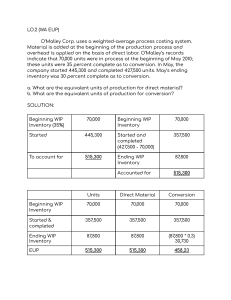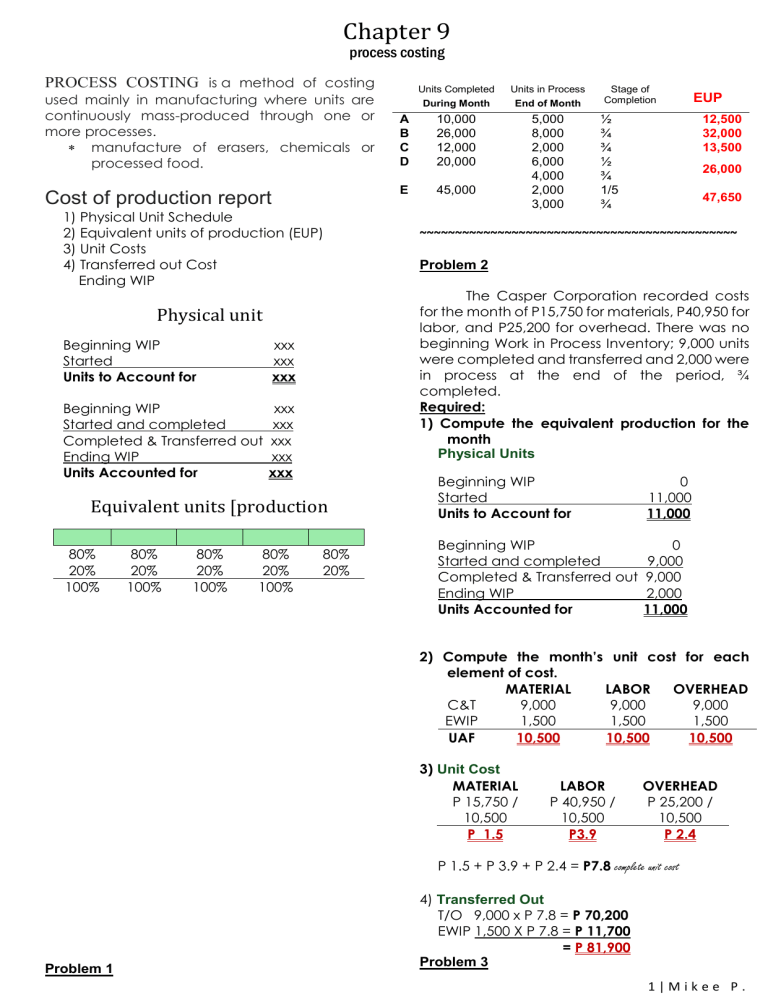
Chapter 9 process costing PROCESS COSTING is a method of costing used mainly in manufacturing where units are continuously mass-produced through one or more processes. manufacture of erasers, chemicals or processed food. Cost of production report 1) Physical Unit Schedule 2) Equivalent units of production (EUP) 3) Unit Costs 4) Transferred out Cost Ending WIP Physical unit Beginning WIP Started Units to Account for xxx xxx xxx Beginning WIP Started and completed Completed & Transferred out Ending WIP Units Accounted for xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx Equivalent units [production 80% 20% 100% 80% 20% 100% 80% 20% 100% 80% 20% 100% 80% 20% Units Completed During Month Units in Process End of Month A B C D 10,000 26,000 12,000 20,000 E 45,000 5,000 8,000 2,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 3,000 Stage of Completion ½ ¾ ¾ ½ ¾ 1/5 ¾ EUP 12,500 32,000 13,500 26,000 47,650 ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Problem 2 The Casper Corporation recorded costs for the month of P15,750 for materials, P40,950 for labor, and P25,200 for overhead. There was no beginning Work in Process Inventory; 9,000 units were completed and transferred and 2,000 were in process at the end of the period, ¾ completed. Required: 1) Compute the equivalent production for the month Physical Units Beginning WIP Started Units to Account for 0 11,000 11,000 Beginning WIP Started and completed Completed & Transferred out Ending WIP Units Accounted for 0 9,000 9,000 2,000 11,000 2) Compute the month’s unit cost for each element of cost. MATERIAL LABOR OVERHEAD C&T 9,000 9,000 9,000 EWIP 1,500 1,500 1,500 UAF 10,500 10,500 10,500 3) Unit Cost MATERIAL P 15,750 / 10,500 P 1.5 LABOR P 40,950 / 10,500 P3.9 OVERHEAD P 25,200 / 10,500 P 2.4 P 1.5 + P 3.9 + P 2.4 = P7.8 complete unit cost Problem 1 4) Transferred Out T/O 9,000 x P 7.8 = P 70,200 EWIP 1,500 X P 7.8 = P 11,700 = P 81,900 Problem 3 1|Mikee P. Compute the equivalent production for the month for each of the following cases: CASE 1 Started in process 10,000 units; completed 8,000 units; work in process, end of period 2,000 units, 3/4 completed. All material are added at the beginning of the process. MATERIAL CC 8,000 8,000 8,000 10,000 2,000 (3/4) 2,000 1,500 10,000 9,500 CASE 2 Received from preceding department 40,000 units; completed 34,000 units; work in process, end of period, 6,000 units, 1/4 completed. All materials are added at the end of the process. MATERIAL CC 34,000 34,000 34,000 40,000 6,000 (1/4) 0 1,500 34,000 35,500 CASE 3 Started in process 40,000 units; completed 34,000 units, closing inventory goods in process 3,000 units. 1/3 completed, and 3,000 units, 1/5 completed. 75% of the materials are added at the beginning of the process and 25% when the process is 1/2 completed. 