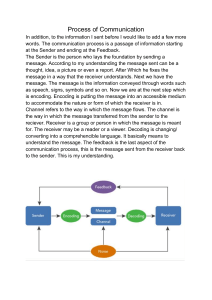
Business communication Business communication Lecture Week 1 & 2 Group – (Accounting & Finance) Mrs. Anastasia Nana Ama Kumi-Korsah Department of Management School of Business University of Cape Coast Presentation outline • Definition of communication • Importance of communication • Business communication • Social communication • Levels of communication • Types of communication Objectives • By the end of this session students should be able to: a. Define the concept of communication b. Outline at least (3) relevance of communication c. Distinguish between business and social communication d. Explain the types of communication e. Describe the levels of communication What is communication • Communication is any means by which a thought is transferred from one person to another Chappel and Read (1984) • It is the transfer of information, feelings or messages that become the common property of both the sender and the receiver. Peretomode (1992) Communication cont. • Communication is simply the process of understanding and sharing meaning. -Pearson & Nelson (2000) • Communication in essence is the process by which parties exchange information, feelings and thoughts in ways that are meaningful and shared for further action. Eessential Components of Communication -Source, Message, Channel, Receiver, Feedback, Environment, Context, Interference Communication cont. • Sender -Originator of the message (source) -Individual, group or organisation -Responsible for how the message will be perceived -Experience, attitude, culture, knowledge, words, nonverbal language will influence the message. Communication cont. • Encoding -Translating ideas into messages and suitable formats. - Choosing just the right order or the perfect words to convey intended meaning. Communication cont. • Message -Stimulus, Idea, thought, information, feelings produced and transmitted to receiver/ audience -Should be clear and concise to convey shared meaning -Message must be crafted to be devoid of ambiguities; sender must pay attention to words, facial expressions, and body language for written and verbal messages Communication cont • Channel -Ways or means through which message(s) move between source and receiver. -Complex messages will require sophisticated channels to ensure clarity and facilitate interaction -Spoken channels; face-to-face conversations, speeches, telephone conversations and voice mail messages, radio, PA systems etc. -Written channels; letters, memorandums, purchase orders, invoices,newspaper and magaz ines articles, blogs, e-mail, texts,tweets etc Communication cont. • Receiver -Endpoint of the message from source -Individual, group or organisation -Knowledge, attitude, trust for source, experiences, culture may influence their interpretations of the message. Communication cont. • Decoding -Activity carried out by the receiver -The process of reducing message into understandable formats -Interpreting, analysing and assigning meaning to the message received. Communication cont. • Feedback -Response from the receiver -Determinant for effective communication -Provides opportunity for sender to clarify or modify message. Communication cont. • Interference/Noise -Distorters of message -anything that blocks or changes the intended meaning of the message from source -Prevents free flow of message between source and destination Communication cont. During feedback the roles of the sender and receiver is reversed? True/ False Noise interferes only with the decoding of messages by the receiver True/ False All noise is bad, because it distorts the communication process True/ False Communication cont. • Effective communication takes preparation, practice, and persistence. • There are many ways to learn communication skills; a. School of experience, b. Hardknocks Why is Communication Important? • Facilitates the transfer of instructions and directives • Ensures integration of various functions of business organisations • Educate organisational members on policies and procedures. • Project the image of the organisation • Stimulate interpersonal relationships in the work place • Promotes creativity and innovation • Prevents conflicts business and social communication Business communication - This is the process of establishing a common understanding between or among people within a business environment Social communication -It is the synergistic emergence of social interaction, social cognition, pragmatics and receptive and expressive language processing. BUSINESSCOMMUNICATIONVRSSOCIAL COMMUNICATION Business Communication Occurs within a business/organisational context Organized, formal and concerned with getting things done Interactions between organizational members Eg. Reports, proposals, appraisals, team workings, presentations, letters, faxes, emails Social Communication Language used in a social context More relaxed, informal and friendly All interactions within a social community Eg. Stories, picnics, retreats, parties Levels of communication Communication exists on a number of levels • Intrapersonal communication - communication within self (personal dialogue) -interpretation of one’s own experiences, attitude and mindset within self. • Interpersonal communication - communication among two or more people E.g. Conversation between management and employees or among employees Levels of communication • Group communication -Communication between a group of people and another group -Interactions within the group itself -A group is often described as a collection of people between 3 and twenty • Organizational communication - communication within an organization - interactions within the organizational context for achieving a common goal Levels of communication - highly contextual and culturally dependent - helps to accomplish tasks relating to specific functional areas - means through which organizations acclimatize to change through individual and organizational creativity and adaptation - helps an organization to complete tasks through the maintenance of policies, procedures or regulations for daily and continuous operations Mass communication - communication with the general public/masses - organizations use their websites or advertisement to reach out to the public Types of communication There are two main types of communication; • Internal communication • External communication Types of communication Internal communication • Communication within the confines of an organization • Usually takes the form or instructions, directives, policies , procedures reports etc. • Covers all official correspondence within the organization. External communication • Work related communication between an organization and the general public • The general public includes customers/clients, professional bodies, government, service companies, training providers, the public at large. • Includes business efforts at direct selling, telephone call backs follow up services descriptive brochures, websites, radio and television advertisements. Conclusion • Communication leads to community, that is, to understanding, intimacy and mutual valuing. - Rollo May • The single biggest problem in communication is the illusion that it has taken place. - George Bernard Shaw