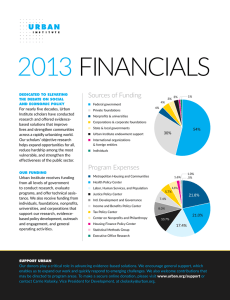
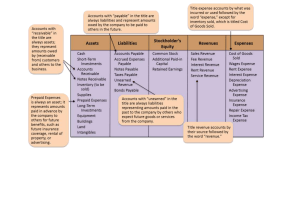
REVISION 1 – MODULE 4 Choose the best answer 1. ……………… is something you plan to do or achieve. A. Objective B. Promotion C. Strategy D. Innovation 2. ………………... is the section of the economy under government control. A. Crisis B. Institution C. Private sector D. Public sector 3. Managers ………… the ………. of their staff to see whether they are reaching their targets. A. perform – tasks B. measure – performance C. supervise- subordinates D. set objectives 4. …………… is a face-to-face disagreement or argument. A. compromise B. connection C. confrontation D. intuition 5. …………… is to do something when necessary without having already planned it. A. interrupt B. improvise C. confront D. stereotype 6. ………….. is to be humiliated or disrespected in public. A. associate B. undermine C. undergo D. lose face 7. The ……………..of Management are the essential, underlying factors that form the foundations of successful management. A. Principles B. Penetration C. Differentiation D. Segmentation 8. …………. is selling unwanted goods very cheaply, usually in other countries. A. copyright B. trademark C. dumping D. generic 9. ……………….. are possibilities of filling unsatisfied needs in sectors in which a company can profitably produce goods or services. A. distribution channel B. market opportunities C. market penetration D. market segmentation 10. The refugees live in …………… housing provided by the authorities. A. generic B. subsidized C. opposed D. classified 11. ……………. is someone who contacts existing and potential customers, and retries to persuade them to buy goods or services. A. sales representative B. wholesaler C. retailer D. consultant 12. ………………. is an intermediary that stocks manufacturers’ goods or merchandise, and sells it to retailers and professional buyers. A. market skimming B. distribution channel C. wholesaler D. market opportunities 13. In ……………, sales volume peaks. A. introduction stage B. growth stage C. maturity stage D. decline stage 14. Costs are reduced due to …………………., so profitability increases. A. macroeconomics B. microeconomics C. scalable schemes D. economies of scale 15. The company can choose between high …………….. to recover development costs, or low ………………. to build market share rapidly, if there are already competitors. A. penetration pricing - skim pricing B. market skimming – price elasticity C. skim pricing- market segmentation D. skim pricing- penetration pricing 16. …………. means a country’s ability produce particular goods more efficiently (using fewer resources and at a lower cost) than some other countries. A. comparative advantage B. absolute advantage C. infant industry D. strategic industry 17. In Italy, authority is important, as is ………………. A. senior B. superior C. hierarchically D. seniority 18. Successful companies are becoming ……………., adapting their products to fit their customers’ strategies. A. sales driven B. market driven C. market driving D. sales driving 1 19. …………. are the attributes or characteristics of a product, such as size, shape, quality, price, reliability, etc. A. distribution channel B. price elasticity C. product differentiation D. product features 20. …………. is the amount of money that you owe to a bank when you have spent more money than is in your bank account. A. cashpoint B. overdraft C. checking account D. current account 21. …………… is a legal agreement by which a bank or similar organization lends you money to buy a house, etc., and you pay the money back over a particular number of years. A. loan B. deposit C. debit card D. mortgage 22. ……………… are private investment funds for wealthy investors that use a wider variety of (risky) investing strategies than traditional investment funds, in order to achieve higher returns. A. Investment banks B. Hedge funds C. Stockbrokers D. Commercial banks 23. Glass-Steagall was …………… in 1999. A. repealed B. returned C. rated D. subprime crisis 24. …………… is money placed in a bank. A. loan B. capital C. equity D. deposit 25. ………… are certificates representing part-ownership of a company. A. stocks B. shares C. bonds D. Both A&B 26. ………….. are certificates of debt issued by governments or companies to raise money. A. stocks B. portfolios C. bonds D. returns 27. …………. is when one company combines with another one. A. takeover bid B. merger C. deregulation D. bankrupt 28. ………. is the ending or relaxing of legal restrictions. A. merger B. takeover bid C. stockbroking D. deregulation 29. ………. is buying and selling stocks or shares for clients. A. deregulation B. stockbroking C. conglomerate D. interest 30. ………. is a group of companies, operating in different fields, which have joined together. A. merger B. conglomerate C. takeover bid D. stockbroking 31. ………. means beingunable to pay debts or continue to do business. A. merger B. liquidate C. bankrupt D. takeover bid 