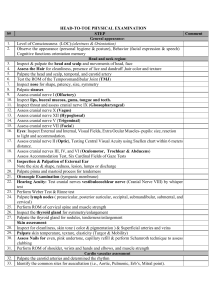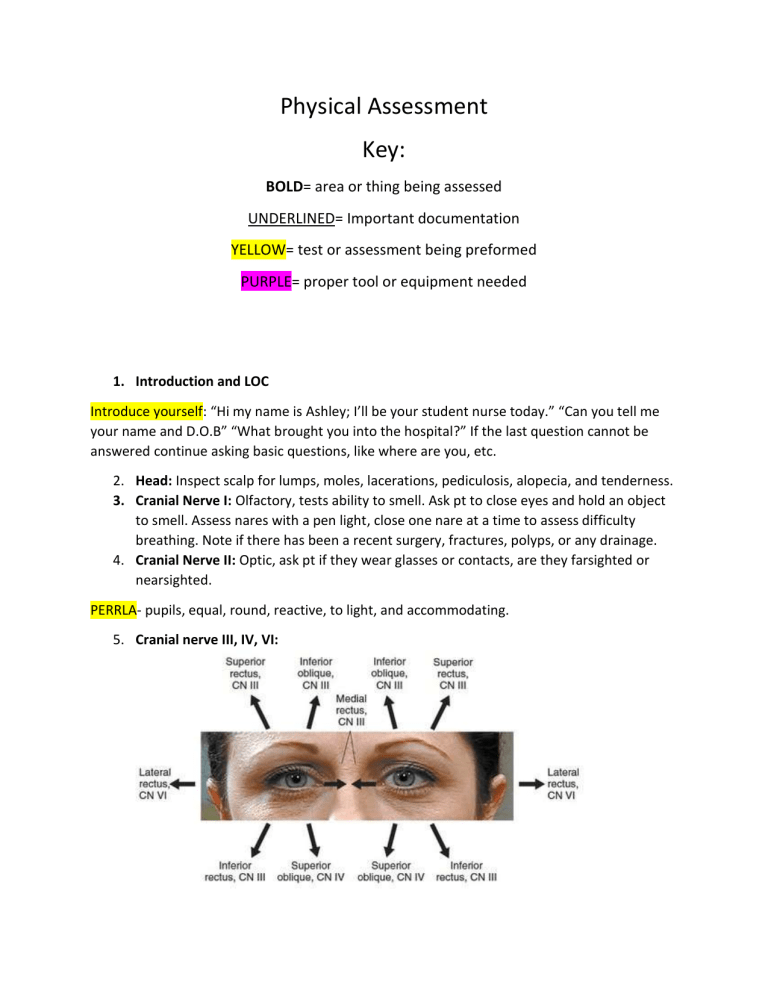
Physical Assessment Key: BOLD= area or thing being assessed UNDERLINED= Important documentation YELLOW= test or assessment being preformed PURPLE= proper tool or equipment needed 1. Introduction and LOC Introduce yourself: “Hi my name is Ashley; I’ll be your student nurse today.” “Can you tell me your name and D.O.B” “What brought you into the hospital?” If the last question cannot be answered continue asking basic questions, like where are you, etc. 2. Head: Inspect scalp for lumps, moles, lacerations, pediculosis, alopecia, and tenderness. 3. Cranial Nerve I: Olfactory, tests ability to smell. Ask pt to close eyes and hold an object to smell. Assess nares with a pen light, close one nare at a time to assess difficulty breathing. Note if there has been a recent surgery, fractures, polyps, or any drainage. 4. Cranial Nerve II: Optic, ask pt if they wear glasses or contacts, are they farsighted or nearsighted. PERRLA- pupils, equal, round, reactive, to light, and accommodating. 5. Cranial nerve III, IV, VI: Pupil reflex test- shine penlight into pupil by approaching from the side to check the reflex action of pupils, should be brisk or sluggish Test EOM’s (extraocular eye movements)- pictured above ^^^ Test accommodation- test by asking pt to look at a faraway object, while assessing the pupil for dilation Convergence- test by using the object and moving it closer to face assessing “cross eyes” 6. Cranial Nerve V: Trigeminal, test sensation. Tell pt to close their eyes and ask them when they feel your touch to the R and L sides of the face. “Any pain during mastication?” 7. Cranial Nerve VII: Facial, tests motor. Ask pt to puff cheeks, smile, and raise eyelids. 8. Cranial Nerve VIII: Acoustic, tests hearing ability. Whisper test- ask pt to repeat what you say, use a 2-syllable word, different tone for each ear. 9. Cranial Nerve IX: Glossopharyngeal, assess pharynx. Ask pt to say “ahh” and swallow. 10. Cranial Nerve X: Vagus, assess pharynx and larynx. Ask pt to swallow and speak. 11. Cranial nerve XII: Hypoglossal, assess movement of tongue. Ask pt to stick tongue out and assess side to side movement. Look under tongue and assess frenulum. 12. Cranial Nerve XI: Spinal, assesses strength and movement of trapezius and sternomastoid muscles. Place hands on top of pt shoulders and ask them to shrug shoulders assessing strength. Repeat process but with pt face, ask them to push their face to the side against your hand. 13. Shoulders: Inspect skin and palpate. Assess motion of head, look to the ceiling, to the chest, ear to shoulder (L & R), and circular motion. 