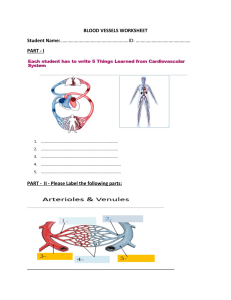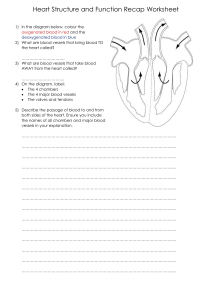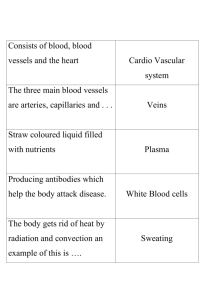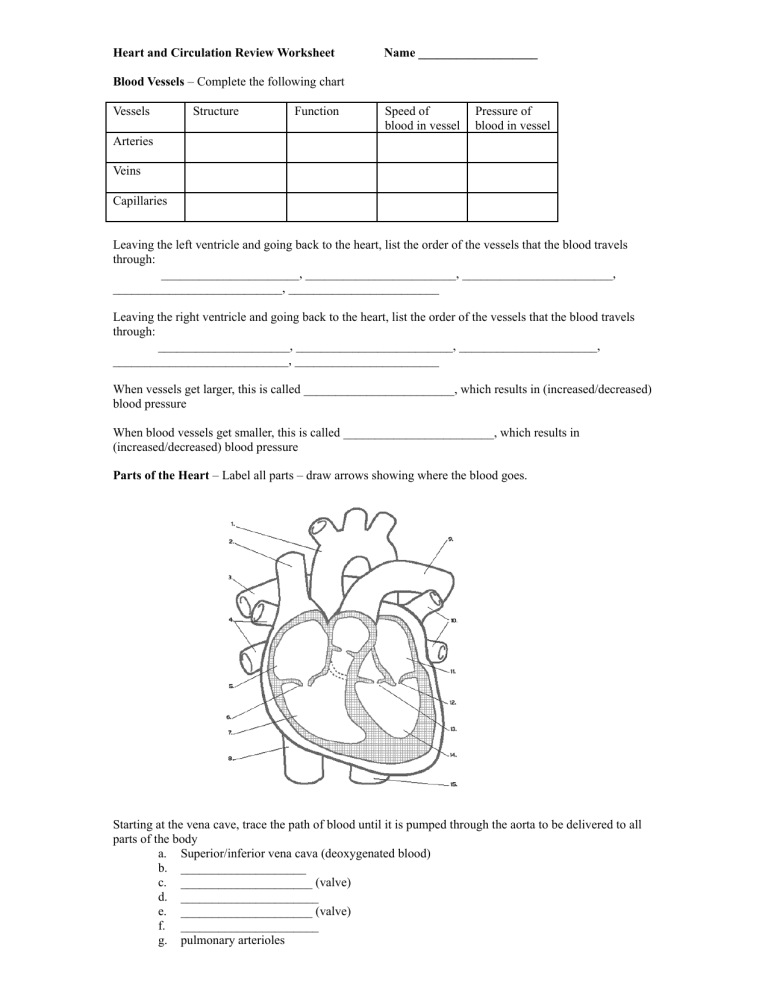
Heart and Circulation Review Worksheet Name ___________________ Blood Vessels – Complete the following chart Vessels Structure Function Speed of blood in vessel Pressure of blood in vessel Arteries Veins Capillaries Leaving the left ventricle and going back to the heart, list the order of the vessels that the blood travels through: ______________________, ________________________, ________________________, ___________________________, ________________________ Leaving the right ventricle and going back to the heart, list the order of the vessels that the blood travels through: _____________________, _________________________, ______________________, ____________________________, _______________________ When vessels get larger, this is called ________________________, which results in (increased/decreased) blood pressure When blood vessels get smaller, this is called ________________________, which results in (increased/decreased) blood pressure Parts of the Heart – Label all parts – draw arrows showing where the blood goes. Starting at the vena cave, trace the path of blood until it is pumped through the aorta to be delivered to all parts of the body a. Superior/inferior vena cava (deoxygenated blood) b. ____________________ c. _____________________ (valve) d. ______________________ e. _____________________ (valve) f. ______________________ g. pulmonary arterioles h. i. j. k. l. m. n. o. capillaries in lungs (red blood cells exchange CO2 for O2 – blood is now oxygenated) pulmonary venules ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ (valve) ______________________ ______________________ (valve) ______________________ (oxygenated blood to all parts of the body Control of the HeartBeat The part of your brain that controls involuntary actions such as the heartbeat is the __________________________. The heart’s tempo is set by the ____________________ located in the right atrium of the heart. Let’s say you are exercising and you need more oxygen. The following order of events would happen: a. the ___________________ in the brain would get the message to speed up the heartbeat. b. A nerve from the brain to the _____________________ in the right atrium would stimulate the pacemaker in the heart c. The nerve impulse will then travel to a second node, the ______________ node. This node sends the message to a bundle of nerves in the septum called the Bundle of His. These nerves will work to contract the ventricles (both ventricles will contract at the same time) Heart Sounds When the heart is contracting it is in the ______________________ phase. When it is relaxing it is in the _____________________ phase. The sounds of the heartbeat are caused by the closing of ____________________. The “lub” sounds are caused by the closing of the ________________ and ___________________ valves. Collectively, these vales are known as the ________________________ valves. The “dubb” sounds are caused by the closing of the ________________ and ___________________ valves. Collectively, these vales are known as the ________________________ valves. Blood Pressure Blood pressure is (higher/lower) in vessels that are closer to the heart. If your blood pressure is too high, your body will try to decrease it through ________________________, which makes the vessels larger, thereby decreasing pressure. If your blood pressure is too low, your body will try to increase it through _____________________________, which makes the vessels smaller, thereby increasing pressure. Capillary Fluid Exchange Fluids need to be exchanged between the blood and the surrounding tissues. This happens in a capillary bed (a group of capillaries). Two types of pressure are involved in this fluid exchange. ____________________ pressure is the pressure that forces fluids out of the vessels ____________________ pressure is the pressure that brings fluids back into the vessels ____________________ pressure is always constant at 25mmHg ____________________ pressure changes. At the beginning of the capillary, it is 35mmHg, near the end of the capillary it is ______________mmHg. At the beginning of the capillary bed, which pressure is higher? ____________________. Where is the fluid going to go? ____________________________ At the end of the capillary bed, which pressure is higher? Where is the fluid going to go? ________________________ All of the fluid is not reabsorbed back into the vessels. Some remains in the tissues and is picked up by the _______________________ system In an individual with high blood pressure, there would be (more/less) movement of fluids out of the vessels.