32. ………. is when one company offers to buy or acquire another one. A. takeover bid B. merger C. liquidate D. stockbroking 33. ………. are the profits made on investments. A. returns B. margin C. portfolios D. stockbroking 34. ………. is all the investments owned by an individual or organization. A. returns B. portfolio C. stockbroking D. equity 35. ………. is the price paid for borrowing money, paid to the lenders. A. conglomerate B. returns C. interest D. deposit 36. Deregulation in the 1980s was one of the factors that led to the ………………………….. A. credit rating B. mutual funds C. subprime crisis D. mortgage payment 37. The value of …………………. fell to almost zero in 2007, and many banks lost billions of dollars. A. collateralized debt B. mortgage-backed securities C. credit crunch D. underlying mortgages 38. The bank makes small loans to a large number of people, which greatly …………… the risk. A. diversifies B. diversify C. diversification D. diversity 39. This process is called ………………..: financial assets like mortgages which produce a cash flow are pooled (grouped together) and converted into securities that are then sold to investors. A. default B. collateral C. cash flow D. securitization 2 40. When many subprime borrowers stopped paying, the value of subprime related securities fell …………….. A. slightly B. risky C. dramatically D. initiatively 41. Costs are reduced due to economies of scale, so …………………. increases. A. profitable B. profits C. unprofitable D. profitability 42. A ……………….. is a massive reduction in the amount of credit available for banks to other banks, businesses and households. A. subprime crisis B. credit crunch C. credit flow D. credit available 43. ………. is the money generated by an investment. A. default B. cash flow C. loan D. interest rate 44. ………. is failure to repay a loan. A. bankrupt B. debt C. default D. write off 45. ………. is cancel a bad debt or a worthless asset from an account. A. write off B. collateralize C. default D. debit 46. ………. is estimates of people’s ability to fullfil their financial commitments. A. collateral B. credit rating C. credit D. mortgage 47. ………. means with property or another asset used as a guarantee of payment. A. collateralized B. write off C. cash flow D. credit rating 48. I believe that good managers basically are good ………………….. of strategies. A. counselor B. executors C. consultancy D. executor 49. Reducing the amount of tax you pay to a legal minimum is called …………….. A. tax evasion B. creative accounting C. money laundering D. tax avoidance 50. ………….. is the total market value of all the goods and services produced in a country during a given period. A. gross domestic product B. balance of payment C. balance of trade D. balance sheet REVISION 2 – MODULE 4 Choose the best answer 1. …………. is all the money that a business spends on goods or services during a given period. A. expenditure B. income C. debts D. liabilities 2. …………. is anything owned by a business – cash, buildings, machines, equipment, etc. A. income B. revenue C. asset D. account 3. ………… means delayed or postponed until a later time. A. payable B. retained C. deferred D. accrued 4. An adjective describing something without a material existence, which you can’t touch. A. current B. intangible C. tangible D. incurred 5. ……………. is all the money received from business activities during a given period. A. asset B. income C. transaction D. budget 6. An adjective describing a liability which has been incurred but not yet invoiced to the company. A. accrued B. deferred C. receivable D. intangible 7. …………… is an entry in an account, recording a payment received. A. debit B. income C. credit D. expenditure 8. ………….. is an entry in an account, recording a payment made. A. credit B. debit C. transaction D. liabilities 9. ………….. is a financial operating plan showing expected income and expenditure. A. account B. budget C. financial statement D. revenue 10. ……………. are all the money that a company will have to pay to someone else in the future, including debts, taxes and interest payments. 3 A. debits B. expenditure C. expenses D. liabilities 11. The distribution of part of the earnings of a company to its shareholders is ……………… A. debit B. dividend C. stock D. share 12. The employees record the ………………… in an expense account. A. income B. goodwill C. retained earnings D. expenditure 13. Profits earned to date but not yet distributed to shareholders by way of dividends are …………….. A. retained earnings B. share premium C. additional paid-in capital D. stock 14. ……………. calculates how much an individual or a company will have to pay to the local and national governments. A. cost accounting B. transactions C. tax accounting D. liabilities 15. ………………. is an intangible asset and also considered as a saleable asset when a business is sold and is sometimes shown in the balance sheet. A. dividend B. goodwill C. share premium