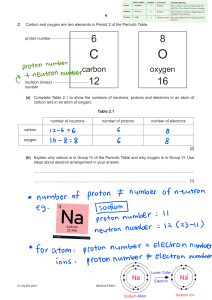
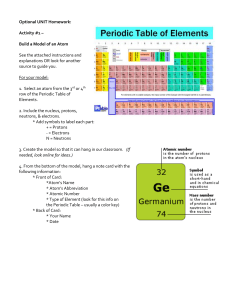
Name ______________________________________________________ Period ______ The Periodic Table as a Tool Test 1. ________ The one- or two-letter abbreviation of an element on the Periodic Table is called it’s… a. short form b. symbol c. letters d. contraction 2. ________ What sub-atomic particles are found in the nucleus of an atom? a. protons and electrons b. electrons and neutrons c. protons and neutrons 3. ________ If the atom to the right does not have an overall charge, which sub-atomic particle is colored in gray in the diagram? a. Protons b. Neutrons c. Electrons 4. ________ What is the atomic number of germanium? a. 32 b. 72.6 c. 40.6 d. 4 5. ________ How many protons does a krypton atom have? a. 18 b. 36 c. 47.8 d. 83.8 6. ________ The electrons of an atom that are in the outermost shell are known as ____ electrons. a. positive b. valence c. wild d. neutral 7. ________ What two parts of the atom have an atomic mass of approximately 1 amu (atomic mass unit)? a. protons and electrons b. electrons and neutrons c. protons and neutrons d. electron shells and electrons 8. ________ What can never change in an element and have that element remain the same? a. the number of electrons b. the number of protons c. the number of neutrons d. the atomic mass 1 9. ________ What is the negatively charged sub-atomic particle of an atom? a. Proton b. Neutron c. Electron 10. ________ What is the overall charge of the nucleus of an atom? a. Positive b. Negative c. Neutral 11. ________ How many neutrons are in a typical fluorine atom? a. 10 b. 9 c. 18.9 d. 17 12. ________ What do the elements He, Ne, and Ar all have in common? a. They are all solids at room temperature b. Their outer shells are not filled c. Their outer shells are filled d. Their inner shells are not filled 13. ________ Atoms of an element that contain different numbers of neutrons are called… a. valence b. isotopes c. families 14. ________ What is the identity of the element that has 19 protons and 22 neutrons? a. Titanium b. Niobium c. Potassium d. Krypton 15. ________ For what reason is atomic mass in a decimal form on the Periodic Table? a. It is the relative atomic mass of all isotopes of the element b. There are parts of protons and neutrons that do not add up to a whole number c. The total mass of all of an atom’s subatomic particles is very specific d. Chemists these days have very precise instruments to measure the atomic mass 16. ________ Dmitri Mendeleev discovered patterns in the properties of elements when he arranged them in order by… a. number of electrons b. number of neutrons c. number of protons d. their mass 17. ________ The vertical (up and down) columns of the Periodic Table are called… a. periods b. rows c. groups 2 18. ________ What are the first two elements in Period 4: a. Be & Mg b. K & Ca c. C & Si d. Ti & Zr 19. ________ These types of elements are found to the right of the stair step line: a. metalloids b. metals c. non-metals 20. ________ What do we call the elements that border the stair-step line? a. transition elements b. metals c. non-metals d. metalloids 21. ________ Which family includes Beryllium and Magnesium? a. Noble gasses b. Alkali metals c. Alkaline earth metals d. Lanthanide series 22. ________ To which family do the most unreactive elements on the Periodic Table belong? a. The Alkali metals b. The Alkaline Earth metals c. The Noble Gases d. The Halogens 23. ________ What happens to the number of valence electrons as you move from left to right across a row or period in the periodic table? a. increase b. decrease c. stay the same d. double 24. ________ What happens to the number of energy levels (shells) as you move down a group or column on the periodic table? a. increase b. decrease c. stay the same d. double 25. ________ The second energy level (L shell) of an atom can hold a maximum of ___ electrons. a. 18 b. 8 c. 2 d. 4 3 26. ________ An atom has 12 electrons. What is the lowest number of energy levels (shells) that could be present in the atom? a. 12 b. 3 c. 4 d. 6 27. ________ How many valence electrons do elements in the Nitrogen family possess? a. 8 b. 7 c. 5 d. 15 28. ________ Which two elements have identical outer electron shells? a. Chlorine and Sodium b. Nitrogen and Oxygen c. Oxygen and Sulfur d. Sodium and Magnesium 29. ________ Which element’s atom does this diagram represent? a. Magnesium b. Calcium c. Sodium d. Carbon 30. ________Which of the following elements could this diagram represent? a. Cesium (Cs) b. Sulfur (S) c. Potassium (K) d. Carbon (C) ? Please write “M” next to properties of metallic elements and “NM” next to properties of non-metallic elements. 31. ________ shiny luster 35. ________ good conductor of heat 32. ________ brittle 36. ________ poor conductor of electricity 33. ________ able to be hammered into sheets 37. ________ yellow in color 34. ________ gas at room temperature 4 38. Draw a Bohr Diagram for Fluorine. 39. Draw a Lewis Dot Diagram for Aluminum. 40. Use the word bank to fill in the parts of the periodic table below: Halogens Lanthanides Noble gasses Transition metals Alkaline earth metals Alkali metals Metals Nonmetals Metalloids Actinides 5 Answer the following questions in complete sentences: 41. How is it possible for an atom to have no charge even though it is made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons? _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ 42. The mass of an atom may be determined by adding the masses of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Why is it unnecessary to include the electrons when determining the mass of an atom? _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ 43. Why is the atomic mass of an element not given as a whole number on the Periodic Table even though each individual atom of the element has a whole number of protons and neutrons? _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ 44. With as much detail as possible, please explain why hydrogen (H) is where it is on the periodic table. _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ 45. With as much detail as possible, please explain why helium (He) is where it is on the periodic table. _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ 6 Periodic Table as a Tool TEST ANSWERS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. B C B A B B C B C A A C B C A D C B C D C C A A B B C C A B M NM M NM M NM NM Al 1) alkali metals 2) alkaline earth metals 3) metals 4) transition metals 5) lanthanides 6) actinides 7) noble gases 8) halogens 9) nonmetals 10) metalloids 7 How is it possible for an atom to have no charge even though it is made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons? An atom has no charge because there are an equal number of positively-charged protons and negatively-charged electrons. The mass of an atom may be determined by adding the masses of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Why is it unnecessary to include the electrons when determining the mass of an atom? The electrons are not necessary to include when determining the mass of an atom because they have virtually no mass at all. Why is the atomic mass of an element not given as a whole number on the Periodic Table even though each individual atom of the element has a whole number of protons and neutrons? The atomic mass on the periodic table is an average weighted mass of all known isotopes of that element. With as much detail as possible, please explain why hydrogen (H) is where it is on the periodic table. Hydrogen is not an alkali metal (it’s not a metal at all), but it is in the same column as the alkali metals because it shares the characteristic of having one valence electron. It is in the first period because it has only one electron shell. It is atomic number 1 because it has just one proton. With as much detail as possible, please explain why helium (He) is where it is on the periodic table. Helium is considered a noble gas and is in the 18th group of the periodic table because it shares the noble gas characteristic of having a full valence electron shell and being relatively unreactive with other elements. Helium does not have 8 valence electrons like the other noble gases- it has only 2, but the first electron shell is ‘full’ with only 2 electrons. Helium is in the first period because it has only one electron shell. It is atomic number 2 because it has two protons. 8