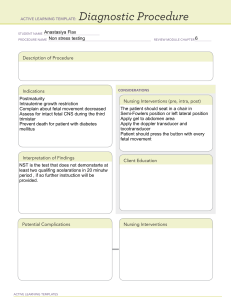
SAS 1 Primary Goal of Maternal and Child Health Nursing - The promotion and maintenance of optimal family health to ensure cycles of optimal childbearing and childrearing. Philosophy of Maternal and Child Health Nursing: Family – centered – assessment data must include family and individual assessment. Community – centered – health of families depends on influences the health of communities Evidence – based – provide a foundation for nursing care, studies, conducts, and etc. Maternal and Child Health Goals and Standards Global Health Goals UN and WHO established Millennium Health Goals in 2000 to improve health world wide MILLENNIUM DEVELOPMENT GOALS – 8 goals; created by UN in 2000; to eradicate poverty, hunger, illiteracy, and disease, expired in 2015. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger Achieve universal primary education Promote gender equality and empower women Reduce child mortality Improve maternal health Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria and other diseases Ensure environmental sustainability Develop a global partnership for development SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS – 17 goals; created by UN in 2015 for year 2030; aims to transform our world and improve people’s lives and prosperity on a healthy planet. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. No poverty No hunger Good health and well-being Quality education Gender equality Clean water and sanitation Affordable and clean energy Decent work and economic growth Industry innovation and infrastructure Reduced inequalities Sustainable cities and communities Responsible consumption and production Climate action Life below water Life of land Peace, justice and strong institutions Partnerships for the goals THEORIES RELATED TO MATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH NURSING - Callista Roy – Adaptation Theory nurses’ role is to help patient adapt to change caused by illnesses or other stressors Dorothea Orem – Self- Care Theory involves examining the patient’s ability for self – care Patricia Benner – Novice – Expert Model describes nurse’s move from novice to expert Scope of Nursing Practice - PHILIPPINE NURSING ACT OF 2002 – RA 9173 6 COMPETENCIES NECESSARY FOR QUALITY CARE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Patient – centered care Teamwork & collaboration Evidence – based practice Quality Improvement Safety Informatics DEFINITIONS OF FAMILY - A group of people related by blood, marriage, or adoption living together Two or more people who live in the same household, share a common emotional bond, and perform certain interrelated social tasks. INFLUENCES OF FAMILY ON ITS MEMBERS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Provides long lasting emotional ties Provides a depth of support Determines how members relate to people Influences what moral values members follow Molds the members’ basic perspectives on the present and future BASIC FAMILY TYPES 1. Family orientation Refers to the family in which a person is raised The family one is born into (e.g., oneself, mother, father, and siblings) 2. Family of procreation the family that we create by getting married and having children the family one establishes (e.g., oneself, spouse, and children) RECOGNIZED FAMILY STRUCTURES Childfree / Childless family – 2 people living together without children Cohabitation family- unmarried couples with children that live together Nuclear family – composed of the parents and children Extended family – nuclear family with other relatives Single parent family – single mother/father and child/ren Blended family – a divorced or widowed person with children marries someone who also has children 7. Dyad family – a newly married / or single couples living together living together as a dyad for companionship and financial security 8. Binuclear family – a family created by divorce or separation when the child is raised in two families 9. Communal family – a group of people who chose to live together as an extended family; motivated by religious values 10. LGBT family – individuals of the same sex live together as partners for companionship, financial security, and sexual fulfillment 11. Foster family – people who officially take a child into their family for a period of time, without becoming the child's legal parents 12. Adoptive family - a family who has welcomed a child born to another into their family and legally adopted that child as their own. 13. Polygamous family – marriage with multiple spouses Polygyny – man with several wives Polyandry – woman with several husbands 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. UNIVERSAL CHARACTERISTICS OF A FAMILY 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Small social system Performs certain basic functions Has structure Has its own cultural values and roles Moves through stages in the life cycle 8 FAMILY TASKS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Physical maintenance Socialization of family members Allocation of resources Maintenance of order Division of labor Reproduction, recruitment and release of family members Placement of members into the larger society Maintenance of motivation and morale FAMILY LIFE CYCLES I. II. III. IV. V. VI. VII. VIII. Marriage The early childbearing family Family with a pre-school child Family with a school-age child Family with an adolescent Launching stage family Family of middle years Family in retirement or old age BOOMERANG GENERATION – young adults return home to live with parents after college until they can afford their own apartment or form a new relationship SANDWICH FAMILY – a family that is squeezed into taking care of both aging parents and a returning young adult EMPTY NEST SYNDROME – a feeling of boredom or grief and loneliness parents may feel when their children leave home for the first time GENOGRAM – diagram that details family structure, provides family history and the roles of various family members over time. Provides a basis for discussion and analysis of family interaction. ECOMAP – to document the fit of a family in their community; a diagram of family and community relationships FAMILY APGAR – a screening tool of the family environment SAS 2 OBSTETRICS – branch of medicine that deals with the care of women during pregnancy, labor, and the period of recovery following childbirth; OBSTARE = to keep watch GYNECOLOGY – study of the female reproductive organ and diseases affecting it ANDROLOGY – study of the male reproductive organ PEDIATRICS – branch of medical science in children and their illnesses; PAIS = child NEONATOLOGY – the branch of medicine concerned with the development and disorders of newborn babies SEXUAL HEALTH – not just an absence of disease, dysfunction, or infirmity but a condition of physical, emotional and psychological well-being GONAD – a body organ that produces the cells necessary for reproduction (e.g., ovary, testes) WOLFFIAN DUCTS (MESONEPHRIC) - are the progenitors of the epididymis, vas deferens, and seminal vesicles in males MÜLLERIAN DUCTS (PARAMESONEPHRIC) - become the fallopian tubes, uterus, and part of the vagina in females ADRENARCHE – awakening of the adrenal glands ANDROGENS – hormones produced by the adrenal glands; testes in males and ovaries in females THELARCHE – beginning of breast development. Starts 1 -2 years before menstruation MENARCHE – the beginning of menstruation SCROTUM – pouch that holds the testis; left scrotum is larger and lower due to longer spermatic cord CREMASTER MUSCLE – responsible for contraction of the scrotum MIDLINE SEPTUM – separates each sac; each compartment contains a testis, its epididymis and a part of the spermatic cord LEYDIG’S CELLS – the primary source of testosterone