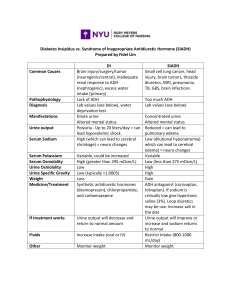
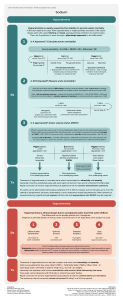
Predisposing Factors LEGENDS Precipitating Factors Malignancies Drugs (e.g. Pulmonary diseases carbamazepine, SSRIs, CNS disturbances amitriptyline) Infections Post-surgery (pain) Age (>30 years old) Family history of SIADH Risk factors/Etiology Diagnostic test Mechanism/ Pathophysiology Nursing Diagnosis Signs and symptoms Nursing Interventions/ Medical Management certain proinflammatory cytokines and pain mediators affects hypothalamus, thus producing more ADH unsuppressed release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) systemic circulation from pituitary and non pituitary sources increased levels and activity of ADH Serum sodium: < 135mEq/L SIADH Dilutional Hyponatremia ADH stimulates AQP2 into the membranes of kidney tubules Blood volume Heart produces natriuretic peptides (ANP,BNP) GFR Renin headache, confusion, lethargy, change in neurological status High USG: > 1.030 serum osmolality: <275 mOsm/kg Risk for injury related to lethargy and change in neurological status Blood pressure Nursing Interventions Assess edema Change position side to side Elevate the head of the bed Deep breatjing technique Angiotensin Aldosterone Blood volume Serum osmolality Renal Adaptation Aquaporins Nursing Interventions Create a daily weight chart and a food and fluid chart. Discuss with the patient the short term and long-term goals of weight loss. Administer anti-emetic drugs as prescribed by the physician Help the patient to select appropriate dietary choices to follow a high caloric diet. Refer the patient to the dietitian. Nursing Interventions C Excess fluid volume related to excessive amount of ADH as manifested by edema and decreased urine output Decreased RAAS activity Naturesis Imbalanced Nutrition: Less Than Body Requirements related to nausea, vomiting, weakness, loss of appetite aeb low serum sodium level weight gain Urine Output Serum osmolality Heart muscle wall stretches Nausea, Vomiting loss of appetite feeling of fullness Edema Increased water retention Cycle continues (unknown mechanism) Electrolyte Imbalance (Hyponatremia) related to the disease process of SIADH aeb nausea, vomiting, low level of sodium, irritability, and fatigue. Nursing Interventions Monitor I & O, daily weights Continuous ECG monitoring Assess and monitor vital signs every 1-2 hours Assess and monitor respiratory status; note changes in respiration, auscultate lungs Administer medication and electrolyte supplements appropriately Monitor lab / diagnostic values Nursing Interventions C concentrated urine urine Na concentration: > 40 mEq/L urine osmolality: > 100 mOsm/kg Decreased reabsorption of water in the kidney Diuresis and Naturesis water and sodium excretion EUVOLEMIA