14. Neck: Inspect area and palpate for nodules, look for lesions, or unusual moles. JVD (jugular vein distention)- Ask pt to look straight ahead and inspect side of neck for bulging of the jugular. Bulging= positive. Must be assessed in supine position. Carotid artery- Palpate carotid one side at a time. Measured 0-3+ (absent to bounding), 2+ is normal. Then auscultate with bell of stethoscope, ask pt to look to turn head away from you, hold their breath and then listen for bruit (an abnormal “swishing sounding.”) Lastly, palpate trachea to make sure it is midline. 15. Thorax: Inspect chest anteriorly and posteriorly, palpate for lumps, check for lesions, edema, and moles. Skin Turgor- pinch skin lightly, if it remains raised then pt is possibly dehydrated. Auscultate lungs- use the diaphragm of the stethoscope, ask pt to take deep breaths in through the nose and out through the mouth as you move over the areas. Chest Expansion- place hands on either side of pt with thumbs close together, ask pt to take deep breaths and make sure the lungs expand equally and bilaterally. AP Diameter- have pt sit up and place one hand on top of breast area and other hand on back, then move hands away from pt and measure the anterior portion of the chest. Should be less than ½ of the transverse of the chest. Breast examination- Ask pt if they do a routine breast exam monthly. 16. Heart: Auscultate all areas using the diaphragm of the stethoscope. Note rate, rhythm, and strength. 17. Abdomen: Ask pt if they have any trouble with appetite, pain, nausea, and bowel habits. Inspect- have pt lay supine and place pillow under the knees. Check for lesions, lumps, striae, pulsations, and abdominal distention. Auscultate- With bell of stethoscope assess abdominal aorta (between the xiphoid process and umbilicus, slightly to the left), should be absent of bruits. With diaphragm of stethoscope assess 4 quadrants from lower right -> upper right -> upper left -> lower left. Listen for one full minute each quadrant, counting bowel sounds. Normal: 5-35 sounds. Palpate- Use light palpation over all areas asking pt if they have any discomfort. 18. Genitourinary: (if female) Ask pt when their last menstrual cycle was, and about self-breast exams. (If male) assess testicles. 19. Upper Ext.: Inspect skin for temperature, color, moles, hair distribution, lumps, and edema. Capillary Refill- press on nailbed or finger, color should return quickly (less than 2 seconds) should be brisk. Check radial and brachial pulses- assess quality, strength, and rate. Should be 2+, easily palpable and bilaterally. Check CMS (circulation, mobility, and sensation)- Ask pt to wiggle fingers, ask pt close eyes and identify where you touch different areas on the upper extremities. Assess for ROM (range of motion)- Active or passive. Assess abduction and adduction of arms, pronation, supination, flexion, and extension. Assess strength- Ask pt to push against your hands, squeeze your hands simultaneously and bilaterally. 20. Back: Have pt sit up and assess skin, spinal column, and buttocks. Palpate along the side of spinal column and ask if feeling any discomfort or pain in different areas.