Français II First Semester Study Guide
advertisement

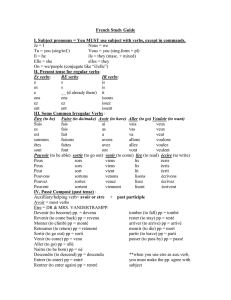
Français II First Semester Study Guide I. Vocabulary A. Unité préliminaire (Chez nous): parts of a house, appliances, chores, etc. (52) B. Unité 1 (La nourriture): table settings, food items, meals, food shops, etc. (54-55) II. Grammar A. être: ( ) (2) je _____________ nous ________________ tu _____________ vous ________________ il/elle/on _____________ ils/elles _________________ past participle: (avoir) + ________________ B. avoir: ( ) (2) je _____________ nous ________________ tu _____________ vous ________________ il/elle/on _____________ ils/elles _________________ past participle: (avoir) + ________________ C. avoir expressions (2) i. avoir…ans vii. avoir honte (de) ii. avoir besoin (de) viii. avoir l’air (de) iii. avoir de la chance ix. avoir peur (de) iv. avoir chaud x. avoir raison v. avoir froid xi. avoir sommeil vi. avoir envie (de) xii. avoir tort D. adjectives (3) i. most come _____________________ the verb. They must always agree with the noun in __________________ and _______________________. ii. possessive adjectives my: ___________ (fem.) ____________ (masc./before vowel) __________ (plural) ex. your (inf.): ___________ (fem.) ___________ (masc./before vowel) __________(plural) ex. his/her/its: ___________ (fem.) ___________ (masc./before vowel) __________ (plural) ex. our: ___________ (fem./masc.) __________ (plural) ex. your (formal): _______________ (fem./masc.) _________________ (plural) ex. their: ______________ (fem./masc.) ______________ (plural) ex. iii. adjectives that come before a noun: BANGS B: A: G: S: N: feminine singular masculine singular (vowel) masculine singular (consonant) feminine plural masculine plural (vowel) masculine singular (consonant) iv. demonstrative adjectives: this, these __________ masc. singular __________ masc. sing. before vowel __________ fem. singular __________ plural E. present tense of regular –er verbs (4) 1. 2. je -_________ nous -___________ tu -_________ vous -___________ il/elle/on -_________ ils/elles -___________ ex. F. present tense of regular –ir verbs (4) 1. 2. ex. je -_________ nous -___________ tu -_________ vous -___________ il/elle/on -_________ ils/elles -___________ G. present tense of regular –re verbs (4) 1. 2. je -_________ nous -___________ tu -_________ vous -___________ il/elle/on -_________ ils/elles -___________ ex. H. common irregular verbs (4-5): ex.: aller, faire, prendre, boire, sortir, dormer, courir, partir, server, conduire, mettre, dire, etc. I. spelling change –er verbs: (5) acheter espérer envoyer j’ tu il/elle/on nous vous ils/elles J. le passé compose (10-11 & handouts) 1. Formation with avoir: a. auxiliary verb: J’ _________ Tu _________ Il/elle/on _________ Nous ___________ Vous ____________ Ils/elles __________ b. past participle: i. the past participle of most regular –er verbs is formed by replacing the –er ending of the infinitive with ___ ii. the past participle of most regular –ir verbs is formed by replacing the –ir ending with ___ iii. the past participle of most regular –re verbs is formed by replacing the –re ending with ___ ex. J’_________________ I spoke/have spoken Tu ________________ you spoke/have spoken Il/elle/on _______________ he/she/it spoke/has spoken Nous ___________________ we spoke/have spoken Vous_____________ you spoke/have spoken Ils/elles __________________ they spoke/have spoken Notes: 1. Some irregular past participles a. Apprendre - __________________ b. Avoir - ______________________ c. Boire - ______________________ d. Comprendre - _________________ e. Courir _______________________ f. Être - ________________________ g. Faire - _______________________ h. Pleuvoir - _____________________ i. Prendre - _____________________ j. Surprendre - ___________________ 2. To make a verb negative in the passé composé, place the ne/n’ and pas around the conjugated form of avoir (auxiliary verb). Ex. On n’a pas fêté mon anniversaire. 3. To ask questions using inversion in the passé composé, invert the subject pronoun and the conjugated form of avoir (auxiliary verb). Ex. Avez-vous fêté votre anniversaire? 