fetal heart rate – 175. In anamnesis: acutening of chronic pyelonephritis during pregnancy. At vaginal examination: the uterine cervix is effaced, opening of uterine cervix 4 cm. Amniotomy is conducted. Amniotic fluid released with blood. What is the doctor’ tactic? Stimulation of labor. Treatment of fetal hypoxia Cesarean section immediately. To appoint tocolitics To appoint coagulants Patient C., 26 years, 18 hours are found in labor: pushing appeared hour ago – on 30 sec. in 3-4 minutes. Fetal heart rate is arhythmical, to 100 in 1 min. It is definite at vaginal examination, that a head is found in narrow part of cavity of small pelvis. Your subsequent obstetric tactic? Obstetrical forceps The cardiomonitoring supervision Cesarean section. To perform perineotomy. Conservative labor Patient N., 33 years, labor I, term gestation 42 weeks. Position of the fetus is longitudinal, cephalic presentation. Amniotic fluid released, were colored by meconium. Auscultation: fetal heart rate arhythmical, to 170 in 1 min. Uterine contractions on 20-25 sec. after 4-5 min. At vaginal examination: cervix is immature. What tactic of conduct of labor? Obstetric forceps The cardiomonitoring supervision Cesarean section. Perineotomy. Conservative labor Patient 28 years with the expressed edema is found in a maternity hall, in the ІІ period of labor. Head of fetus in narrow part of small pelvis. Head pains began, twinkling of “spots” before eyes, contractions of muscles of the face. BP - 170/110 mm Hg. What is tactic of conduct of labor? Obstetric forceps Conservative conduct of labor C. D. E. The Vacuum-extraction of the fetus Labor stimulation Cesarean section A. B. * C. D. E. 777. A. B. C. * D. E. 778. A. * B. C. D. E. 779. A. B. C. * D. E. 780. 781. C. In patient 25 years (labor III) after excessive uterine contractions and pushing at a highly standing head and positive Vasten’s sign. Uterine contractions stopped suddenly, bloody excretions from a vagina appeared, fetal heart rate was not listened. The condition of patient suddenly became worse, BP went down to 70 mm Hg, pulse 140 in a 1 minute, a skin is pale-grey. What is the reason of the shock condition? Threatened rupture of uterus Abruptio placentae Uterine rupture Syndrome of squeezing of lower hollow vein Placenta previa Postpartum patient., 26 years, transferred from the department of physiological obstetrics in observative on a 4 day of puerperal period. Labor are second, coursed normally. Perineal rupture of the ІІ degree sutured by cetgut and silk stitches. A postnatal period during the first two days coursed without complications. At the end of the third day the body temperature increased to 37,30С, head ache appeares, pain in the area of perineum and vagina. Breasts are not tense, hyperemia is not present. Abdomen is soft, uterine fundus on 3 transversal fingers below than umbilicus, an uterus is dense, unpainful. Lochia rubra, in normal amount. Stitches on a perineum are covered by a festering discharges, surrounding tissue are edematic, hyperemia present, painful at palpation. What complication of puerperal period take place? Puerperal parametritis Puerperal endometritis Trombophlebitis of pelvis veins Mastitis Postpartum ulcer Patient C. 21р., complains of insignificant excretions from sexual ways, itching of external genital organs, which appeared after sexual intercourse. At the examination there is hyperemia of vaginal vault and cervix . In the area of posterior fornix there are accumulation of liquid, greyish-yellow, foamy excretions. What is previous diagnosis? Acute trihomoniasis Acute gonorrhoea Urogenital chlamidiosis Micoplasmosis Ureaplasmosis Female patient, 28 years old, has IIB type of PAP-smear. She has been treated by coagulation. When she should visit obstetritian-gynecologist next time? In 2 years after coagulation Control assessment (colposcopy, cytological test, bacterioscopy) should be performed after next menstruation In 1 year In 3 months after coagulation There is no correct answer Female patient, 25 years old, has IIIA type of PAP-smear. When she should visit obstetritian-gynecologist next time? In 1 year Control assessment (colposcopy, cytological test, bacterioscopy) should be performed after next menstruation Should be directed to the oncological hospital D. In 3 months A. B. C. * D. E. 782. A. B. C. D. E. * 783. A. * B. C. D. E. 784. A. B. C. D. * E. 785. A. B. * E. 786. A. B. C. * D. E. 787. A. B. C. D. E. * 788. A. B. C. * D. E. 789. A. B. C. D. * E. 790. A. B. C. D. * E. 791. A. B. * In 6 months What treatment should be prescribed to the 48-year old female patient with severe cervical dysplasia with involved cervical canal and ovarian cyst? Electroconization of cervix uteri Electrocoagulation of cervix uteri Total hysterectomy with adnexa uteri Solcovagin treatment Total hysterectomy without adnexa uteri Female patient, 33 year old, complains for genital itching, pain in vagina, white discharge. During assessment: mucous – edematous, hyperemic, in folders – whitish cheeslike dischurge. Primary diagnose? Trichomonal colpitis Chlamidia colpitis Urogenital mycoplasmosis Bacterial colpitis Candidiasis colpitis Female patient, 34 year old, complains for genital itching, pain in vagina, white discharge. During assessment: mucous – edematous, hyperemic, in folders – whitish cheeslike dischurge. Choose appropriate medication: cifran Flagil Dyflucan Trichopol Levamisole 43 years old patient complains of contact bleeding in the last 6 months. In the speculum - the cervix looks like cauliflower. Schiller tests are positive. Bimanually: Cervix is increased in size, limited in mobility. What is the most likely diagnosis? Fibroids Cervical polyp Cervical pregnancy Cervical cancer Leukoplakia Patient 58 -year old complaints of bloody discharge from the genital tract. Menopause has been for 8 years. Gynecological examination: Uterus is somewhat enlarged, firm, limited in mobility, appendages of the uterus are not defined, the parameters are free. After fractional curettage of the uterus, it’s obtained considerable tissue scraping. What is the most likely diagnosis? Cervical cancer Adenomyosis Chorionepithelioma Hysterocarcinoma Hormone-producing ovarian tumor Patient 60-year old was admitted to the gynecology department with complaints of a slight bloody discharge from the genital tract, which appeared after 4 years of menopause. During speculum examination: cervix cylindrical epithelium non injuried. Bimanual examination: uterus is in anteflexio versio, slightly increased in size, mobile. Adnexes are not define. After diagnostic curettage of the uterus,has received special-shaped scraping. What is the most likely diagnosis? Menopausal bleeding Hysterocarcinoma C. D. E. 792. A. B. * C. D. E. 793. A. B. C. * D. E. 794. A. B. * C. D. E. 795. A. B. C. D. E. * 796. A. * B. C. D. Fibroids of the uterus Ovarian dysfunction Adenomyosis of the uterus Patient 64 –year old admitted to the Department with uterine bleeding and anemia. After 12-years of absence of menstruation, 7-8 months ago had appeared firstly serous, watery then bloody-serous, such as "meat slops" discharge from the vagina and abdominal pain. Which pathology is most likely? Incomplete abortion Cancer of the uterus Molar pregnancy Chorionepithelioma Internal genital endometriosis Patient 56, complains of general weakness, dull abdominal pain, increased abdomen. Menopause for 5 years. On examination, marked ascites. During bimanual examination: size of the uterus is small , shifted to the right, left and posteriorly is palpable firm, nodular, nonmoveable tumor formation, 10 x 12 cm in size .Wich is the most likely diagnosis? Colon tumor Subserous hysteromyoma Ovarian cancer tubo-ovarian abscess Genital endometriosis Patient 48 years complained of dull pain, gravity in the lower regions of the abdomen, a significant increase in the abdomen for the last 4 months. Menses were normal. Gynecological examination revealed: cervix is normal, the uterus