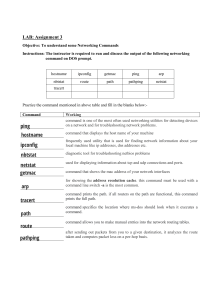
Chapter 21 Network Troubleshooting Lab Name___________________________ When communicating between machines on different networks, packets are sent via the default gateway on the way into and out of the LAN. The routing is done using (Layer 3) IP addresses. If the computers on the same network, then the IP address gets resolved to a (layer 2) Media Access Control (MAC) address to communicate with the computer. The MAC addresses are hard-coded onto the Ethernet card by the company that made the card. The ability to retrieve and change your IP configuration is an important skill. In this lab, you will use the ipconfig command in Windows to view the configuration information. You will then use the Local Area Connection Properties window to change the IP address in Windows. Computers use both MAC and IP addresses to communicate with one another across networks. In this lab, two computers will “talk” to each other via ping messages. You will then modify the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) table of one of the computer to demonstrate the relationship between the IP and MAC addresses for a machine. The ping (Packet Internet Groper) is a basic utility that is used for testing the connectivity between two computers. This message name was derived from the sound that sonar on a submarine makes and is used in a similar way. A “signal” or request is sent out to probe for the existence of the target along a fixed “distance.” The distance between two computers can be measured using time to live (TTL). The TTL is decremented by at least one for each router it passes through, also known as a hand-off point or (HOP). It may be decremented by more than one if the router holds on to it for more than one second, which rarely is the case. Ping operates using Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) to test for connectivity; so, in case where ICMP is restricted, the ping utility may not be useful. Ping is usually implemented using ICMP echo messages, although other alternatives exist. When you use the ping command in this lab, you will see that although you are using the IP address as the target of the ping, it is actually the MAC address that is used to communicate with that computer. IP addresses are used to transfer data from one network to another, whereas MAC addresses are used to send information from one device to another on the same network. It is ARP that resolves the IP addresses to their associated MAC addresses. ARP is a Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) tool that is used to modify the ARP cache. The ARP cache contains recently resolved MAC addresses of IP hosts on the network. The utility used to view and modify the ARP protocol is also called arp. 1 Chapter 21 Network Troubleshooting Lab As you progress through the labs you will see how a computer obtains both MAC addresses and IP addresses in order to communicate. This is the question you should be considering: How does the computer know that the information it is getting is correct? Learning Objectives After completing this lab, you will be able to Retrieve IP address configuration information via the command line List the switches that can be added to the ipconfig command to increase its functionality Use the Windows Graphical Interface (GUI) to configure a network card to use a given IP address Determine your machine’s MAC address Determine your machine’s assigned network resources Understand how to test network connectivity between two computers List the options that can be added to the ping command to increase functionality Use the arp command to view and manage the ARP cache on a computer. Lab 1.1: Windows Client Configuration Materials and Setup You will need the following: Windows 7 Windows Server 2008 R2 2 Chapter 21 Network Troubleshooting Lab Lab Steps at a Glance – Overview of what you will be doing in this lab Step 1: Start both Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7 VMs. At first, you will not login to Windows 2008 Server as of yet, only to the Windows 7 machine. (Since you are an admin, you are automatically logged on when you turn on the Windows 7 VM.) Step 2: View network card configuration using the ipconfig command Step 3: Change the IP address of the Windows 7 machine Step 4: Verify the new IP address. Use the ipconfig command to verify that the IP address has changed. Step 5: Change Windows 7 machine back to the original address Step 6: Ping the Windows Server machine from the Windows 7 PC Step 7: Change IP address of Windows Server 2008 machine and try and ping Windows 7. Step 8: Ping Windows Server 2008 machine from Windows 7 machine after IP address on Windows Server 2008 machine is changed. Step 9: Change subnet mask of Windows Server 2008 Machine and ping from Windows 7 machine Step 10: Put IP and Subnet Mask address back to their pre lab setting and view and modify the ARP table. Lab Steps - step-by-step instructions Step 1: Start Windows 7 machine and Server 2008 R2 machine. Do not log in to Server 2008 yet. Step 2: View the network card configuration using the ipconfig command On the Windows 7 PC, you will view the network card configuration using ipconfig. This utility allows administrators to view and modify network card settings. 