or androgens in males. CORPUS SPONGIOSUM – contains the urethra which serves as a passage for both sperm and urine PENILE ARTERY – supplies blood to the penis GLANS – bulging, sensitive ridge of tissue at the end of the distal end of the penis; similar to clitoris PREPUCE/FORESKIN – retractable casing of skin, protects the glans PHIMOSIS – condition in which the prepuce is too tight that it interferes with the flow of urine EPIDIDYMIS – a tightly coiled tube responsible for conducting sperm from the tubule to the vas deferens; storage of immature sperm ASPERMIA – absence of sperm OLIGOSPERMIA – fewer than 20 million sperm per milliliter VAS DEFERENS – an additional hollow tube surrounded by arteries and protected by thick fibrous coating, which altogether, are referred to as the spermatic cord; site severed during vasectomy PROSTATE GLAND – secretes a thin, alkaline fluid that protects the sperm by increasing the naturally low pH level of the urethra BULBOURETHRAL GLAND – supply one more source of alkaline fluid to help ensure the safe passage of spermatozoa SEMEN – 60% prostate gland; 30% seminal vesicles; 5% epididymis; 5% bulbourethral glands URETHRA - duct that transmits urine from the bladder to the exterior of the body during urination MONS PUBIS – pad of adipose tissue located over the symphysis pubis – the pubic bone joint; protects the junction of the pubic bone from trauma LABIA MAJORA – 2 folds of adipose tissue covered by loose connective tissue and epithelium; protects the external genitalia and inner vulva structures LABIA MINORA – 2 flat hairless, reddish folds of connective tissue; located between labia majora; protects and obscures the vestibule, urinary meatus and vaginal os FOURCHETTE - torn during childbirth and site of episiotomy VESTIBULE – contains openings to the urethra, vagina, skene’s glands and Bartholin glands GLANS CLITORIS – rounded organ of erectile tissue; site of sexual arousal and orgasm in females SKENE’S GLANDS – located on each side of the urinary meatus; produce alkaline mucus for lubrication and protection BARTHOLIN GLANDS – located each side of the vaginal opening; secrete alkaline substance to lubricate the vaginal orifice and neutralize the acidity of the vagina; site of Bartholin’s cyst (Bartholinitis) PERINEAL MUSCLE – located posterior to the fourchette; muscular area stretched during childbirth HYMEN – tough but elastic tissue that covers the vagina IMPERFORATE HYMEN – hymen so complete it does not allow passage of menstrual blood from the vagina or for sexual relation until it is surgically incised. OVARIES – size and shape of almonds; produce, mature and discharge egg cells; produce estrogen and progesterone and initiate and regulate menstrual cycle; organ of ovulation, oogenesis, and hormone production - TUNICA ALBUGINEA – protective layer of epithelium CORTEX – filled with ovarian and graafian follicle MEDULLA – contains nerves, blood vessels, lymphatics FALLOPIAN TUBES/OVIDUCTS/UTERINE DUCTS – convey the ovum from the ovaries to the uterus and to provide a place for fertilization of the ovum by the sperm - INTERSTITIAL – most proximal; lies within uterine walls; most dangerous site for ectopic pregnancy ISTHMUS – next distal portion; extremely narrow; site for bilateral tubal ligation AMPULLA – 3rd and longest portion; site of fertilization INFUNDIBULLUM – most distal; rim is covered in fimbriae, that helps guide the ovum into the fallopian tube. UTERUS – hollow. Muscular, pear-shaped organ located in the lower pelvis - CORPUS – uppermost part and forms the bulk of the organ FUNDUS – uppermost part of the corpus ISTHMUS – short segment between the body and the cervix; incision area for cesarean birth; the lower uterine segment during pregnancy CERVIX - lowest portion of the uterus its central cavity is termed cervical canal opening of the canal at the junction of the cervix and isthmus is the internal cervical os the distal opening to the vagina is the external cervical os the level of the external os is at the level of the ischial spines ENDOMETRIUM – inner layer of mucous membrane; innermost layer - composed of 3 layers; compact; spongy and basal basal layer is unaffected by hormones compact and spongy are sloughed off during menses; greatly affects by hormones MYOMETRIUM – middle layer of muscle fibers; 3 interwoven layers of smooth muscles arranged in longitudinal, transverse and oblique directions; provides strength to the organ during contractions PERIMETRIUM – an outer layer of connective tissue that provides support MACKENRODT LIGAMENTS - main support of the uterus; damage to this ligament results to uterine prolapse - occurs when pelvic floor muscles and ligaments stretch and weaken until they no longer provide enough support for the uterus PERITONEAL LIGAMENTS – the sides of the uterus and assists in holding the uterus in propped forward - - RIGHT LIGAMENT - connects the uterus to the labia majora and gives stability to the uterus ANTERIOR LIGAMENT provides support to the uterus in connection with the bladder CYSTOCELE – herniation of the bladder to the vagina due to overstretching POSTERIOR LIGAMENT forms the cul – de – sac or pouch of Douglas RECTOCELE – herniation of the rectum to the vagina due to damage VAGINA hollow and musculo-membranous rigae makes the vagina elastic and expand during childbirth from the cervix of the uterus to the external vulva organ of intercourse and birth canal FORNICES – recesses at the cervical end of the vagina; posterior, anterior and lateral - POSTERIOR FORNIX – site where the semen pools after intercourse Lined with stratified squamous epithelium similar to the cervix DODERLEIN’S BACILLUS – provides some sort of protection in the vagina against certain potentially harmful bacteria. BULBOCAVERNOUS MUSCLE – acts as a voluntary sphincter MAMMARY GLANDS – located anterior to the pectoralis major muscle; divided into 15 – 20 lobes divided in lobules LOBULES – clusters of acinar cells/acini – sac like terminal parts of the gland emptying through a narrow lumen of duct lined with epithelial cells that secretes milk and colostrum - is the first milk your body produces during pregnancy. - MYOEPITHELIUM – contracts to expel milk from the acini into the lactiferous or milk ducts towards the nipple LACTIFEROUS SINUSES/AMPULLA – serves as milk reservoirs; located posterior to the nipple AREOLA - - - MONTGOMERY’S TUBERCLES – sebaceous glands that makes the areola appear rough Stimulation leads the anterior pituitary glands to secrete oxytocin, which makes the myoepithelium to contract, pushing milk forward to the nipples (letdown reflex / milk ejection reflex) Increase in progesterone and estrogen, 3 – 4 days before menses increase vascularity of the breasts, induce growth of ducts and acini, promotes H2O retention, resulting in breast swelling, tenderness and discomfort. After menses, regression occurs and H2O is lost and reaches minimal alteration levels 5 – 7 days after menses. BREAST SELF – EXAMINATION – best done after menses ESTROGEN – development of the ductile structure of the breast PROGESTERONE – development of the acinar structures of the breast HUMAN PLACENTAL LACTOGEN (HPL) – breast development during pregnancy OXYTOCIN – let down reflex or milk ejection reflex PROLACTIN – directly stimulates milk production FALSE PELVIS – upper half that supports the uterus during late months of pregnancy and aids in directing fetus into the true pelvis for birth TRUE PELVIS – inlet, pelvic cavity, outlet LINEA TERMINALIS – imaginary line that divides pelvis into true and false pelvises SAS 3 CHARACTERISTICS OF A NORMAL MENSTRUAL CYCLE - Beginning o MENARCHE – first occurrence of menstruation o Average age: 12.4 years old o Average range: 9 – 17 years old - INTERVAL BETWEEN