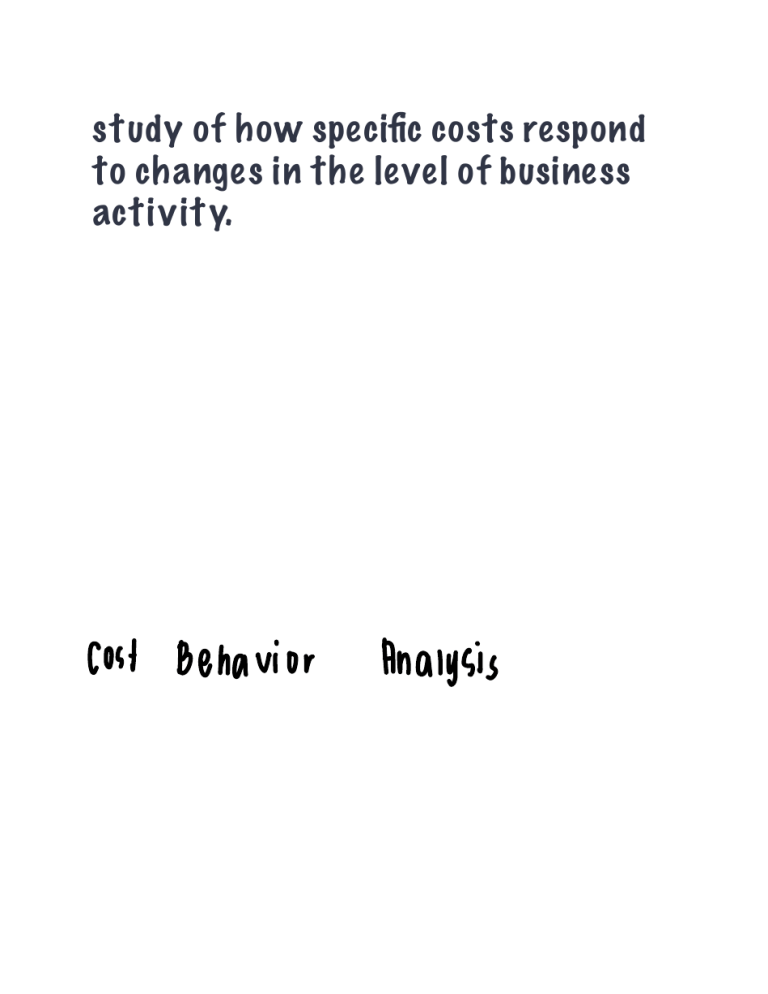
study of how specific costs respond to changes in the level of business activity. Cost Behavior Analysis iden-tifies the activity that causes changes in the behavior of costs ACTIVITY INDEX costs that vary in total directly and proportionately with changes in the activity level. Variable costs remains the same per unit at every level of activity. variable lost costs that remain the same in total regardless of changes in the activity level. Fixed costs costs per unit vary inversely with activity: As volume increases, unit cost declines, and vice versa. Fixed costs the relationship between the behavior of a variable cost and changes in the activity level curvilinear The range over which a company expects to operate during a year is called the ______ of the activity index Relevant Range Nonlinear Fixed lost costs that contain both a variableand a fixed-cost element mixed cost also called the normal or practical range. Relevant Range uses the total costs incurred at the high and low levels of activity to classify mixed costs into fixed and variable components high - low method A better approach, which uses information from all the data points to estimate fixed and variable costs, is called Regression Analysis study of the effects of changes in costs and volume on a company’s profits cost volume ( WP ) profit Analysis important in profit planning cost volume profit Analysis It also is a critical factor in such management decisions as setting selling prices, determining product mix, and maximizing use of production facilities. cost volume ( WP ) profit Analysis classifies costs as variable or fixed and computes a contribution margin Cup Income statement is the amount of revenue remaining after deducting variable costs. It is often stated both as a total amount and on a per unit basis. contribution margin _______are costs that contain both a variable- and a fixed-cost element._____, therefore, change in total but not proportionately with changes in the activity level. mixed costs Cvp income statement formula sales "÷:i::r.in net income contribution margin unit formula unit Less selling price : unit variable cost unitwnmbnmagin contribution margin expressed as a percentage of sales contribution margin patio CVP analysis considers the interrelationships among the components Volume 1. or 2. unit } Variable . a. total 5. sales of activity level selling prices fixed mix costs costs per unit difference between actual or expected sales and sales at the break-even point Margin of safety level of activity at which total revenue equals total costs. BREAKEVEN POINT percentage of each dol- lar of sales that is available to apply to fixed costs and contribute to net income; calculated as unit contribu- tion margin divided by unit selling price. WNTRLBUTION RATIO MARGIN contribution unit margin contribution unit selling ratio margin price formula ÷ A key relationship in CVP analysis is the level of activity at which total revenues equal total costs (both fixed and variable) BREAK - EVEN POINT The process of finding the break-even point is called BREAK EVEN Analysis difference between actual or expected sales and sales at the break-even point Margin of safety measures the “cushion” that a particular level of sales provides. Margin of safety margin of safety in dollars divided by actual (or expected) sales. margin of safe in ratio tells us how far sales can drop before the company will be oper- ating at a loss. Margin of safety margin be of safety expressed Dollars and can through Ratio relative percentage in which a company sells its multiple products. sales mix is important to managers because different products often have substantially different contribution margins Sales mix







