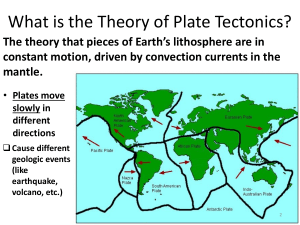
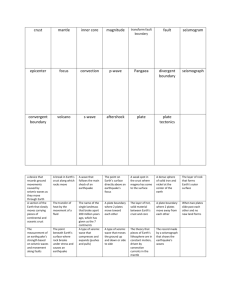
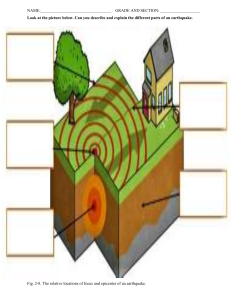
Grade 10 Science ST 1 QUARTER EXAMINATION Score: Name: Grade & Section: Direction: Choose the letter of the best answer. Write the letter before each number. 1. The idea proposed by Alfred Wegener to explain the continental shapes and positions is known as . A. Pangaea C. Plate Tectonics B. Elastic Rebound D. Continental Drift 2. When a volcanic eruption spews gases and ash into the air, which two spheres are interacting? A. hydrosphere and geosphere C. geosphere and atmosphere B. biosphere and geosphere D. biosphere and atmosphere 3. According to the Continental Drift Theory, the Earth was one big supercontinent called: A. Gondwana C. Laurasua B. Pangaea D. Panthalassa 4. When Earth’s crust bends, forces act towards each other, this phenomenon may result to: A. earthquake C. tsunami B. folding D. faulting 5. When the Earth’s crust cracks and tension forms or develops, this phenomenon is called: A. earthquake C. tsunami B. folding D. faulting 6. The supercontinent called Pangaea was believed to exist million years ago. A. 120 C. 200 B. 100 D. 300 7. The Earth is estimated to be around 4.6 billion years old, this data was based from: A. the presence of heat in the earth’s core C. the amount of gases in the atmosphere B. record of earthquake on Earth D. rock and fossils record 8. 80% of all earthquakes occur in the . A. Atlantic Belt C. Mediterranean-Asiatic Belt B. Caribbean Belt D. Pacific Belt 9. This explains the concept of earthquake, where rocks bend until the strength of th rock is exceeded and rupture occurs. A. Sea-floor Spreading C. Plate Tectonics B. Elastic Rebound D. Continental Drift 10.Tsunamis are big waves that are caused by: A. Strong winds C. earthquake or volcano eruption on land B. Cyclones D. underwater earthquake or volcanic eruption 11. These are push and pull waves that expand in the direction the waves travel; has the greatest velocity of all earthquake waves. A. P waves C. Love waves B. S waves D. Rayleigh waves 12. This wave moves up and down and side-to-side. The second wave you feel in an earthquake. A. P waves C. Love waves B. S waves D. Rayleigh waves 13. Earthquake epicentres are identified through . A. Richter Scaling C. Triangulation Method B. Seismographic Method D. Scaling Method 14. The largest earthquake recorded in the world happened in . A. Alaska C. USA B. Chile D. Japan 15. Which clue is used to show that the continents used to fit together in a super continent millions of years ago? A. GPS data C. fossils and rocks record B. gravitational changes D. magnetic poles shifting 16. When two continental plates collide, edges of the continents are pushed upward to form: A. rift valley C. trench B. continental mountain range D. volcano 17. Which of the following best describes how heat travels through the Earth’s layers? A. heat from radiation in the core passes through convection currents in the mantle B. heat from convection currents in the core passes through radiation in the mantle C. heat from the core passes through conduction to the mantle D. heat from the mantle passes to the core and to the lithosphere 18. To locate the epicenter of an earthquake, a seismologist must determine all of the following EXCEPT: A. the velocity of both P waves and S waves B. the types of fault from which it originated C. the difference in travel times between P waves and S waves D. the distance from the epicenter to at least three different seismological stations 19. All of the following are true of tsunami EXCEPT: A. they can travel at speeds greater than 500 miles per hour. B. they are caused by undersea earthquakes. C. they are often responsible for the destruction of ships at sea. D. they can often form waves more than 100 feet high. 20. The point on Earth's surface directly above the focus of an earthquake is the . A. focus C. fault B. epicenter D. inner core 21. What does a seismograph record? A. the Mercalli scale rating for an earthquake B. the speed of seismic waves C. the ground movements caused by seismic waves D. the location of the epicenter 22. The higher the waves on a seismogram the . A. stronger the earthquake C. closer the earthquake B. weaker the earthquake D. None of these 23. Scientists think that convection currents flow in Earth's