CYCLES o Average: 28 days o 23 – 35 days is unusual - DURATION OF MENSTRUAL FLOW o Average: 4 – 6 days o 2 – 9 days is abnormal - AMOUNT OF MENSTRUAL FLOW o Average: 30 – 80 mL per menstrual period o Saturation of pad in less than 1 hour is abnormal bleeding - COLOR OF MENSTRUAL FLOW o Dark red; combination of blood mucus and endometrial cells - ODOR o Similar to marigolds MENSTRUAL CYCLE - Definition: episodic uterine bleeding in response to the cyclic hormonal changes Purpose: to bring an ovum to maturity and renew uterine tissue bed that is responsible for the growth of the fertilized ovum. Release is triggered by FSH, ovaries in females excrete a high level of estrogen HYPOTHALAMUS - Releases of GnRH (aka LHRH) to initiate the menstrual cycle GnRH stimulates pituitary glands to send gonadotrophic hormone to the ovaries to produce estrogen ↑ estrogen, release of GnRH is repressed and no further menstrual cycles will occur GNrH – Gonadotropin – Releasing Hormone LHRH – Luteinizing hormone – releasing hormone PITUITARY GLAND - - Under the influence of GnRH Anterior lobe of pituitary gland (adenohypophysis) produces two hormones: Follicle – stimulating hormone (FSH) Is a hormone active early in the cycle that is responsible for maturation of the ovum Luteinizing hormone (LH) Responsible for ovulation, or release of mature egg from the ovary Stimulates growth of the uterine lining during the second half of the menstrual cycle Is a hormone that becomes most active at the midpoint of the cycle FSH and LH are called gonadotropic hormones because they cause growth (trophy) in the gonads (ovaries). OVARIAN CYCLE A. PROLIFERATIVE PHASE – day 1 – 14 of a 28-day menstrual cycle Oocytes are activated by FSH to begin grow and mature As oocyte grow, its cells produce a clear fluid called follicular fluid – contains a high degree of estrogen and progesterone. As the follicle surrounding oocyte grows, it is propelled toward the surface of the ovary as a clear blister called Graafian follicle - a mature fluid-filled cavity presents inside the ovary which contains the female gamete/ovum. ↑ LH, prostaglandins are released and the graafian follicle ruptures (ovulation) Happens on the 14th day before the onset of the next cycle OOCYTE – immature female egg OVUM – mature female egg ESTROGEN – menstruation hormone PROGESTERONE – pregnancy hormone B. LUTEAL PHASE – day 15 – 28 Ovum and follicular fluid have been discharged from the ovary and ↓ FSH ↑ LH, directs the follicle cells left behind in the ovary to produce a lutein – a bright – yellow fluid high in progesterone With lutein production, the follicle is renamed a corpus luteum - responsible for the production of the hormone progesterone during early pregnancy. If conception does occur, fertilized ovum implants on the endometrium of the uterus. Corpus luteum remains for 16 – 20 weeks of the pregnancy. If conception does not occur, unfertilized ovum atrophies after 4 – 5 days. Corpus luteum remains for only 8 – 10 days, and as it regresses, it gradually replaced by corpus albicans – regressed form of corpus luteum. Body temperature drops slightly due to low levels of progesterone and remains for approximately 24 hours until progesterone level again decreases. UTERINE CYCLE - The uterus also changes monthly as a result of stimulation from the estrogen and progesterone produced by the ovaries A. PROLIFERATIVE PHASE – day 4 or 5 - 14 Immediately after menstrual flow, the endometrium is one cell layer in depth. Ovaries begins to produce estrogen and the endometrium beings to proliferate. Due to rapid growth, it increases the thickness of the endometrium eightfold. Also known as estrogenic, follicular, or postmenstrual phase B. SECRETORY PHASE – day 14 – 24 After ovulation, the formation of progesterone in the corpus luteum causes the gland of the uterine endometrium to become corkscrew or twist in appearance. The capillaries of the endometrium increase in amount of rich, spongy velvet. Also known as pregestational, luteal, premenstrual, or secretory phase C. ISCHEMIC PHASE – day 24 – 28 If fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum regresses after 8 -10 days Production of progesterone and estrogen decreases The endometrium begins to degenerate Capillaries rupture and the endometrium sloughs off D. MENSTRUAL PHASE – 1st day of menstrual flow to 5 days Menstrual flow is composed of blood from the ruptured capillaries, mucin from the gland (protein), fragments of endometrial tissue, microscopic, atrophied, and unfertilized ovum OVULATION TESTS A. B. FERN TEST – arborization or ferning ↑ Estrogen = fern like pattern forms ↑ Progesterone = pattern no longer discernible SPINNBARKEIT TEST - ↑ Estrogen = cervical mucus stretches into long strands MENSTRUAL DISORDERS DYSMENORRHEA - painful menstruation MENORRHAGIA – abnormally heavy menstrual flow METRORRHAGIA – bleeding between menstrual periods AMENORRHEA – absence of menstrual flow MENOPAUSE – cessation of menstrual cycle Age range: 40 – 55 years old Mean average: 51. 3 years old Female smokers tend to have earlier menopause PERIMENOPAUSAL – used to denote the period during which menopausal changes occur POSTMENOPAUSAL – describes the time of like following the final menses SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF MENOPAUSE Periods of amenorrhea Hot flashes – can be accompanied by heart palpitations and can occur up to 20 – 30 episodes a day; sip cold drink or use a hand fan Vaginal dryness leading to dyspareunia – painful intercourse; use lubrication jelly such as KY jelly before intercourse Osteoporosis – lack of bone mineral density Urinary incontinence – practice Kegel exercise to help strengthen bladder supports SAS 4 GENETIC REPLACEMENT THEORY - is an experimental technique that uses genes to treat or prevent disease GENE EDITING - DNA is inserted, deleted, modified or replaced in the genome of a living organism targets the insertions of site - specific locations GENETIC DISORDERS - Inherited or genetic disorders are can be passed from one generation to the next due to disorders in the gene or chromosome structure May occur in the ovum and a sperm fuse or even in the meiotic division phase of the gametes 50% of 1st trimester spontaneous miscarriages GENETICS – the study of genes and heredity CYTOGENETICS - the study of chromosomes by light microscopy and the method by which chromosomal aberrations are identified MENDELIAN INHERTIANCE - Discovered by GREGOR MENDEL – describes the principle of generic inheritance When dominant gene is paired with non-dominant (recessive) ones, the dominant genes are always expressed in preference to the recessive genes. HOMOZYGOUS – two identical copies HETEROZYGOUS – two different alleles GENES Are the basic units of heredity that determine both physical and cognitive characteristics of people Basic unit of genetic information Determines the inherited characters Are composed of segments of DNA, which are woven into strands in the nucleus of all body cells to form chromosome ALLELES – Are the two like genes on autosomes PHENOTYPES – Refers to a person’s outward appearance or the expression of genes GENOTYPE – Refers to a person’s actual gene composition GENOME - Is the complete set of genes present (about 50,000 – 100,000) The collection of genetic information CHROMOSOME – Storage unit of genes DNA - A nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions specifying the biological development of all cellular forms of life DOMINANT – allele is expressed even if it is paired with a recessive gene RECESSIVE – allele only visible when paired with another recessive allele AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE – disease does not occur unless 2 genes for the disease are present AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT – either a person has 2 unhealthy genes X – LINKED DOMINANT – genes are located on and transmitted only by the female sex chromosome (X CHROMOSOME) - ALPORT’S SYNDROME – progressive kidney failure disorder X – LINKED RECESSIVE – only males have the disorder MULTIFACTORIAL INHERITANCE from multiple gene combinations plus environmental factors heart disease, diabetes mellitus, cleft palate, neural tube defects, pyloric stenosis CHROMOSOMAL ABNORMALITIES (CYTOGENIC DISORDERS) abnormalities due to fault in the number / structure of chromosome which results in missing or distorted genes when chromosomes are photographed and displayed, the resulting arrangement is termed a KARYOTYPE - an individual's complete set of chromosomes FLOURESCENT IN SITU HYBRIDIZATION (FISH) – the number of chromosomes and specific parts of chromosomes can be identified by karyotyping or by this process NONDISJUNCTION - uneven division; resulting 1 sperm/ovum having 24 & the other 22 If fused with a normal sperm/ovum, the zygote will have 47 or 25 chromosomes DOWN SYNDROME (TRISOMY 21) – presence of all or a portion of a third chromosome 21. TURNER SYNDROME – a condition that affects only females, results when one of the X chromosomes (sex chromosomes) is missing or partially missing KLINEFELTER SYNDROME – where boys and men are born with an extra X chromosome. DELETION ABNORMALITIES - Chromosome disorder in which part of the chromosome breaks during cell division, causing the affected person to have the normal amount of chromosome +/- an extra portion of a chromosome e.g., 45.75 or 47.5 CRI-DU-CHAT SYNDROME (46XY5q-) – 1 portion of chromosome 5 is missing TRANSLOCATION ABNORMALITIES A child gains an additional chromosome through another route Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21) MOSAICISM when the nondisjunction disorder occurs after fertilization of the ovum, as the structure begins mitotic cell division Occurs when a person has two or more genetically different sets of cells in his or her body ISOCHROMOSOME - Chromosome accidentally divides not by a vertical separation but by a horizontal one, a new chromosome with mismatched long and short arms can result. Turner’s Syndrome GENETIC COUNSELING - the giving of advice to prospective parents concerning the chances of genetic disorders in a future child MATERNAL SERUM SCREENING A. ALPHAFETOPRIOTEIN (AFP) - secreted by the fetal liver peaks in maternal serum between 13 and 32 weeks; level is elevated with fetal spinal cord disease - decreased with fetal chromosomal disorder like Trisomy 21 B. CHORIONIC VILLI SAMPLING – involves retrieval and analysis of chorionic villi from the growing placenta for chromosome or DNA analysis C. AMNIOCENTESIS – withdrawal of AF through the abdominal wall for analysis at the 14 th to 16th week D. PERCUTANEOUS UMBILICAL BLOOD SAMPLING / CORDOCENTESIS – is the removal of fetal cord blood at 17 weeks using amniocentesis methods CHROMOSOMAL ABNORMALITIES PATAU SYNDROME (TRISOMY 13) – 47xy13+ or 47XY13- Extra chromosome 13, severely cognitively challenged Midline body disorders like cleft lip/palate, heart defects, abnormal genitalia, microcephaly, microphthalmia, low-set ears Most do not survive beyond early childhood EDWARD’S SYNDROME (TRISOMY 18) – 47XX18+ or 47XY18+ - Have 3 copies of chromosome 18 Severely cognitively challenged, SGA, low-set ears, small jaw, congenital heart defects, misshapen fingers and toes, rocker-bottom feet Do not survive beyond early infancy CRI – DU – CHAT SYNDROME (5p-) – 46XX5p- or 45XY5p- Result of missing portion of chromosome 5 Abnormal cry, small head, wide-set eyes, downward slant to the palpebral fissure, severely cognitively challenged TURNER SYNDROME (MONOSOMY X) – 45XO AKA GONADAL DYSGENESIS - Only 1 functional X chromosome Short in stature Streak ovaries, sterile and secondary sex characteristics except for pubic hair, do not develop during puberty Hairline at the nape of the neck is low-set Webbed and short neck Newborn may have edema of the hands and feet and anomalies like coarctation of the Aorta and kidney disorders Learning disabilities Human growth hormone and estrogen therapy may cause appearance of sex characteristics KLINEFELTER SYNDROME – 47XXY - Males with extra X chromosome No development of secondary sex characteristics during puberty; small testes with ineffective sperm, gynecomastia, increased risk for breast CA FRAGILE X SYNDROME (FXS) – 46XY23q- Most common cause of cognitive challenge in males X-linked -1 long arm X chromosome is defective Before puberty, boys demonstrate maladaptive behaviors like hyperactivity or autism, reduced intellectual functioning with marked deficits in speech and arithmetic Large head, long face with high forehead, prominent lower jaw, large, protruding ears, hyper extensive joints, cardiac disorders After puberty, large testicles Fertile DOWN SYNDROME (TRISOMY 21) – 47XY21+ or 47XX231+ - Most frequently occurring chromosomal abnormality (1 in 800 pregnancies) Broad and flat nose Eyelids have extra fold of tissue at the inner canthus (epicanthal fold) Palpebral fissure tends to slant upward Iris may have white specks called BRUSHFIELD SPOTS Tongue may protrude since oral cavity is small Back of the head is flat Poor muscle tone Cognitively challenged to some degree (50 – 70%) Short neck, extra pad of fat at the base of the head causes puppy’s neck SAS 5 CULTURE – a set of traditions a specific social group uses and transmits to the next generation DIVERSITY – a mixture or variety of sociodemographic groups, experiences, and beliefs TRANSCULTURAL NURSING – care guided by cultural aspects and respects individual differences CULTURE-SPECIFIC VALUES – norms and patterns of behavior unique to one particular culture ETHNICITY – refers to a cultural group into which the person is born; sometimes used in a narrower context to mean only RACE RACE – refers to a category of people who share a socially recognized physical characteristic; refer to a group of people who share the same ANCESTRY STEREOTYPE – a wide held but fixed and oversimplified image or idea of a particular type of person or thing PREJUDICE – preconceived opinion that is not based on reason or actual experience DISCRIMINATION – the unjust or prejudicial treatment of different categories of people or things, especially on the grounds of race, age or sex SEX – biological, based on reproductive organs; may be male, female or intersex SEX ROLE – biological function, which a male or female assumes because of the basic physiological or anatomical differences between the sexes GENDER – masculinity or femininity; refers to the social attributes and opportunities associated with being male and female GENDER IDENTITIY – refers to a person’s deeply felt internal and individual experiences of gender, which may or may not correspond with the sex assigned at birth HETEROSEXUAL – finds sexual fulfillment with someone of the opposite sex HOMOSEXUAL – finds sexual fulfillment with someone of the same sex GAY – male individuals attracted to male partners LESBIAN – female individuals attracted to female partners ASEXUAL – someone who does not experience or feel sexual attraction INTERSEX – someone who is born with a reproductive organ that does not fit the typical female or male definitions QUEER – umbrella term; does not categorize sex, sexuality or gender CROSS DRESSING / TRANSVESTISM – act of wearing items of clothing commonly associated with the opposite sex within a particular society MSM – men who have sex with men WSW – women who have sex with women BISEXUAL – an individual attracted to both men and women CISGENDER – when individuals feel that their gender and their sex match TRANSGENDER – when individuals feel that their gender and their