34,000 3,000 (1/3) 40,000 6,000 3,000 (1/5) MATERIAL 34,000 2,250 0 2,250 0 38,500 CC 34,000 1,000 6,000 35,600 The following data appeared in the accounting records of the Beautiful Company. Started in Process 12,000 Units Completed & Transferred 10,500 units Work in Process, end the month 1,500 untis Stage of completion 2/5 complete Costs: Materials P 72,000 Labor 88,800 Overhead 44,400 One half of the materials are added at the beginning of the process and the balance when the untis are one-half completed. Required: Calculate the ff: 1) Equivalent production for materials and conversion cost. Physical Units Beginning WIP Started Units to Account for 0 12,000 12,000 Beginning WIP 0 Started and completed 10,500 Completed & Transferred out 10,500 Ending WIP 1,500 Units Accounted for 12,000 Equivalent units production MATERIAL LABOR C&T 10,500 10,500 EWIP 750 600 11,250 11,100 2) Cost of the untis completed and transferred. 3) cost of the units in process at the end of the month. 2-3 answer: Unit cost MATERIAL P 72,00 / 11,250 P 6.4 CONVERSION COST P 133,200 / 11,100 P 12 P 6.4 + P 12 = P 18.4 Transferred Out C&T 10,500 x P 18.4 P 193,200 EWIP – M 750 x P 6.4 = P 4,800 – CC 600 x P 12 = P 7,200 EWIP 12,000 P 205,200 Problem 4 2|Mikee P ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Problem 5 ABM Company uses two departments to produce a product. The following data were taken from the books for the month of January, 2019. Dept 1 Units: Started Completed &Trasferred In process, End Stage of completion Costs: Materials Labor Factory Overhead Dept 2 60,000 40,000 20,000 75% 30,000 10,000 80% P 480,000 330,000 220,000 P 245,000 190,000 114,000 Required: Cost of production report 0 40,000 40,000 Beginning WIP 0 Started and completed 30,000 Completed & Transferred out 30,000 Ending WIP 10,000 Units Accounted for 40,000 C&T EWIP MATERIAL 30,000 5,000 35,000 TRANS IN 30,000 10,000 40,000 CC 30,000 8,000 38,000 COSTS ARE TREATED LIKE A MATERIAL BUT ARE ALWAYS ADDED AT THE BEGINNING Unit cost DEPARTMENT 1 Physical Units Beginning WIP Started Units to Account for 0 60,000 60,000 Beginning WIP 0 Started and completed 40,000 Completed & Transferred out 40,000 Ending WIP 20,000 Units Accounted for 60,000 Equivalent units production MATERIAL 40,000 20,000 60,000 Beginning WIP Started Units to Account for Equivalent units production Department 1 - all materials added at the beginning of the process Department 2 - 50% of the materials are added at the beginning of the process remaining 50% added at the end of the process. C&T EWIP Physical Units CONVERSION COST 40,000 15,000 55,000 Unit cost MATERIAL P 480,000 / 60,000 CONVERSION COST P 550,000 / 55,000 P 8 P 10 TRANS IN P 720,000 / 40,000 P 18 MATERIAL P 245,000 / 35,000 P 7 CC P 304,000 / 38,000 P8 P 8 + P 7 + P 18 = P 33 Transferred Out C&T 30,000 x P 33 EWIP – T/in 10,000 x P 18 –M 5,000 x P 7 – CC 8,000 x P 8 EWIP = P 990,000 = P 180,000 = P 35,000 = P 64,000 P 279,000 P 1,269,000 Department 1 Department 2 P 480,000 P 245,000 330,000 190,000 220,000 114,000 P 1,030,000 P 549,000 = P 1,579,000 EWIP 310,000 C&T & EWIP 1,269,000 P 8 + P 10 = P 18 Transferred Out C&T 40,000 x P 18 = P 720,000 