A. continents C. asthenosphere B. inner core D. lithosphere 24. A boundary where plates move away from each other is called: A. divergent C. transform B. convergent D. shear 25. A deep crack in the earth’s surface is called a : A. ridge C. fold B. plate D. fault 26. How does the plates move at a transform boundary? A. they move toward each other C. they move past each other B. they move away from each other D. they do not move 27. A boundary where plates move away from each other is called: A. divergent boundary C. transform boundary B. shear boundary D. convergent boundary 28. What kind of plate boundary results to the formation of most volcanoes? A. divergent boundary C. transform boundary B. shear boundary D. convergent boundary 29. What kind of plate boundary results to the formation of San Andreas fault? A. divergent boundary C. transform boundary B. shear boundary D. convergent boundary 30. When magma reaches the earth’s surface, it is called: A. rock C. lava B. magma D. caldera 31. The very large, bowl-shaped depression on top of a volcano due to eruption is called a: A. peak C. crater/caldera B. ridge D. vent 32. The three types of volcanoes are cinder-cone, shield, and: A. vent C. caldera B. viscous D. composite 33. The highest mountain in the Philippines is . A. Mount Kilauea C. Mount Mayon B. Mount Apo D. Mount Arayat 34. The outer core is made up of: A. solid iron and nickel C. solid iron and aluminum B. liquid iron and nickel D. liquid iron and aluminum 35. Scientists believed that this layer is responsible for Earth’s magnetic field. A. asthenosphere C. mantle B. crust D. core 36. These are processes that are caused by forces from within the earth. A. earthquake C. endogenic B. erosion D. exogenic 37. These are processes that come from forces on or above the Earth’s surface. A. earthquake C. endogenic B. erosion D. exogenic 38. The most abundant element in the earth’s crust is: A. carbon C. iron B. oxygen D. silicon 39. The inside of the Earth consists of four major layers. Which is the hottest layer? A. inner core C. mantle B. crust D. outer core 40. The order of the layers from the inside of the Earth outward is: A. inner core, outer core, mantle, crust C. inner core, outer core, crust, mantle B. outer core, inner core, mantle, crust D. mantle, inner core, outer core, crust 41. The thinnest layer of the earth is the: A. inner core C. mantle B. crust D. outer core 42. The Himalayan mountains are thought to have been formed by the collision of A. two continental plates C. two oceanic plates B. two transform faults D. an oceanic plate and a continental plate 43. Subduction is: A. where denser plates sink into the mantle B. where ridge valleys form C. occurring mostly in the Atlantic Ocean D. occurring where continental plates diverge 44. What are the two type of crust? A. thick and thin C. ocean and basin B. continental and oceanic D. lower and upper 45. What drives tectonic plate movement? A. magnetic field C. convection currents B. gravity D. pressure 46. What do transform plate boundaries create? A. hurricanes C. trenches B. portal to purgatory D. earthquakes 47. Rising magma that results from subduction may produce… A. fossil layers C. volcanic island arcs B. sea-floor spreading D. deep-sea sediment 48. How do scientists use sound waves to figure out the shape of the ocean floor? A. the longer it takes a sound wave to return to the ship, the deeper the water is B. the longer it takes a sound wave to return to the ship, the more shallow the water is C. the longer it takes a sound to return to the ship, the colder the water is D. the less time it takes a sound wave to return to the ship, the deeper the water is 49. What two specific continents fit together most noticeably? A. Antarctica and Africa C. Africa and North America B. South America and Africa D. South America and Europe 50. Which statements below best explains Wegener’s hypothesis of continental drift? A. Volcanic activity slowly reshapes the continents throughout the earth’s geologic history B. The continents shift locations as a result of major catastrophe like meteorite impacts and earthquakes C. The continents rapidly change places from one hemisphere to another when Earth’s magnetic field reverses. D. The continents were once part of the same landmass and have drifted very slowly to their current positions.