sex do not match GENDER EXPRESSION – way in which a person acts to communicate gender within a given culture through clothing, communication, pattern and interests SEXUALITY – totality of being; the sum of a person’s sexual behaviors and tendencies, and the strength of such tendencies, it begins at birth and lasts a life time SEX – never changing, biologically determined GENDER – ever changing, socially, culturally determined SAS 6 FERTILIZATION - - the beginning of pregnancy union of the ovum and spermatozoon sperm is functional for 48 - 72 hours critical time for intercourse is about 72 hours (48 hours before ovulation + 24hours) mature ovum is surrounded by the zona pellucida (ring of mucopolysaccharide fluid) and corona radiata (circle of cells), both serve to increase the bulk of the ovum and as buffers against injury ejaculation of 2.5 ml of semen contains 50 – 200M sperm during ovulation, cervical mucus is thin making the sperm able to penetrate it CAPACITATION – changes in the plasma membrane of the sperm head which reveals the spermbinding receptor sites HYALURONIDASE – released by the sperm and dissolves the protective corona radiata HYDATIDIFORM MOLE – multiple sperm enter leading to abnormal growth - after entry, chromosomal material fuse forming a ZYGOTE mitosis begins within 24 hours when zygote reaches the body of the uterus, it is bumpy in appearance called MORULA a BLASTOCYTE then attaches to the endometrium IMPLANTATION / NIDATION – contact between the blastocyte and the endometrium occurs 8 -10 days after fertilization 3 PHASES OF IMPLANTATION - - APPOSITION – blastocyte brushes against the endometrium (secretory phase of MC) ADHESION – blastocyte attaches to the surface of the endometrium INVASION – blastocyte settles down into the soft folds of the endometrium receiving nourishment of glycogen – mucoprotein from the endometrial gland Invasion is possible since trophoblast cells produce proteolytic enzymes - involved in rebuilding of the endometrium and play an important role in the process of implantation and placental development. Establishes a communication network with the blood system of the endometrium Occasionally, vaginal spotting occurs with implantation because capillaries are ruptures by the implanting cells ONCE IMPLANTED, ZYGOTE IS AN EMBRYO THE DECIDUA Corpus luteum in the ovary continue to function with the influence of HCG secreted by the trophoblast cells ENDOCRINE FUNCTIONS: - PROLACTIN – promotes milk production RELAXIN – peptide hormones that relaxes CT of symphysis pubis and pelvic ligaments, promotes cervical dilation PROSTAGLANDINS – potent, hormone-like fatty acid Endometrium continues to grow in thickness and vascularity and is termed DECIDUA PARTS OF THE DECIDUA - DECIDUA BASALIS – lies directly under the embryo DECIDUA CAPSULARIS – portion that stretches or encapsulates the surface of the trophoblast DECIDUA VERA – the remaining portion of the uterine lining CHORIONIC VILLI On the 11th – 12th day, miniature villi or probing fingers called chorionic villi reach out to the endometrium Chorionic villi have a center core of loose connective tissue surrounded by a double layer of trophoblast cells Center core of chorionic villi contains fetal capillaries 2 OUTER PORTION LAYERS - - SYNCYTIOTROPHOBLAST Outer layer or syncytial layer Produce HCG, somatomammotropin (human placental lactogen) hormone, estrogen and progesterone CYTOTROPHOBLAST / LANGHANS LAYER Inner layer, present at 12 days gestation This layer disappears between 20 – 24th week PLACENTA - Latin for pancake - Serves as fetal lungs, kidneys, GIT, a separate endocrine organ throughout the pregnancy Covers half the surface area of the internal uterus FETAL CIRCULATION - - 12th day of gestation – maternal blood begins to collect at the intervillous spaces of the uterine endometrium surrounding the chorionic villi 3rd week – O2 and nutrients like glucose amino acids, fatty acids, minerals, vitamins and water diffuse from the maternal blood through the layers of the chorionic villi to the capillaries and are transported to the developing embryo No direct exchange of blood between embryo and mother, only by selective osmosis through the chorionic villi Almost all drugs and alcohol perfuse across the placenta COTYLEDONS – 30 mature placenta segments which makes the maternal side rough and uneven BRAXTON HICKS – contractions that are barely noticeable; aid in maintaining pressure in the intervillous spaces by closing off the veins during contractions UTERINE PERFUSION AND PLACENTAL CIRCULATION - Efficient when the woman lies on her left side listing the uterus away from the inferior vena cava, preventing blood from being trapped in her lower extremities PLACENTA WEIGHT - AT TERM: 400g – 600g (1lb), 1/6 of baby’s weight FUNCTION OF PLACENTA ENDOCRINE FUNCTION - - - - HUMAN CHORIONIC GONADOTROPHIN ensure that the corpus luteum continues to produce E/P suppresses maternal immunologic response to prevent/rejection of placental tissue if fetus is male, it influences testes to produce testosterone 8th week – outer layer of placenta begins to produce P so CL is no longer needed and HCG levels decrease Present in blood and urine ESTROGEN Contributes to mammary gland development Stimulates uterine growth to accommodate growing fetus PROGESTERONE Maintains endometrial lining Reduce contractility of uterine muscles preventing premature labor After placental synthesis on the 12th week, progesterone rises progressively HUMAN PLACENTAL LACTOGEN (HUMAN CHORIONIC SOMATOMAMMOTROPIN) Growth promoting and lactogenic (milk-producing) Promotes mammary gland growth Regulates maternal glucose, protein and fat levels so that adequate amounts are always available to the fetus Present in maternal serum and urine UMBILICAL CORD - It provides a circulatory pathway that connects the embryo to the CV of the placenta Transports O2 and nutrients to the fetus from the placenta and to return waste products to the placenta Outer surface is covered with amniotic membrane 2 arteries, 1 vein 1 vein, 1 artery – anomalies of the kidney and heart No nerve supplies PLACENTAL MEMBRANES A. AMNIOTIC MEMBRANE - Chorionic villi become smooth chorion - Smooth chorion becomes chorionic membrane – outermost fetal membrane which supports the sac that contain amniotic fluid - Inner layer becomes the amniotic membrane or amnion - Covers the fetal surface making it shiny FUNCTIONS - Supports and produces amniotic fluid Produces phospholipids that initiate formation of prostaglandins that initiate labor by producing contractions B. AMNIOTIC FLUID - Fetus continually swallows AF, from the intestine, to the bloodstream, to the umbilical arteries to the placenta - Volume at term: 800 – 1200mL - Slightly alkaline: pH 7.2 - If unable to swallow: ESOPHAGEAL ATRESIA - a birth defect in which part of a baby's esophagus does not develop properly ANACEPHALY - a serious birth defect in which a baby is born without parts of the brain and skull. HYDRAMNIOS occurs, a condition that occurs when too much amniotic fluid builds up during pregnancy. (>2000 mL AF or > 8cm pockets of fluid in ultrasound) OLIGOHYDRAMNIOS – reduction in the amount of AF maybe be due to kidney disturbance (<300 ml or > 1 cm no pocket on UTZ) FUNCTIONS - Shields fetus from pressure or blow to the abdomen Regulates temperature Aids in muscular development since it allows fetus to move freely Protects umbilical cord from pressure thus protecting the fetal 02 supply STEM CELLS First 4 days of life – TOTIPOTENT STEM CELLS – have the potential to form a complete human being Next 4 days, cells begin to differentiate and slated to become specific body cells called PLURIPOTENT STEM CELLS - have the ability to undergo self-renewal and to give rise to all cells of the