4. Place the adverbs déjà, encore, bien, mal, and beaucoup between the auxiliary verb or pas and the past participle. Ex. Tu as déjà mangé la pizza. 5. The past participle of spelling-change –er verbs has no spelling changes. Ex. Vous avez envoyé la letter. 6. The passé composé of il faut is il a fallu; that of il y a is il y a eu. 2.Formation with être: a. auxiliary verb: Je ______________ Tu ______________ Il/elle/on__________ Nous _____________ Vous _____________ Ils/elles ____________ b. past participle: D D R E M R R T S R V A A M N P *P Notes: 1. The past participles of verbs conjugated with être agree with their subjects in number and in gender. a. Ex. Charles, tu es allé à Montréal? b. Ex. Florence est partie en vacances. c. Ex. Mes frères sont rentrés. d. Elles sont arrivées hier soir. 2. To make a verb negative in the passé composé, place ne/n’ and pas around the auxiliary verb, in this case, être. a. Ex. Emma et Elodie ne sont pas sorties? 3. The verb passer takes être when it means to pass by, but it takes avoir when it means to spend time. a. Ex. Maryse est passée par la douane (Maryse passed through customs) b. Ex. Maryse a passé trois jours à la campagne (Maryse spend three days in the country) 4. To form a question using inversion in the passé composé, invert the subject pronoun and the conjugated form of être. a. Ex. Est-elle descendue à l’hôtel? 5. Place short adverbs such as déjà, encore, bien, mal, and beaucoup between the auxiliary verb être or pas and the past participle. 6. Past participles of nonreflexive verbs conjugated with être agree with the subject (i.e. Céline et Hervé sont parties de Québec.), HOWEVER, if one of these verbs has a direct object, avoir must be used. a. Ex. Céline est descendue de l’autocar but Elle a descendu sa valise. K. l’imparfait (11 & handout) 1. To form the imparfait, drop the __________ending from the ___________ form of the present tense and replace it with these endings. je -__________ nous -_____________ tu -__________ vous -_____________ il/elle/on -____________ ils/elles -______________ 2. The only verb that does not form the imparfait in this way is être. j’ ______________ nous __________________ tu _______________ vous __________________ il/elle/on ________________ ils/elles ___________________ Note: 1. Verbs whose infinitives end in –ger add an e before all endings of the imparfait except in the nous and vous forms. Verbs whose infinitives end in –cer change c to ç before all endings except in the nous and vous forms. tu voyageais but nous voyagions les invités commençaient but vous commenciez je mangeais but nous mangions 2. The nous and vous forms of infinitives ending in –ier contain a double i in the imparfait. Vous skiiez en janvier Examples: Nous étudiions jusqu’à minuit parler finir vendre boire nous form: je tu il/elle/on nous vous ils/elles L. direct object pronouns:____________________________________________ (14 & handout) i. forms: ii. when used with the passé compose, the past participle must agree with the DOP in _____________________ and ______________________ ex. M. indirect object pronouns: _______________________________________ (14-15 & handout) i. forms: N. the imperative: command forms (15) i. with tu, nous, and vous ii. same as regular present tense forms except for the tu form of –er verbs (drop the “s”) iii. avoir and être are irregular avoir être (tu) (nous) (vous) iv. an object pronoun can be added to the end of an affirmative command. Use a hyphen to separate them. Use moi and toi for the first and second-person object pronouns. ex. O. uses of the passé composé and the imparfait (26-29, 40-41, & handout) passé composé P. savoir and connaître: ( imparfait ) (42-43) i. savoir: ( ) je ______________________ nous ______________________ tu ______________________ vous ______________________ il/elle/on _______________________ ils/elles ______________________ past participle: (avoir) + ________________ ex. ii. connaître: ( ) je ______________________ nous ______________________ tu ______________________ vous ______________________ il/elle/on _______________________ ils/elles ______________________ past participle: (avoir) + ________________ ex.