of normal size, painless, mobile on both sides of the uterus palpable tumor size of 10 - 12 cm, dense texture, irregular surface, motionless. In the abdominal cavity is defined by a significant amount of free fluid. What is the most likely diagnosis? Cirrhosis Ovarian Cancer Benign ovarian tumors tubo-ovarian abscess Genital endometriosis Patient aged 47 complained of heavy menstrual flow. Last menstrual period was 10 days ago. Gynecological examination: the cervix is cylindrical, deformed by old scar , the anterior lip with leukoplakia. The body of the uterus enlarged to 14 - 15 weeks of pregnancy, with a rough surface, solid, mobile, painless. Appendages are not palpable. The vaults are deep. Which treatment should you choose? Conservative myomectomy hormone therapy antiinflammatory, antibacterial therapy haemostatic therapy Hysterectomy Patient age 47 suffer from uterine cancer 8 years, not being treated over the past year, the tumor grew to the size of 15-week pregnancy. What is the plan of surgical treatment? Total hysterectomy with appendages Enucleation of myoma nodes Supravaginal hysterectomy without adnexal Supravaginal hysterectomy with appendages E. Total hysterectomy without appendages 797. Patient 45- year old complains of contact bleeding during past 5 months. In the speculum: cervix enlarged, looks like cauliflower, bleeds when touched by the probe. In bimanual examination uterus has thick consistency. The body of the uterus is not enlarged, reduced mobility. Appendages are not palpable, the parameters are free. The vaults are deep. What is possible diagnosis? Polyposis of the cervix Hysterocarcinoma Protruded myoma Cervical pregnancy Cervical cancer The patient 58- year after 10 years of menopause had heavy uterine bleeding. Bimanual and speculum examination cause heavy bleeding, other pathologies haven’t been identified. A possible diagnosis? Incomplete abortion Hemorrhagic metropatiya Schroeder Hysterocarcinoma Myoma Violation of the menstrual cycle, climacteric period The patient, aged 45, complained of dull abdominal pain, weakness, appetite loss, weight loss for the last 3 months to 12 kg, an increase in the abdomen. Examination revealed: Ascites, on the side of right adnexa palpated dense, nodular, limited mobility of the tumor. In the clinical analysis of blood increased ESR to 50 mm / h. A possible diagnosis? Cyst Ectopic pregnancy Fibroids of the uterus Ovarian cancer Right-hand adnexitis The patient F, 57- year old, complains of dull pain in lower quadrants for last 1,5 years. Examination revealed: the patient's ovarian tumor captures both the ovary, fallopian tube and uterus, germinates in the parameter reaches the walls of the pelvis, there are not any metastasis to distant organs and lymph nodes. Which is stage of the process? III A III B III b IV IV B The patient T, 42 -year old, complains of dull abdominal pain, weakness, loss of appetite and weight loss for the last 3 months, increasing of the abdomen. Examination revealed: cancer of the body of the uterus with local growth and localization at the bottom of the uterus, without deep invasion, there are not any metastasis to distant organs and lymph nodes. Which is the optimal surgery? Radical Wertheim Hysterectomy Hysterectomy without appendages Hysterectomy with appendages Supracervical hysterectomy Can be restricted by radiotherapy and chemotherapy. A. B. C. D. E. * 798. A. B. C. * D. E. 799. A. B. C. D. * E. 800. A. B. C. * D. E. 801. A. * B. C. D. E. 802. A. B. C. D. * E. 803. A. B. C. D. E. * 804. A. * B. C. D. E. 805. A. B. C. * D. E. 806. A. B. C. D. * E. 807. A. * B. C. After instructing a 20-year-old nulligravid client about adverse effects of oral contraceptives, the doctor determines that further instruction is needed when the client states which of the following as an adverse effect? Weight gain. Nausea. Headache. Ovarian cancer. Nothing of the above Patient 45- year old complains of contact bleeding during past 5 months. In the speculum: cervix enlarged, looks like cauliflower, bleeds when touched by the probe. In bimanual examination uterus has thick consistency. The body of the uterus is not enlarged, reduced mobility. Appendages are not palpable, the parameteriums are free. The vaults are deep. What is the most likely diagnosis? Polyposis of the cervix Hysterocarcinoma Birth of fibromatous node Cervical pregnancy Cervical cancer Patient age 49 suffer from uterine cancer 2 years, not being treated over the past year, the tumor grew to the size of 13-week pregnancy. What is the plan of surgical treatment? Total hysterectomy with appendages Enucleation of myoma nodes Supra-vaginal hysterectomy without appendages Supravaginal hysterectomy with appendages Hysterectomy without appendages The patient 64 year- old after 12 years of menopause had heavy uterine bleeding. Bimanual and speculum examination cause heavy bleeding, other pathologies haven't been identified. What is possible diagnosis? Incomplete abortion Hemorrhagic metropatiya Uterus cancer Myoma Disorders of the menstrual cycle The patient, aged 45, complained of dull abdominal pain, weakness, appetite loss, weight loss for the last 3 months to 10 kg, an increase in the abdomen. Examination revealed: Ascites, on the side of left adnexa palpated dense, nodular, limited mobility of the tumor. In the clinical analysis of blood increased ESR to 50 mm / h. A possible diagnosis? Cyst Ectopic pregnancy Fibroids of the uterus Ovarian cancer Left side adnexitis The patient O, 55 years old, complains of dull pain in right lower quadrant for last few months. Examination revealed: the patient's ovarian tumor is confined to one ovary, there are not any metastasis to distant organs and lymph nodes. Which is stage of the process? IA IB II A D. E. 808. A. B. C. * D. E. 809. A. B. C. D. * E. 810. A. B. C. D. E. * 811. A. B. * C. D. E. 812. A. B. * C. D. E. II B III B The patient C, 45 years old, complains of dull abdominal pain, weakness, loss of appetite and weight loss for the last 5 months. Which process does the type V reflect in Pap smear test? Normal epithelium Moderate dysplasia. Cancer. Inflammation. Suspicion of malignization The patient C, 38- year old, complains of excessive with odor discharge from the vagina lately. Which process does the type IIA reflect in Pap smear test? Normal epithelium. Moderate dysplasia. Cancer. Inflammation. Suspicion of malignization. A woman complains of periodic pains and feeling of weight in lower parts of an abdomen. Sometimes each evening there is a subfebril temperature. Menstruations are normal. Sexual life from 20 years. Two normal labors in anamnesis. The patient’ condition is satisfactory. Pulse -79 in a minute, BP 120/70 mm Hg. Vaginally: bilateral tumors of adnexa are palpated, tumors are immobile, a small pelvis is filled by tumors, on the lower pole of tumors the painful growths are palpated. Blood test of ESR- 60 mm/hr, moderate lymphopenia, insignificant eozinophylia. Diagnosis? Bilateral tubo-ovarian tumors of inflammatory genesis Bilateral cystomas of ovaries Stage IIIOvarian Cancer Stage I Ovarian Cancer Stage II Ovarian Cancer Patient 20 year old is delivered in the gynecological department in the severe condition with complaints of acute permanent pain in the area of left labia pudenda majora, impossibility of movement. Objectively: temperature of body is 38,1 C. At the examination : left labia pudenda majora is slightly swollen, skin above it and lower part of vagina is swollen, hyperhemia is present. At palpation the pain is present. Inguinal lymphatic nodes are enlarged, especially to the left. Laboratory: high leucocytosis, rise ESR to 33 mm/hr. What is possible diagnosis? False abscess of Bartholin's gland The true abscess of Bartholin's gland Cyst of Bartholin's gland An abscess of steam of urethral glands Cystitis Patient 25 years, complains of considerable foamy excretions from the vagina, pain at sexual intercourse, itching in vagina. Menstrual function is normal. There were 2 labors and two abortions. Is ill about one week. At examination: edema, erythema of vaginal mucous, excretions are yellow and foamy. What is most reliable diagnosis? Acute gonorrhea Trichomoniasis. Candidosis Bacterial vaginosis Chlamidiasis 813. A. B. C. D. E. * 814. A. * B. C. D. E. 815. A. B. C. D. * E. 816. A. B. C. D. * E. 817. A. B. C. D. * E. The patient 36 years complains of pain in lower parts of abdomen, rise of body temperature to 37,7 – 38oC, purulent-bloody excretions from a vagina. 