1. To open the command prompt, click Start; in the Search Programs and Find Files Box type cmd and press ENTER. 3 Chapter 21 Network Troubleshooting Lab (some of you may already have a shortcut to the command line and that fine to use instead) 2. At the command prompt, type ipconfig /? and press ENTER a. Observe the options available for ipconfig. You may have to scroll up to see all of the information b. Which options are available to you as an administrator? ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ 3. Type ipconfig and press ENTER, as shown in Figure 1-1. a. What is your IP address? _____________________ b. What is your subnet mask?____________________ 4. Type ipconfig /all and press ENTER. Note: Instead of retyping “ipconfig”, at the C :> prompt, you can press the up arrow on your keyboard or the F3 key to repeat the last command you typed in a. Observe the new information. b. What is the MAC address (physical address) of your computer?______________________ c. What is you DNS server address (s)?_________________________ d. Is there more than one DNS server? ________ If so, what is the address? _______________ 5. Type exit and press ENTER 4 Chapter 21 Network Troubleshooting Lab Figure 1-1 The ipconfig command Step 3: Change the IP address of the Windows 7 machine. You will access the Local Area Connection Properties dialog box and change the host portion of the IP address. 1. Click START | CONTROL PANEL | NETWORK AND SHARING CENTER. 2. Click change adapter settings 3. Right-click Local Area Connections and select Properties. 4. Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and click Properties. 5 Chapter 21 Network Troubleshooting Lab 5. In the IP address text box, you will see the IP address 192.168.100.101, as shown in Figure 1-2. Change the last octet (101) to 110. 6. Click OK. 7. In the Local Area Connection Properties window, click Close. 8. Click Close to close the Network Connections window. Figure 1-2 Internet Protocols (TCP/IP) Properties Window Step 4: Verify the new IP address. Use ipconfig command to verify that the IP address has changed. 1. To open the command prompt, click Start; in the Search Programs and Files box, type cmd and then press ENTER. 2. Type ipconfig and press ENTER 3. Observe that your IP address has changed. 6 Chapter 21 Network Troubleshooting Lab 4. Type exit and press ENTER Step 5: Change the IP address of the Windows 7 machine back to the original address. 1. Click START | CONTROL PANEL | NETWORK and INTERNET | NETWORK and SHARING CENTER 2. Click Change Adapter Settings 3. Right-click Local Area Connection and select Properties 4. Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and click Properties 5. In the IP Address text box, you will see the IP address 192.168.100.110. Change the last octet (110) to 101 as shown in Figure 1-2. 6. Click OK 7. In the Local Area Connection Properties window, click Close. 8. Click Close to close the Network Connections window. Step 6: Ping the Windows 2008 Server machine from the Windows 7 PC. 1. On the Windows 7 PC, click Start; in the Search Programs and Files box, type cmd and then press ENTER. 2. To view the ping help file, type ping /? at the command line and then press ENTER. Observe the different options you can use with ping. 3. To ping the IP address of the Windows 2008 Server computer, type ping 192.168.100.102 at the command line and press ENTER. a. Observe the information displayed b. What is the time value observed for all four replies?_____________ c. What is the TTL observed?_____________________ d. What does this number refer to? (Hint: see page 1)__________________ 7 Chapter 21 Network Troubleshooting Lab Step 7: LOGON TO SERVER 2008 R2 1. Use right CTRL and DELETE to access the logon screen. The password for Server 2008 is Admin-Password. Step 8: You are now going to change the IP address and subnet mask address of Server 2008 1. Click START | CONTROL PANEL | NETWORK AND INTERNET | SHARING CENTER | CHANGE ADAPTER SETTINGS | right-click Local Area Connection | left-click Properties. Figure 1-3 2. Click INTERNET PROTOCOL VERSION 4 (TCP/IPv4) | PROPERTIES 3. Open Properties for Internet Protocol Version 4(TCP/IPv4) Figure 1-5 Figure 1-3 Network Connections Page 8 Chapter 21 Network Troubleshooting Lab Figure 1-4 Local Area Connection Properties. 9 Chapter 21 Network Troubleshooting Lab If on your machine the default gateway is populated, take out the IP address and leave this box blank Figure 1-5 Server IP address and subnet mask Step 9: You are now going to change the IP address and Subnet mask in Server 2008. Figure 1-6 1. You will change the IP address to 191.168.0.2 2. You will change the Subnet mask to 255.255.255.224 3. Click Ok then Click Close 10 Chapter 21 Network Troubleshooting Lab Figure 1-6 New IP address and Subnet Mask Step 10: You are now going to ping Windows 7 from Windows Server 2008. 1. In Windows 2008 click START | Search Programs and Files | and type cmd and press ENTER. 2. At the command prompt type ping 192.168.100.101. What response do you get from the ping? Why do you think you get that response? 11 Chapter 21 Network Troubleshooting Lab Step 11: Switch back to Windows 7. You are now going to ping Server 2008 from Windows 7. 