Thermal Energy Transfer: Conduction & Convection Explained
advertisement

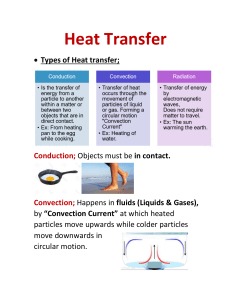
THERMAL ENERGY TRANSFER. Conduction and convection By Munkonge c. jr THERMAL ENERGY TRANSFER Are ways in which heat can travel. These are conduction, convection and radiation. Conduction: is the transfer of heat through collision of particles; It is the transfer of heat from one part of matter to another without movement of particles. • meaning there must be contact between atoms(bodies). Therefore, conduction is also defined as the transfer of heat through solids, though it also occurs in liquids, but hardly in gases because atoms are too far apart, while no conduction occurs in a vacuum. EXPERIMENT TO SHOW THE BEST CONDUCTOR OF HEAT. STICK A PIN AT THE END OF EACH ROD USING WAX OR VASELINE AND HEAT THE RODS WITH UNIFORM HEAT AT THE OTHER END FROM THE PINS. THE ONE THAT DROPS THE PIN FIRST IS THE BEST CONDUCTOR WHILE THE LAST ONE TO DO SO IS THE LEAST CONDUCTOR. EXPERIMENT TO SHOW THAT WATER IS A POOR CONDUCTOR OF HEAT SET THE APPARATUS AS SHOWN IN THE DIAGRAM. HEAT THE WATER AT THE TOP OF THE TEST TUBE UNTIL THE WATER BOILS. OBSERVATION: WATER AT THE TOP BOILS WHILE AT THE BOTTOM IT REMAINS COLD AND THE ICE DOES NOT MELT. NOTE: ICE IS WRAPPED IN A WIRE GAUZE TO MAKE IT SINK TO THE BOTTOM SINCE ICE FLOATS ON WATER. Conduction is fastest in metals because they have many electrons that are free to move. These electrons quickly move when heated and pass on the heat to other electrons and atoms in cooler parts. Materials that allow heat to easily pass through are called conductors of heat, e.g. metals. Materials that do not allow heat to easily pass through are known as insulators e.g. plastic, wood, rubber and air. Metals and concrete feel cooler when you touch them because it is transferred from the human body to the metal or concrete. USES OF CONDUCTORS MAKING SAUCEPANS, BOILERS, KETTLES, POTS, RADIATORS USES OF INSULATORS WOOD IS USED IN MAKING HANDLES OF SAUCEPANS AND POTS. CORK IS USED FOR TABLE MATS. Uses of Air as an insulator Air is one of the best insulators. Certain houses have double walls separated by an air space. Some windows are double glazed with an airspace in between too. The air traps heat, hence such buildings keep warmer in winter and cooler in summer. Wool, fur, feathers, fiberglass and polystyrene foam are very good heat insulators because they trap air and are used for lagging(insulating hot water pipes, cylinders, ovens, refrigerators and walls and roofs of houses. A pullover/jersey made of wool fibres keeps one warm because it traps air which is an excellent insulator itself. CONVECTION Is the transfer of heat by the movement of hot particles to cooler regions. It occurs in fluids (Liquids and gases). Convection in liquids: when water particles at the bottom of a pot are heated, they move faster and further apart making them less dense, so they rise to the surface of the liquid. The cooler particles at the surface are denser hence sink to the bottom, become heated and less denser hence also rise and push the now cooler particles down. The transfer of heat by movement of all particles in a fluid forming a cycle is called a Convection current. CONVECTION IN AIR when air near the ground is heated, it becomes less dense and rises. The cooler air goes down. ❖ CONVECTION CANNOT OCCUR IN SOLIDS BECAUSE PARTICLES DO NOT MOVE FREELY but ONLY VIBRATE IN A FIXED POSITION. sea breeze ❖ During the day, the land heats up quickly, while water being a poor conductor remains cold. Air on land becomes hot, less dense, rises and is replaced by cool air from the sea. This is why the beach is usually cool during the day. Land breeze: At night, the land cools fast, the water remains warm. So warm air above the sea rises and is replaced by cool air from the land.