3 days ago artificial abortion was done at pregnancy 8-9 weeks. Objectively: external genital organs without pathology, uterine cervix with the signs of endocervicitis. The uterine body is enlarged to 5-6 weeks of pregnancy, the mobile is limited, soft, not painful. Adnexa are not determined, a region of them is unpainful. Parametrium are free. Excretions festering. Blood test: hemoglobin — 100 g/l, leucocytes — 12x109 /l. What agent is the most reliable cause of endometritis? Gardnerella Trichomonas Candidosis Doderlein's bacillus Gonococcus Patient 46 year old complains of bloody excretions from genital organs after the sexual contact or weight lifting. Bloody excretions are unconnected with a menstrual cycle. At a speculum examination: cervix is cylindric, exernal os is closed, on a front part of the cervix a lot of the nipple excrescences are visible, cervix is covered by festering excretions and easily bleed at contact. Body of uterus and adnexa on either side without pathology. Parametriums are free. What is the most reliable diagnosis? Cancer of cervix The true erosion. Simple pseudo erosion The endometriosis Papillary pseudo erosion The chief complaint interview on a client reveals vaginal discharge with itching and burning. The client also reveals she experiences dyspareunia. If her diagnosis is monilial vulvovaginitis, you would expect the wet mount slide to contain which of the following? Bacteria Clue cells Trichomonads Candida albicans All of the above At 35 years old patient it’s revealed intraepithelial cervical cancer. Which intervention would you recommend: Hysterectomy with appendages Hysterectomy without adnexa Cryolysis Electro-conization of the cervix uteri None of the above 69 year old patient complains on spotting from the genital tract after 18-year postmenopausal period. The patient is treated by a therapist about hypertension. Blood pressure rises to 200/100 mm Hg At the time of the inspection - 170/90 mm Hg . Her height is 165 cm and weight is 98 kg. At gynecological examination: cervix is not changed, spotting, infiltrates in the pelvis does not. Probable diagnosis: Adenomyosis Dysfunctional uterine bleeding Cervical cancer Endometrial cancer Hysteromyoma 818. A. * B. C. D. E. 819. A. * B. C. D. E. 820. A. B. * C. D. E. 821. A. B. * C. D. E. 822. A. B. * C. D. E. 823. Patient 23 years is delivered in the gynecological department in the severe condition with complaints of acute permanent pain in the area of left labia pudenda majora, impossibility of movement. Objectively: temperature of body 38,7. At a review: left labia pudenda majora is slightly swollen, skin above it and lower part of vagina is swollen, hyperhemia is present. At palpation the pain become severe. Inguinal lymphatic nodes are enlarged, especially to the left. Laboratory: high leucocytosis, rise ESR to 25 mm/hr. What is the diagnosis? The true abscess of bartolin gland False abscess of bartolin gland Cyst of bartolin gland An abscess is steam of urethral glands Vestibulitis Patient 22 years. Complains of pain in a right labia pudenda majora, rise of body temperature to 38.0 °C. At the review of genital organs the considerable increasing of right large sexual lip definites, especially in the lower third. Erythema, edema, at palpation acutely painful, fluctuation is determined. To conduct vaginal examination due to acute pain is impossible. Blood test: Leucocytes — 10,0 x 109 per cu mm, Rod-nuclear — 10%.What method is main? The dissection and drainage of abscess To withdraw a bartolin gland within the limits of healthy tissue To appoint physical therapy procedures To appoint compresses with liniment To expect a spontaneous regeneration of abscess Patient A.complains for discharge from vagine, genital itching. Objectives: vaginal mucous is edematous, hyperemic, foamy discharge. Diagnose? Purulent colpitis Trichomonal colpitis Urogenital clamidiosis Bacterial colpitis Gonorrheal colpitis Female patient, 30 years old, has IIA type of PAP-smear. When she should visit obstetritian-gynecologist next time? In 1 year In 1 month to confirm effectiveness of treatment Should be directed to the oncological hospital In 6 months There is no correct answer Female patient, 35- year old, has IIB type of PAP-smear. When she should visit obstetritian-gynecologist next time? In 1 year Control assessment (colposcopy, cytological test, bacterioscopy) should be performed after next menstruation Should be directed to the oncological hospital In 6 months There is no correct answer Patient 25 years, complains about considerable foamy discharge from the vagina, pain at sexual intercourse, itching in vagina. Menstrual function is normal. There were 1 labor and one abortion. She is ill about a week. At examination: vaginal walls with edema, erythema, dischage are yellow and foamy. What is most reliable diagnosis? A. * B. C. D. E. 824. A. * B. C. D. E. 825. A. * B. C. D. E. 826. A. * B. C. D. E. 827. A. B. C. Trichomoniasis. Acute gonorrhea Candidosis Bacterial vaginosis Chlamidiasis The patient 35 years complains on pain in lower parts of abdomen, rise of body temperature to 37,7 – 38oC, purulent-bloody excretions from a vagina. 7 days ago artificial abortion was done at pregnancy 9-10 weeks. Objectively: external genital organs without pathology, uterine cervix with the signs of endocervicitis. The uterine body is enlarged to 5-6 weeks of pregnancy, the mobile is limited, soft, not painful. Adnexa are slightly determined, regions of them are painful. Parametrium are free. Excretions festering. Blood test: hemoglobin — 105 g/l, leucocytes — 13x109 /l. What agent is the most reliable cause of endometritis? Gonococcus Gardnerella Trichomonas Syphylis Doderleyn’ bacilli Patient 43- year old appealed to female dispensary with complaints of the presence of cervical erosion which was exposed at routine medical examination by the midwife. In anamnesis: labors-4, abortions-5. Меnarche at 12 years, menstruations every 28 days, during 3 days, are regular, unpainful. Sexual life from 19 years. At colposcopy: on the uterine cervix the area of transformation is found out. The biopsy is carried out and the diagnosis of displasia is confirmed. At cytological examination reveals IIIB type of Pap’ smear. Define the necessary volume of treatment of the patient: Cervical diatermoconisation The diatermocoagulation of the cervix The total hysterectomy without adnexa The criodestruction of the cervix Subtotal hysterectomy of cervix In the gynecological department a woman 25- year old appealed with complaints about the rise of temperature of body to 38,60С, pain in lower parts of abdomen, dyzuria. Became ill 3 days before, when the indicated complaints appeared after artificial abortion. At gynecological examination: the uterine cervix is cylinder, external os is closed. Body of uterus a few enlarged, painful, soft. The adnexa of uterus are not palpated. Excretions festering-bloody. In the blood test leycocytosis with displacement of formula of blood to the left, speed-up ESR. What diagnosis is most credible? Acute endometritis Acute endocervicitis Acute salpingoophoritis Acute cystitis Piosalpinx Female patient, 35 year old, year ago masculinization signs appeared: hair on the mammary glands and face, voice timbre has changed, menstruation ceased. Before: menstruation was regular, in anamnesis – 1 delivery and 2 artificial abortion. Gynecological assessment: atrophy of mammory glands, uterus hypoplasia, tumour near the uterus – 7 cm in diameter with glandular surface. What is the diagnosis? Policystic syndrom Genital infantilism False female hermafroditism D. * E. 828. A. B. C. D. * E. 829. A. B. C. D. * E. 830. A. B. C. D. E. * 831. A. B. C. D. E. * 832. A. B. C. D. E. * 833. A. B. C. D. Androblastoma Androgenital syndrom The chief complaint interview on a client reveals vaginal discharge with itching and burning. The client also reveals she experiences dyspareunia. If her diagnosis is vulvovaginitis, you would expect the wet mount slide to contain which of the following? Bacteria Clue cells Trichomonads Budding hyphae All of the above At 35 year old patient was revealed intraepithelial cervical cancer. Which intervention would you recommend: hysterectomy with appendages hysterectomy without adnexa cryolysis Electro-conization of the cervix uteri none of the above A 32 year old patient complains of dischurge from vagine, genital itching. Objectives: vaginal mucous is edematous, hyperemic, foamy discharge. Diagnose? Purulent colpitis Urogenital chlamidiosis Candidosis Gonorrheal colpitis Trichomonal colpitis Female patient, 35- year old, has IIB type of PAP-smear. When she should visit obstetritian-gynecologist next time? In 1 year Should be directed to the oncological hospital In 6 months There is no correct answer Control assessment (colposcopy, cytological test, bacterioscopy) should be performed after next menstruation What treatment should be prescribed to the 46-year old female patient with severe cervical dysplasia with involved cervical canal and ovarian cyst? Electrocauterizing conization of cervix uteri Electrocoagulation of cervix uteri Solcovagin treatment Uterus exterpation without adnexa uteri Hysterectomy with adnexa uteri Female patient, 35- year old, complains of genital itching, pain in vagina, white discharge. During assessment: mucous – edematous, hyperemic, in folders – whitish cheeslike dischurge.What is the pimary diagnose? Trichomonal colpitis Chlamidia colpitis Urogenital mycoplasmosis Gonorrea E. * 834. A. B. C. D. E. * Candidosis colpitis Woman 30- year old came to the gynecologist on the medical examination. No complaints. In anamnesis delivery - 1, abortion - 1. Menstruation is regular. Objectively: the cervix is cylindrical, uterus body of normal size, firm, mobile, painless. On both sides of the uterus palpable tumor (8 x 10 cm on the left, 10 x 12 cm on the right) tight elastic consistency, with a smooth surface, mobile, painless. The fluid in the abdominal cavity has not defined. What is the most likely diagnosis? Ovarian Endometriosis Krukenberg’ Canser Abdominal pregnancy Fibromatosis of the uterus Bilateral cysts Назва наукового напрямку (модуля): Семестр: 10 Акушерство та гінекологія СРС Опис: 5 курс 10 семестр Перелік питань: 1. A. B. C. D. * E. 2. A. * B. C. D. E. 3. A. * B. C. D. E. 4. A. * B. C. D. E. 5. A. B. * C. D. E. 6. A. What is the less crown-rump length of 7 months embryo when the heartbeat must be seen on ultrasound? 2 mm 4 mm 5 mm 7 mm 10 mm A definitive diagnosis can be made when a gestational sac containing a yolk sac is visualized within the uterine cavity. of an intrauterine pregnancy of the tubal pregnancy of missed abortion uterine polyp molar pregnancy Crown-rump length of 7 mm on ultrasound at the first visit is revealed, heartbeat can’t be seen clear, you should: repeat the ultrasound after 11 days diagnose an “early pregnancy loss” and make D and C diagnose an ectopic pregnancy prescribe progestines prescribe misoprostol An “early pregnancy loss” which is defined by American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists could be diagnosed with ultrasound: the absence of cardiac activity in an embryo 11 days or more after a scan that showed a gestational sac with a yolk sac the presence of cardiac activity in an embryo 2 weeks or more after a scan that showed a gestational sac without a yolk sac Mean sac diameter of 25 mm or greater and active embryo Mean sac diameter of 15 mm or greater and embryo with a heartbeat the presence of cardiac activity in an embryo 11 days or more after a scan that showed a gestational sac with a yolk sac An “early pregnancy loss” which is defined by American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists could be diagnosed with ultrasound: the presence of cardiac activity in an embryo 11 days or more after a scan that showed a gestational sac with a yolk sac the absence of cardiac activity in an embryo 2 weeks or more after a scan that showed a gestational sac without a yolk sac the presence of cardiac activity in an embryo 2 weeks or more after a scan that showed a gestational sac without a yolk sac Mean sac diameter of 25 mm or greater and active embryo Mean sac diameter of 15 mm or greater and embryo with a heartbeat An “early pregnancy loss” which is defined by American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists could be diagnosed with ultrasound: the presence of cardiac activity in an embryo 11 days or more after a scan that showed a gestational sac with a yolk sac B. C. * D. E. 7. A. * B. C. D. E. 8. A. * B. C. D. E. 9. A. B. C. * D. E. 10. A. * B. C. D. E. 11. A. the presence of cardiac activity in an embryo 2 weeks or more after a scan that showed a gestational sac without a yolk sac Mean sac diameter of 25 mm or greater and no embryo Mean sac diameter of 25 mm or greater and active embryo Mean sac diameter of 15 mm or greater and embryo with a heartbeat Oligohydramnios as ultrasound diagnosis means: is defined as an amniotic fluid index (AFI) less than 5 cm or a maximum vertical pocket less than 2 cm is defined as an amniotic fluid index (AFI) less than 15 cm or a maximum vertical pocket less than 12 cm is defined as an amniotic fluid index (AFI) less than 25 cm or a maximum vertical pocket less than 22 cm is defined as an amniotic fluid index (AFI) less than 0,5 cm or a maximum vertical pocket less than 0,2 cm is defined as the single smallest vertical pocket of amniotic fluid without evidence of umbilical cord or fetal parts visualized in utero The SDP specifically single deepest pocket (SDP) technique records is: the single largest vertical pocket of amniotic fluid without evidence of umbilical cord or fetal parts visualized in utero the single smallest vertical pocket of amniotic fluid without evidence of umbilical cord or fetal parts visualized in utero the single largest transverse pocket of amniotic fluid without evidence of umbilical cord or fetal parts visualized in utero the summative measurement of the single deepest vertical pocket of fluid without evidence of cord or fetal parts noted in all four quadrants of the uterus is defined as an amniotic fluid index (AFI) less than 15 cm or a maximum vertical pocket less than 12 cm The AFI (amniotic fluid index) technique is the summative measurement of the single deepest vertical pocket of fluid without evidence of cord or fetal parts noted in all four quadrants of the uterus. the single largest vertical pocket of amniotic fluid without evidence of umbilical cord or fetal parts visualized in utero the single smallest vertical pocket of amniotic fluid without evidence of umbilical cord or fetal parts visualized in utero the summative measurement of the single deepest vertical pocket of fluid without evidence of cord or fetal parts noted in all four quadrants of the uterus the single largest transverse pocket of amniotic fluid without evidence of umbilical cord or fetal parts visualized in utero the single smallest transverse pocket of amniotic fluid without evidence of umbilical cord or fetal parts visualized in utero Polyhydramnios which is a term to describe: an abnormally large amount of fluid significantly low amniotic fluid significantly large intestinum of the fetus significantly large stomach of the fetus significantly large head of the fetus Polyhydramnios is defined by an AFI greater than 4 cm or a single deepest vertical pocket (SDP) greater than 8 cm B. * C. D. E. 12. A. B. C. * D. E. 13. A. B. C. * D. E. 14. A. B. C. * D. E. 15. A. * B. C. D. E. 16. A. * B. C. D. E. 17. A. * B. C. an AFI greater than 24 cm or a single deepest vertical pocket (SDP) greater than 8 cm an AFI greater than 14 cm or a single deepest vertical pocket (SDP) greater than 8 cm an AFI greater than 34 cm or a single deepest vertical pocket (SDP) greater than 8 cm an AFI greater than 24 cm or a single deepest vertical pocket (SDP) greater than 28 cm What is gestational Age when Mean Transvaginal Gestational Sac Diameter is 8 mm (mm)? 