1. In Windows 7 Click Start | Search Programs and Files | type cmd and press ENTER. 2. At the command line type ping 192.168.0.2. What happens? Can you successfully ping the IP address? ___________ Step 12: Now you are going to change the IP address and Mask address of the Windows 7 Computer. 1. In Windows 7 Click START | CONTROL PANEL | NETWORK AND SHARING CENTER | CHANGE ADAPTER SETTINGS | right-click on Local Area Connection| left-click on PROPERTIES. Click on IP Protocol Version 4 | PROPERTIES Figure 1-7 Figure 1-7 Local Area Connection and IPv4 properties 2. Change IP address from 192.168.100.101 to 192.168.0.4 12 Chapter 21 Network Troubleshooting Lab 3. Change Subnet mask from 255.255.255.0 to 255.255.255.224 Changes should look be like what is in Figure 1-8 Figure 1-8 New IP address and Subnet Mask Step 13: You will now ping Server 2008 from Windows 7. 1. In Windows 7 Click START | Search Programs and Files | type cmd | press ENTER 2. At the command prompt type ping 192.168.0.2 Now what happens? ___________________________________________________ Step 14: Now you will ping Windows 7 from Server 2008. 1. At the command prompt in Server 2008 type ping 192.168.0.4 What happens?______________________________________________ 13 Chapter 21 Network Troubleshooting Lab Step 15: You will now change the Subnet mask on the Windows 7 computer from 255.255.255.224 back to 255.255.255.0 2. Click START | CONTROL PANEL | NETWORK AND SHARING CENTER | CHANGE ADAPTER SETTINGS | right-click on Local Area Connection| left-click on PROPERTIES. Click on IP Protocol Version 4 | PROPERTIES Figure 1-9 Figure 1-9 IPv4 settings Step 16: You will now ping Server 2008 from Windows 7. 3. In Windows 7 Click START | Search Programs and Files | type cmd | press ENTER 4. At the command prompt type ping 192.168.0.2. What happens? ________________________________________ Step 17: You will now ping Windows 7 from Server 2008. 14 Chapter 21 Network Troubleshooting Lab 1. In Server 2008 Click START | Search Programs and Files | type cmd | press ENTER 2. At the command prompt type ping 192.168.0.4 Does the ping still work? _________ These devices do not have the same subnet mask, so do they still communicate? If so, can you explain why? ____________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 3. You will now change the IP Address on the Windows 7 computer from 192.168.0.4 to 192.168.0.33 and leave the subnet mask to 255.255.255.0 4. You will now ping Windows 7 from Server 2008: At the command prompt in Windows Server 2008 type ping 192.168.0.33 Does the ping still work? _________ Can you explain why or why not? _______________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 5. You will now change the IP Address on the Windows 7 computer back from 192.168.0.33 to 192.168.0.4 Leave the subnet mask to 255.255.255.0 Step 18: View and Modify the ARP table. At the Windows 7 machine, you will view the ARP cache, using the arp utility. 1. Close the current command prompt window if you have one open. 2. Select Start | All Programs | Accessories and then right-click Command Prompt. Click Run as Administrator 3. In the User Account Control dialog box, click Yes. 4. At the command line, type arp /? and press ENTER. a. Observe options for this command b. Which command(s) display(s) the current ARP under Example _________ 15 Chapter 21 Network Troubleshooting Lab 5. At the command line, type arp –a and press ENTER. 6. Observe the entry. Notice that the MAC address for the Windows 2008 Server machine is listed. (Physical address next to 192.168.0.2 shown as dynamic) 7. At the command line, type arp –d and press ENTER. (the d- option deletes the ARP cache.) 8. Observe the entries. (Don’t worry if no entries are listed; you are simply deleting what is in the ARP cache) 9. At the command line , type arp –a and press ENTER, as shown in Figure 1-10 10. Observe that the arp cache has no entries 11. At the command line type ping 192.168.0.2 and press ENTER 12. At the command line, type arp –a and press ENTER. a. Observe the entry. Notice the MAC address is once again listed. b. How does using the ping utility cause the machine’s MAC address to be populated in the ARP cache? Figure 1-10 The arp command in Windows 16 Chapter 21 Network Troubleshooting Lab 1. You have been called in to troubleshoot a client's computer, which is unable to connect to the local area network. What command would you use to check the configuration? What information would you look for? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 2. If you needed to obtain a user's MAC address as well as the user's network configuration information, what command and switch would you enter? 3. To use the Windows GUI utility to adjust IP settings, including DNS and gateway information, what steps would you take? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 4. You have just pinged a remote computer. You would now like to retrieve the MAC address of the remote computer locally. How would you obtain the remote computer's MAC address? _____________________ 5. You are about to run some network traffic analysis tests, you need to clear your ARP cache. How would you go about performing this task? ____________________ 6. What information does ping return to the user? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 17