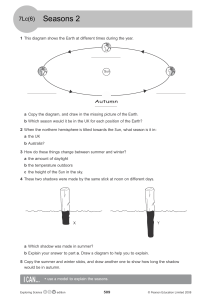
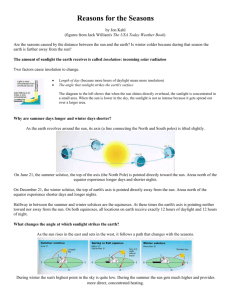
Environmental Science How can Climate Change be responsible for this flooding? Phenomenon: The Earth is closest to the Sun in January. Chapter 3.3 – Earth’s Spheres Essential Question: What causes seasons and climate? Objective: To understand the cause of climate. Scientific Concept: Patterns Seasons: Four divisions of the year marked by specific weather patterns and the position of the Earth relative to the sun. Equator: Imaginary line exactly halfway through a planet. Tropics: Northern or Southern line where the sun is directly overhead. Poles: Arctic and Antarctic Circles in which the noon sun can’t be seen in the winter, and the midnight sun can be seen in the summer. Rotation on Axis: Causes day and night. ~24 hours Revolution around the Sun: Causes seasons, one revolution is called a year. ~365.25 days Axial Precession: Earth’s wobble around the axis. Currently at 23.5 degrees. Solstice: The point at which the Earth’s tilt is pointed toward or away from the sun. (Tropics at noon) Summer Solstice has the most hours of daylight. Winter solstice has the least hours of daylight. Equinox: The point at which the Earth’s tilt is sideway to the sun. (Equator at noon) 12 hours of daylight. Vernal = Spring Autumnal = Fall Summer Path Spring/Fall Path Winter Path