12-13 weeks 24 weeks less than 5-6 weeks 10-11 weeks 16-17 weeks What is gestational Age (wk) when Mean Transvaginal Gestational Sac Diameter is 16 mm (mm) and emryo is visible? 12-13 weeks 24 weeks 6-7 weeks 10-11 weeks 16-17 weeks a serious developmental defect of the central nervous system in which the brain and cranial vault are grossly malformed Gastroshchizis Omphalocele Anencephaly Gastroptosis Aneuploidy The greatest risk factor for vertical mother-to-child transmission of HIV is thought to be advanced maternal disease, likely due to a high maternal HIV viral load Smoking alcohol taking intensive antiretroviral therapy mild antiretroviral therapy Indications for amniocentesis: to deliver intra-amniotic dye in cases in which premature rupture of membranes is suspected to measure fetal abdomen to treat HIV infection to prevent influenza transmission to measure fetal head Amnioreduction is: Procedure to reduce uterine distention and decreases risk for preterm premature rupture of membranes and preterm delivery Is referred to as artificial rupture of membranes (AROM) is the procedure by which the amniotic sac is deliberately ruptured so as to cause the release of amniotic fluid, usually performed for the purpose of inducing or expediting labor. is a medical procedure used in prenatal diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities and fetal infections, and also for sex determination, in which a small amount of amniotic fluid, which contains fetal tissues, is sampled from the amniotic sac surrounding a developing fetus D. E. 18. A. * B. C. D. E. 19. A. * B. C. D. E. 20. A. B. * C. D. E. 21. A. B. C. * D. E. 22. A. B. C. D. * E. 23. A. B. * C. D. E. is a procedure to deliver intra-amniotic dye in cases in which premature rupture of membranes is suspected is a procedure for determining fetal lung maturity Indications for amnioreduction: setting of twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS), where it is performed to reduce fluid volume in the recipient twin and thereby increase blood flow to the donor twin by decreasing pressure inside the amniotic cavity to deliver intra-amniotic dye in cases in which premature rupture of membranes is suspected determining fetal lung maturity Is referred to as artificial rupture of membranes (AROM) is the procedure by which the amniotic sac is deliberately ruptured so as to cause the release of amniotic fluid, usually performed for the purpose of inducing or expediting labor. to treat HIV infection Missed, incomplete, or inevitable abortion present before 13 weeks' gestation needs therapy: misoprostol as an alternative to surgery Progestines Antiviral therapy Combined oral contraceptives Oxytocin 10 IU Missed, incomplete, or inevitable abortion present before 13 weeks' gestationneeds therapy: Antiviral therapy performance of suction Progestines Combined oral contraceptives Oxytocin 10 IU Missed, incomplete, or inevitable abortion present before 13 weeks' gestationneeds therapy: Combined oral contraceptives Oxytocin 10 IU performance of dilation and curettage Progestines Antiviral therapy The most common cancers found in pregnant women mirror those found in their nonpregnant counterparts, to include the following EXCEPT: Thyroid cancer Lymphoma Colorectal carcinoma (0.10-1.0 cases per 1000 pregnancies) Osteosarcoma Colorectal carcinoma (0.10-1.0 cases per 1000 pregnancies) What is a success rate of medical abortion with the combination of mifepristone and vaginal or buccal misoprostol to 63 days gestation? of 53-55% of 93-95% of 83-85% of 73-75% of 63-65% 24. A. B. C. D. * E. 25. A. B. C. D. * E. 26. A. B. C. D. * E. 27. A. B. C. D. * E. 28. A. * B. C. D. E. 29. A. B. * C. D. E. 30. A. B. Cardiac conditions that still carry maternal mortality rates and may be the indication for medical abortion include EXCEPT: mitral stenosis, coarctation of the aorta, severe uncorrected tetralogy of Fallot, aortic stenosis history of myocardial infarction moderate arterial hypertension presence of artificial heart valves Maternal medical conditions that carry significant risks in pregnancy and may be maternal indications for abortion include the following EXCEPT: severe diabetes with retinopathy with cardiac or renal complications advanced cardiac or respiratory disease, sickle cell disease femur fracture psychiatric disease Fetal conditions that are incompatible with life include the following EXCEPT: Anencephaly trisomy 13 trisomy 18 esophageal or duodenal atresia thanatophoric dysplasia A cephalic disorder in which the prosencephalon (the forebrain of the embryo) fails to develop into two hemispheres is defined as: Aneuploidy ventricular atresia Wilson disease Holoprosencephaly Anencephaly Medical abortion is contraindicated in patients with: chronic steroid use Mild hypertensia Moderate anemia HIV infection after rape Medical abortions are indicated for women who consent to elective medical abortion. What is maximal gestational age for the FDA-approved protocol with misoprostol from the LMP? 38 days 49 days 63 days 75 days 90 days What is the tablets appointment schedule for medical abortion? On day 1, mifepristone 200 mg PO once as a single dose (FDA-approved regimen), levonorgestrel after 24 hours On day 1, mifepristone 800 mg PO once as a single dose (FDA-approved regimen), is administered in the office. Misoprostol 100 mcg buccal administration is then administered at home 24-48 h after the mifepristone dose C. * D. E. 31. A. B. C. * D. E. 32. A. B. * C. D. E. 33. A. * B. C. D. E. 34. A. B. C. D. E. * 35. A. B. C. D. * E. 36. A. On day 1, mifepristone 200 mg PO once as a single dose (FDA-approved regimen), is administered in the office. Misoprostol 800 mcg buccal administration is then administered at home 24-48 h after the mifepristone dose On day 1, ulipristal acetate 30 mg, is administered in the office. Misoprostol isn’t necessary On day 1Misoprostol 800 mcg buccal administration; mifepristone isn’t necessary Method of selective reduction (selective fetocide) is following: Gel with prostaglandins into cervix Oxytocin 10 IU intravenously Cord occlusion techniques, such as Nd:YAG laser photocoagulation; fetoscope cord ligation; bipolar cord coagulation; and monopolar cord coagulation Misiprostol vaginally 800 mg Fetocide is forbidden nowadays Method of selective reduction (selective fetocide) is following: Misiprostol vaginally 800 mg Cord occlusion techniques, such as embolization with alcohol or enbucrilate gel; Gel with prostaglandins into cervix Oxytocin 10 IU intravenously Fetocide is forbidden nowadays Pregnant women are: at increased risk for severe complications from influenza infection as compared with non-pregnant women and the general population at the same level risk for severe complications from influenza infection as compared with non-pregnant women and the general population at reduced risk for severe complications from influenza infection as compared with non-pregnant women and the general population at minimal risk for severe complications from influenza infection as compared with non-pregnant women and the general population at 100% lethal risk from influenza infection as compared with non-pregnant women and the general population The inactivated influenza vaccine is recommended for: all pregnant women only in 1-st trimester all pregnant women only in 2-nd trimester all pregnant women only in 3-rd trimester Can’t be used in pregnant women all pregnant women in all trimesters Live