D. capital 16. ………….. is inspecting and reporting on accounts and financial records. A. balance sheet B. managerial accounting C. auditing D. bookkeeping 17. ………… is using all available accounting procedures and tricks to disguise the true financial position of a company. A. managerial accounting B. creative accounting C. cost accounting D. bookkeeping 18. …………… is writing down the details of transactions (debits and credits). A. cash flow statement B. income statement C. bookkeeping D. records 19. ………….. is a statement showing the differences between the revenues and expenses of a period. A. income statement B. cash flow statement C. balance sheet D. loss account 20. ………….. is a statement showing the value of a business’s assets, its liabilities, and its capital or shareholders’ equity. A. cash flow statement B. balance sheet C. income statement D. profit account 21. …………… is a statement giving details of money coming into and leaving the business, divided into day-to-day operations, investing and financing. A. balance sheet B. income statement C. cash flow statement D. expenses 22. …………… is money owed by customers for goods or services purchased on credit. A. total receivables B. account payable C. accrued expenses D. retained earnings 23. …………… is money owed to suppliers for purchases made on credit. A. prepaid expenses B. account payable C. retained earnings D. accrued expenses 24. …………… is money paid in advance for goods and services. A. retained earnings B. accrued expenses C. prepaid expenses D. goodwill 25. …………… are profits that have not been distributed to shareholders. A. goodwill B. additional paid-in capital C. accrued expenses D. retained earnings 26. …………… is the difference between the purchase price of acquired companies and their net tangible assets. A. property B. additional paid-in capital C. goodwill D. intangibles 27. …………… are the total amount of money owed that the company will have to pay out. A. accrued expenses B. additional paid-in capital C. total liabilities D. deferred income 28. …………… are expenses such as wages, taxes and interest that have not yet been paid at the date of the balance sheet. A. accrued expenses B. total liabilities C. deferred income D. prepaid expenses 29. …………… is capital that shareholders have contributed to the company above the nominal or par value of the stock. 4 A. additional paid-in capital B. shares C. stocks D. equity 30. …………… are assets whose value can only be turned into cash with difficulty (e.g. reputation, patents, trademarks, etc.) A. total liabilities B. shareholders’ equity C. tangibles D. intangibles 31. …………… is all the money belonging to the company’s owners. A. shareholders’ equity B. total liabilities C. current assets D. equivalent 32. …………… is the expenses specific to providing the company’s services. A. R & D B. interest income net C. ordinary shares D. cost of revenue 33. …………… are additional expenses involved in running the company. A. interest income net B. administrative expenses C. share premium D. net income 34. …………… is loss of value of intangible assets. A. amortization B. depreciation C. dividends paid D. unusual expense 35. …………… is loss of value of tangible assets. A. amortization B. depreciation C. dividends paid D. unusual expense 36. Often economists talk about notions of ………………. or the fact that markets are not working properly. A. free markets B. restriction C. market failure D. protectionism 37. Profits made by selling assets are generally liable to a ……………………. A. capital gains tax B. value-added tax C. wealth tax D. capital transfer tax 38. The annual tax imposed on people’s fortunes is a ………………. A. value-added tax B. wealth tax C. direct tax D. corporate tax 39. Making false declarations to the tax authorities is called ………………. A. fiscal policy B. tax avoidance C. tax evasion D. sales duty 40. A small mistake or exception in a tax law, which allows you to avoid paying something, is called …………. A. an escape B. an excuse C. a loophole D. tax havens 41. They disapprove of laws that prevent physicians …………. some drugs. A. prescribed B. prescribing C. described D. describing 42. ………… are positive or negative consequences (benefits or costs) of economic activities experienced by other people. A. allocation B. infrastructure C. outcome D. externalities 43. A tax levied at a higher rate on higher income is called a ……………. A. flat tax B. progressive tax C. regressive tax D. direct tax 44. A tax paid on property, sales transactions, imports, and so on is a/an …………… A. direct tax B. indirect tax C. income tax D. wealth tax 45. In introduction stage, promotion is aimed at educating potential consumers about the product, and building product ………………. A. production B. aware C. segmentation D. awareness REVISION 3 – MODULE 4 Choose the best answer 1. …………. is a period in which radical innovations destroy established companies or