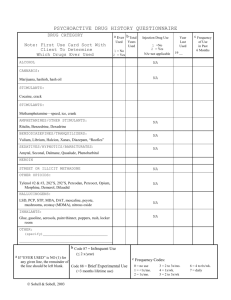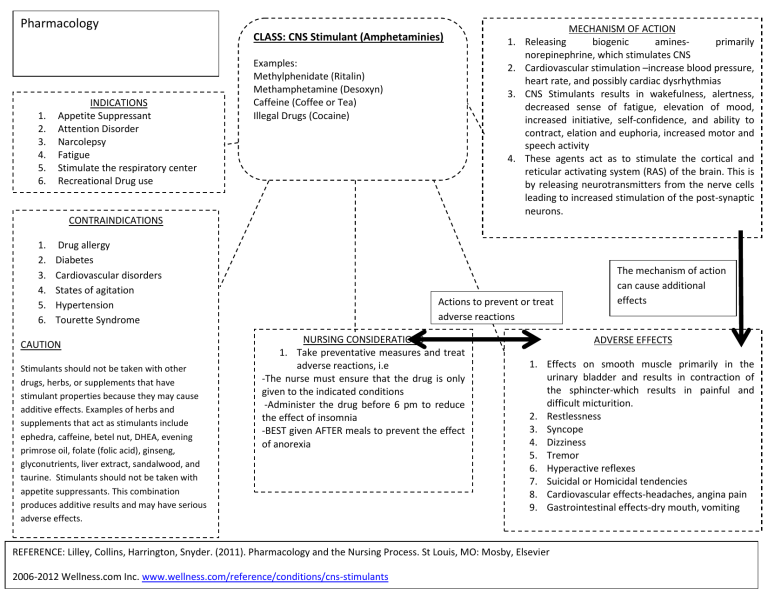
Pharmacology CLASS: CNS Stimulant (Amphetaminies) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. INDICATIONS Appetite Suppressant Attention Disorder Narcolepsy Fatigue Stimulate the respiratory center Recreational Drug use Examples: Methylphenidate (Ritalin) Methamphetamine (Desoxyn) Caffeine (Coffee or Tea) Illegal Drugs (Cocaine) CONTRAINDICATIONS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Drug allergy Diabetes Cardiovascular disorders States of agitation Hypertension Tourette Syndrome CAUTION Stimulants should not be taken with other drugs, herbs, or supplements that have stimulant properties because they may cause additive effects. Examples of herbs and supplements that act as stimulants include ephedra, caffeine, betel nut, DHEA, evening primrose oil, folate (folic acid), ginseng, glyconutrients, liver extract, sandalwood, and taurine. Stimulants should not be taken with appetite suppressants. This combination produces additive results and may have serious adverse effects. MECHANISM OF ACTION 1. Releasing biogenic aminesprimarily norepinephrine, which stimulates CNS 2. Cardiovascular stimulation –increase blood pressure, heart rate, and possibly cardiac dysrhythmias 3. CNS Stimulants results in wakefulness, alertness, decreased sense of fatigue, elevation of mood, increased initiative, self-confidence, and ability to contract, elation and euphoria, increased motor and speech activity 4. These agents act as to stimulate the cortical and reticular activating system (RAS) of the brain. This is by releasing neurotransmitters from the nerve cells leading to increased stimulation of the post-synaptic neurons. Actions to prevent or treat adverse reactions NURSING CONSIDERATIONS 1. Take preventative measures and treat adverse reactions, i.e -The nurse must ensure that the drug is only given to the indicated conditions -Administer the drug before 6 pm to reduce the effect of insomnia -BEST given AFTER meals to prevent the effect of anorexia ADVERSE EFFECTS 1. Effects on smooth muscle primarily in the urinary bladder and results in contraction of the sphincter-which results in painful and difficult micturition. 2. Restlessness 3. Syncope 4. Dizziness 5. Tremor 6. Hyperactive reflexes 7. Suicidal or Homicidal tendencies 8. Cardiovascular effects-headaches, angina pain 9. Gastrointestinal effects-dry mouth, vomiting REFERENCE: Lilley, Collins, Harrington, Snyder. (2011). Pharmacology and the Nursing Process. St Louis, MO: Mosby, Elsevier 2006-2012 Wellness.com Inc. www.wellness.com/reference/conditions/cns-stimulants The mechanism of action can cause additional effects