Attenuated Influenza Vaccine (LAIV) in pregnancy is recommended for: all pregnant women only in 1-st trimester all pregnant women only in 2-nd trimester all pregnant women only in 3-rd trimester is not approved in pregnant women all pregnant women in all trimesters The following recommendations regarding Tdap immunization (Tetanus toxoid, reduced diphtheria toxoid and acellular pertussis) in pregnancy are provided by ACIP and endorsed by ACOG. But choose one incorrect postulate: Tetanus toxoid, reduced diphtheria toxoid and acellular pertussis (Tdap) immunization is recommended once during each pregnancy, including in women with prior vaccination. B. C. D. * E. 37. A. B. C. D. * E. 38. A. B. C. * D. E. 39. A. B. C. D. * E. 40. A. B. C. D. * E. 41. A. B. Optimal vaccine timing is between 27 and 36 weeks with ideal administration as early as possible in that window to maximize passive neonatal immunity. Tdap may also be given at any time in pregnancy. Tdap can’t be given while pregnancy at all Optimal vaccine timing is between 11 and 12 weeks with ideal administration as early as possible in that window to maximize passive neonatal immunity. Hepatitis A virus (HAV) in pregnancy. Choose the incorrect answer: Pregnancy is not a contraindication to vaccine administration and ACIP and ACOG advise Pregnant women who have been exposed to individuals with HAV infection and have not previously been immunized should receive post-exposure prophylaxis as described above. Immune globulin does not pose a risk in pregnancy and exposed pregnant women should receive both immune globulin and HAV immunization as soon as possible after exposure. can’t be given while pregnancy at all HAV vaccine in pregnancy for women in whom the risk of HAV infection exceeds the theoretical risk of immunization (pregnant women who plan to travel to areas where there is an increased risk for exposure to hepatitis A) can be vaccinated Hepatitis B (HBV) in pregnancy. Choose the incorrect answer: ACIP and ACOG recommend HBV immunization for pregnant women at risk of infection. Pregnancy is not a contraindication to hepatitis B vaccine. Pregnancy is a contraindication to hepatitis B vaccine. Routine prenatal screening for HBsAg is recommended to detect HBV carriers and to ensure neonatal immunoprophylaxis at birth if needed. HBV infection in pregnancy, both acute and chronic infection, poses a risk of vertical transmission with perinatally-acquired infection conferring the greatest risk of long-term consequences. Meningococcal Disease in pregnancy. Choose the incorrect answer: Neisseria meningitis is the encapsulated gram-negative bacterium All meningococcal vaccines are inactivated and therefore low risk for adverse outcomes in pregnant women or their offspring. ACIP recommends that pregnant women at increased risk for meningococcal disease be immunized according to existing adult recommendations. can’t be given while pregnancy at all Neisseria meningitis causes significant morbidity and mortality through meningococcal meningitis and bacteremia Anthrax immunization in pregnancy. Choose the incorrect answer: Given the low-risk of anthrax exposure, pre-event immunization is not recommended for pregnant women, as the benefit of immunization does not outweigh the theoretical risk of immunization. the high morbidity and mortality of anthrax disease is observed Individuals at highest risk of exposure include military populations, environmental investigators, postal processing staff and individuals with laboratory exposures can’t be given while pregnancy at all pregnant women with an exposure to anthrax should receive AVA vaccination and anti-microbial treatment Poliovirus, vaccination in pregnancy. Choose the incorrect answer: Pregnancy is a precaution to immunization with inactivated polio vaccine (IPV). ACIP recommends that inactivated polio vaccine (IPV) be considered for pregnant women at risk for exposure to wild-type poliovirus. C. D. * E. 42. A. B. C. D. E. * 43. A. B. C. D. E. * 44. A. B. C. D. E. * 45. A. * B. C. D. E. 46. A. * B. C. D. E. adults at increased risk include: travelers to areas or countries where polio is epidemic or endemic, individuals working with poliovirus in a laboratory setting, and healthcare workers in close contact with patients who may have poliovirus can’t be given while pregnancy at all IPV may be administered to pregnant women Rhabdovirus infection vaccination in pregnancy. Choose the incorrect answer: Pregnancy is not an absolute contraindication to rabies immunization Pregnant women at high risk for rabies exposure should be considered for pre-exposure immunization Post-exposure immunization is recommended for pregnant women in 1st trimestr. Post-exposure immunization is recommended for pregnant women in 2nd trimestr. Pregnancy is an absolute contraindication to rabies immunization. Measles, Mumps, Rubella vaccination in pregnancy. Choose the incorrect answer: No cases of congenital rubella syndrome have been reported after inadvertent MMR immunization in pregnancy. MMR immunization in pregnancy should not be considered an indication for pregnancy termination. Pregnant women should be screened for rubella immunity in pregnancy. Rubella non-immune women should be offered MMR immunization postpartum, prior to hospital discharge. Women should be advised to wait 4 weeks after immunization before becoming pregnant, due to the theoretical risk of immunization with a live vaccine. Pregnancy is a contraindication for MMR immunization. Women should be asked about their pregnancy status prior to immunization. Routine pregnancy testing is not recommended prior to vaccine administration. Is highly recommended at all terms of pregnancy routinely. Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) immunization in pregnancy. Choose the incorrect answer: Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) is a herpes virus that causes chickenpox and shingles. Varicella non-immune pregnant women should be immunized immediately postpartum, prior to hospital discharge. A second dose should be administered 4 weeks after the first dose, at the postpartum visit. Varicella vaccination in pregnancy should not be considered an indication for pregnancy termination. No cases of congenital varicella syndrome have been reported after varicella immunization. Varicella vaccination in pregnancy should not be considered an indication for pregnancy termination. Breastfeeding and Vaccines in pregnancy. What is the exception for vaccination while breastfeeding: smallpox and yellow-fever all live-attenuated vaccines are safe to administer to breastfeeding women influenza HPV (human papillomavirus) Hepatitis B, A The DFW Metroplex Cooperative RMS Group follow-up protocol for fetal wastage syndrome that is associated with hypercoagulable blood protein/platelet defects includes all medications EXCEPT: Warfarin Initial dose: 2 to 5 mg orally once a day, maintenance dose: 2 to 10 mg orally once a day Aspirin: 81 mg/d, start preconception (time of diagnosis) and Calcium: 500 mg/d by mouth (PO) Heparin: 5000 U SC q12h immediately postconception (added to aspirin, both to term) Prenatal vitamins (Iron: 1 tab/d PO, Folic acid: 1 mg/d PO) Dalteparin: 5000 U SC q24h immediately postconception (added to aspirin, both to term) 47. A. B. C. D. * E. 48. A. B. C. D. * E. 49. A. B. * C. D. E. 50. A. B. * C. D. E. 51. A. B. C. D. * E. 52. A. * B. C. D. E. Laboratory assessment for fetal wastage syndrome that is associated with hypercoagulable blood protein/platelet defects is necessary routinely EXCEPT: Fetal activity chart daily, starting at 28 weeks Biophysical profile and color Doppler flow ultrasonography of umbilical artery at 32, 34, 36, and 38 weeks Complete blood cell (CBC)/platelet count and heparin level (anti–factor Xa method) weekly for 4 weeks; then CBC/platelet count and heparin level monthly to term CT scan of uterus CBC/platelet count and heparin level monthly to term Mifepristone (Mifeprex, RU-486), choose false postulate: It is blocking progesterone (it is antiprogesterone) It provokes decidual necrosis and detachment of the pregnancy at the endometrium and uterine contractions ensue. It provokes abortion It is a hormone that maintains pregnancy It provokes softening and dilation of cervix; Carboprost tromethamine (Rx), choose false postulate: It is prostaglandin similar to F2-alpha It is blocking progesterone (it is antiprogesterone) It produces myometrial contractions that induce hemostasis at placentation site It has longer duration than dinoprost It is used for refractory postpartum uterine bleeding Methotrexate, choose false postulate: Is for Neoplasms treatment, Antineoplastic dosage range: 30-40 mg/m?