industries. A. creative accounting B. creative destruction C. consumption D. endogenous business cycle 5 2. …………. is a state of balance, for example when supply is the same as demand. A. equilibrium B. surplus C. deficit D. excess 3. A downturn that lasts more than 6 months is called a ………………… A. depression B. recession C. downswing D. downside 4. A downturn that lasts for a year or two is generally called a ………………… A. depression B. slump C. Both A & B D. downswing 5. Eventually the economy will reach a ……….. or bottom out, and there will be recovery or an upturn. A. upturn B. downturn C. trough D. save 6. When interest rates rise, people have to pay more on their …………… or rent. A. consumption B. mortgage C. savings D. investment 7. When the ……………. occurred in 2008, financial institutions began to go bankrupt. A. subprime crisis B. credit crunch C. Keynesianism D. monetarism 8. A raise in employee wages can ...................... production. A. expose B. unfetter C. enable D. stimulate 9. When companies have rivals that offer a better product at the same or better price, they often experience a ……………… in their stock market profile. A. upturn B. downturn C. boost D. expansion 10. A stock market is in ……………… when it changes from a bear market to a bull market. A. upturn B. downturn C. boost D. expansion 11. …………. is an amount of money that is smaller than is needed (e.g. when spending exceeds revenues). A. equilibrium B. surplus C. deficit D. peak 12. …………. is an excess: a quantity that is larger than is needed. A. boom B. surplus C. deficit D. contract 13. You might call something ........................ if its quality is not as good as another. A. superior B. inferior C. high-risk D. inefficient 14. …………. is government actions concerning taxation and public expenditure. A. fiscal policy B. monetary policy C. Keynesianism D. monetarism 15. ………….. is government or central bank actions concerning the rate of growth of the money in circulation. A. fiscal policy B. monetary policy C. Keynesianism D. monetarism 16. ……………. is the economic theory that government monetary and fiscal policy should stimulate business activity and increase employment in a recession. A. fiscal policy B. monetary policy C. Keynesianism D. monetarism 17. An alternative view to the stockholder model exemplified by Friedman’s article is the …………………. A. cardholder model B. free trade model C. customer model D. stakeholder model 18. Business owners want their bottom line to be as profitable as possible. To …………, the owner must be diligent in cutting costs and boost productivity among employees. A. provide employment B. maximize profits C. conform to rules D. conduct business 19. According to ………….. model, business managers have responsibilities to all the groups of people with a stake in or an interest in or a claim on the firm. A. stockholder B. shareholder C. simplified D. stakeholder 20. The U.S. economic system of …………………… operates according to five main principles: the freedom to choose our businesses, the right to private property, the profit motive, competition, and consumer sovereignty. A. discrimination B. free enterprise C. unbusinesslike D. customs 21. ………….are supporters, people who argue in favour of something. A. protestors B. proponents C. voters D. counselor 6 22. A …………. is one that is particularly important to a country’s economy. A. infant industry B. strategic industry C. absolute advantage D. protectionism 23. …………… investors seek to invest in firms which make a positive contribution to the quality of environment and quality of life. A. Ethical B. Embodied C. Undermining D. Discriminated 24. There are companies which are probably doing very good things for the community so that they can improve their ………….. with their external stakeholders. A. reputation B. elimination C. supply chain D. responsibility 25. If there is something going wrong within their supply chain management, with regard to human rights, low-cost …………….., working hours, then probably they don’t really have a good response from their own employees. A. labour child B. produces C. child labour D. goods 26. I think it is very important to listen to all different stakeholders, internal and external, to develop a …………… approach to corporate social responsibility. A. responsive B. serious C. holistic D. significant 27. …………….. are government policies or regulations that restrict international trade. A. tariffs B. trade barriers C. quotas D. inefficiency 28. Trade .................... is how countries raise tariffs and reduce imports to protect their domestic industries. A. analogy B. stimulation C. protectionism D. simulation 29. A …………. is a tax charged on imports. A. tariff B. quota C. inefficiency D. protectionism 30. A …………. is a maximum quantity of goods of a specific kind that can be imported into a country. A. tariff B. quota C. protectionism D. restriction 7