EWIP – M 20,000 x P 8 = P 160,000 – CC 15,000 x P 10 = P 150,000 EWIP P 310,000 P 1,030,000 DEPARTMENT 2 3|Mikee P. Chapter 10 Average and fifo costing Problem 1 A company’s record shows the following information concerning the work in process in a chemical plant. a) Beginning inventory – 10,000 units (materials are 80% complete; conversion costs are 60% complete) b) Transferred out – 50,000 units c) Ending inventory – (materials are 50% complete, conversion costs are 40% complete) d) Started this month – 45,000 units Requirements: Compute the equivalent units for materials and conversion costs using FIFO and Average. Physical Units Beginning WIP Started Units to Account for 10,000 45,000 55,000 Beginning WIP Started and completed Completed & Transferred out Ending WIP Units Accounted for 5,000 ✓ 45,000 ✓ 50,000 5,000 ✓ 55,000 Equivalent units production FIRST IN - FIRST OUT WEIGHETD AVERAGE Materials CC Materials CC 2,000 4,000 40,000 40,000 50,000 50,000 ✓ 2,500 2,000 2,500 2,500 ✓ 44,500 46,000 52,500 52,500 ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Problem 2 A company’s record show the following information concerning the work in process at an assembly plant: a) Beginning inventory – (materials are 60% complete; conversion costs are 75% complete) b) Transferred out – 50,000 units c) Ending inventory – 10,000 (materials are 60% complete, conversion costs are 80% complete) d) Started this month – 45,000 units Requirements: Compute the equivalent units for materials and conversion costs using FIFO and Average. Physical Units Beginning WIP Started Units to Account for 15,000 45,000 60,000 Beginning WIP Started and completed Completed & Transferred out Ending WIP Units Accounted for 15,000 ✓ 35,000 ✓ 50,000 10,000 ✓ 60,000 4|Mikee P Equivalent units production FIRST IN - FIRST OUT WEIGHETD AVERAGE Materials CC Materials CC 6,000 3,750 35,000 35,000 50,000 50,000 ✓ 6,000 8,000 6,000 8,000 ✓ 47,000 46,750 56,000 58,000 Problem 3 A company uses the FIFO method to account for its work in process inventories. The account records show the following information: Beginning work in process inventory Materials P 360 Conversion costs 180 Debits to work in process inventory this period: Materials P 3,714 Conversion costs 2,258 Units: Beginning inventory 300 units Percent of completion (materials, 60%, conversion cost, 30%) Started this period 2,000 units Ending inventory 600 units Percent of completion: (materials, 40%, conversion cost, 20%) Requirements: 1) Compute the equivalent units for materials and conversion costs. 2) Compute the unit cost for materials and conversion costs. 