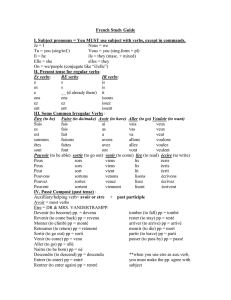
Le Passé Composé Formation The Perfect Tense in French is formed of two parts: 1) an AUXILIARY VERB + 2) a PAST PARTICIPLE The auxiliary verb is always the present tense of either AVOIR or ETRE. The past participle is formed from the verb being used in the sentence, as explained below. AVOIR VERBS Auxiliary verb is the present tense of avoir: J'ai Tu as Il/elle a nous avons vous avez ils / elles ont Regular Verbs form their past participle in the following ways: -ER Verbs jouer = joué aimer > to like, to love -RE Verbs vendre = vendu attendre: to wait (for) -IR Verbs finir = fini Abolir > to abolish arriver > to arrive, to happen défendre: to Agir > to act defend Avertir > to warn descendre: to Bâtir > to build descend Choisir > to choose chanter > to sing chercher > to look for commencer > to begin entendre: to hear établir > to establish danser > to dance étendre: to stretch étourdir > to stun, demander > to ask for fondre: to melt dépenser > to spend pendre: to hang, Finir > to finish suspend Grossir > to gain (money) détester > to hate perdre: to lose donner > to give prétendre: to claim écouter > to listen to rendre: to give étudier > to study fermer > to close goûter > to taste jouer > to play laver > to wash manger > to eat nager > to swim parler > to talk, to back, return weight, get fat Guérir > to cure, heal, recover Maigrir > to lose weight, get thin répandre: to spread, scatter deafen, make dizzy Nourrir > to feed, nourish répondre: to answer Obéir > to obey vendre: to sell Punir > to punish Réfléchir > to reflect, think speak Remplir > to fill passer > to pass, spend Réussir > to succeed (time) Rougir > to blush, turn red porter > to wear, to carry rêver > to dream sembler > to seem skier > to ski Vieillir > to grow old travailler > to work trouver > to find voler > to fly, to steal Thus, when we put it all together, we end up with sentences like: J'ai joué au tennis. -> (I played tennis / have played tennis) Mon frère a vendu son vélo. -> (My brother sold his bike / has sold his bike) Elles ont fini les devoirs. -> (They finished / have finished the homework) Nous avons regardé un très bon film à la télé. -> (We watched a very good film on TV.) Tu as attendu un autobus ou un train? -> (Are you waiting for a bus or a train?) Vous avez choisi, Madame? -> (Have you chosen, madame?) IRREGULAR VERBS: A number of verbs do not form their past participle following the rules above. These need to be learned separately, and the main ones as as follows: avoir = eu être = été faire = fait boire = bu conduire = conduit connaître = connu courir - couru croire = cru devoir = dû dire = dit dormir - dormi écrire = écrit falloir = fallu lire = lu mettre = mis prendre=pris ouvrir = ouvert pleuvoir = plu comprendre = compris apprendre=appris pouvoir = pu recevoir = reçu rire = ri savoir = su tenir = tenu vivre = vécu voir - vu vouloir = voulu suivre = suivi e.g. J'ai ouvert mes cadeaux après le petit déjeuner. Nous avons fait de la natation au centre sportif. Pierre et Paul ont lu un bon livre. ETRE VERBS A number of verbs take ETRE as their auxiliary verb instead of AVOIR. The Auxiliary verb is therefore the present tense of ETRE: Je suis Tu es Il/elle est nous sommes vous êtes ils / elles sont The main verbs involved here are as follows. They often come in opposites, and there are a few irregulars to look out for: aller = allé venir = venu entrer = entré sortir = sorti arriver = arrivé partir = parti descendre = descendu monter = monté naître = né mourir = mort rester = resté tomber = tombé retourner = retourné rentrer = rentré revenir = revenu There is one further point to bear in mind here. The past participle of a verb taking être as an auxiliary verb needs to agree with its subject. If the subject of the sentence is feminine, we add an "e", and if the subject is plural we add an "s". The verb aller can therefore have the following forms: (m = masculine, f = feminine) je suis allé (m) je suis allée (f) tu es allé (m) tu es allée (f) il est allé elle est allée nous sommes allés (m or mixed) nous sommes allées (f) vous êtes allé (m singular) vous êtes allée (f singular) vous êtes allés (m or mixed plural) vous êtes allées (f plural) ils sont allés elles sont allées Or, summarised more simply, as follows, whereby we can add agreements as necessary: je suis allé(e) tu es allé(e) il est allé elle est allée nous sommes allé(e)(s) vous êtes allé(e)(s) ils sont allés elles sont allées e.g. Je suis allé au cinéma hier soir. Nous sommes partis à 8h30. Vous êtes restés à la maison hier soir? Elle est venue chez nous le weekend dernier. Reflexive Verbs in the Perfect Tense ALL reflexive verbs take ETRE as their auxiliary verb, and consequently their past participle also needs to agree. The reflexive pronoun goes before the auxiliary verb. The verb "se coucher" looks like this in all its forms with possible agreements where needed: je me suis couché (e) tu t'es couché(e) il s'est couché elle s'est couchée nous nous sommes couché(e)s vous vous êtes couché(e)(s) ils se sont couchés elles se sont couchées A few examples: Lundi matin je me suis levé à six heures. Ma mère s'est dépêchée pour ne pas être en retard. Marie et Claire se sont coiffées avant de sortir. Use of the Perfect Tense: The perfect tense is used to talk about things that you did in the past on one occasion which are completed, and no longer happening now. Activité 1- Paasé compose avec AVOIR fait avons ai pu a ai a vu a bu a du mis plu ont Prendu lu avez avons vu Activité 2 Lisez et répondez aux questions Sylvie s’est réveillée à six heures. Elle est restée un peu au lit et elle s’est levée à six heures et demie. Ensuite, elle s’est habillée et elle a pris son petit-déjeuner. Elle s’est préparée pour partir à l’école : elle s’est brossé les dents et elle a mis son manteau. Elle est partie de chez elle à sept heures et quart. Elle a travaillé de huit heures à quinze heures. Après l’école, elle est allée se promener dans un parc. Elle est rentrée pour faire ses devoirs. Après elle as regardé la télévision. Elle a mangé avec ses parents, puis elle a fait la vaisselle. Ensuite, elle a téléphoné à une amie et elle a pris son bain. Finalement, elle s’est couchée à vingt et une heures. 1. Underline the verb avoir and être. 2. Circle the past participle. bold 3. Answers the following questions: - At what time she got up? 6 in the morning - What did she done after breakfast? She dressed herself - She worked between which times? From 8am to 3 pm - What did she done in the evening? She went for a walk in the park, did her homework and watched tv Challenge : describe what you did yesterday.