/week to 100-12,000 mg/m? with leucovorin rescue It is blocking progesterone (it is antiprogesterone) Primarily affects rapidly dividing cells first, such as trophoblast cells. Is an antimetabolite that works by blocking enzyme dihydrofolate reductase, thereby inhibiting folate production and, thus, DNA synthesis Can be used for ectopic pregnancy management (Off-label), 50 mg/m? IM; Methotrexate, choose usage in gynecologic practice: Indicated for management of severe, active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in adults who have had an insufficient response or intolerance to an adequate trial of first-line therapy including full dose NSAIDs Meningeal Leukemia, Osteosarcoma For symptomatic control of severe, recalcitrant, disabling psoriasis in adults not adequately responsive to other forms of therapy; use only with established diagnosis (by biopsy and/or after dermatologic consultation) Trophoblastic neoplasms: 15-30 mg/day PO/IM for 5 days; may be repeated Myasthenia Gravis, Orphan designation for treatment of myasthenia gravis Oxytocin (Pitocin), choose FALSE postulate: provoke cervical effacement and dilatation has vasopressive and antidiuretic effects. controls postpartum bleeding or hemorrhage oxytocin is less effective than misoprostol for labor induction Produces rhythmic uterine contractions and can stimulate the gravid uterus 53. A. * B. C. D. E. 54. A. B. * C. D. E. 55. A. B. C. * D. E. 56. A. B. * C. D. E. 57. A. * B. C. D. E. 58. A. B. * C. D. E. 59. A. B. C. * D. Elective cerclage at 14-16 weeks: Recommendations: in high risk cases, as identified from the history of previous mid-trimester pregnancy losses Is recommended when there is bloody discharge from the vagina Is recommended to correct the position of the fetus Is recommended with placenta previa Is recommended when placental abruption is diagnosed Recommendations for cervical cerclage: Is recommended when there is bloody discharge from the vagina Cervical cerclage in response to shortened cervical length (as detected by ultrasound) is a reasonably successful option Is recommended to correct the position of the fetus Is recommended with placenta previa Is recommended when placental abruption is diagnosed Emergency or rescue cerclage: Recommendations: Is recommended to correct the position of the fetus Is recommended with placenta previa can be used up to 25-26 weeks, in response to an open cervix with bulging membranes; can be used up to 35-36 weeks, in response to an open cervix with bulging membranes; Is recommended when placental abruption is diagnosed Cervical cerclage in response to shortened cervical length (as detected by ultrasound) was predictive of delivery at less than 35 weeks. In women with ultrasound-indicated cerclage, optimized cut-off was 10 mm In women with ultrasound-indicated cerclage, optimized cut-off was 20 mm In women with ultrasound-indicated cerclage, optimized cut-off was 30 mm In women with ultrasound-indicated cerclage, optimized cut-off was 40 mm In women with ultrasound-indicated cerclage, optimized cut-off has no meaning Choose the correct answer (cervical length and risk of preterm labor) Rates of preterm labor increase fourfold among women with a cervical length of less than 25 mm at 24 weeks' gestation. Cervical length is unimportant clinical sign Normal cervical length in pregnancy is more than 50 mm Normal cervical length in pregnancy is more than 60 mm Normal cervical length in pregnancy is more than 70 mm Choose the correct answer (cervical length and risk of preterm labor) Normal cervical length in pregnancy is more than 50 mm Cervical length, as determined on ultrasonograms, is inversely proportional to the risk of preterm labor. Normal cervical length in pregnancy is more than 60 mm Normal cervical length in pregnancy is more than 70 mm Cervical length is unimportant clinical sign Choose the correct answer (cervical length and risk of preterm labor) Normal cervical length in pregnancy is more than 70 mm Cervical length is unimportant clinical sign The cervical length decrease to less than 34 mm at 28 weeks' gestation Normal cervical length in pregnancy is more than 50 mm E. 60. A. B. C. D. E. * 61. A. B. C. * D. E. 62. A. B. C. D. * E. 63. A. B. C. D. * E. 64. A. B. C. D. E. * Normal cervical length in pregnancy is more than 60 mm Choose the only FALSE answer about cervical incompetence and preterm labor: The typical clinical scenario is that of ‘silent’ or ‘painless’ dilatation of the cervix, leading to bulging fetal membranes extruding through the external os. Cervical incompetence is a frequent cause of inevitable miscarriage in the second trimester, and it is often associated with a poor fetal outcome. It is a functional condition associated with a history of recurrent and usually painless, spontaneous second-trimester abortions. Cervical incompetence is defined as cervical dilatation without uterine contractions. Cervical incompetence is a frequent cause of inevitable miscarriage in the first trimester, and it is often associated with a poor fetal Choose the correct answer about cervical incompetence and preterm labor: The typical clinical scenario is extremely painful dilatation of the cervix, leading to bulging fetal membranes extruding through the external os. Cervical incompetence is the most rare cause of inevitable miscarriage in the second trimester, and it is often associated with a poor fetal outcome. It is a condition associated with a history of recurrent and usually painless, spontaneous second-trimester abortions. Cervical incompetence is defined as cervical dilatation with regular uterine contractions. Pregnant women with cervical incompetence usually present with silent cervical dilatation between 6 and 8 weeks of gestation. Choose the only FALSE answer about cervical incompetence and preterm labor: When the cervix reaches 4 cm or more, active uterine contractions or rupture of membranes may ensue. Cervical incompetence may occur with clinically significant cervical dilation of 2 cm or more but with minimal symptoms. Pregnant women with cervical incompetence usually present with silent cervical dilatation between 16 and 24 weeks of gestation. Pregnant women with cervical incompetence usually present with silent cervical dilatation between 6 and 8 weeks of gestation. Fetal fibronectin isn’t an accurate test for cervical incompetence. Fetal fibronectin (FFN) Choose false postulate about fetal fibronectin (FFN): FFN is a glycoprotein found in amniotic fluid, placental tissue and the deciduas basalis. It is normally found in the cervicovaginal secretions before 16 weeks of pregnancy, a time at which the fusion between the amnion and the decidua is not yet completed. it is not normally present in the cervicovaginal secretions after 22 weeks appears after some antibiotics use In women being screened for preterm labor, FFN provides a good negative predictive test (ie, a negative FFN rules out preterm labor). Choose false postulate about fetal fibronectin (FFN) FFN cannot be used as a test for cervical incompetence. In women being screened for preterm labor, FFN provides a good negative predictive test (ie, a negative FFN rules out preterm labor). It appears in the secretions due to disruption of the chorionic-decidual interface and is often secondary to infection. Cervical incompetence manifests around 16-20 weeks, a time when FFN may be found in the cervicovaginal secretions in normal conditions. FFN is the best to choose as a test for cervical incompetence. 