3) Compute the cost of goods transferred out. 4) Compute the cost of the ending inventory. Physical Units Beginning WIP Started Units to Account for 300 2,000 2,300 Beginning WIP Started and completed Completed & Transferred out Ending WIP Units Accounted for 300 ✓ 1,400 ✓ 1,700 600 ✓ 2,300 Equivalent units production FIRST IN - FIRST OUT WEIGHETD AVERAGE Materials CC Materials CC 120 210 1,400 1,400 1,700 1,700 ✓ 240 120 240, 120 ✓ 1,760 1,730 1,940 1,820 Unit cost FIRST IN - FIRST OUT Materials CC 3,714 2,258 1,760 1,730 P 2.11 P 1.31 = P 3.42 WEIGHETD AVERAGE Materials CC 4,074 2,438 1,940 1,820 P 2.10 P 1.34 = P 3.44 Cost of goods transferred out FIRST IN - FIRST OUT Beg WIP 540,000 M (120 X P2.11) 253.20 CC (210 X P1.31) 275.10 Current (1,400 x P3.42) TOTAL M (240 x P2.11) CC (120 x P1.31) WEIGHETD AVERAGE 1,068.30 4,788 5,856.30 Current (1,700 x P3.44) ENDING WORK IN PROCESS 506.40 157.20 663.60 M (240 x P2.10) CC (120 x P1.34) 5,848 504 160.80 664.80 Problem 4 5|Mikee P. The beginning work in process inventory showed a balance of P48,240. Of this amount, P16,440 is the cost of direct materials, and P31,800 are conversion costs. There were 8,000 units in the beginning inventory that were 30% complete with respect to both direct materials and conversion costs. During the period, 17,000 units were transferred out and 5.000 remained in the ending inventory. The units in the ending inventory were 80% complete with respect to direct materials and 40% complete with respect to conversion costs. Costs incurred during the period amounted to P126,852 for direct materials and P219,120 for conversion costs. Requirements: Compute for the following using FIFO and Average 1) Equivalent production for materials and conversion costs. 2) Cost per equivalent unit for materials and conversion costs. Physical Units Beginning WIP Started Units to Account for 8,000 14,000 22,000 Beginning WIP Started and completed Completed & Transferred out Ending WIP Units Accounted for 8,000 ✓ 9,000 ✓ 17,000 5,000 ✓ 22,000 Equivalent units production FIRST IN - FIRST OUT WEIGHETD AVERAGE Materials CC Materials CC 5,600 5,600 9,000 9,000 17,000 17,000 ✓ 4,000 2,000 4,000 2,000 ✓ 18,600 16,600 21,000 19,000 Unit cost FIRST IN - FIRST OUT WEIGHETD AVERAGE Materials CC Materials CC 126,852 219,120 143,292 250,920 18,600 16,600 21,000 19,000 P 6.82 P 13.20 P 6.82 P 13.21 = P 20.02 = P 20.03 Cost of goods transferred out FIRST IN - FIRST OUT Beg WIP 48,240 M (5,600 x P6.82) 38,192 CC (5,600 x P13.20) 73,920 Current (9,000 x P20.02) TOTAL M (4,000 x P6.82) CC (2,000 x P13.20) PROBLEM 5 6|Mikee P WEIGHETD AVERAGE 160,352 180,180 340,532 Current (17,000 x P20.03) ENDING WORK IN PROCESS 27,280 26,400 53,680 M (4,000 x P6.82) CC (2,000 x P13.21) 340,510 27,280 26,420 53,700 Auto Novelties, Inc. manufactures a small robot that can be moved around by remote control. It can be used as a novelty to serve food and drinks to guests, and with a special attachment it can vacuum the carpet. The materials are all added at the beginning of the Assembly Operation (the first operation). Labor and added uniformly during the month. Data for the month of July in the assembly Operation are given as follow Units Work in process, July 1 15,000 Units started in process 250,000 Costs Work in process, July Materials 1 P210,000 Labor and overhead 60,000 July costs: Materials 3,500,000 Labor and overhead 1,458,000 The inventory of work in process on July 1 was