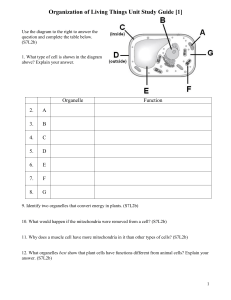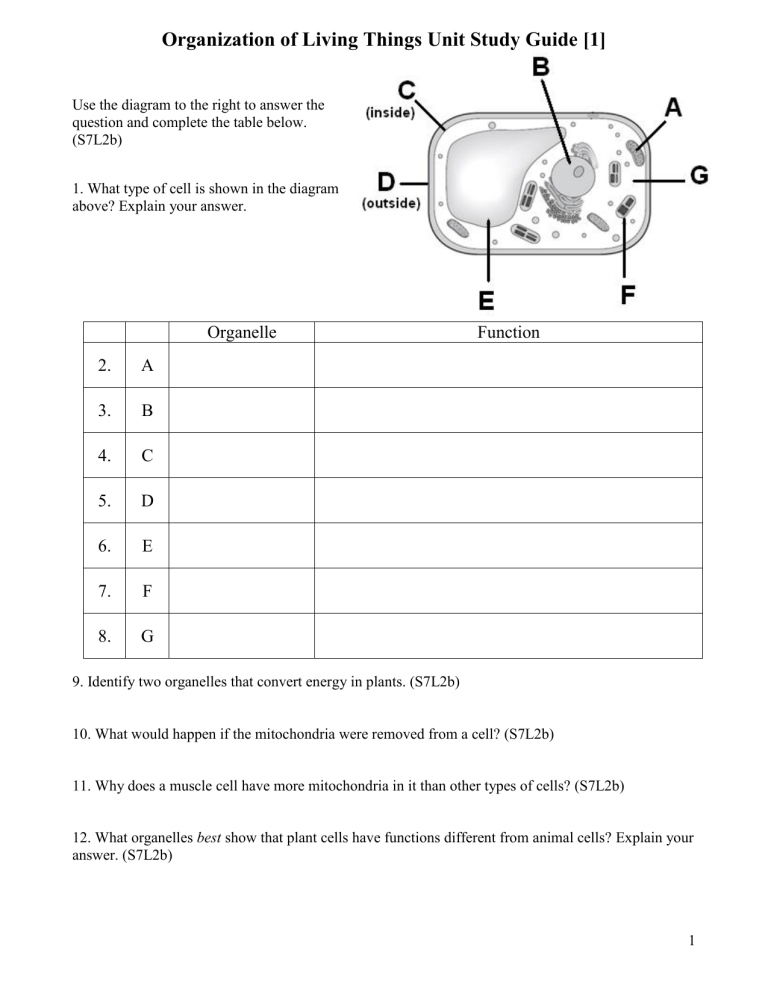
Organization of Living Things Unit Study Guide [1] Use the diagram to the right to answer the question and complete the table below. (S7L2b) 1. What type of cell is shown in the diagram above? Explain your answer. Organelle 2. A 3. B 4. C 5. D 6. E 7. F 8. G Function 9. Identify two organelles that convert energy in plants. (S7L2b) 10. What would happen if the mitochondria were removed from a cell? (S7L2b) 11. Why does a muscle cell have more mitochondria in it than other types of cells? (S7L2b) 12. What organelles best show that plant cells have functions different from animal cells? Explain your answer. (S7L2b) 1 Organization of Living Things Unit Study Guide [1] 13. Cells and their organelles are often compared to the parts of a factory. Explain to which part of a factory the nucleus of a cell is most often compared. (S7L2b) 14. Explain the difference between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell. (S7L2b) 15. Identify whether each cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Explain your answer. (S7L2b) 16. Identify whether the following statements are True or False. If the statement is False, explain why it is False. (S7L2c) a. You are made up of about 100 trillion cells, but you began as a single cell. b. The stomach, heart, and a plant leaf are all examples of a tissue in the body. c. A tissue is more complex than an organ. 17. Identify the images below as one of the following: organ, tissue, organism, organ system (S7L2c) 18. Put the levels of organization from the images to the right in order from simple to more complex. (S7L2c) 19. Which basic level of organization is not identified in the levels above? Unlike the other levels, why is this one normally not visible? 2