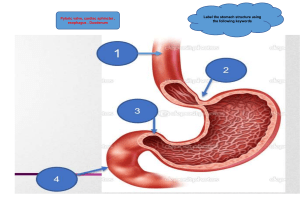
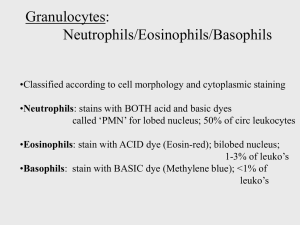
Ameloblasts and thymus – what is the unique feature common to both? Their functions disappear later in life; age-factor Which is the primary lymphoid identified in mammals? The ONLY primary lymphoid identified in mammals is the Thymus What is the relationship of large intestine with erythropoiesis? Bacterial population in large intestine produces vitamin B 12 and K required for erythropoiesis. Where are Herring bodies located? Herring Bodies located in the Posterior Pituitary/neurohypophysis Specific proteolytic enzyme from small intestinal mucosa is: Leucine aminopeptidase Glycogen is stored in what organs/cells in human body? Liver and muscles Microvilli are present in which cells – zymogenic cells, hepatocytes, enterocytes, parietal cells Classify the tissue type of following cells: enterocytes, parietal cells, alpha cells, gustatory cells, melanocytes, pinealocytes, olfactory cells Skeletal muscles are present in want parts of GI – internal anal sphincter, external anal sphincter, upper esophagus, lower esophagus, stomach, ileum, colon, gallbladder, gastroesophageal sphincter, tongue, pharynx What is the unique histological feature and or location of each of the following? Peyer’s patches Axons of neurohypophysis Pars media of anterior pituitary Pineal gland Thymus Lymph node Tonsils Gallbladder Where do you find - Reed-Sternberg cells, peri-arterial lymphoid sheath, Schweiger-Siedel sheath, sulcus terminalis, Meissner’s plexus, Auerbach’s plexus, tunica adventitia, chyme, chyle, rugae, secretory canaliculi, Paneth cells, Brunner’s glands,