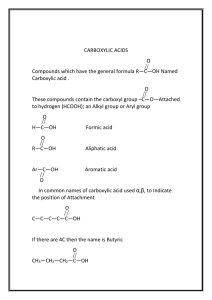
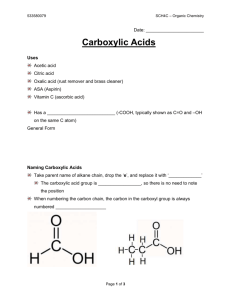
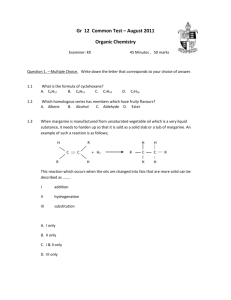
Reactions of Functional Groups Functional Group Reaction Example Alkane Combustion alkane + O2 CO2 + H2O Alkene / Alkyne + H2O add H and OH alcohol asymmetric + HX add H and X alkylal halide + X2 add X and X alkyl halide symmetrical + H2 add H and H alkane/ene alkene/yne alkene/yne X is alkene/yne halid alkene/yne e Addition ** alkynes may undergo two additions in a row to become an alkane Symmetrical Alkene: identical groups on either side of double bond CH2=CH2 Asymmetrical Alkene: different groups on either side of double bond CH2=CHCH3 MARKOVNIKOV’S RULE: “the rich get richer” In an addition reaction, H or OH is added to the more substituted carbon atom (C atom bonded to the largest number of C atoms) symmetrical + asymmetrical 1 isomer H3C CH3CH=CHCH3 + HOH H2 C Cl2 + asymmetrical CH2=CHCH3 + CH OH H CH Cl CH CH3 CH3 Cl 2 isomers (one is more observed due to asymmetrical Markovnikov’s Rule) CH2=CHCH2CH3 + Aromatic Compound s will NOT undergo addition Substitution (replace H or Functional Group) Substitution (with halogen acid) HBr H Br CH2 CH Br CH2 CH3 H CH CH2 + more observed CH2 CH3 no addition + Br FeBr3 + Br Br alcohol + halogen acid alkyl halide + water OH + HBr Br + Alcohols Elimination (with strong acid and dehydration agent) HBr alcohol OH alkene H2SO4 + water + H2O H2O alcohol + [O] aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid 1° alcohol aldehyde carboxylic acid 2° alcohol ketone 3° alcohol no reaction Oxidation Alkyl Halides Substition (with OH of base) alkyl halide + base alcohol + halogen acid Br + + OH -OH aldehyde + [O] Br - carboxylic acid O O Oxidation + C [O] C H OH Aldehydes aldehyde + [H] 1° alcohol O OH Reduction + C [H] C H H ketone Oxidation + ketone Ketones [O] no reaction [H] 2° alcohol + O OH Reduction + C [H] C carboxylic acid + base salt + water O Neutralizatio n O + C + NaOH C OH H2O ONa carboxylic acid + alcohol ester + water O Carboxylic Acids Condensatio n or Esterification O + HO C CH3 + C OH O H2O CH3 carboxylic acid + amine amide + water O O +H2N C CH3 + C OH NH H2O CH3 carboxylic acid + [H] aldehyde and alcohol O Reduction + C O C H salt of carboxylic acid + alcohol O C [H] H ester + base Hydrolysis + C OH Esters OH O [H] CH3 + NaOH H2SO4 O C + ONa HO CH3 amide + water carboxylic acid + amine O Amides Hydrolysis C HN CH3 + NaOH H2SO4 O C + OH H2N CH3