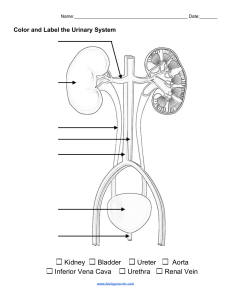
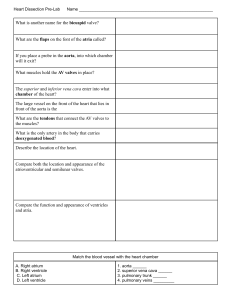
Final Review Study Questions 1. What are the entrance valves of the heart called? 2. What is the Pericardium? 3. Where is the apex of the heart located? 4. The heart is what type of pump? 5. The right and left side of the heart is separated by the _____? 6. Which valves are called the semilunar valves? 7. The myocardium is made of _____. 8. Which 2 chambers are known as the “receiving” chambers? 9. What are the 2 lower chambers called? 10.Where is the mitral valve located? 11.What happens when the myocardium is stimulated? 12.Where does the myocardium receive its nourishment? 13.What happens when the blood supply to the myocardium stops? 14.Why is the cardiac tissue unique? 15.Which blood vessel leaves the heart and carries blood to all parts of the body? 16.What is the systole phase? 17.What is the largest chamber of the heart? 18.What is the function of each valve in the heart? 19.What is another name for the SA node? 20.Define superior vena cava. 21.Define inferior vena cava. 22.Oxygenated blood is returned to the heart via the _____. 23.From the right ventricle, the blood is pumped to the lungs through the right and left _____. 24.Define inhalation and exhalation. 25.The superior vena cava services the _____. 26.the inferior vena cava services the _____. 27.What is the GSV? 28.What is pulmonary circulation? 29.What is systemic circulation? 30.What is vascular circulation? 31.What is the difference between arteries and veins? 32.What phase does the bottom number of blood pressure represent? 33.An increase in blood volume leads to an increase in _____. 34.What is orthostatic hypotension? 35.High cholesterol levels (LDL) produces plaque in arterial walls causing _____. 36.How is blood pressure measured? 37.What is the approximate diameter of the arteries? 38.What is the normal range for an adult’s blood pressure? 39.What is the normal range for a child’s blood pressure? 40.Do neonates and infants generally have lower blood pressure? 41.What is hypotension? 42.What is hypertension? 43.List steps in performing a blood pressure. 44.What is the major cause of artherosclerosis? 45.What causes angina? 46.What is the major cause of heart failure? 47.What is ischemia? 48.What is valvular insufficiency? 49.What type of infection can cause rheumatic fever? 50.What can cause a myocardial infarction? 51.Why would someone feel heart pain? 52.List 4 things that happen in the process of a myocardial infarction. 53.What is a thrombus? 54.What is an embolus? 55.What is pericarditis? 56.What is Myocarditis? 57.What is Endocarditis? 58.Systole, the chambers do what? 59.Diastole, the chambers do what? 60.What is the purpose of the Conduction System? 61.What is the function of the SA node? 62.Where is the AV Bundle located? 63.Where is the Bundle of His located? 64.Blood enters the heart through which two veins? 65.What is the P wave representing? 66.When does a U wave occur? 67.The QRS complex occurs when _____. 68.What does the T wave show? 69.What letters are used to represent a complete cardiac cycle? 70.Each small square represents _____ seconds. 71.How many leads are used in a 12 lead EKG? 72.What are precordial leads and where are they placed? 73.What is another name for Bi-polar leads? 74.Where do you place a limb lead if patient had a right arm amputation? 75.Another name for a resting EKG is _____. 76.When do you standardize for an EKG? 77.What color is the ground lead? 78.What purpose does the gel serve on the electrode? 79.What is a lead? 80.What number does each large square represent on an EKG? 81.Which lead is the ground electrode? 82.What is the difference between agonal and asystole? 83.What are the characteristics of a normal sinus rhythm? 84.How do you differentiate between the 4 heart blocks? 85.Can patient movement effect the EKG? 86.What does the term paroxysmal mean? 87.What does repolarization mean? 88.What does depolarization mean? 89.Artificial pacemakers have markers called _____. 90.What does a PVC look like? 91.A sinus arrhythmia can be caused my what? 92.Where is the impulse coming from in a normal sinus rhythm of 80 beats per minute? 93.What does the term bradycardia mean? 94.In atrial fibrillation, what do the p waves look like?