65. A. B. C. D. E. * 66. A. B. C. D. * E. 67. A. B. C. D. * E. 68. A. B. C. D. E. * 69. A. B. * C. D. E. 70. A. B. C. D. * E. 71. Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS). Choose the FALSE answer: TTTS is the result of an intrauterine blood transfusion from one twin (donor) to another twin (recipient). TTTS only occurs in monozygotic (identical) twins with a monochorionic placenta. The donor twin is often smaller with a birth weight 20% less than the recipient's birth weight. The donor twin is often anemic and the recipient twin is often plethoric with hemoglobin differences greater than 5 g/dL. need an urgent fetocide of one of the fetuses Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS). Choose the FALSE answer: Monozygotic twins with monochorionic, diamniotic placentation or monochorionic, monoamniotic placentation are at risk for TTTS TTTS is a specific complication of monozygotic twins with monochorionic placentation. The most common vascular anastomosis is a deep, artery-to-vein anastomosis through a shared placental cotyledon. Can be effectively treated with antibiotics Severe TTTS has a 60-100% fetal or neonatal mortality rate. Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS). Choose the FAlSE answer: Acute exsanguination of the surviving twin into the relaxed circulation of the deceased twin can result in intrauterine CNS ischemia. Fetal demise of one twin is associated with neurologic sequelae in 25% of surviving twins. Severe TTTS has a 60-100% fetal or neonatal mortality rate. Can be effectively treated with glucose, protein, antihypoxant solutions intravenous supply The recipient twin can also develop hypertension, hypertrophic cardiomegaly, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and hyperbilirubinemia after birth. Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS). Choose a FALSE postulate: The recipient twin can also develop hypertension, hypertrophic cardiomegaly, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and hyperbilirubinemia after birth. The recipient twin can also develop hypertension, hypertrophic cardiomegaly, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and hyperbilirubinemia after birth. The recipient twin can become hydropic because of hypervolemia. The donor twin can become hydropic because of anemia and high-output heart failure. Can be effectively treated with glucose, protein, antihypoxant solutions intravenous supply Management of severe TTTS: Amniotomy at any term Fetoscopic laser photocoagulation of chorionic plate vessels is a highly specialized procedure Fetocide Antibiotics administration Glucose, protein, antihypoxant solutions intravenous supply Fetal death can occur at any gestational age and usually results from fetal hypoxia acidosis, and compromise. The signs are EXCEPT: a maternal PaO2 less than 60 mm Hg (oxygen saturation < 90%) decrease in maternal mean blood pressure of 20% during pregnant surgery a decrease in maternal hematocrit greater than 50% moderate obesity oxygen saturation < 90% Choose the laboratory tests data those can’t be correct: A. B. C. * D. E. 72. A. B. C. * D. E. 73. A. B. C. * D. E. 74. A. * B. C. D. E. 75. A. B. * C. D. E. 76. A. B. C. * D. E. 77. A. * B. C. D. E. Total cholesterol (mg/dL) Pregnant 250; Nonpregnant 120; Triglycerides (mg/dL) Pregnant 230; Nonpregnant 45-150 Total cholesterol (mg/dL) Pregnant 120; Nonpregnant 250; Chloride (mEq/L) Pregnant 90-105; Nonpregnant 100-106 Bicarbonate (mEq/L) Pregnant 17-22; Nonpregnant 24-30 Choose the laboratory tests data those can’t be correct: PO2 (mm Hg) Pregnant 98-100; Nonpregnant 101-104 PCO2 (mm Hg) Pregnant 35-50; Nonpregnant 25-30 PCO2 (mm Hg) Pregnant 85-90; Nonpregnant 25-30 Chloride (mEq/L) Pregnant 90-105; Nonpregnant 100-106 Bicarbonate (mEq/L) Pregnant 17-22; Nonpregnant 24-30 Choose the correct management for hyperemesis gravidarum: Oxytocine 10 IU Ampicillin Intravenous hydration should be administered to patients who are unable to tolerate oral fluids for a prolonged period and if clinical signs of dehydration develop. Tranexamic acid Ceftriaxone Level A and Level B recommendations for Hyperemesis gravidarum management include: Use Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) alone or in combination with doxylamine as first-line pharmacotherapy, as they are safe and effective. Ampicillin is helpful Progestines are highly recommended Tranexamic acid Ceftriaxone Level A and Level B recommendations for Hyperemesis gravidarum management include: Ceftriaxone Methylprednisolone has been effective in some refractory cases of severe nausea and vomiting of pregnancy; however, it should be considered a last-resort treatment as a result of its risk profile. Tranexamic acid Ampicillin is helpful Progestines are highly recommended Level A and Level B recommendations for Hyperemesis gravidarum management include: Tranexamic acid Ceftriaxone Ginger may be used as a nonpharmacologic option, as it has had some beneficial effects in the treatment of nausea and vomiting of pregnancy. Ampicillin is helpful Progestines are highly recommended Clinical event associated with chorioamnionitis, choose the correct answer: Prolonged rupture of the fetal membranes (>18 hours) Mild hypertensive disorders Myopia in woman A glass of wine occasionally during pregnancy Bicycle ride 78. A. B. C. * D. E. 79. A. * B. C. D. E. 80. A. B. C. D. * E. 81. A. B. C. D. E. * 82. A. B. C. D. E. * 83. A. B. C. * D. E. Clinical events associated with chorioamnionitis, choose the correct answer: Myopia in woman A glass of wine occasionally during pregnancy Preterm premature rupture of fetal membranes (before labor onset) Mild hypertensive disorders Bicycle ride Therapy for the mother and/or neonate with chorioamnionitis includes early delivery, supportive care, and antibiotic administration. What antibiotics should be avoided: gentamicin Cefoxitin Clindamycin Ampicillin Metronidazole Maternal fever (intrapartum temperature >100.4°F or >38.0°C). Baseline fetal tachycardia (>160 beats per min for 10 min or longer, excluding accelerations, decelerations, and periods of marked variability), Maternal leukocytosis (total blood leukocyte count >15,000 cells/?L) in the absence of corticosteroids, Definite purulent fluid from the cervical os, polyhydroamnion and uterine tenderness; The following signs are typical in obstetrics for diagnosis: Thyroid cancer in pregnancy Uterine rupture Placenta abruption Chorioamnionitis Start of normal labor What medications can not cause abnormal uterine bleeding: Adrenal steroids Psychotropic medications Tranquilizers affecting neurotransmission Ginseng use Tranexamic acid Common laboratory studies for patients with abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) include all EXCEPT: human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), complete blood count (CBC), thyroid functions and prolactin, liver functions, coagulation studies/factors, and other hormone assays as indicated Pap smear, endometrial sampling Blood type, Rh factor IgG to Rubella, Toxoplasma, Smallpox High-risk women >35 years with chronic eugonadal anovulation, obesity, hirsutism, diabetes, or chronic hypertension and with abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) are at extreme risk for endometrial hyperplasia/carcinoma, and what procedure must be recommended: Pap smear Coagulation factors Endometrial sampling Thyroid and liver function tests Complete blood count 84. A. B. C. D. E. * Low-dose combination hormonal contraceptive therapy (20-35 ?g ethinylestradiol) is the mainstay of treatment or at least acceptable for all EXCEPT: adolescents up to age 18 years in women aged 19-39 years; in prepuberty (8-10 years) for women aged 40 years or older Menopause over a year