tissues of the body. Next few days, MULTIPOTENT CELLS - have the capacity to self-renew by dividing and to develop into multiple specialized cell types present in a specific tissue or organ. PRIMARY GERM LAYERS - At implantation, blastocyte has differentiated with 2 separate cavities appear in the inner structure: AMNIOTIC CAVITY – large cavity, lined with the ectoderm YOLK SAC – smaller cavity, lined with entoderm cells YOLK SAC - supply nourishment only until implantation After implantation, it serves as a source of RBCs until the hematopoietic system is mature enough to take over, then it atrophies - Between the amniotic cavity and the yolk sac, a 3 rd layer of primary cells, the MESODERM, forms. Development continues until the 3 germ layers meet at a point called EMBYRONIC SHIELD Each germ layer develops into specific body systems - EMBRYONIC PRIMARY GERM LAYERS - ECTODERM – forms the exoskeleton CNS (brain and spinal cord) Peripheral Nervous System Skin, hair, nails Sebaceous glands Sense organs Mucous membranes of anus, mouth and nose Tooth enamel Mammary glands - MESODERM – develops into organs Supporting structures (connective tissues, bones, cartilage, muscle, ligaments, and tendons) Dentin of the teeth Upper portion of the urinary system (kidneys and ureters) Reproductive system Heart Circulatory system Blood cells Lymph vessels - ENTODERM – forms the inner lining of the organs Lining of the pericardial, pleural and peritoneal cavities Lining of the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, tonsils, parathyroid Thyroid, thymus glands Lower urinary system (bladder and urethra) SAS 7 1st TRIMESTER: ACCEPTING THE PREGNANCY Task: accept the reality of the pregnancy Maladaptation: Denial AMBIVALENCE – combination of pleasure and anxiety SONOGRAM – seeing the fetal outline on screen may promote acceptance 2nd TRIMESTER: ACCEPTING THE BABY Task: accepting the reality of having a baby QUICKENING – 1st moment the woman feels fetal movement, proof of child’s existence Mother starts to imagine, role-play, fantasize A good way to measure acceptance is how well she follows prenatal instructions 3rd TRIMESTER: PREPARING FOR PARENTHOOD - Nest Building Interested in attending prenatal and childbirth classes EMOTIONAL RESPONSES TO PREGNANCY 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Ambivalence - combination of pleasure and anxiety Grief Narcissism Introversion vs Extroversion Body image and boundary Stress Couvade Syndrome Emotional lability Changes in sexual desire Changes in the expectant family PRESUMPTIVE SIGNS OF PREGNANCY - Least indicative of pregnancy and individually may be symptoms of other conditions Subjective - Amenorrhea – absence of menstrual cycle - Nausea and vomiting - Breast changes: tingling, darkening, enlargement - Urinary frequency - Fatigue – due to increase in estrogen - Skin changes: Chloasma – a pigmentation disorder of the skin characterized by darker skin patches that primarily affect the face and other sun-exposed areas. Linea nigra – line of dark pigment on the abdomen Striae gravidarum – red streaks on abdomen - Diaphoresis - excessive, abnormal sweating - Leukorrhea – a thick, whitish, yellowish or greenish vaginal discharge - Weight gain - Quickening – fluttering sensation, mother’s perception of fetal movement 18 – 20th week for primipara 14 – 16th week for multipara PROBABLE SIGNS - Can be documented by the examiner Objective More reliable but still not positive or true diagnostic finding - Uterine enlargement - Goodell’s Sign – softening of the cervix - Hegar’s Sign – softening of the lower uterine segment Chadwick’s Sign – bluish discoloration of the cervix, vagina and perineum McDonald’s Sign – ease in flexing the body of the uterus against the cervix Braxton – Hicks contractions – painless and irregular, relieved by walking Ballottement – fetal rebound against examination Positive pregnancy test: (+) HCG POSTIVE SIGNS OF PREGNANCY - Fetal parts on palpation by examiner Fetal skeleton on X-ray (safe from 16 weeks) Fetal outline on ultrasonography Fetal Heart Tone is audible - Normal range: 120 -150 bpm - FUNIC souffle – sound of blood in the cord - Uterine souffle – NOT a diagnostic sign STUFFINESS – nasal congestion due to increased estrogen levels PSEUDOANEMIA - Pallor of the skin and mucous membranes without the blood signs of anemia HYPERPTYALISM - overproduction of saliva HYPEREMESIS GRAVIDARUM - extreme, persistent nausea and vomiting during pregnancy DANGER SIGNS OF PREGNANCY - Vaginal bleeding Persistent vomiting Chills and fever Sudden escape of clear fluid from the vagina Abdominal or chest pain PREGNANCY – INDUCED HYPERTENSION (PIH) - Rapid weight gain (over 2lbs/wk in the 2nd trimester, 1lb/wk in the 3rd trimester) Swelling of the face or fingers Flashes of light or dots before the eyes Dimness or blurring of vision Severe, continuous headache Decreased urine output INCREASE OR DECREASE IN FETAL MOVEMENT – fetus lacks oxygen PREPARING FOR LABOR LIGHTENING settling of the fetal head into the inlet of the true pelvis SHOW the release of the cervical plug (operculum) that formed during pregnancy RUPTURE OF THE MEMBRANES A sudden gush of clear fluid (amniotic fluid) from the vagina indicates rupture of the membranes EXCESS ENERGY Feeling extremely energetic is a sign of labor important for women to recognize. It occurs as part of the body’s physiologic preparation for labor UTERINE CONTRACTIONS True labor contractions usually start in the back and sweep forward across the abdomen like the tightening of a band. They gradually increase in frequency and intensity SAS 8 ASSESSING FETAL WELL – BEING QUICKENING – felt by the mother at 18 – 20 weeks and peaks at 28 – 38 weeks SANDOVSKY METHOD - Mother lies in a left recumbent position after a meal and record how many fetal movements she feels for 1 hour If <10 movements per hour, repeat for another hour If 10 for 2 hours, notify physician CARDIFF METHOD (COUNT-TO-TEN/FETAL KICK COUNT) - Mother records time interval it takes to feel 10 movements (usually within 60 seconds) Done at the same time daily, preferably after breakfast (most active), lie on left side after stimulating activity like walking Warning: > 1 hour for 10 FM or <10 FM in 12 hours Alarm: weaker movements < 3 FM in 12 hours FETAL HEART RATE: 120 – 160 bpm 1. RHYTHM STRIP TESTING test for good baseline rate and presence of long- and short-term variability SEMI-FOWLERS’S POSITION – to prevent supine hypertension and for comfort External fetal heart rate and uterine contraction monitors are attached abdominally TOCOTRANSDUCER – over fundus measure contractions and fetal movement ULTRASOUND – over abdominal site where FHR is distinct FHR is recorded for 20 minutes BASELINE READING – average rate of fetal heartbeat per minute SHORT-TERM VARIABILITY (BEAT-TO-BEAT VARIABILITY) Small changes in rate from second to second if fetal parasympathetic NS receives adequate O2 and nutrients LONG-TERM VARIABILITY Differences in heart rate over the 20-minute period 2. NON-STRESS TESTING (NST) Measures the response of the FHR to fetal movement SEMI-FOWLERS’S POSITION – to prevent supine hypertension and for comfort External fetal heart rate and uterine contraction monitors are attached abdominally TOCOTRANSDUCER – over fundus measure contractions and fetal movement ULTRASOUND – over abdominal site where FHR is distinct With fetal movement, FHR increases 15 bpm and remain elevated for 15 seconds It should decrease as fetus quiets No increase in beats, poor O2 perfusion is suggested NST is done for 10 – 20 minutes REACTIVE (NORMAL) - 2 accelerations of FHR (by 15 beats or more) lasting for 15 seconds occur after movement within the chosen time period NON-REACTIVE - No acceleration with the fetal movement, no