complete as to materials but only 2/3 complete as to labor and overhead. On July 31, the inventory consisted of 20,000 units that were 40% complete with respect to labor and overhead. Required: Using average method and FIFO method compute for 1) Equivalent production for materials, labor and overhead 2) Unit cost for materials, labor and overhead 3) Total costs of units completed ad transferred 4) Total costs of units in process, end Physical Units Beginning WIP Started Units to Account for 15,000 250,000 265,000 Beginning WIP Started and completed Completed & Transferred out Ending WIP Units Accounted for 15,000 ✓ 20,000 ✓ 245,000 20,000 ✓ 265,000 Equivalent units production FIRST IN - FIRST OUT WEIGHETD AVERAGE Materials CC Materials CC 0 5,000 230,000 230,000 245,000 245,000 ✓ 20,000 8,000 20,000 8,000 ✓ 250,000 243,000 265,000 253,000 Unit cost FIRST IN - FIRST OUT Materials CC 3,500,000 1,458,000 250,000 243,000 P 14 P6 = P 20 WEIGHETD AVERAGE Materials CC 3,710,000 1,518,000 265,000 253,000 P 14 P6 = P 20 Cost of goods transferred out FIRST IN - FIRST OUT Beg WIP 270,000 M (0 x P14) 0 CC (5,000 x P6) 30,000 Current (230,000 x P20) TOTAL M (20,000 x P14) CC (8,000 x P6)) WEIGHETD AVERAGE 30,000 4,600,000 4,900,000 Current (245,000 x P20) ENDING WORK IN PROCESS 280,000 48,000 328,000 M (20,000 x P14) CC (8,000 x P6) 4,900,000 48,000 328,000 7|Mikee P. Problem 6 At the beginning of September, the Ellery Company had P 27,950 (direct materials - P7.800, conversion cost - P 20,150) in Department A's beginning work inprocess inventory. The inventory consisted of 15,500 units which had 100% of direct materials and 65% of conversion cost. During September, 36,000 units were started in process. Costs incurred during the month were: direct materials - P54.000, conversion costs P 79.000. As the 48,000 units were completed, they were immediately transferred to Department B. At the end of September, 3,500 were still in process and are 100% complete as to materials, and 45% converted. Required: Using average method and FIFO method determine the following 1) Equivalent production for materials and conversion cost 2) Unit cost for materials and conversion cost 3) Total costs of units completed and transferred 4) Total costs of units in process, end Physical Units Beginning WIP Started Units to Account for 15,500 36,000 51,500 Beginning WIP Started and completed Completed & Transferred out Ending WIP Units Accounted for 15,500 ✓ 32,500 ✓ 48,000 3,500 ✓ 51,500 Equivalent units production FIRST IN - FIRST OUT WEIGHETD AVERAGE Materials CC Materials CC 0 5,425 32,500 32,500 48,000 48,000 ✓ 3,500 1,575 3,500 1,575 ✓ 36,000 39,000 51,500 49,575 Unit cost FIRST IN - FIRST OUT Materials CC 54,000 79,000 36,000 39,500 P 1.50 P2 = P 3.50 WEIGHETD AVERAGE Materials CC 61,800 99,150 51,500 49,575 P 1.20 P2 = P 3.20 Cost of goods transferred out FIRST IN - FIRST OUT Beg WIP 27,950 M (0 x P1.50) 0 CC (5,425 x P2) 10,850 Current (32,500 x P3.50) TOTAL M (3,500 x P1.50) CC (1,575 x P2) 8|Mikee P WEIGHETD AVERAGE 38,800 