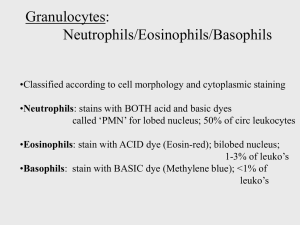
Principles of Immunology Organs of the Immune System Primary Lymphoid Organs Bone Marrow and Thymus Maturation Site Secondary Lymphoid Organs Spleen, lymph nodes, MALT (mucosal associated lymph tissue) GALT (gut associated lymph tissue) Trap antigen, APC, Lymphocyte Proliferation, provide site to interact Lymphatic System Network of vessels Collects fluid from tissues, return to blood Major cell is lymphocyte Unidirectional Often first place where antigens are detected 1. Primary lymphoid organs Thymus Bilobed Organ on Top of Heart Reaches Max. Size During Puberty 70g infants, 3 g in adults 95-99% Of T Cells Die in Thymus self reactivity or no reactivity to Ag Consists of Cortex and Medulla Rat Thymocytes Thymus Function Takes in immature T cells and puts out mature (immunocompetent) T cells Increased diversity of T cells T cell selection Thymus T cell selection Based on MHC/Ag complex recognition Recognize MHC/Non self AG complexes Recognize MHC/Self Ag complexes Athymic condition Bone marrow Structure Microscopic Less well defined than thymus Role of stromal cells Function Hematopoiesis B cell maturation B cell selection Puts out mature, naive B cells 2. Secondary lymphoid organs Lymph Nodes Structure Gross Bean-shaped structures Drains major segments of lymphatic system Lymph Nodes Structure Microscopic Major cell types Lymphocytes Macrophages Dendritic cells Cortex/paracortex/medulla Follicles Primary Secondary Lymph Nodes Function 1st line of response to antigens Secondary follicle (Germinal center) is site of B cell proliferation, mutation, differentiation Specificity is high >90% of B cells die through apoptosis After Ag stimualtion lymphocyte numbers up by 50X in efferent lymphatic vessel Lympadenopathy Spleen Structure Gross Ovoid organ in upper left of abdomen Microscopic Compartmentalized Red pulp White pulp Periarticualr lymphoid sheath Site of Ag presentation Major cell types Lymphocytes Macrophages Dendritic cells RBCs Spleen Function Filters out older RBCs Responds to Ag in circulatory system Produces activated B cells Splenectomy Tonsils Follicular structure Contains lymphocytes, macrophages, mast cells Germinal centers appear in response to Ag Protective role in URI (Upper respiratory Infection) Appendix Associated with intestines Responds to Ag Role in GI immune response MALT Lymphoid tissues below epithelium Presence of B cells Ag presented through unique cell (M cell) Preferentially responds with IgA antibody