movement, low short-term FHR variability (<6 bpm) throughout the testing period 20 minutes without fetal movement – sleeping fetus; give CHO snack or stimulate by a loud sound If not responsive after 1 hour, contraction stress testing 3. VIBROACOUSTIC STIMULATION A specially-designed acoustic stimulator is applied to the mother’s abdomen to produce a sharp sound 80 decibels at a frequency of 80 Hz, to startle and wake the fetus In a NST with no acceleration within 5 minutes, a single 1-2 second sound stimulation is applied to the lower abdomen (may be repeated at the end of 10 minutes if no movement) 4. CONTRACTION STRESS TESTING FHR is analyzed in conjunction with contractions (achieved by nipple stimulation to release oxytocin) Baseline FHR is obtained then mother rolls nipple until contraction begins, recorded by a uterine monitor 3 contractions lasting for 40 seconds or more in a 10-minute window RESULTS - Normal – no FHR decelerations with the contractions Abnormal – (+) -50% more of contractions cause late decelerations (dip in FHR towards end of contraction and continues after the contraction) 3 TYPES OF DECELERATIONS - EARLY DECELERATION – begins on or after onset of contraction and ends when contraction ends; due to head compression during labor LATE DECELERATION – begin after onset and peak of uterine contraction and ends after contraction; due to uteroplacental insufficiency VARIABLE DECELERATION – u, w, or v shape, unrelated to contraction, due to cord compression 5. ULTRASONOGRAPHY Ask mother to drink a full glass of water every 15 minutes beginning 90 minutes before the procedure and should not void before the procedure PURPOSE - Diagnose a pregnancy - Confirm presence, location, size of placenta and amniotic fluid - Establish fetal growth and rule out abnormalities - Establish sex, presentation, and position of fetus - Predict maturity via the measurement of the biparietal diameter of the head - Discover complications of pregnancy 6. BIPARIETAL DIAMETER - Side to side measurement of the fetal head via ultrasound - If 8.5 cm greater, infant will weight more than 2500g (5.5lbs) - Diameter of 8.5 cm indicates fetal age of 40 weeks - Head circumference of 34.5 mc indicates 40-week fetus - Femoral length 7. HAASE’S RULE - Determines length of fetus in cm 8. DOPPLER UMBILICAL VELOCIMETRY - Measures velocity at which RBCs in the blood volume are flowing - Helps determine vascular resistance in women with diabetes and hypertension and whether placental insufficiency occurred 9. PLACENTAL GRADING - Based on the amount of Ca deposits in the base of the placenta via UTZ 10. AMNIOTIC FLUID ASSESSMENT - Decrease in amniotic fluid, risk of cord compression 11. ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY - May be recorded as early as 11th week of pregnancy 12. MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING - To diagnose complications like ectopic pregnancy 13. MATERNAL SERUM ALPHA-FETOPROTEIN - checks the level of alpha-fetoprotein produced by your baby as a way to assess your little one's risk of a neural tube defect or a chromosomal abnormality. 14. TRIPLE SCREENING - Analysis of 3 indicators; MSAFP, unconjugated estriol, and HCG 15. CHORIONIC VILLI SAMPLING - Biopsy and chromosomal analysis of CV - COELOCENTESIS – transvaginal aspiration of fluid from the extraembryonic cavity 16. AMNIOCENTESIS - Aspiration of amniotic fluid from the uterus for analysis - If mother is Rh(-), Rhlg or RhoGAM is administered within 72 hours to prevent fetal isoimmunization - COLOR: Strong yellow – suggest blood incompatibility Green – meconium staining, suggesting fetal distress - LECITHIN/SPHINGOMYELIN RATIO - PHOSPHATIDYGLYCEROL & DESATURATED PHOSPHATIDYCHOLINE Present only in mature lung function (35 – 35 weeks) - BILIRUBIN DETERMINATION Done if blood incompatibility is suspected Sample must be blood-free to avoid false-positive results - CHROMOSOME ANALYSIS To detect chromosomal diseases Fetal skin cells present in AF may be cultured and stained for karyotyping - FETAL FIBRONECTIN Detected if there is damage in fetal membranes - INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM - ALPHA-FETOPROTEIN Present if fetus has an open body defect causing leakage of AFP into the AF - ACETYLCHOLINETERASE Present in AF if neural tube defect is present 17. SHAKE TEST - If bubbly, the ratio is mature 18. PERCUTANEOUS UMBILICAL BLOOD SAMPLING / CORDOCENTESIS / FUNICENTESIS - Aspiration of blood from umbilical vein for testing - CBC, direct COOMB’S test, blood gases, karyotyping is done KLEIHAUER-BETKE TEST – to ensure that the blood is fetal blood 19. AMNIOSCOPY - Visual inspection of the AF through the cervix and membranes with an amnio scope - To detect meconium staining 20. FETOSCOPY - Fetus is visualized by a fetoscope - Confirm intactness of the spinal column - obtain biopsy samples of the fetal tissue and fetal blood samples - perform elemental surgery (shunt for hydrocephalus) - AMNIONITIS – infection of the amniotic fluid 21. BIOPHYSICAL PROFILE - Also known as FETAL APGAR - Fetal reactivity, fetal breathing movements, fetal body movements, fetal tone, amniotic fluid volume - Fetal heart and breathing record measures CNS function SAS 9 OVULATION AGE – measured from the time of ovulation LENGTH OF PREGNANCY – from the 1st day of LMP is the gestational age OVULATION AGE AND GESTATIONAL AGE – measured in lunar months (4-week periods) or trimesters (3-month periods) PREGNANCY – 10 lunar months (40 weeks or 280 days); fetus grows in utero for 9.5 lunar months or 3 full trimesters (38 weeks or 266 days) 4th GESTATIONAL WEEK - Length: 0.75 – 1 cm Weight: 400 mg Spinal cord formed and fused Lateral wing forming body are folded toward to fuse at midpoint Head holds forward, prominent, 1/3 of entire structure Back is bent so head almost touches tip of tail Rudimentary heart bulges on anterior surface Arm and leg buds Rudimentary eyes, ears, nose are discernible 8th GESTATIONAL WEEK - Length: 1 inch Weight: 20 g Organogenesis complete Heart with septum and valves, beats Discernible facial features Arms and legs developed External genitalia present but undiscernible Primitive tail regressing Abdomen is large due to rapid growing fetal intestines Ultrasound shows gestational sac 12th GESTATIONAL WEEK - Length: 7 – 8 cm Weight: 45 g Nail beds on fingers and toes forming Spontaneous movements possible but too faint to be felt Bone ossification centers forming Tooth buds present Sex distinguishable by outward appearance Kidney secretion begins but urine not yet evident in the amniotic fluid Heartbeat audibles through doppler technology Reflexes present like Babinski reflex 16th GESTATIONAL WEEK - Length: 10 – 17 cm Weight: 55 – 120 g Fetal heart sounds audible with ordinary stethoscope Lanugo is well formed Liver and pancreas functioning Active swallowing of amniotic fluid demonstrating intact though uncoordinated swallowing reflex Urine is present in amniotic fluid Sex can be determined by ultrasound 20th GESTATIONAL WEEK - Length: 25 cm Weight: 223 g Spontaneous movements felt by the mother Antibody production possible Hair forms, including eyebrows and hair on the head Meconium present in the upper intestine Brown fat Vernix caseosa begins to form Definite sleep/wake patterns 24th GESTATIONAL WEEK - Length: 28 – 35 cm Weight: 550 g Passive ab transfer Meconium is present as far as the rectum Active production of lung surfactants begins Eyebrows and eyelashes well – defined Eyelids now open Pupils capable of reacting to light Hearing can be demonstrated by response to sudden sound 28th GESTATIONAL WEK - Length: 35 – 38 cm Weight: 1,200 g Lung alveoli begin to mature, surfactant present in amniotic fluid Testes begin to descend in scrotal sac from the lower abdominal