113,750 152,550 Current (48,000 x P3.2) ENDING WORK IN PROCESS 5,250 3,150 8,400 M (3,500 x P1.2) CC (1,575 x P2) 153,600 4,200 3,150 7,350 PROBLEM 14 The following were taken from the books of Michelle Company for the month of June, 2019. The company uses FIFO in costing finished goods and goods sold Inventories, June 1 Materials P 50,000 Finished goods ( 5,000 units) 75,000 The transactions for the month of June are as follows: 1) Purchased materials on account, P 180,000 2) Issued materials - Dept. 1 P 90,000, Dept. 2 - P112,500 3) The total payroll for the month amounted to P 135,600 distributed as follows: Dept. 1-P 64,800, Dept. 2-P 61,600 and the balance - indirect labor 4) Factory overhead applied amounted to Dept 1-P 59,400, Dept. 2-P 50,600 5) Units completed and transferred to finished goods - 40.000 6) Sold 25.000 units at P 400.000 QUANTITY DATA DEPARTMENT 1 60,000 45,000 60% Units Started Uunits Completed Stage of Completion DEPARTMENT 2 40,000 80% Materials, in both departments, are added 100% at the beginning! Requirements: 1. Journal entries to record the above transactions (1) Raw materials Inventory Accounts Payable 180,000 180,000 (2) Work in Process – Dept 1 Work in Process – Dept 2 Raw Materials Inventory 64,800 112,500 202,500 (3) Work in Process – Dept 1 Work in process - Dept 2 Factory overhead control Accrued payroll 64,800 61,600 9,100 135,600 (4) Work in Process – Dept 1 59,400 Work in Process – Dept 2 50,600 Factory overhead applied 110,000 (5) Work in Process – Dept 2 Work in Process – Dept 1 171,000 171,000 Finished Goods Inventory Work in Procfess – Dept 2 354,000 354,000 (6) Accounts Receivable Sales (25 untis) 400,000 400,000 Cost of Goods Sold Finished Goods Inventory Beginning Finished Goods Current (at P8.85) Units Sold 252,000 252,000 5,000 75,000 20,000 177,000 25,000 252,000 2. Cost of units completed and transferred - Dept. 1 Physical Units Beginning WIP 15,500 Started 36,000 Units to Account for 51,500 Beginning WIP Started and completed Completed & Transferred out Ending WIP Units Accounted for 15,500 32,500 48,000 3,500 51,500 EUP FIRST IN - FIRST OUT Materials CC BWIP S&T EWIP 45,000 45,000 15,000 15,000 60,000 54,000 UNIT COSTS FIRST IN - FIRST OUT Materials CC 90,000 124,200 60,000 54,000 P 1.50 P 2.30 = P 3.80 TRANSFERRED OUT COSTS BWIP Current Cost (45,000 x P3.8) ENDING WIP M (15,000 x P1.5) CC (9,000 x P2.3) 171,000 171,000 22,500 20,700 9|Mikee P. 43,200 3. Cost of units completed and transferred - Dept. 2 Physical Units Beginning WIP Started 45,000 Units to Account for 45,000 Beginning WIP Started and completed Completed & Transferred out Ending WIP Units Accounted for Materials 40,000 40,000 5,000 45,000 EUP FIRST IN - FIRST OUT Trans in CC BWIP S&T EWIP UNIT COSTS FIRST IN - FIRST OUT Materials CC 90,000 124,200 60,000 54,000 P 1.50 P 2.30 = P 3.80 TRANSFERRED OUT COSTS BWIP Current Cost (45,000 x P3.8) 171,000 171,000 ENDING WIP M (15,000 x P1.5) 22,500 CC (9,000 x P2.3) 20,700 43,200 4. Cost of goods sold statement 10 | M i k e e P /