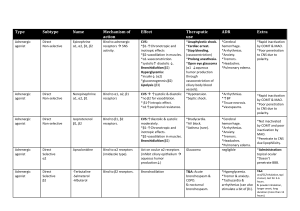
Pharm Quiz 2 Study Guide Adrenergic agonists: stimulate more than one of the adrenergic receptor sites Adrenergic antagonists (adrenergic blockers): drugs that block the effects of adrenergic neurotransmitters, block alpha and beta receptor sites Adrenergic: drugs that stimulate the sympathetic (fight or flight response) nervous system are called adrenergic agonists. sympathetic nervous system aka “adrenergic system”. 1. Epinephrine (adrenaline) - A hormone and a medication, but we are focusing on the medication form - Treat life threatening allergic reactions or anaphylaxis - Use in emergency situations - Alpha (1) and Beta (1 and 2) Adrenergic agonist, also called “sympathomimetic” - IM or IV usually 0.1-0.3 mg - Mode of action: induces increased vascular smooth muscle contraction, increases heart rate - Pharmacokinetics: acts rapidly because its IV or IM, inactivated in GI tract, half life: <5 min (really quick) - Side effects: restlessness, tremor, tachycardia, dysrhythmias, pulmonary edema 2. Albuterol - Beta 1 adrenergic agonist - Mode of action: activates only beta 2 adrenergic receptors, so response is relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle and bronchodilation - Side effects: tachycardia, palpitations, dysrhthymia, tremors, headache, nervousness - PO oral inhalation usually 32 mg per day - Treat or prevent bronchospasm 3. Atenolol - Beta 1 blocker, by blocking these receptors atenolol decreases the heart rate - decreases sympathetic outflow to the periphery - treats hypertension, angina - contraindicted in bradycardia, acute heart failure - half life: 6-7 hours - 50% absorbed in GI tract - tablets and IV: max 100 mg / day - side effects: bradycardia, tachycardia, heart failure, bronchospasm, Cholinergic: drugs that stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system 4. Bethanechol - Treats urinary retention - Promotes contraction of the bladder - Half life: unkown - PO 200 mg/day max typical does 5-10 mg 5. Atropine - Anticholinergic - Useful primarily as an agent to increase heart rate when bradycardia is present Also can be used when someone overdoses on Bethanechol IV: 0.5mg- 1mg per dose Half life: 2-4 hours 6. Benztropine Anticholinergic agent Treats parkinsonism PO/IM/IV: 0.5-6 mg per dose, 8 mg daily max Half life: unknown 7. Tolterodine Tartrate Anticholinergic, blocks cholinergic receptors PO: 1-4 mg per dose , max 4 mg daily Decreases urinary frequency, urgency, and incontinence Half life: 2-4 hours Page 186 in your text addresses Bethanechol – it is Bethanechol chloride. I would review the information in your text that covers the prototype – such as Page 187 Prototye Drug chart 16.1 This covers a lot of information needed. Other help for studying – the purple boxes that cover more information – such as page 188 Table 16.2 – Effects of Cholinergic Agonists. I hope this helps. Professor Caflisch