cavity Blood volume of retina are thin and susceptible to damage from high O2 32th GESTATIONAL WEEK - Length: 38 – 43 cm Weight: 1,600 g Subcutaneous fat begins to be deposited Fetus responds by movement to sound outside mother’s body Active Moro reflex Birth position is assumed Iron stores beginning to be developed Fingernails grow to reach end of fingertips 36th GESTATIONAL WEEK - Length: 42 – 48 cm Weight: 1,800 g – 2,700 g (5 - 6 lbs.) Body stores of glycogen, irons and carbohydrates and calcium are deposited Additional amount of subcutaneous fat is deposited Sole of foot has only 1 or 2 crisscross creases Lanugo begins to diminish Most babies turn into a vertex or head-down position during this month 40th GESTATIONAL WEEK - Length: 48 – 52 cm (crown to rump, 35 – 37 cm) Weight: 3,000g (7 – 7.5 lbs.) Fetus kicks actively causing discomfort Fetal hemoglobin begins conversion to adult hemoglobin FETOPLACENTAL CIRCULATION i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. vii. viii. ix. x. 12th day – maternal blood collects in the intervillous spaces of the endometrium surrounding the chorionic villi 3rd week – fetal blood beings t exchange nutrients with maternal blood by osmosis O2 blood from placenta enters umbilical vein Ductus Venosus (supplies liver) Inferior vena cava Right atrium Foramen ovale Left atrium Left ventricle Aorta SHUNTS OR BYPASSES FORAMEN OVALE – between right and left atrium DOCTUS VENOSUS – bypasses the liver DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS – bypasses the lungs UMBILICAL VEIN – carries oxygenated blood and nutrients to fetus UMBILICAL ARTERIES – carries carbon dioxide and other wastes from fetus to maternal circulation Pressure is higher on the Right side of the heart before birth SAS 10 TERATOGEN any factor, chemical or physical that adversely affects the fertilized ovum, embryo or fetus TIMING OF THE INSULT before implantation, zygote is destroyed or unaffected during organogenesis, very vulnerable 3rd trimester, the harm decreases SYPHILIS AND TOXOPLASMOSIS – affects fetus throughout the pregnancy LEAD – has affinity for nervous tissues THALIDOMIDE – causes limb defects TETRACYCLINE – causes tooth enamel and bone deformities TERATOGENIC MATERIAL INFECTIONS - Involves STI or systemic infections Viral, bacterial or protozoan Most cause relatively mild, flulike symptoms in a woman but more serious effects on a fetus TORCH INFECTIONS - Toxoplasmosis Other infections like syphilis, Hepatitis B virus and HIV Rubella Cytomegalovirus Herpes simplex virus TORCH SCREEN - Immunologic tests on the pregnant woman – to identify fetal risk factors Immunologic test on new born – to detect if antibodies vs the teratogens are present Negative result = normal Positive IgM abs = recent or current infection Positive IgG = maternal abs crossed placenta TOXOPLASMOSIS - an infectious disease caused by a parasite that spreads from animals to humans. INFANTS - CNS damage Hydrocephalus Microcephaly Intracerebral calcification Retinal deformities MEDICATION - SULFONAMIDES – increase bilirubin levels in the newborn; does not prevent deformities PYRIMETHAMINE – anti-protozoal drug also anti-folic acid FOLIC ACID SPIRAMYCIN – experimental use RUBELLA - a contagious viral infection best known by its distinctive red rash. Also called German measles. DIAGNOSTICS - Rubella titer is obtained on 1st prenatal visit Immunization cannot be done during pregnancy; wait for 3 months before getting pregnant MATERNAL - mild rash mild systemic illness CONGENITAL RUBELLA: fetal damage from maternal infection - deafness mental and motor challenges cataracts cardiac defects (PDA, pulmonary stenosis) restricted intrauterine growth (SGA) thrombocytopenic purpura dental and facial clefts CYTOMEGALOVIRUS - a member of the herpes virus family; droplet transmission DIAGNOSTICS - isolation of CMV antibodies from the mother or the infant’s blood serum TREATMENT - no treatment or vaccine available FETAL SYMPTOMS - neurological damage (hydrocephalus, microcephaly, spasticity eye damage (optic atrophy, chorioretinitis) deafness chronic liver disease skin covered with large Petechiae (blueberry-muffin lesions) HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS (GENITAL HERPES INFECTION) - a common sexually transmitted infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV) DIAGNOSTICS - 1st episode genital herpes infection is systemic and crosses the placenta to the fetus 1st trimester infection: severe congenital anomalies or spontaneous miscarriage 2nd or 3rd trimester: high incidence of premature birth, intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), continuing infection of the newborn at birth If reoccurrence, the mother’s antibodies to the virus in her system prevents the spread of the virus to the fetus across the placenta If genital lesions are present at birth, cesarean is recommended to avoid direct exposure MEDICATION - IV ACYCLOVIR or ORAL ACYCLOVIR (ZOVIRAX) SYPHILIS - a chronic bacterial infection that can be transmitted through sexual contact DIAGNOSTICS - if detected in 1st trimester and treated with antibiotics, fetus is rarely affected If detected beyond 18th week, deafness, cognitive challenge, osteochondritis and fetal death are possible CONGENITAL SYPHILIS: congenital anomalies, extreme rhinitis (sniffles), characteristic syphilis rash, Hutchinson teeth MEDICATION - BENZATHINE PENICILLIN ZIKA VIRUS - Spreads through infected mosquito bites – Aedes aegypti Can be passed from pregnant mother to fetus Transmitted through mosquito bites, body fluids like blood and semen DIAGNOSTICS - Infection during pregnancy can cause a birth defect called microcephaly and other severe fetal brain defects PREVENTION - Avoid traveling to areas with Zika Use safe sex practices like condoms Avoid intercourse with someone who has traveled to a Zika risk area SAS 11 PROSTAGLANDIN THEORY - Initiation of labor is a result from the release of ARACHIDONIC ACIDS produced by STEROID ACTION on lipid precursors. Arachidonic acids are said to increase prostaglandin synthesis which in turn causes uterine contractions OXYTOCIN THEORY - - Pressure on the cervix stimulates the hypophysis to release oxytocin from the maternal posterior pituitary gland. As pregnancy advances, the uterus becomes more sensitive to oxytocin. Presence of oxytocin causes the initiation of contraction of the smooth muscles of the body. UTERINE STRETCH THEORY - The idea is based on the concept that any hollow body organ when stretched to its capacity will inevitably contact to expel its contents. Uterus is compared to a balloon of which is=f the point of elasticity is met, it will burst thus labor process occurs. PLACENTAL DEGENERATION THEORY - Because of decreased blood supply and functional capacity, the uterus starts to contract PROGESTERONE DEPRIVATION THEORY - Decreased amount of progesterone initiates uterine motility PREMONITORY SIGNS OF LABOR 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Lightening Increased level of activity Braxton Hicks Contractions Ripening of the Cervix Slight loss of weight FALSE CONTRACTIONS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Begin and remain irregular Felt 1st abdominally and remain confined to the abdomen and groin Often disappear with ambulation and sleep Do not increase in duration, frequency and intensity Do not achieve cervical dilation TRUE CONTRACTIONS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Begin irregularly but become regular and predictable Felt 1st in the lower back and sweep around to the abdomen in a wave Continue no matter what the woman’s level of activity Increase in duration, frequency and intensity Achieve cervical dilation SIGNS OF TRUE LABOR 1. Uterine contractions 2. Show 3. Rupture of the membranes